
Chapter 9 OTHER SEPARATION PROCESSES ◆ Physical/Mechanical Separations ◆ Diffusional/equilibration separations
Chapter 9 OTHER SEPARATION PROCESSES ◆ Physical/Mechanical Separations ◆ Diffusional/equilibration separations

Physical/Mechanical Separations ◆ Filtration ◆ Expression ◆ Centrifugation ◆ Cyclone
Physical/Mechanical Separations ◆ Filtration ◆ Expression ◆ Centrifugation ◆ Cyclone
Diffusional/equilibration separations ◆ Crystallization ◆ Distillation ◆ Absorption/Stripping ◆ Extraction ◆ Adsorption ◆ Ion Exchange ◆ Dialysis/Electrodialysis
Diffusional/equilibration separations ◆ Crystallization ◆ Distillation ◆ Absorption/Stripping ◆ Extraction ◆ Adsorption ◆ Ion Exchange ◆ Dialysis/Electrodialysis
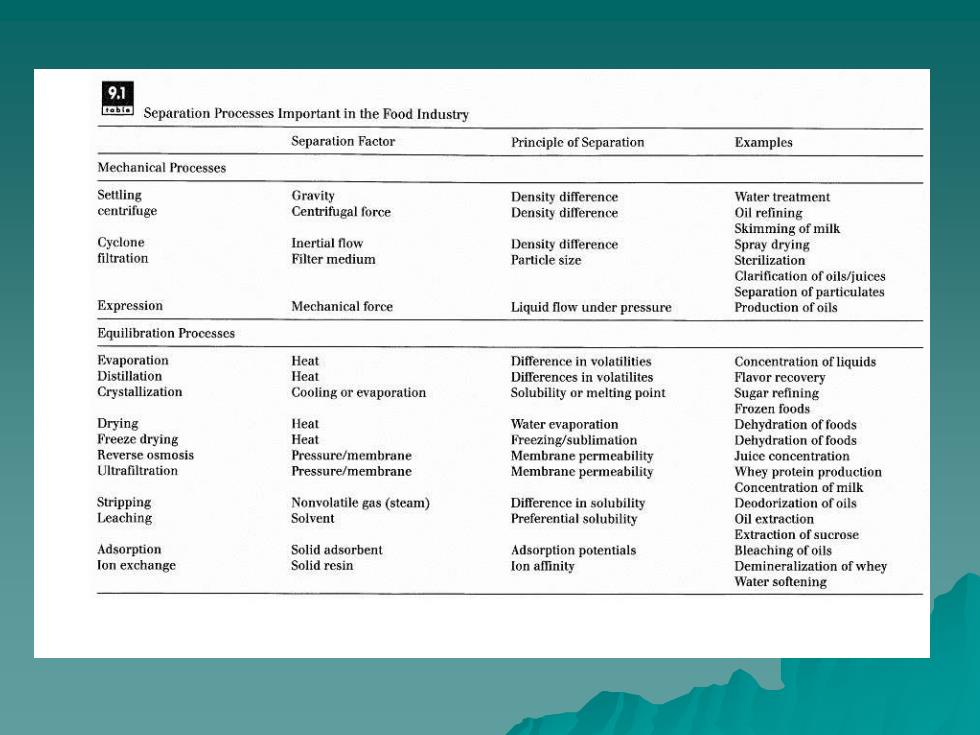
9.1 rebia Separation Processes Important in the Food Industry Separation Factor Principle of Separation Examples Mechanical Processes Settling Gravity Density difference Water treatment centrifuge Centrifugal force Density difference Oil refining Skimming of milk Cyclone Inertial flow Density difference Spray drying filtration Filter medium Particle size Sterilization Clarification of oils/juices Separation of particulates Expression Mechanical force Liquid flow under pressure Production of oils Equilibration Processes Evaporation Heat Difference in volatilities Concentration of liquids Distillation Heat Differences in volatilites Flavor recovery Crystallization Cooling or evaporation Solubility or melting point Sugar refining Frozen foods Drying Heat Water evaporation Dehydration of foods Freeze drying Heat Freezing/sublimation Dehydration of foods Reverse osmosis Pressure/membrane Membrane permeability Juice concentration Ultrafiltration Pressure/membrane Membrane permeability Whey protein production Concentration of milk Stripping Nonvolatile gas (steam) Difference in solubility Deodorization of oils Leaching Solvent Preferential solubility Oil extraction Extraction of sucrose Adsorption Solid adsorbent Adsorption potentials Bleaching of oils Ion exchange Solid resin lon affinity Demineralization of whey Water softening

