
Antibody Production,Regulation Diversity Southern Blotting to Detect lg Genes Hybrid Cell DNA Extraction Cleaved into fragments with restriction enzymes Separation by electrophoresis ■ Transferred Nitrocellulose ■■ 。 Incubate with P32labeled mRNA or cDNA probe (known, or H chain genes) onta e that hybridize with probe Immunoglobulin Genes Somatic cell hybridization techniques have been used to determine the chromosomal location of antibody genes.Murine B lymphocytes may be fused to another mammalian cell line to form unstable hybrids whose e chromosom s are randomly lost.The DNA of each hybrid is then probed ith radiolabeled copy DNA corresponding to kappa,lambda,or H chain regions for the presence of complementary H or L chain antibody genes.By correlating loss of a particular mouse chromosome with loss of a particular antibody gene,we can determine the chromosomal location of gene families. Using this approach,it became clear that three unlinked families of genes encode H and L chains and are located on separate chromosomes.Each family consists of a
Antibody Production, Regulation & Diversity Immunoglobulin Genes Somatic cell hybridization techniques have been used to determine the chromosomal location of antibody genes. Murine B lymphocytes may be fused to another mammalian cell line to form unstable hybrids, whose chromosomes are randomly lost. The DNA of each hybrid cell line is then probed with radiolabeled complementary, or copy, cDNA corresponding to kappa, lambda, or H chain regions for the presence of complementary H or L chain antibody genes. By correlating loss of a particular mouse chromosome with loss of a particular antibody gene, we can determine the chromosomal location of gene families. Using this approach, it became clear that three unlinked families of genes encode H and L chains and are located on separate chromosomes. Each family consists of a
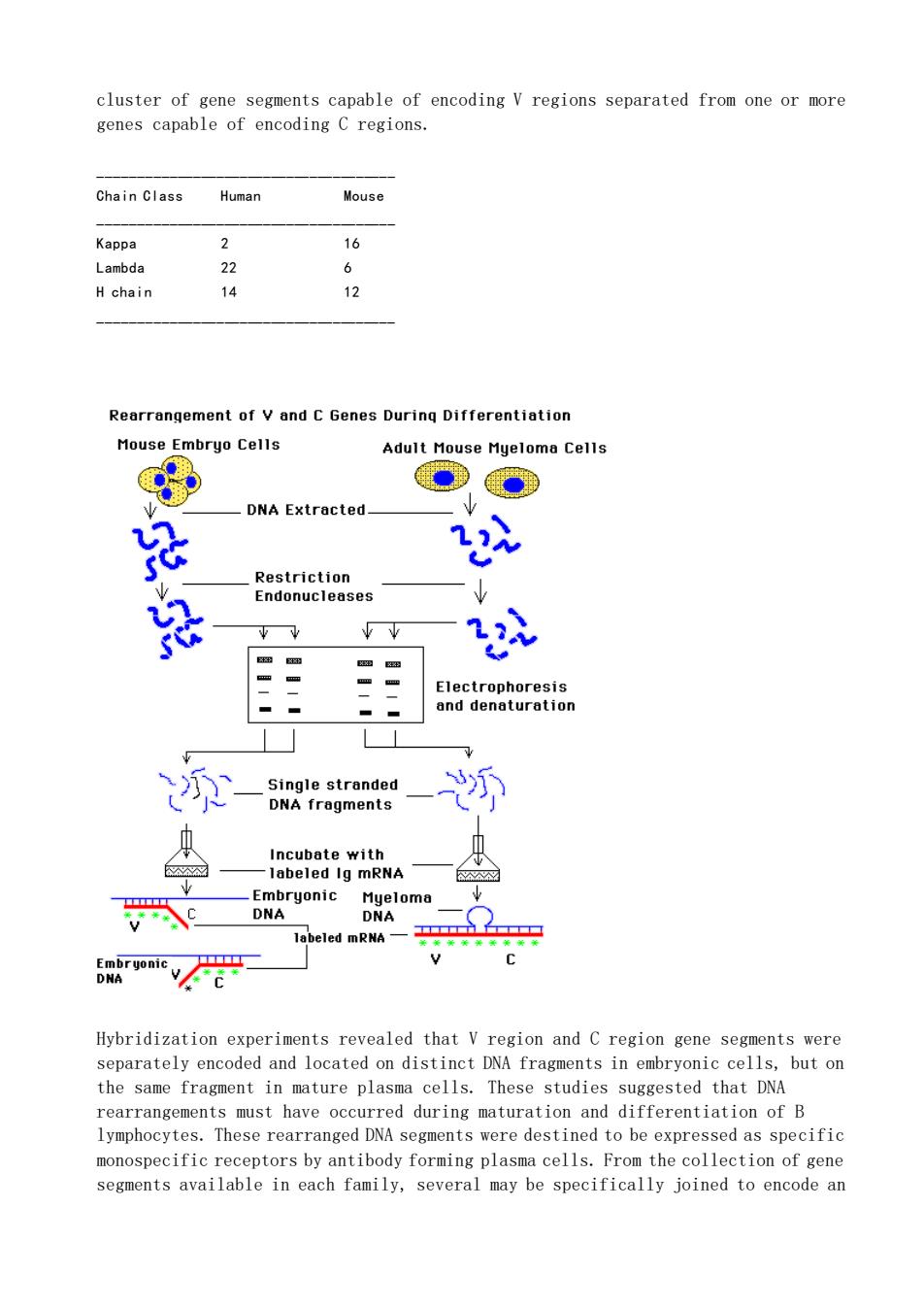
