
Nonspecific Immunity Immunity is mediated by humoral and cellular effectors.Certain immune responses are antigen specific.They are provoked by unique determinants of the antigens and effectors produce antibodies or T cells which are antigen specific.This requires selection of effectors of appropriate specificity for clonal expansion before an effective response can be observed.In contrast,other imune responses can be evoked by infectious agents or injury in a generalized,antigen nonspecific manner.These responses are not induced by unique determinants.In addition,the effectors produced recognize conserved,rather than unique,determinants. Anti gen Speci fic and Anti gen nonspecific Immuni ty Antigen Specific Immunity Nonspecific Immunity Innate immunity Taesels T and B Cells not needed Antibodies and T cells and sp ecifically Rapidly evoked,generalized Activated defense and activated in a nonspecific manner
Nonspecific Immunity Immunity is mediated by humoral and cellular effectors. Certain immune responses are antigen specific. They are provoked by unique determinants of the antigens and effectors produce antibodies or T cells which are antigen specific. This requires selection of effectors of appropriate specificity for clonal expansion before an effective response can be observed. In contrast, other immune responses can be evoked by infectious agents or injury in a generalized, antigen nonspecific manner. These responses are not induced by unique determinants. In addition, the effectors produced recognize conserved, rather than unique, determinants
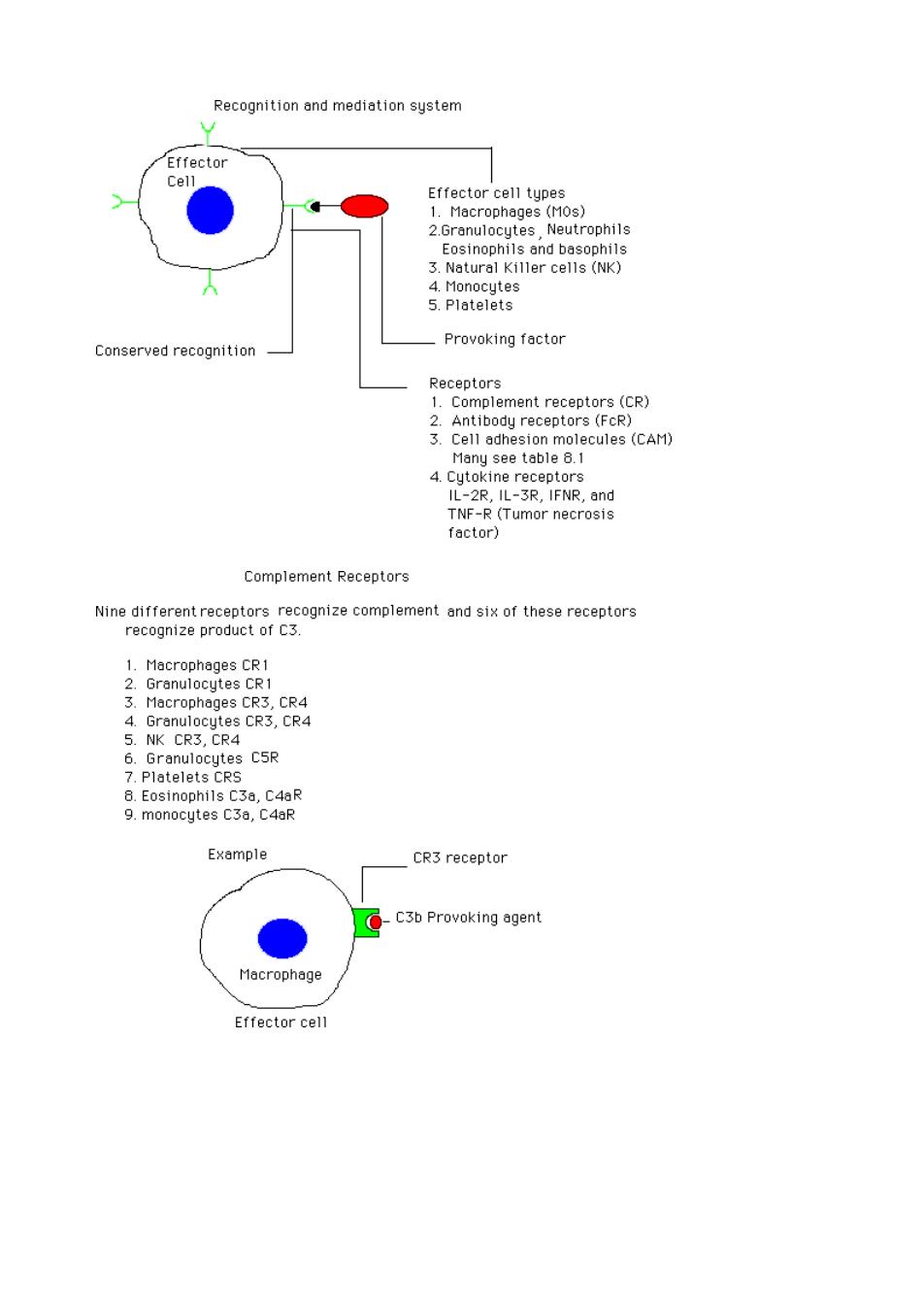
Recognition and mediation system Effecto cell tupe Macrophages(MOs) nd h 3.Netural Killer cells (NK) Conserved recognitio Provoking factor TNE-ST factor) Complement Receptors Nine different receptors recognize complement and six of these receptors recognize product of C3. 1.Macrophages CR1 Rca7, K L es CSR Example CR3 receptor C3b Provoking agent Macrophage Effector cell
