
Chapter 2 THERMAL PROCESSING PRINCIPLES ⚫ INFLUENCE OF ELEVATED TEMPERATURES ON MICROBIAL POPULATIONS ⚫ ESTABLISHMENT OF PRODUCT SHELF LIFE AND SAFETY ⚫ INFLUENCE OF THERMAL PROCESS ON PRODUCT QUALITY ⚫ INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS CALCULATIONS
Chapter 2 THERMAL PROCESSING PRINCIPLES ⚫ INFLUENCE OF ELEVATED TEMPERATURES ON MICROBIAL POPULATIONS ⚫ ESTABLISHMENT OF PRODUCT SHELF LIFE AND SAFETY ⚫ INFLUENCE OF THERMAL PROCESS ON PRODUCT QUALITY ⚫ INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS CALCULATIONS

Vocabulary ⚫ microbial population elevated temperature viability vegetative Salmonella spp., Listeria or Escherichia coli-any Clostridium botulinum function of time logarithmic microbial spores abruptly semilogarithmic coordinates decimal reduction time, or D-value food spoilage microorganisms decimal reduction curve
Vocabulary ⚫ microbial population elevated temperature viability vegetative Salmonella spp., Listeria or Escherichia coli-any Clostridium botulinum function of time logarithmic microbial spores abruptly semilogarithmic coordinates decimal reduction time, or D-value food spoilage microorganisms decimal reduction curve