cluster of gene segments capable of encoding V regions separated from one or more genes capable of encoding C regions. Chain Class Human Mouse Kappa 2 16 Lambda 22 6 H chain 14 12 Rearrangement of v and C Genes During Differentiation Mouse Embryo Cells Adult Mouse Mueloma cells ●● DNA Extracted. 2 .Restriction Endonucleases V 业业 11 听 Incubate with Ig mRNA ompryonic Hyeloma 6raiv/ Hybridization experiments revealed that V region and C region gene segments were separately encoded and located on distinct DNA fragments in embryonic cells,but on the same fragment in mature plasma cells.These studies suggested that DNA rearrangements must have occurred during maturation and differentiation of B lymphocytes.These rearranged DNA segments were destined to be expressed as specific monospecific eptors by antibody forming plasma cells.From the collection of gen segments available in each family,several may be specifically joined to encode an
cluster of gene segments capable of encoding V regions separated from one or more genes capable of encoding C regions. ______________________________________ Chain Class Human Mouse ______________________________________ Kappa 2 16 Lambda 22 6 H chain 14 12 ______________________________________ Hybridization experiments revealed that V region and C region gene segments were separately encoded and located on distinct DNA fragments in embryonic cells, but on the same fragment in mature plasma cells. These studies suggested that DNA rearrangements must have occurred during maturation and differentiation of B lymphocytes. These rearranged DNA segments were destined to be expressed as specific monospecific receptors by antibody forming plasma cells. From the collection of gene segments available in each family, several may be specifically joined to encode an
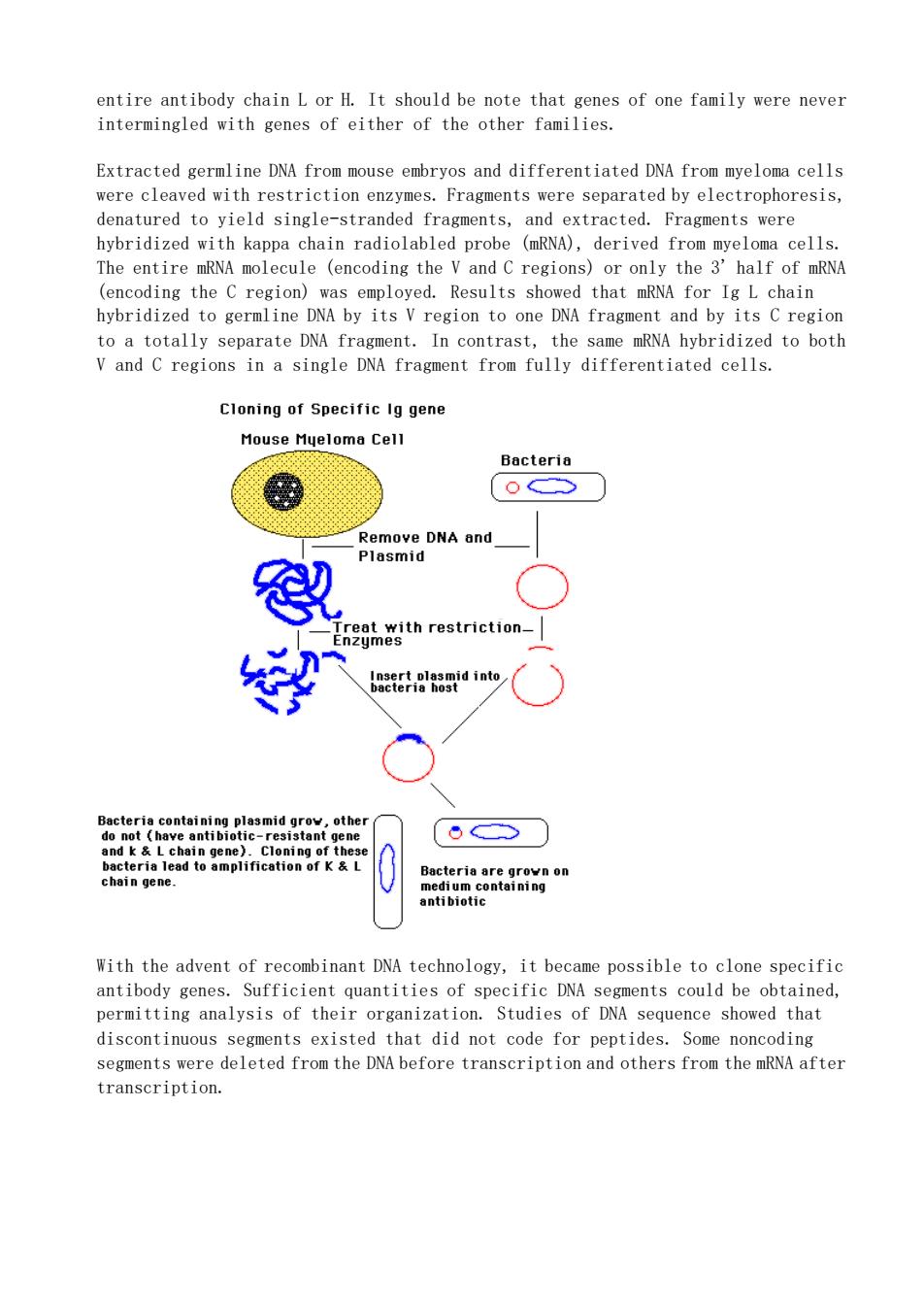
entire antibody chain L or H.It should be note that genes of one family were never intermingled with genes of either of the other families. Extracted germline DNA from mouse embryos and differentiated DNA from myeloma cells were cleaved with restriction enzymes.separated, denatured to yield single-stranded fragments,and extracted.Fragments were hybridized with kappa chain radiolabled probe (mRNA),derived from myeloma cells. The entire mRNA molecule (encoding the V and C