
Textbook Mark Allen Weiss,Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C,China Machine Press
Textbook ◼ Mark Allen Weiss, Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C, China Machine Press

Grading Final exam:70% ■Others:30%
Grading ◼ Final exam: 70% ◼ Others: 30%
What are Data Structures and Algorithms? Data Structures are methods of organizing large amounts of data. An algorithm is a procedure that consists of finite set of instructions which,given an input from some set of possible inputs,enables us to obtain an output if such an output exists or else obtain nothing at all if there is no output for that particular input through a systematic execution of the instructions
What are Data Structures and Algorithms? ◼ Data Structures are methods of organizing large amounts of data. ◼ An algorithm is a procedure that consists of finite set of instructions which, given an input from some set of possible inputs, enables us to obtain an output if such an output exists or else obtain nothing at all if there is no output for that particular input through a systematic execution of the instructions
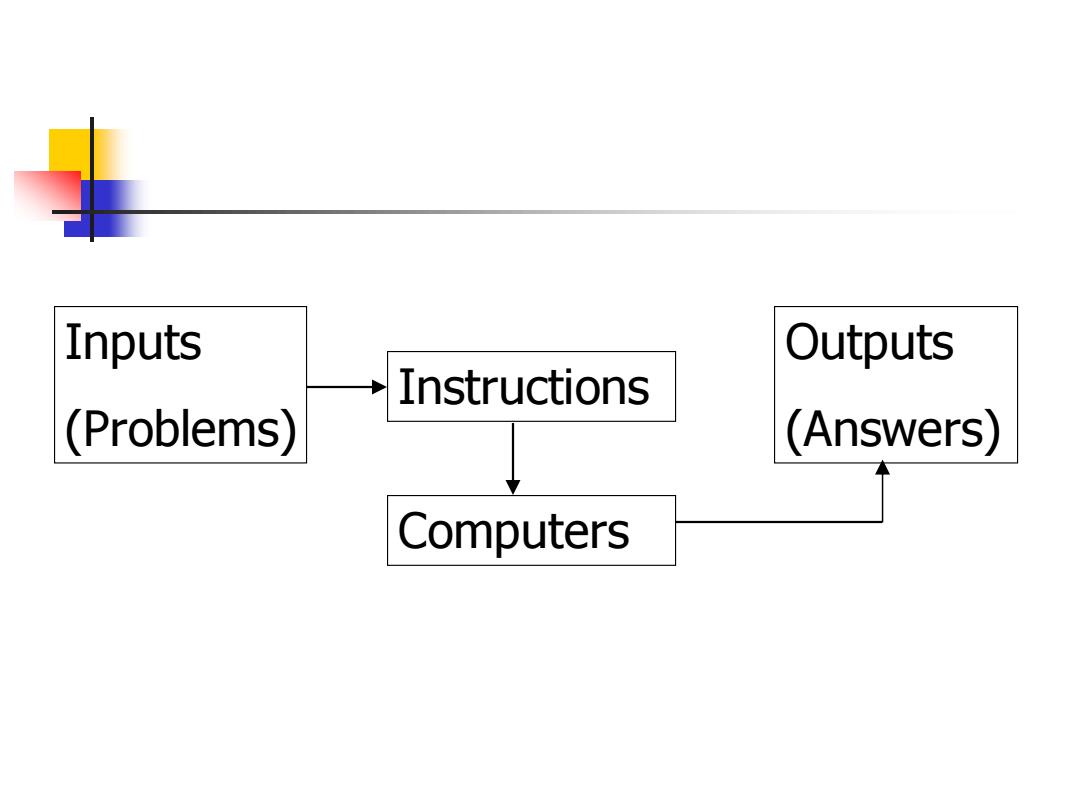
Inputs Outputs Instructions (Problems) (Answers) Computers
Instructions Inputs (Problems) Outputs (Answers) Computers
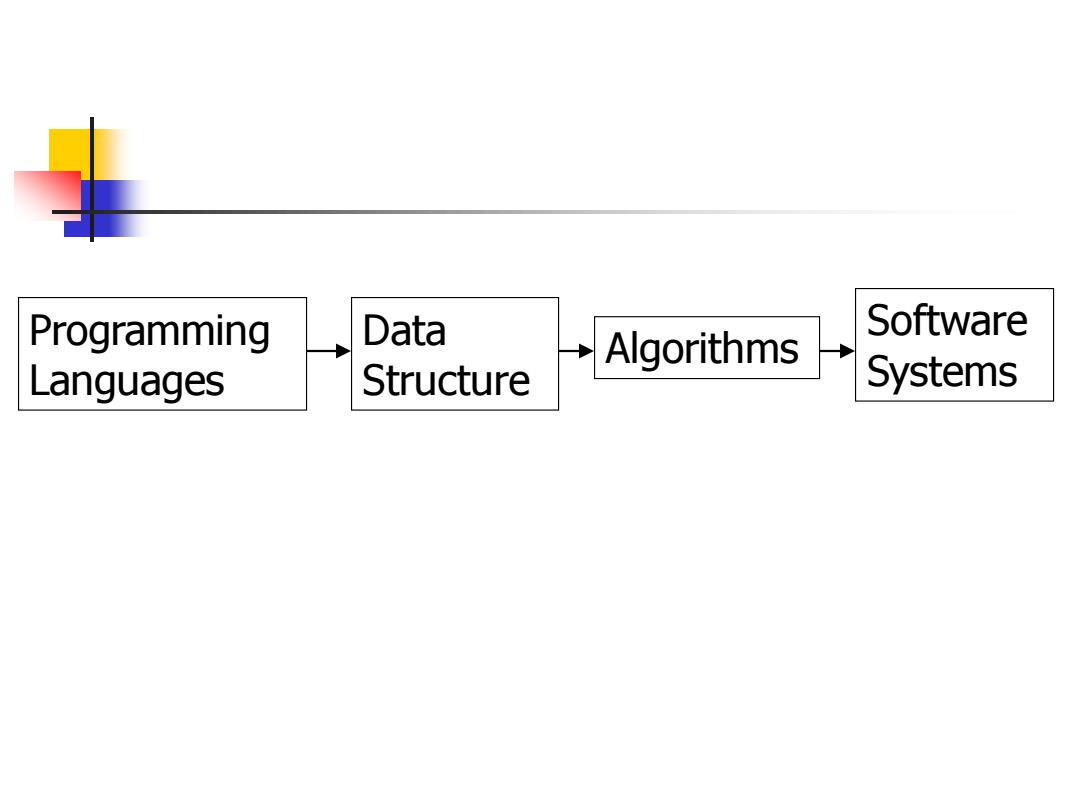
Programming Data Software Algorithms Languages Structure Systems
Programming Languages Data Structure Algorithms Software Systems

