
REFRIGERATED STORAGE INTRODUCTION PRINCIPLES OF REFRIGERATED STORAGE CONTROL OF MICROBIAL GROWTH DURING REFRIGERATEED STORAGE ESTABLISHING SHELF-LIFE IN REFRIGERATED FOODS DETERIORATION OF PRODUCT QUALITY
REFRIGERATED STORAGE INTRODUCTION PRINCIPLES OF REFRIGERATED STORAGE CONTROL OF MICROBIAL GROWTH DURING REFRIGERATEED STORAGE ESTABLISHING SHELF-LIFE IN REFRIGERATED FOODS DETERIORATION OF PRODUCT QUALITY

INTRODUCTION Primary purpose of refrigerating foods is to extend shelf life by slowing down degradation reactions and limiting microbial growth. Through reduction in rates of chemical, biochemical, and microbial kinetics, low-temperature storage can extend the shelf life of fresh and processed foods By holding food in the temp. range of -l to 8℃
INTRODUCTION Primary purpose of refrigerating foods is to extend shelf life by slowing down degradation reactions and limiting microbial growth. Through reduction in rates of chemical, biochemical, and microbial kinetics, low-temperature storage can extend the shelf life of fresh and processed foods By holding food in the temp. range of -l to 8℃

Deferent Food’s Optimal Storage Temp
Deferent Food’s Optimal Storage Temp

Slow Down The Reaction Rate limits the rate of chemical, biochemical, and physicochemical changes. rates of lipid oxidation nonenzymatic browning sugar conversion enzymic browning respiration reactions The sum of all these effects results in extended shelf life for refrigerated foods
Slow Down The Reaction Rate limits the rate of chemical, biochemical, and physicochemical changes. rates of lipid oxidation nonenzymatic browning sugar conversion enzymic browning respiration reactions The sum of all these effects results in extended shelf life for refrigerated foods

5.1 table Typical Foods Needing Refrigerated Storage Dairy:milk,yogurt,cheese,cream,butter,etc. Meats:beef,pork,chicken,turkey,seafood,etc. Deli salads:macaroni salad,tuna salad,cole slaw,potato salad,etc. Pasta(fresh) Vegetables Eggs Salads:caesar salad,prepared salads,etc. Dips,dressings,and sauces:mayonnaise,mustard,ketchup,etc. Spreads:margarine,blends,etc. Ready-to-eat meals:pizza,prepared lunches,etc. Refrigerated dough products:cinnamon rolls,croissants,biscuits,etc. Pastries and desserts:cakes,pudding,etc. Fruit juices and drinks:orange juice,apple juice,etc
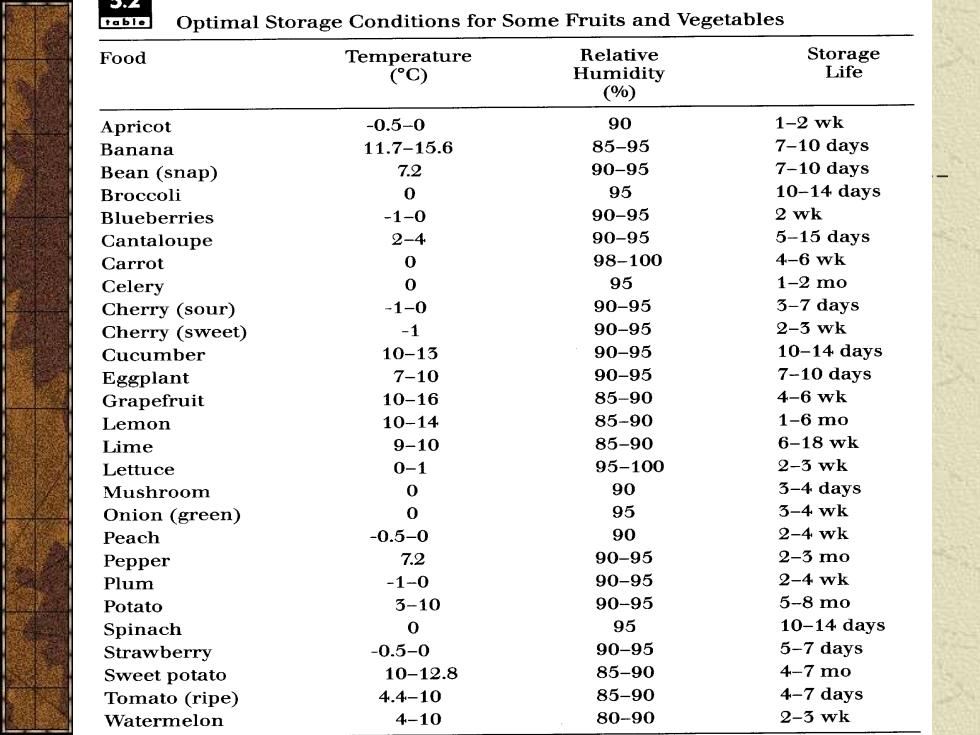
2.k table Optimal Storage Conditions for Some Fruits and Vegetables Food Temperature Relative Storage (°C) Humidity Life (%) Apricot -0.5-0 90 1-2wk Banana 11.7-15.6 85-95 7-10 days Bean (snap) 72 90-95 7-10 days Broccoli 0 95 10-14 days Blueberries -1-0 90-95 2 wk Cantaloupe 2-4 90-95 5-15 days Carrot 0 98-100 4-6wk Celery 0 95 1-2mo Cherry (sour) -1-0 90-95 3-7 days Cherry (sweet) -1 90-95 2-3wk Cucumber 10-13 90-95 10-14 days Eggplant 7-10 90-95 7-10 days Grapefruit 10-16 85-90 4-6wk Lemon 10-14 85-90 1-6mo Lime 9-10 85-90 6-18wk Lettuce 0-1 95-100 2-3wk Mushroom 0 90 3-4 days Onion (green) 0 95 3-4wk Peach -0.5- 90 2-4wk Pepper 7.2 90-95 2-3mo Plum -1-0 90-95 2-4wk Potato 3-10 90-95 5-8mo Spinach 0 95 10-14 days Strawberry -0.5-0 90-95 5-7 days Sweet potato 10-12.8 85-90 4-7m0 Tomato (ripe) 4.4-10 85-90 4-7 days Watermelon 4-10 80-90 2-3wk

GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF REFRIGERATED STORAGE Pretreatment Chilling Processes Chilling of Solid Foods. Chilling of Liquid Food Refrigerated Storage Temperature. Air Circulation. Air Composition
GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF REFRIGERATED STORAGE Pretreatment Chilling Processes Chilling of Solid Foods. Chilling of Liquid Food Refrigerated Storage Temperature. Air Circulation. Air Composition

GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF REFRIGERATED STORAGE Refrigerated Transport Mechanical Refrigeration Systems. Eutectic Plate Systems. Liquid Nitrogen. Retail Storage Refrigerated Cabinets for Food Service Home Refrigeration
GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF REFRIGERATED STORAGE Refrigerated Transport Mechanical Refrigeration Systems. Eutectic Plate Systems. Liquid Nitrogen. Retail Storage Refrigerated Cabinets for Food Service Home Refrigeration
CONTROL OF MICROBIAL GROWTH DURING REFRIGERATED STORAGE Low temperatures slow the rate of each step in the microbial growth cycle, resulting in longer lag phase, slower growth in the exponential phase, and reducing the generation time Some pathogens can grow at low temperatures (Clostridium botulinum type E at 5.5℃; Listeria moncytogenes at 3℃)
CONTROL OF MICROBIAL GROWTH DURING REFRIGERATED STORAGE Low temperatures slow the rate of each step in the microbial growth cycle, resulting in longer lag phase, slower growth in the exponential phase, and reducing the generation time Some pathogens can grow at low temperatures (Clostridium botulinum type E at 5.5℃; Listeria moncytogenes at 3℃)
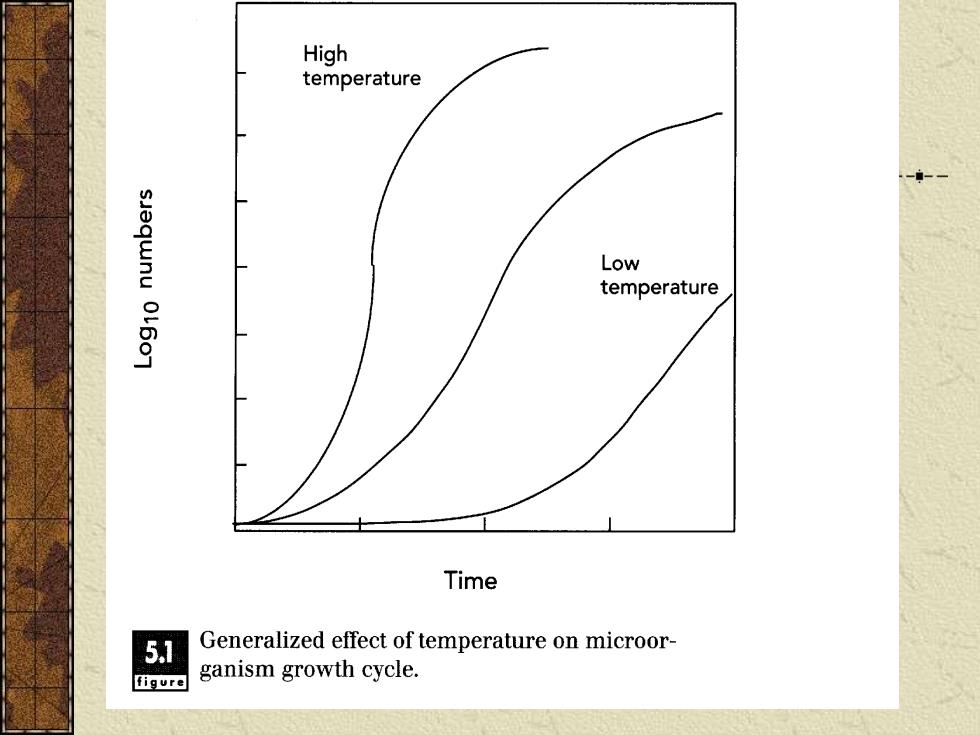
High temperature Low temperature Time 5.1 Generalized effect of temperature on microor- figure ganism growth cycle