regions)or only the 3'half of mRNA (encoding the C region)was employed.Results showed that mRNA for IgL chain hybridized to germline DNA by its Vregion to one DNA fragm to a totally separate DNA fragment.In contrast,the same mRNA hybridized to both V and C regions in a single DNA fragment from fully differentiated cells. Cloning of Specific Ig gene Mouse Myeloma Cell Bacteria (o ve DNA and restriction inte 85 and k With the advent of recombinant DNA technology,it became possible to clone specific antibody genes.Sufficient quantities of specific DNA segments could be obtained, permitting analysis of their organization.Studies of DNA sequence showed that discontinuous segments existed that did not code for peptides. Some noncoding segments were deleted from the DNA before transcription and others from the mRNA after transcription
entire antibody chain L or H. It should be note that genes of one family were never intermingled with genes of either of the other families. Extracted germline DNA from mouse embryos and differentiated DNA from myeloma cells were cleaved with restriction enzymes. Fragments were separated by electrophoresis, denatured to yield single-stranded fragments, and extracted. Fragments were hybridized with kappa chain radiolabled probe (mRNA), derived from myeloma cells. The entire mRNA molecule (encoding the V and C regions) or only the 3' half of mRNA (encoding the C region) was employed. Results showed that mRNA for Ig L chain hybridized to germline DNA by its V region to one DNA fragment and by its C region to a totally separate DNA fragment. In contrast, the same mRNA hybridized to both V and C regions in a single DNA fragment from fully differentiated cells. With the advent of recombinant DNA technology, it became possible to clone specific antibody genes. Sufficient quantities of specific DNA segments could be obtained, permitting analysis of their organization. Studies of DNA sequence showed that discontinuous segments existed that did not code for peptides. Some noncoding segments were deleted from the DNA before transcription and others from the mRNA after transcription