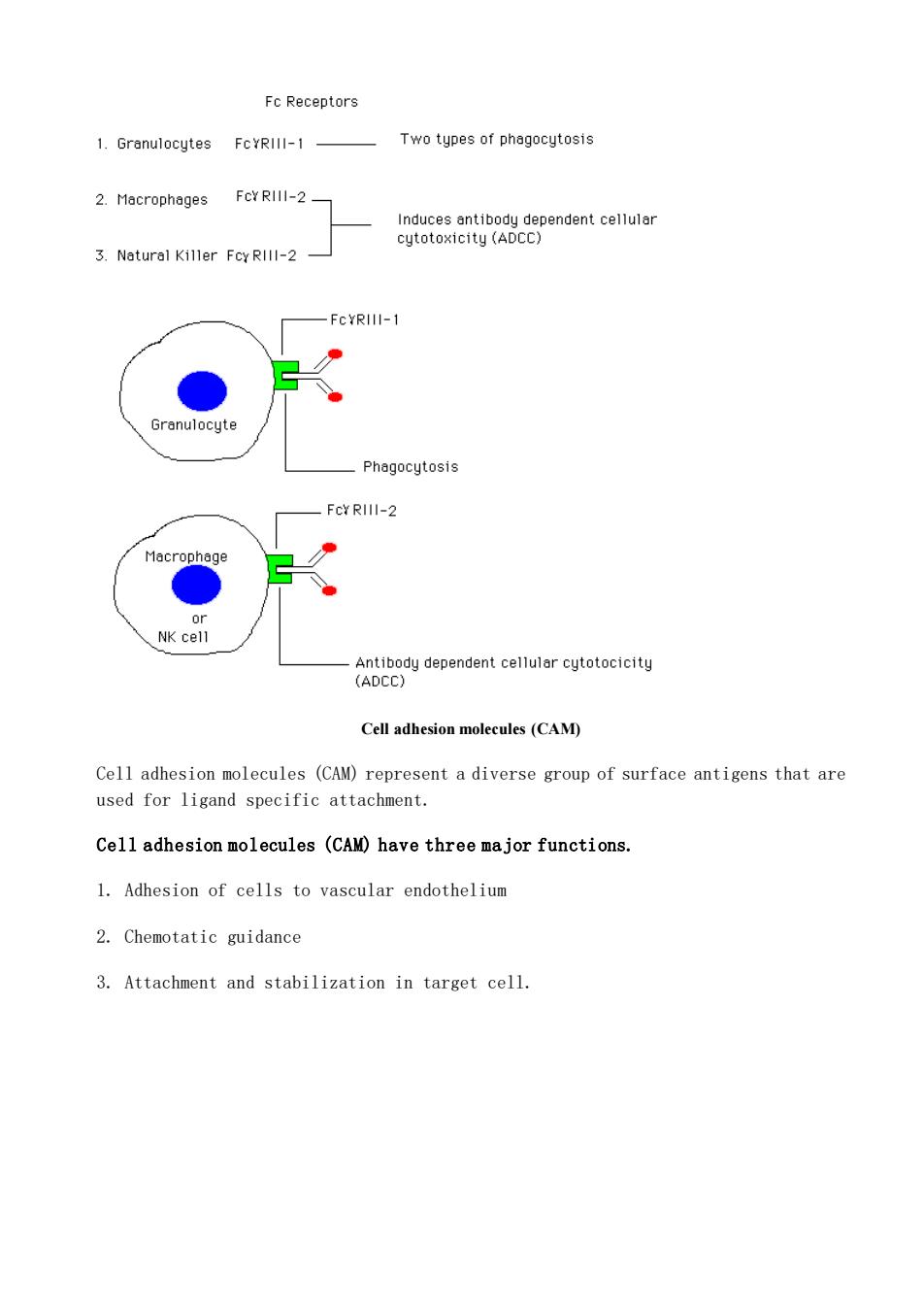
FcReceptors 1.Granulocytes FcYRIlI-1 Two types of phagocytosis 2.Macrophages FCY RIII-2_ aoi6nnty08ecterendentceluia 3.Natural Killer Fcy RIll-2 -FCYRIlI-1 Phagocytosis FcY RIII-2 Macrophage NK cell Cell adhesion molecules(CAM) Cell adhesion molecules(CAM)represent a diverse group of surface antigens that are used for ligand specific attachment. Cell adhesion molecules (CAM)have three major functions. 1.Adhesion of cells to vascular endothelium 2.Chemotatic guidance 3.Attachment and stabilization in target cell