Contents Chapter 3 Lists,Stacks,and Queues Chapter 4 Trees Chapter 5 Hashing Chapter 6 Priority Queues(Heaps) Chapter 7 Sorting Chapter 8 The Disjoint Set ADT Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms Chapter 10 Algorithm Design Techniques
Contents Chapter 3 Lists, Stacks, and Queues Chapter 4 Trees Chapter 5 Hashing Chapter 6 Priority Queues (Heaps) Chapter 7 Sorting Chapter 8 The Disjoint Set ADT Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms Chapter 10 Algorithm Design Techniques
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) One of the basic rules concerning programming is to break the program down into modules. Each module is a logical unit and does a specific job. Its size is kept small by calling other modules. Modularity has several advantages.(1)It is much easier to debug small routines than large routines;(2) It is easier for several people to work on a modular program simultaneously;(3)A well-written modular program places certain dependencies in only one routing,making changes easier
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) ◼ One of the basic rules concerning programming is to break the program down into modules. ◼ Each module is a logical unit and does a specific job. Its size is kept small by calling other modules. ◼ Modularity has several advantages. (1) It is much easier to debug small routines than large routines; (2) It is easier for several people to work on a modular program simultaneously; (3) A well-written modular program places certain dependencies in only one routing, making changes easier

Abstract Data Types (ADTs) An abstract data type (ADT)is a set of operations. Abstract data types are mathematical abstractions; nowhere in an ADT's definition is there any mention of how the set of operations is implemented. Objects such as lists,sets,and graphs,along with their operations,can be viewed as abstract data types,just as integers,reals,and booleans are data types.Integers,reals,and booleans have operations associated with them,and so do ADTs
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) ◼ An abstract data type (ADT) is a set of operations. ◼ Abstract data types are mathematical abstractions; nowhere in an ADT’s definition is there any mention of how the set of operations is implemented. ◼ Objects such as lists, sets, and graphs, along with their operations, can be viewed as abstract data types, just as integers, reals, and booleans are data types. Integers, reals, and booleans have operations associated with them, and so do ADTs

Abstract Data Types (ADTs) The basic idea is that the implementation of the operations related to ADTs is written once in the program,and any other part of the program that needs to perform an operation on the ADT can do so by calling the appropriate function. If for some reason implementation details need to be changed,it should be easy to do so by merely changing the routings that perform the ADT operations. There is no rule telling us which operations must be supported for each ADT;this is a design decision
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) ◼ The basic idea is that the implementation of the operations related to ADTs is written once in the program, and any other part of the program that needs to perform an operation on the ADT can do so by calling the appropriate function. ◼ If for some reason implementation details need to be changed, it should be easy to do so by merely changing the routings that perform the ADT operations. ◼ There is no rule telling us which operations must be supported for each ADT; this is a design decision

The List ADT The form of a general list:A,A,A3,...,Ai The size of this list is M An empty list is a special list of size 0; ■ For any list except the empty list,we say that A1 follows (or succeeds)A,(/1): The first element of the list is A1,and the last element is A.We will not define the predecessor of A or the successor of Awv. The position of element A,in a list is /
The List ADT ◼ The form of a general list: A1 , A2 , A3 , …, AN; ◼ The size of this list is N; ◼ An empty list is a special list of size 0; ◼ For any list except the empty list, we say that Ai+1 follows (or succeeds) Ai (i1); ◼ The first element of the list is A1 , and the last element is AN . We will not define the predecessor of A1 or the successor of AN. ◼ The position of element Ai in a list is i