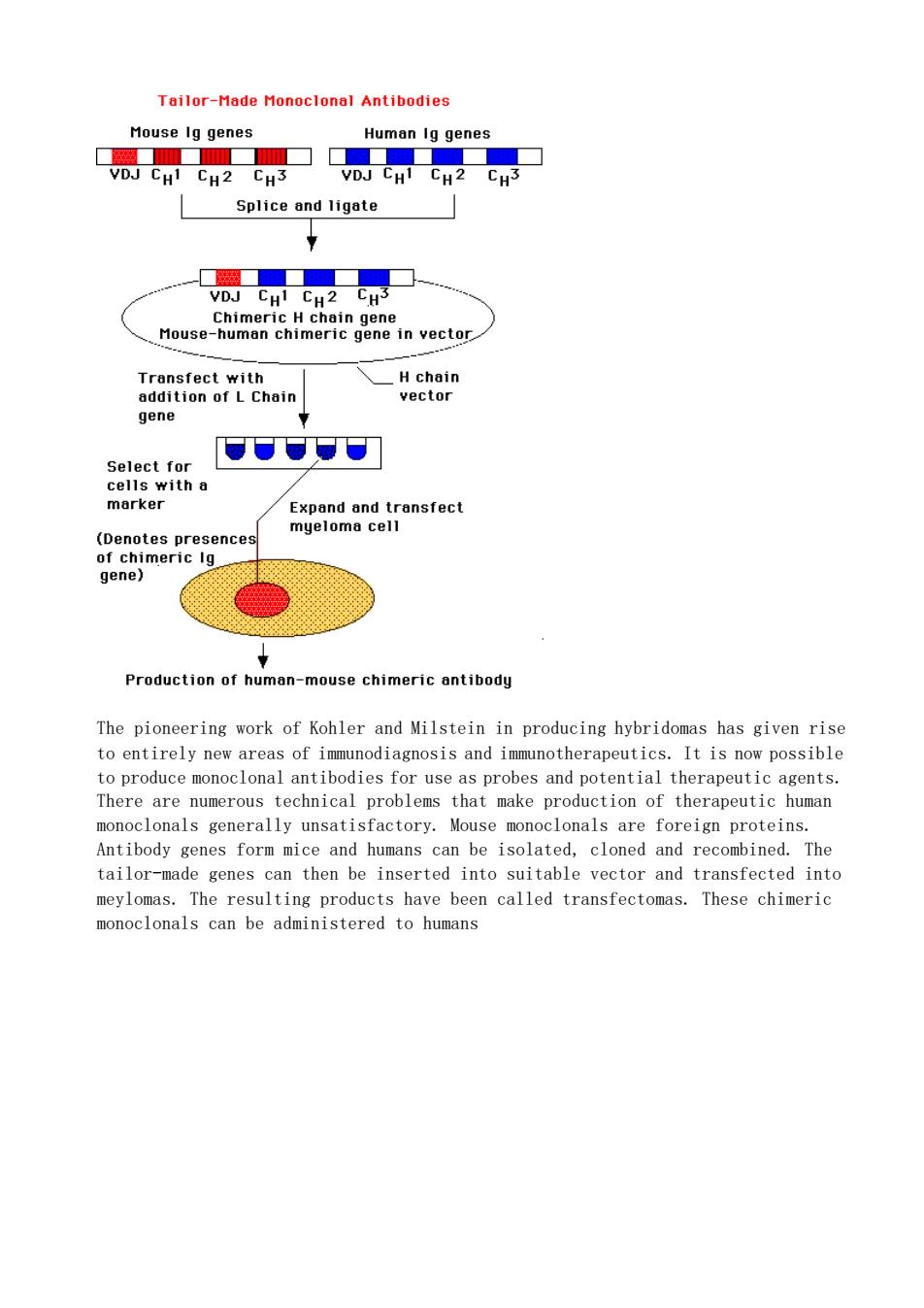
Tailor-Made Monoclonal Antibodies Mouse Ig genes Human Ig genes 隔WWT2cT CHI CH2 CH3 DJ CHI CH2 CH3 Splice and ligate 口 CH CHZ H .Mouse-human chimeric gene in vector Transfect with H chain Select for (penotes p of chimeric la gene) Production of human-mouse chimeric antibody The pioneering work of Kohler and Milstein in producing hybridomas has given rise to entirely new areas of immunodiagnosis and immunotherapeutics.It is now possible to produce monoclonal antibodies for use as probes and potential therapeutic agents. There are numerous technical problems that make production of therapeutic human monoclonals generally unsatisfactory.Mouse monoclonals are foreign proteins. Antibody genes form mice and humans can be isolated cloned and recombined.The tailor-made genes can then be inserted into suitable vector and transfected into meylomas.The resulting products have been called transfectomas.These chimeric monoclonals can be administered to humans
The pioneering work of Kohler and Milstein in producing hybridomas has given rise to entirely new areas of immunodiagnosis and immunotherapeutics. It is now possible to produce monoclonal antibodies for use as probes and potential therapeutic agents. There are numerous technical problems that make production of therapeutic human monoclonals generally unsatisfactory. Mouse monoclonals are foreign proteins. Antibody genes form mice and humans can be isolated, cloned and recombined. The tailor-made genes can then be inserted into suitable vector and transfected into meylomas. The resulting products have been called transfectomas. These chimeric monoclonals can be administered to humans

Recombination of Y-J gene segment of the Kappa chain 5 Germline DNA 阝 L YK2 L J1J2J3J4J5 Ck Rearrangement of DNA 5'B cell DNA LYKI L YK2 LYK3J2J3J4J5 Primary RNA Transcription 】R%下 VK3动2J34J5 A-A-A- VK3 2C Poly A tail Light Chain Gene Organization There are three peptide segments in each L chain and are coded by three distinct genes, V,J,and C.In the kappa family there are a large number of V gene segments and five joining (J)segments and