Cell adhesion molecules (CAM) Cell adhesion molecules (CAM) represent a diverse group of surface antigens that are used for ligand specific attachment. Cell adhesion molecules (CAM) have three major functions. 1. Adhesion of cells to vascular endothelium 2. Chemotatic guidance 3. Attachment and stabilization in target cell
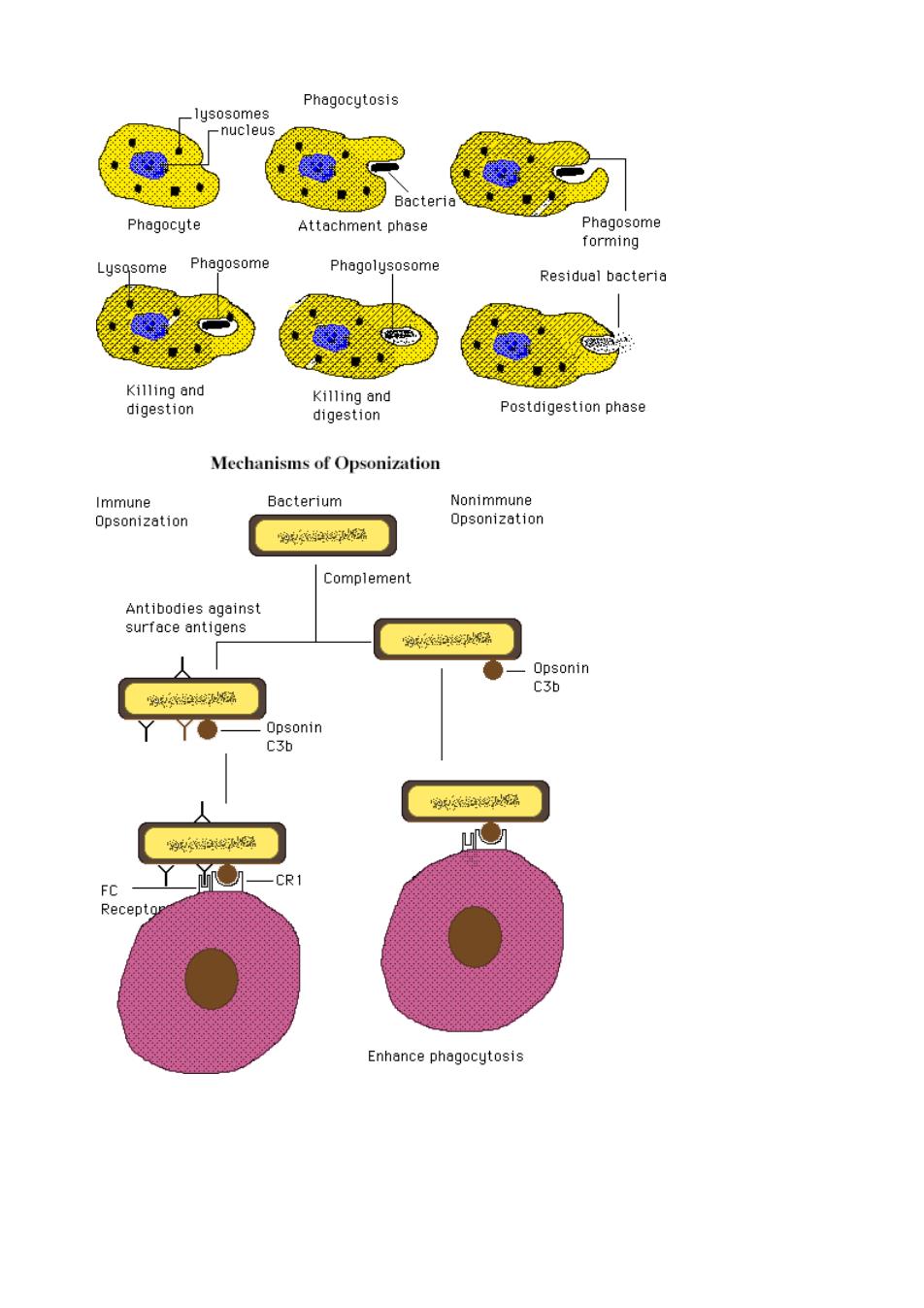
Phagocytosis lusosomes Attachment phase Phagosome forming Phagosome Phagolysosome Residual bacteria Killing and digestion Postdigestion phase Mechanisms of Opsonization mmune Bacterium Nonimmune Opsonization Opsonizatior 7】 Complement Opsonin Enhance phagocytosis
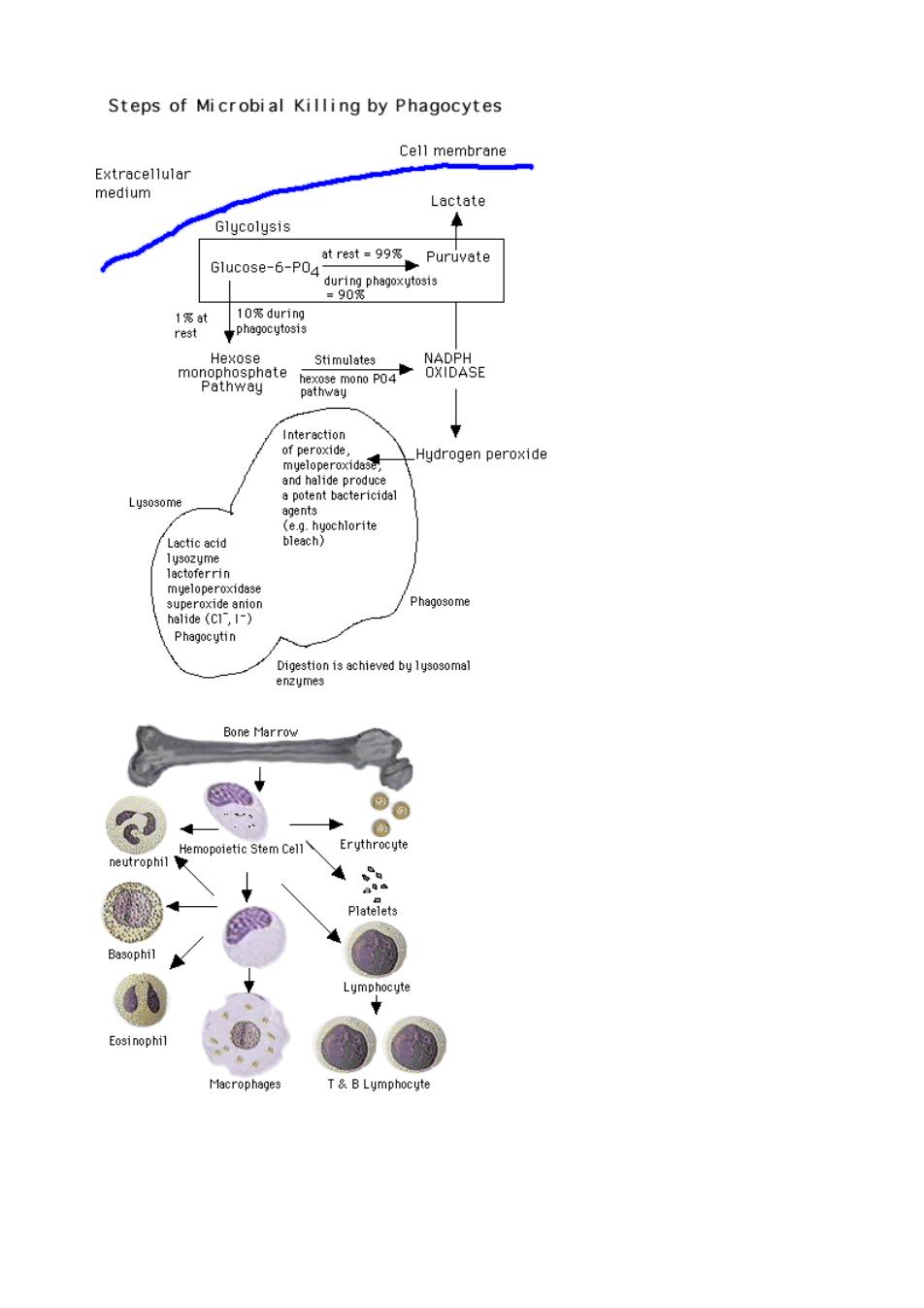