Vocabulary ⚫ thermal resistance curve thermal resistance constant or Z-value, thermal death time (F) survivor curve linear relationship commercial sterilization yeast and molds acidity, or pH low- acid anaerobic Low Acid Canned Food pathogen Spoilage probability quality attributes heat-sensitive nutrients flavor, texture, and color over-processing lethal rate lethality
Vocabulary ⚫ thermal resistance curve thermal resistance constant or Z-value, thermal death time (F) survivor curve linear relationship commercial sterilization yeast and molds acidity, or pH low- acid anaerobic Low Acid Canned Food pathogen Spoilage probability quality attributes heat-sensitive nutrients flavor, texture, and color over-processing lethal rate lethality
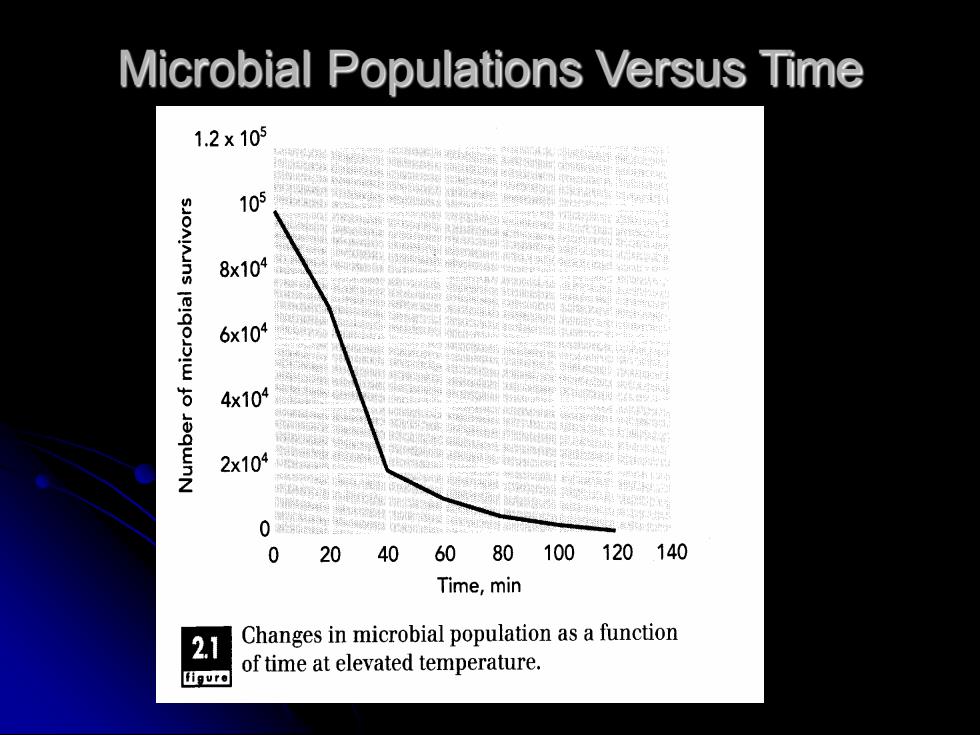
Microbial Populations Versus Time
Microbial Populations Versus Time
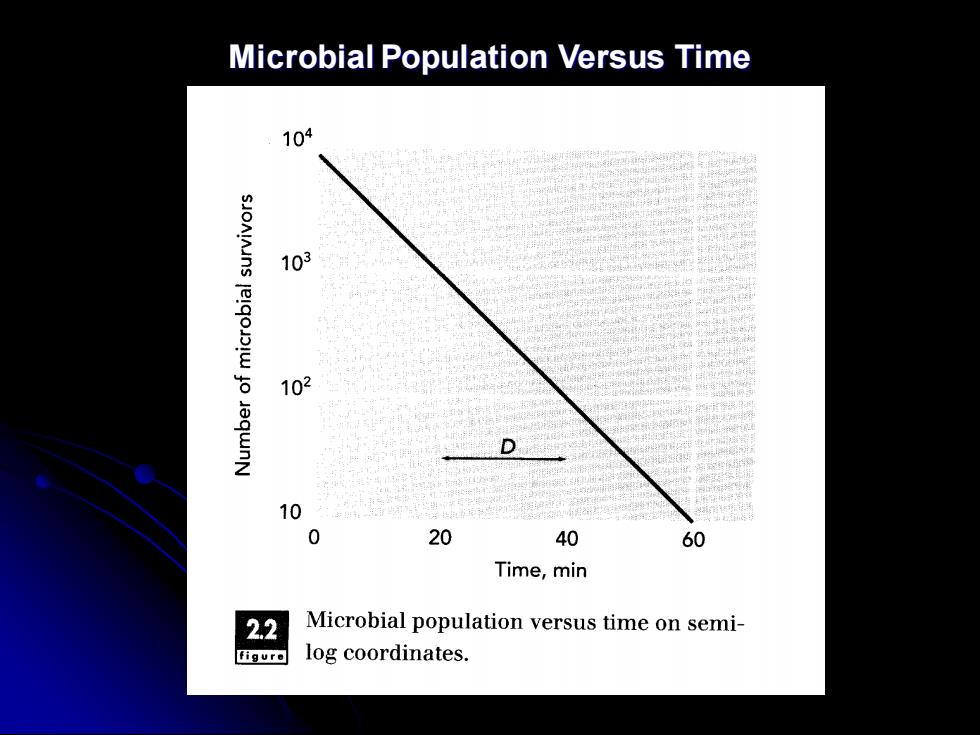
Microbial Population Versus Time
Microbial Population Versus Time