a single C segn ment.By ontrast,in the lambda family,there are fewer V gene segments and a similar number of J genes but several C genes.The V and J gene segments encode V regions and C genes encode C regions.The L chain is encoded by three distinct gene segments that must be joined to form a functional antibody gene. Joining of Gene Segments During the r ess of differentiation of a pluripotent stem cell into a mature antigen reactive B cell,DNA rearrangements take place.In the kappa family one of the many B gene segments will become joined directly to one of the J gene segments.The V-J segment will be joined to the C segment to form a functional antibody gene.The joining of these segments is brought about through the activity of recombinase enzymes. Each germline V gene contains a region encoding the V segment and a leader sequence The leader sequence encodes a leader peptide that controls passage of new protein
Light Chain Gene Organization There are three peptide segments in each L chain and are coded by three distinct genes, V, J, and C. In the kappa family there are a large number of V gene segments and five joining (J) segments and a single C segment. By contrast, in the lambda family, there are fewer V gene segments and a similar number of J genes but several C genes. The V and J gene segments encode V regions and C genes encode C regions. The L chain is encoded by three distinct gene segments that must be joined to form a functional antibody gene. Joining of Gene Segments During the process of differentiation of a pluripotent stem cell into a mature antigen reactive B cell, DNA rearrangements take place. In the kappa family one of the many B gene segments will become joined directly to one of the J gene segments. The V-J segment will be joined to the C segment to form a functional antibody gene. The joining of these segments is brought about through the activity of recombinase enzymes. Each germline V gene contains a region encoding the V segment and a leader sequence. The leader sequence encodes a leader peptide that controls passage of new protein
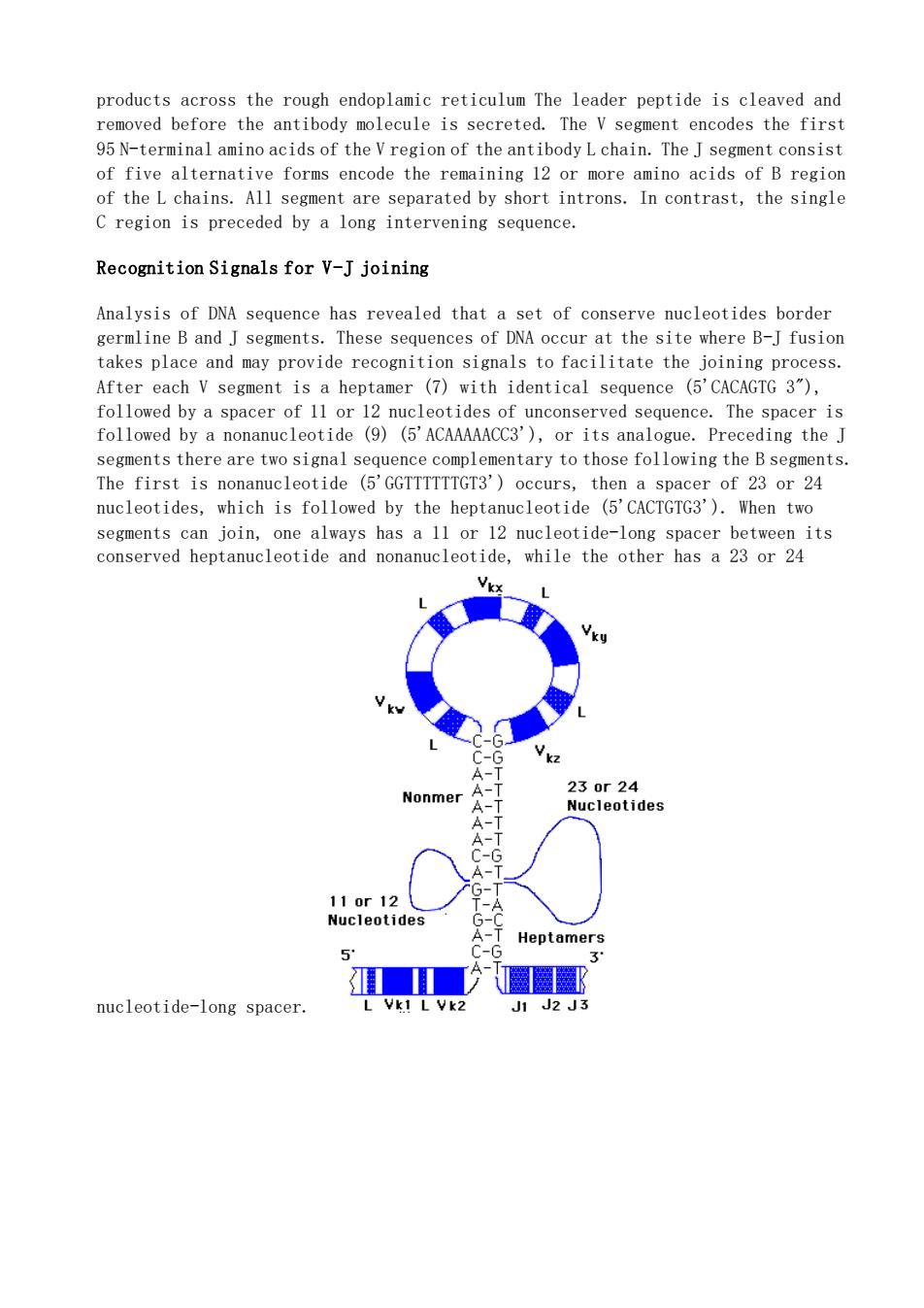