Steps of Microbial Killing by Phagocytes Cell membrane Lactate Glycolysis Glucose-6-PO, phago Stimulates _Hydrogen peroxide Phagosome h2atinisetieve时y1ygeo3somal Bone Marrov Basophil acrophage B Lymphocyte
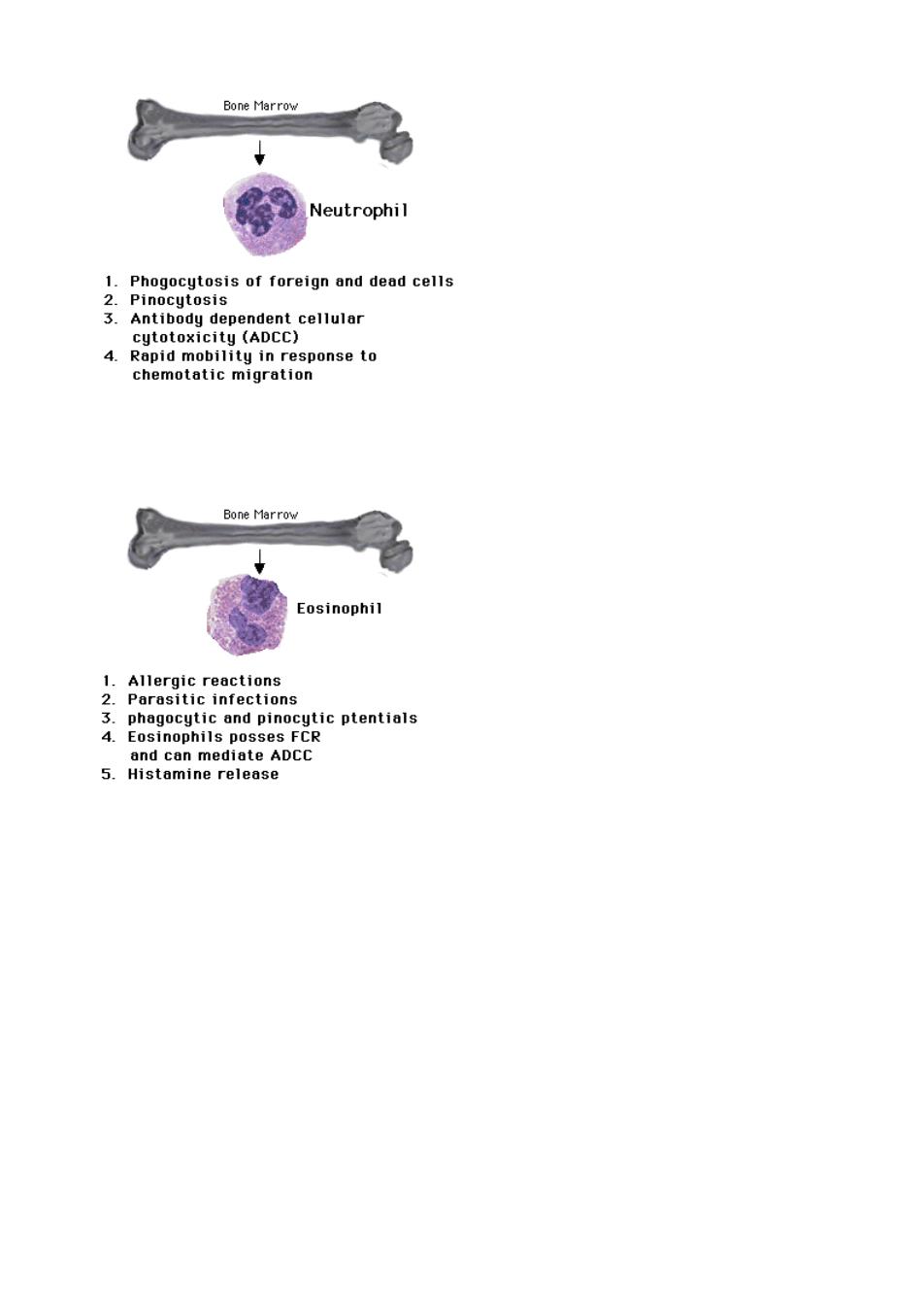
Bone Marro Neutrophil P8gsororelgnndeadcene 3 dependent cellur 4.Rapid mobility in response to chemotatic migration Bone Marro Eosinophil 1234 ae9oAiapsenoeicptentia1s and can mediate ADCC 5.Histamine release

Bone Merrow ●】 Basophil Active in alleraic re i ons nagocytosis anc Bone Marrow 12 3.Release of histamine