survivor curve ⚫ When the microbial populations as a function of time are presented on semilogarithmic coordinates, a linear decrease in microbial population with time is observed. It is the survivor curve. It is emphasized that these relationships occur when the environment around the population is at a constant temperature throughout the period of exposure
survivor curve ⚫ When the microbial populations as a function of time are presented on semilogarithmic coordinates, a linear decrease in microbial population with time is observed. It is the survivor curve. It is emphasized that these relationships occur when the environment around the population is at a constant temperature throughout the period of exposure

Definition of Decimal Reduction Time ⚫On survivor curve, the time required for a one log cycle reduction in microbial population is the decimal reduction time (D), or D- value
Definition of Decimal Reduction Time ⚫On survivor curve, the time required for a one log cycle reduction in microbial population is the decimal reduction time (D), or D- value
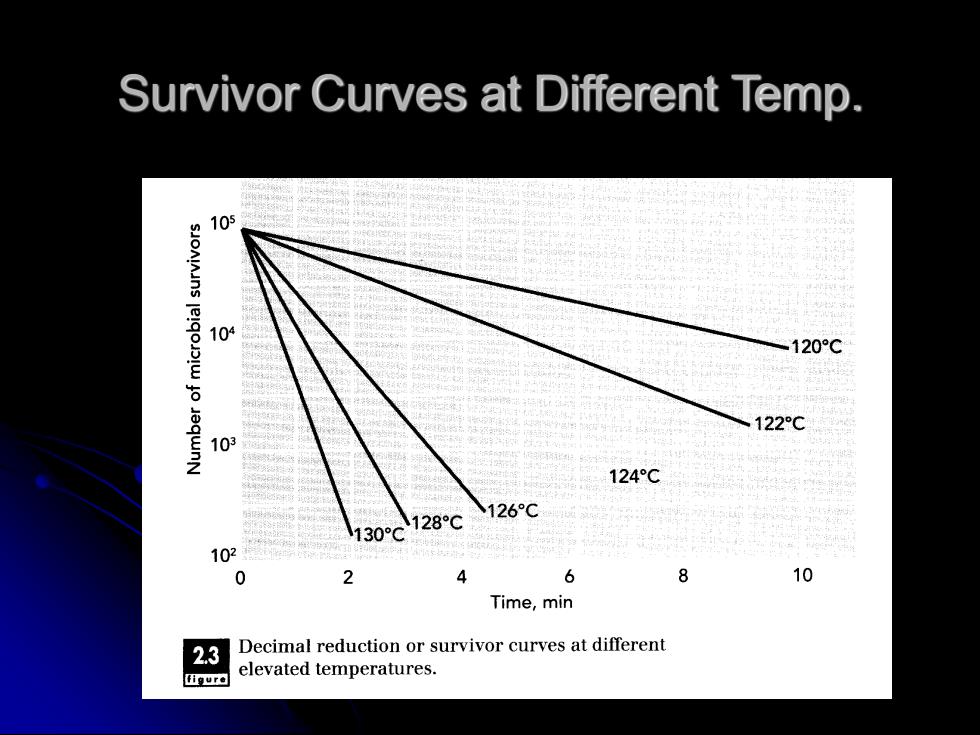
Survivor Curves at Different Temp
Survivor Curves at Different Temp

thermal Resistance Curve ⚫ A plot of decimal reduction time as a function of temperature on semilog coordinates results in a linear relationship. This linear relationship is the thermal resistance curve for a given microbial population
thermal Resistance Curve ⚫ A plot of decimal reduction time as a function of temperature on semilog coordinates results in a linear relationship. This linear relationship is the thermal resistance curve for a given microbial population
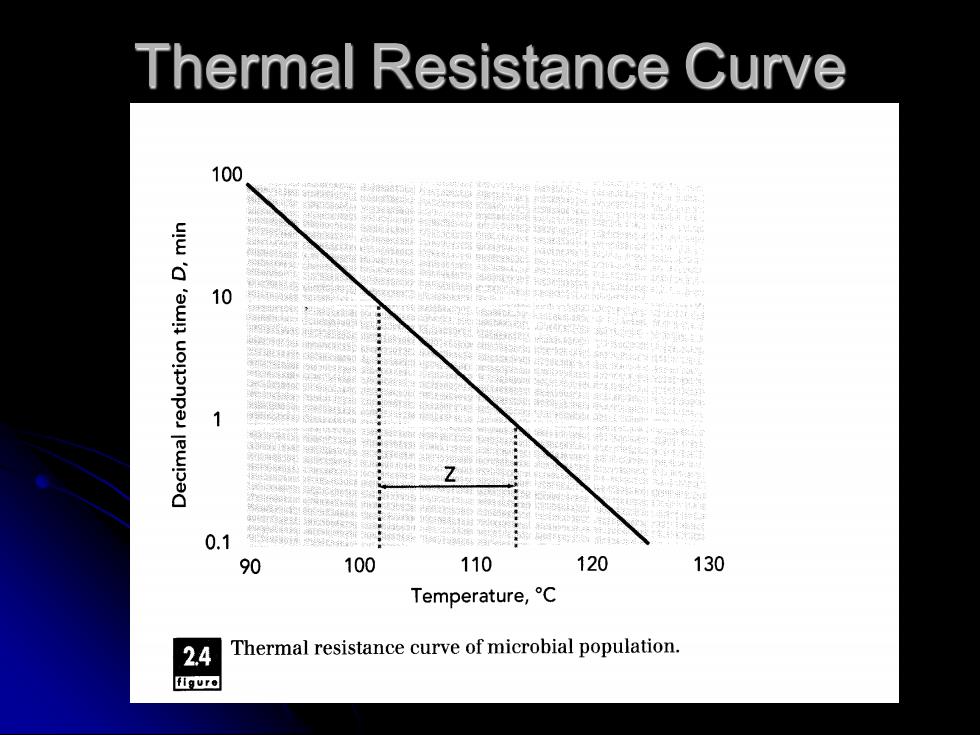
Thermal Resistance Curve
Thermal Resistance Curve