products across the rough endoplamic reticulum The leader peptide is cleaved and removed before the antibody molecule is secreted.The V segment encodes the first 95terminal amin acids of the Vregion of the antibody Lchain.TheJsegent conist of five alternative forms encode the remaining 12 or more amino acids of B region of the L chains.All segment are separated by short introns.In contrast,the single C region is preceded by a long intervening sequence. Recognition Signals for V-J joining Analysis of DNA sequence has revealed that a set of conserve nucleotides border ents.These sequences of DNA occur at the site where B-J fusior joining process After each V segment is a heptamer (7)with identical sequence (5'CACAGTG 3"), followed by a spacer of 11 or 12 nucleotides of unconserved sequence.The spacer is followed by a nonanucleotide (9)(5'ACAAAAACC3'),or its analogue.Preceding the J segments there are two signal sequence complementary to those following the B segments. The fir st is n cleotide (5'GGTTTTTTGT3')o curs. of 23 or 24 nucletides,hich is followed by the heptanucletide(CACG).When two segments can join,one always has a 11 or 12 nucleotide-long spacer between its conserved heptanucleotide and nonanucleotide,while the other has a 23 or 24 Nonmer 110r12 Nucleotides nucleotide-long spacer
products across the rough endoplamic reticulum The leader peptide is cleaved and removed before the antibody molecule is secreted. The V segment encodes the first 95 N-terminal amino acids of the V region of the antibody L chain. The J segment consist of five alternative forms encode the remaining 12 or more amino acids of B region of the L chains. All segment are separated by short introns. In contrast, the single C region is preceded by a long intervening sequence. Recognition Signals for V-J joining Analysis of DNA sequence has revealed that a set of conserve nucleotides border germline B and J segments. These sequences of DNA occur at the site where B-J fusion takes place and may provide recognition signals to facilitate the joining process. After each V segment is a heptamer (7) with identical sequence (5'CACAGTG 3"), followed by a spacer of 11 or 12 nucleotides of unconserved sequence. The spacer is followed by a nonanucleotide (9) (5'ACAAAAACC3'), or its analogue. Preceding the J segments there are two signal sequence complementary to those following the B segments. The first is nonanucleotide (5'GGTTTTTTGT3') occurs, then a spacer of 23 or 24 nucleotides, which is followed by the heptanucleotide (5'CACTGTG3'). When two segments can join, one always has a 11 or 12 nucleotide-long spacer between its conserved heptanucleotide and nonanucleotide, while the other has a 23 or 24 nucleotide-long spacer
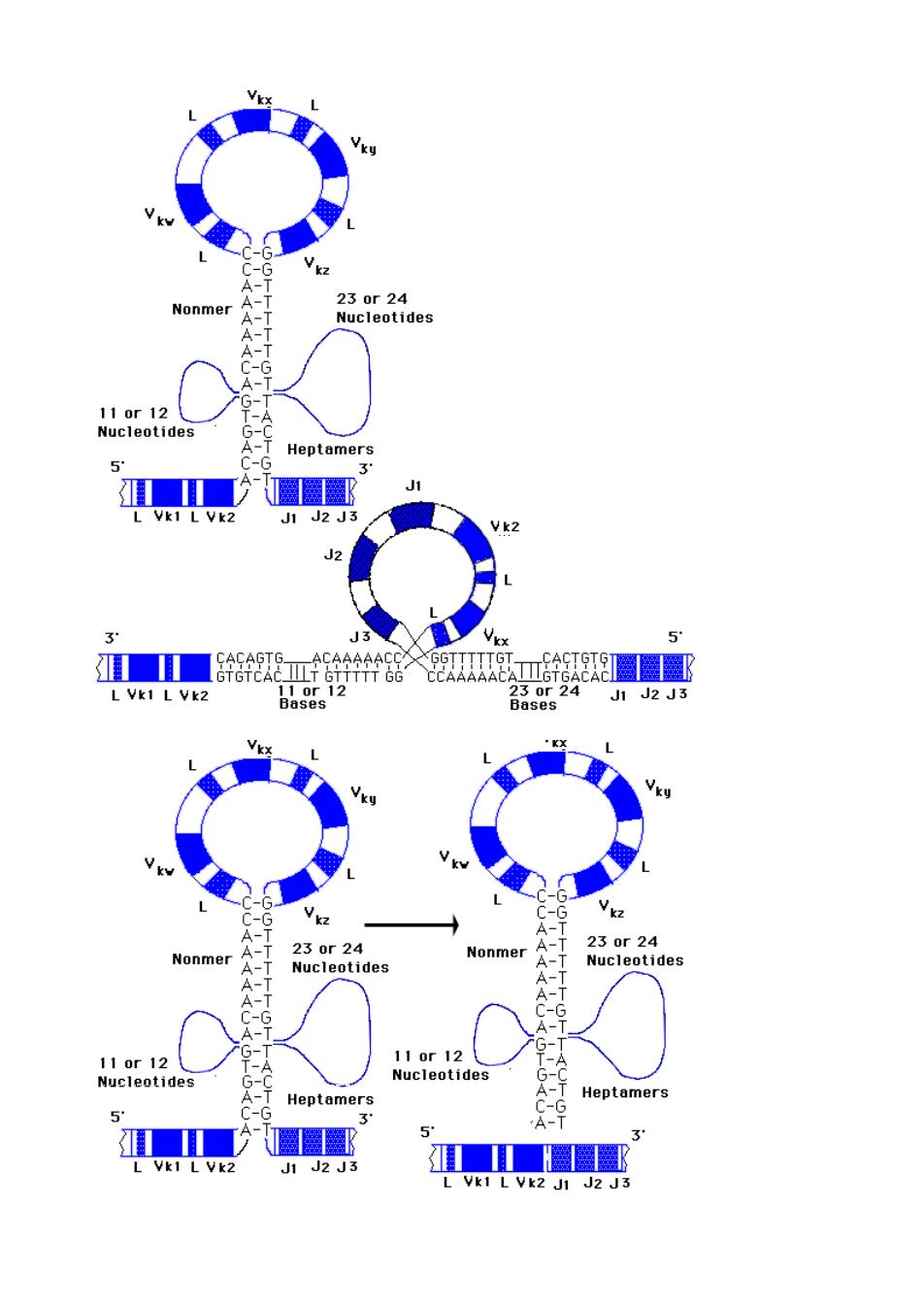
Nonmer 230r24 cleotides 110r12 Nucleotides Heptam 5 5 kz Nonmer 4 110r12 Neieolae Nucleotides Heptamers A- 5 J1 J2 J3 Vk2 J1 J2 J

5 21 The loop is discarded ■■凰re yonte品Regions L Yk1 L Yk2J1 J2 J3

Recombination of v-J-D gene segment of heavy chain ■■邒Ⅻ■邝圈鹽形丞 ,HLH2 Hn 041-12 Rearrament of DNA DH4 Cell DNA ■飞 ,H1LH2245 C Transcription DH4 Primary RNA Transcript J2 J3 J4 J5 mRNA J2 C Heavy Chainμ Heavy Chain Variable Region Diversity H chain diversity is generated by mechanisms quite similar to those previously described for L Chains.There are many V genes in the H chain gene family (perhaps as seen over30),which may encode the leader and the main region to the 5 residue There are also a number of functional J segments (dour in mice,an five in humans),which may encode part of the CDR3 and all of the last frame work region (FR4)described for the L chains.The process is somewhat more complex,since 10 to 20 short DNA segments,known as D,or diversity,segments are located between the H and J segments.D segments encode two to 14 amino acids in the hypervarible region,or complementary region 3(CDR3) and,therefore,are critically involved in determining the specificity of an antibody