Bone Merrow (FC.MHC. Inflammatory Responses 1.Redness (Increase blood flow)vessels dilate. 2.Heat (Increase blood flow)vesseks dilate. Transudate (0.2%protein) Exudate (5%protein) Serous exudate (no cells) Purulent exudate (rich in cells manily neutrophils) Hemorrhagic exudate (blood) Fibrinous exudate (fibrin) 3.Swelling (Increase vasular permeability) 4.Pain
Inflammatory Responses 1. Redness (Increase blood flow) vessels dilate. 2. Heat (Increase blood flow) vesseks dilate. Transudate (0.2% protein) Exudate (5% protein) Serous exudate (no cells) Purulent exudate (rich in cells manily neutrophils) Hemorrhagic exudate (blood) Fibrinous exudate (fibrin) 3. Swelling (Increase vasular permeability) 4. Pain
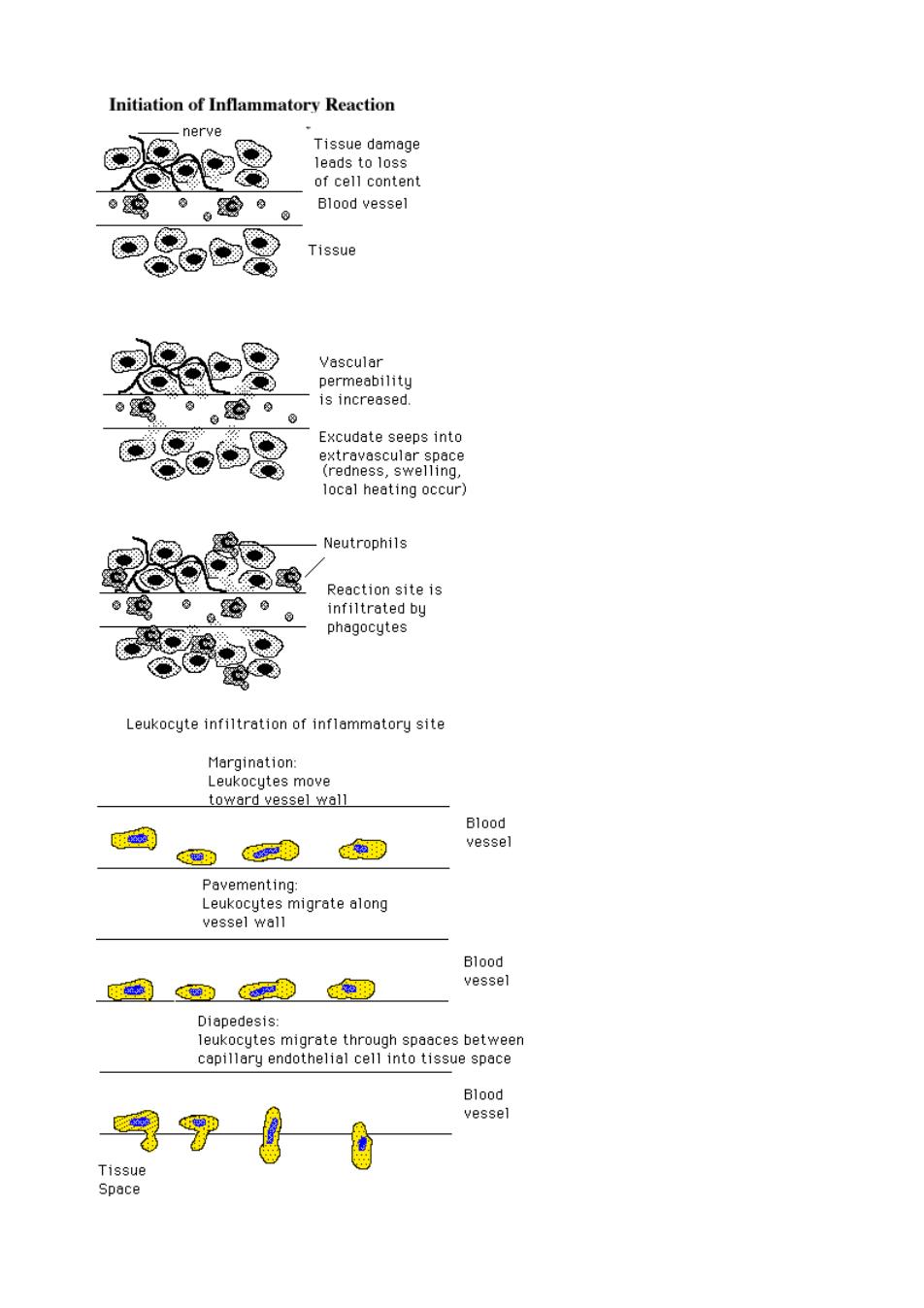
Initiation of Inflammatory Reaction nerve Tissue damage of cell content 减。。©。。 Blood vessel 8 Tissue 。。运9。 is increased Excudate seeps into local heating occur) Neutrophils Reaction site is 。。。 8 Leukocute infiltration of inflammatory site toward vessel wall C种0 羽 Bedl nigraotealong vessel wall od 60羽 Diapedesis: 8习美
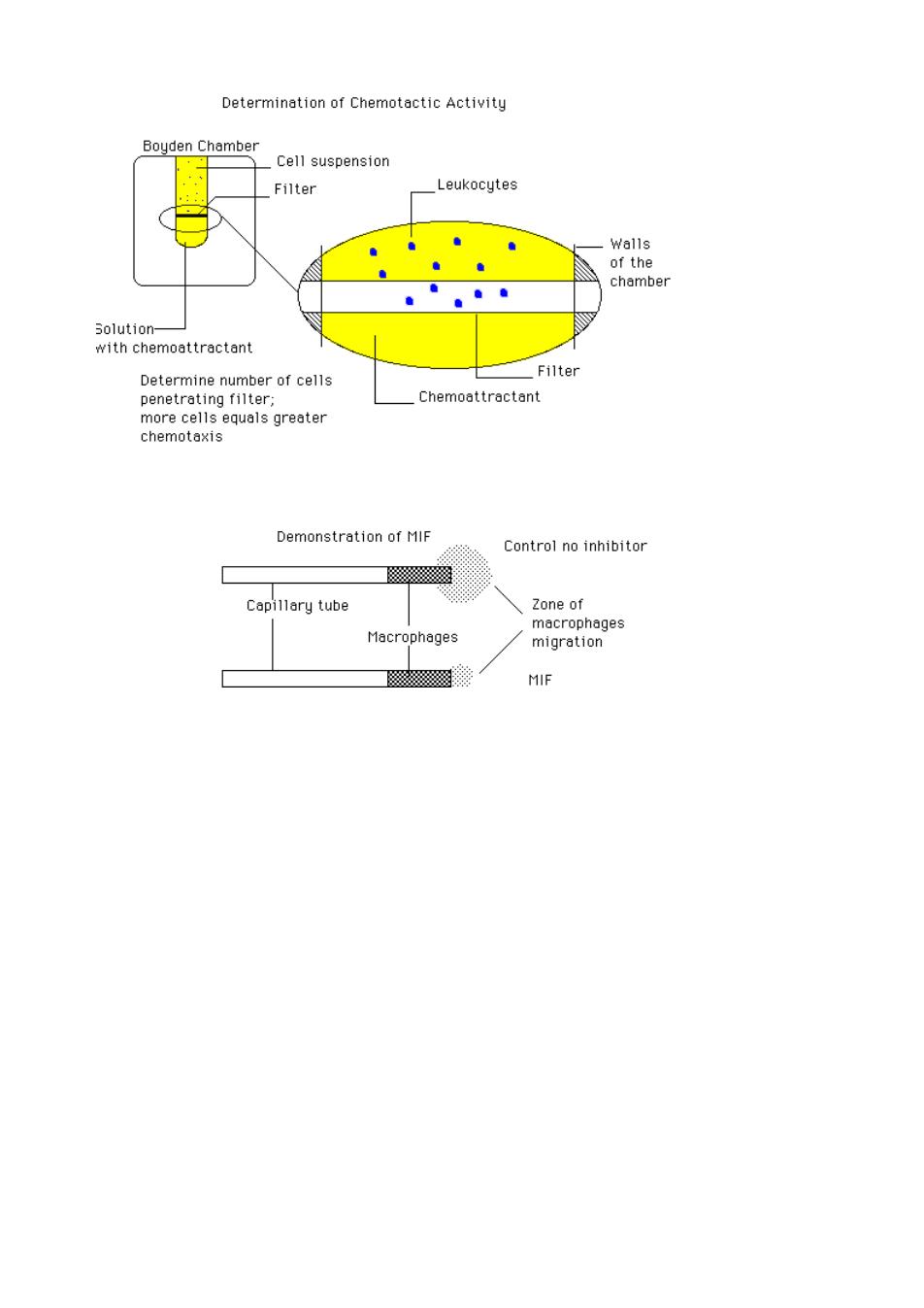
Determination of Chemotactic Activity Bouden Chamber Cell suspensior _Filter _Leukocytes Walls Determine number of cells penetrating filter: Demonstration of MIF Control no inhibitor Copiary tube macrophages ge: migration MIF