Filtration ◆ Used to clarify fluid foods( fruit juices or vegetable oils) and to remove microorganisms from either air or fluid foods and to separate solid from liquid phases. In some cases, the material that remains on the filter is the valuable component (crystal slurry from liquid in sugar refining, separation of proteins or yeast). The material that passes through the filter is the desired product (fruit juice or vegetable oil Clarification, sterilized water or air)
Filtration ◆ Used to clarify fluid foods( fruit juices or vegetable oils) and to remove microorganisms from either air or fluid foods and to separate solid from liquid phases. In some cases, the material that remains on the filter is the valuable component (crystal slurry from liquid in sugar refining, separation of proteins or yeast). The material that passes through the filter is the desired product (fruit juice or vegetable oil Clarification, sterilized water or air)

Principles of Operation. ◆ Filtration involves passing a material through a filter medium that retains particles of a certain size, Filtration is distinguished from other membrane separations (ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis) in terms of the size of particles that are separated. A fluid containing solid matter is forced through a filter medium, with the solid particles being retained by the filter and the liquid passing through
Principles of Operation. ◆ Filtration involves passing a material through a filter medium that retains particles of a certain size, Filtration is distinguished from other membrane separations (ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis) in terms of the size of particles that are separated. A fluid containing solid matter is forced through a filter medium, with the solid particles being retained by the filter and the liquid passing through

9.2 table Applications of Filtration in the Food Processing Industry Refining operations Fat fractionation (palm oil,palm kernel oil,milk fat,etc.) Sugar refining (lactose,sucrose,etc.) Salt,organic acids,etc. Removal of microorganisms Cold pasteurization (beer) Air sterilization Clarification Fruit juices (apple juice,etc.) Vegetable oils Separation of malt,hops,and yeast in brewing Separation of cheese curd from whey
Configurations ◆ plate-and-frame ◆ continuous rotary filter
Configurations ◆ plate-and-frame ◆ continuous rotary filter

Factors influencing filtration ◆ Size of the pores in the filter medium ◆ The viscosity of the carrier fluid ◆ The amount and characteristics of suspended solids to be filtered ◆ The external pressure applied ◆ Filter aids, such as diatomaceous earth or perlite
Factors influencing filtration ◆ Size of the pores in the filter medium ◆ The viscosity of the carrier fluid ◆ The amount and characteristics of suspended solids to be filtered ◆ The external pressure applied ◆ Filter aids, such as diatomaceous earth or perlite
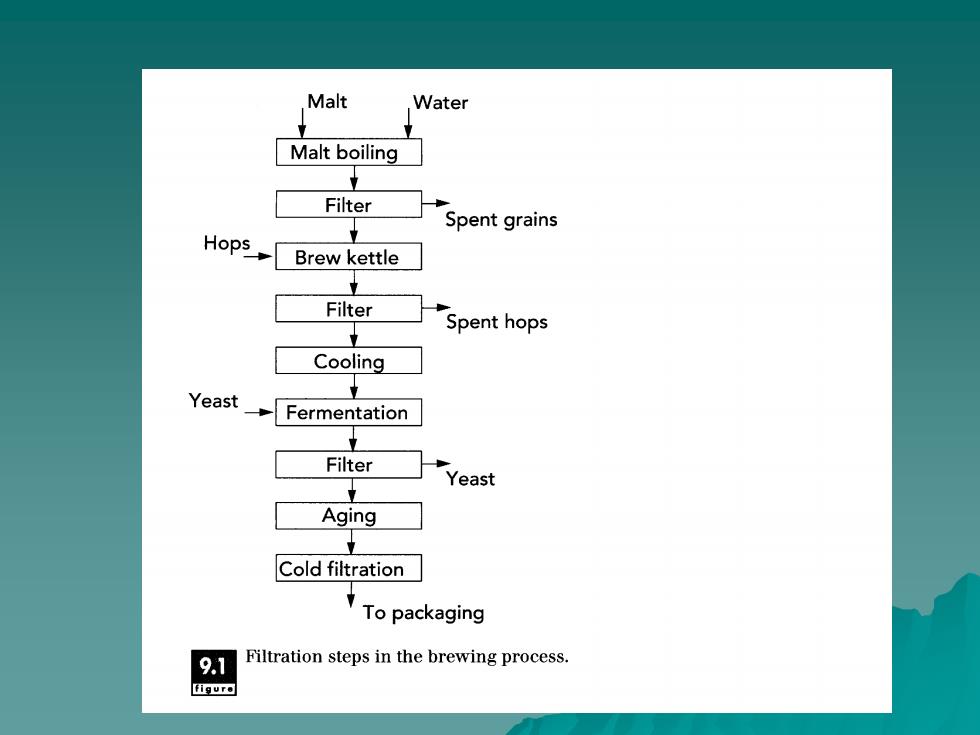
Malt Water Malt boiling Filter Spent grains Hops Brew kettle Filter Spent hops Cooling Yeast Fermentation Filter Yeast Aging Cold filtration To packaging 9.1 Filtration steps in the brewing process. 9ur