Heavy Chain Variable Region Diversity H chain diversity is generated by mechanisms quite similar to those previously described for L Chains. There are many V genes in the H chain gene family (perhaps over 300), which may encode the leader and the main region to the 95 residue, as seen for L chains. There are also a number of functional J segments (dour in mice, and five in humans), which may encode part of the CDR3 and all of the last frame work region (FR4) described for the L chains. The process is somewhat more complex, since 10 to 20 short DNA segments, known as D, or diversity, segments are located between the H and J segments. D segments encode two to 14 amino acids in the hypervarible region, or complementary region 3 (CDR3), and, therefore, are critically involved in determining the specificity of an antibody

Arrangement of genes encoding C chains. S..C..Cs Sy- TX■XE YH DH JH .M☐ H M H M H MY M G 21 S Splice Signals Intron ce signals Recombination of VH-DH-JH segments During differentiation of pluripotent stem cells,a DH segment,JH segment,and B segment,in this example DH4,JH2 and BH2,become joined.The rearranged genes are then transcribed.A second transcription follows, whereby introns re removed and mRNA is formed and translated into specific Ig H chains These gene segments obviously contribute significantly to the generation of hypervariablility in the V regions.When three segments of DNA randomly join to encode the entire H chain V region,they enhance the recombination possibilities.Thus,if there were 300 VH,12 D,and four alternative J Gene se gments and one of each becomes ociated formed (400) chains could be
Recombination of VH-DH-JH segments During differentiation of pluripotent stem cells, a DH segment, JH segment, and B segment, in this example DH4, JH2 and BH2, become joined. The rearranged genes are then transcribed. A second transcription follows, whereby introns re removed and mRNA is formed and translated into specific Ig H chains. These gene segments obviously contribute significantly to the generation of hypervariablility in the V regions. When three segments of DNA randomly join to encode the entire H chain V region, they enhance the recombination possibilities. Thus, if there were 300 VH, 12 D, and four alternative J Gene segments and one of each becomes randomly associated during the differentiation, 14,400 different chains could be formed (300 x12 x 4 =14,400)