
概念:某些细菌生长到一 定阶段或在一定环境条件 下,细胞的正常生长和分 裂停止,细胞内细胞质浓 缩,逐步行成一个圆形、 椭圆形或圆柱形的,对不 良环境有较强抵抗力的特 殊结构,称为芽胞。芽胞 成熟后可自行从芽胞囊中 释放出来。因芽胞的形成 都是在细胞内,故又称内 生孢子。 ﹙十﹚芽胞(endospore,spore) 芽胞 芽胞囊
概念:某些细菌生长到一 定阶段或在一定环境条件 下,细胞的正常生长和分 裂停止,细胞内细胞质浓 缩,逐步行成一个圆形、 椭圆形或圆柱形的,对不 良环境有较强抵抗力的特 殊结构,称为芽胞。芽胞 成熟后可自行从芽胞囊中 释放出来。因芽胞的形成 都是在细胞内,故又称内 生孢子。 ﹙十﹚芽胞(endospore,spore) 芽胞 芽胞囊
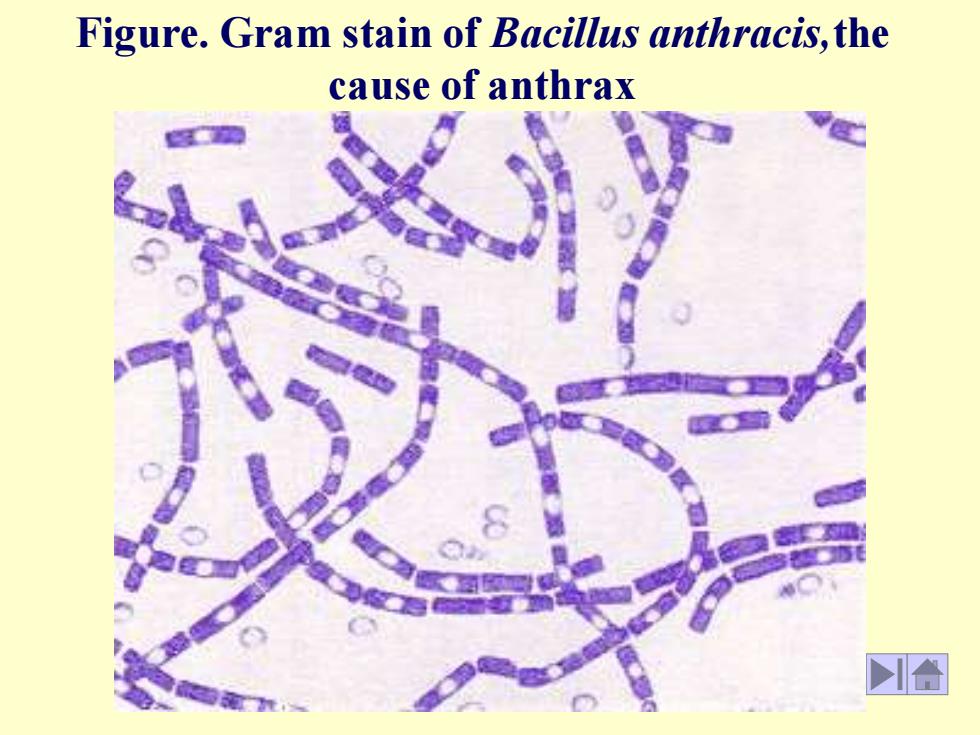
Figure. Gram stain of Bacillus anthracis,the cause of anthrax
Figure. Gram stain of Bacillus anthracis,the cause of anthrax
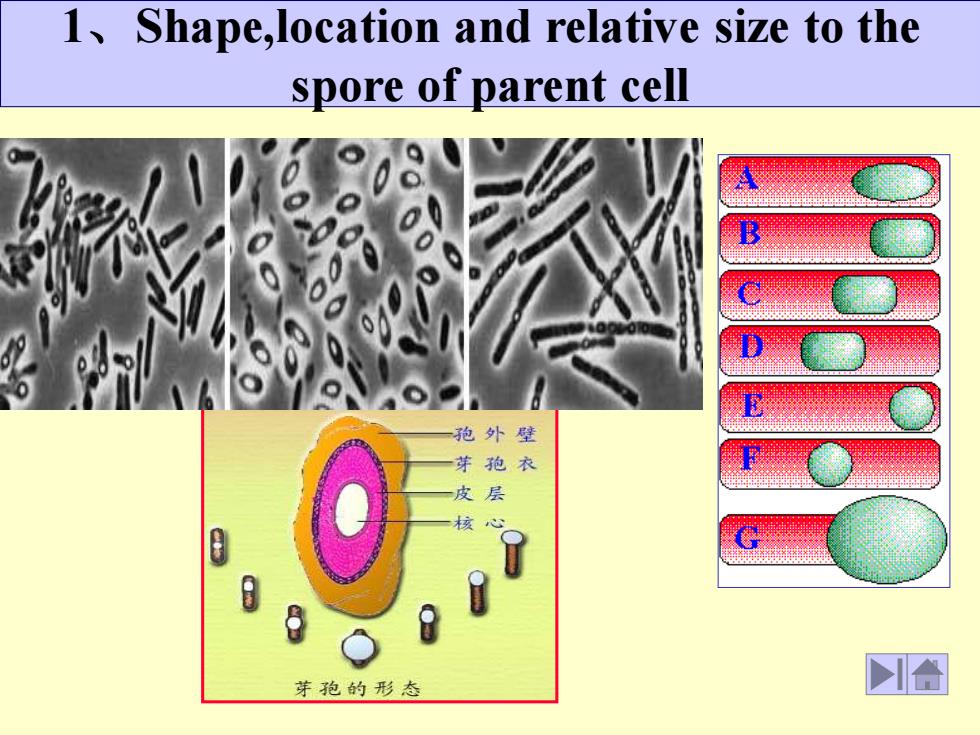
1、Shape,location and relative size to the spore of parent cell
1、Shape,location and relative size to the spore of parent cell

在杆菌中能形成芽孢的种类较多,在 球菌和螺旋菌中只有少数菌种可形成 芽孢。 产生芽孢的几个属: ▪(Bacillus)芽孢杆菌属 ▪(Clostridium)梭状芽孢杆菌属 ▪(Sporosarcina)芽孢八叠球菌属 2、能形成芽孢的细菌种类
在杆菌中能形成芽孢的种类较多,在 球菌和螺旋菌中只有少数菌种可形成 芽孢。 产生芽孢的几个属: ▪(Bacillus)芽孢杆菌属 ▪(Clostridium)梭状芽孢杆菌属 ▪(Sporosarcina)芽孢八叠球菌属 2、能形成芽孢的细菌种类
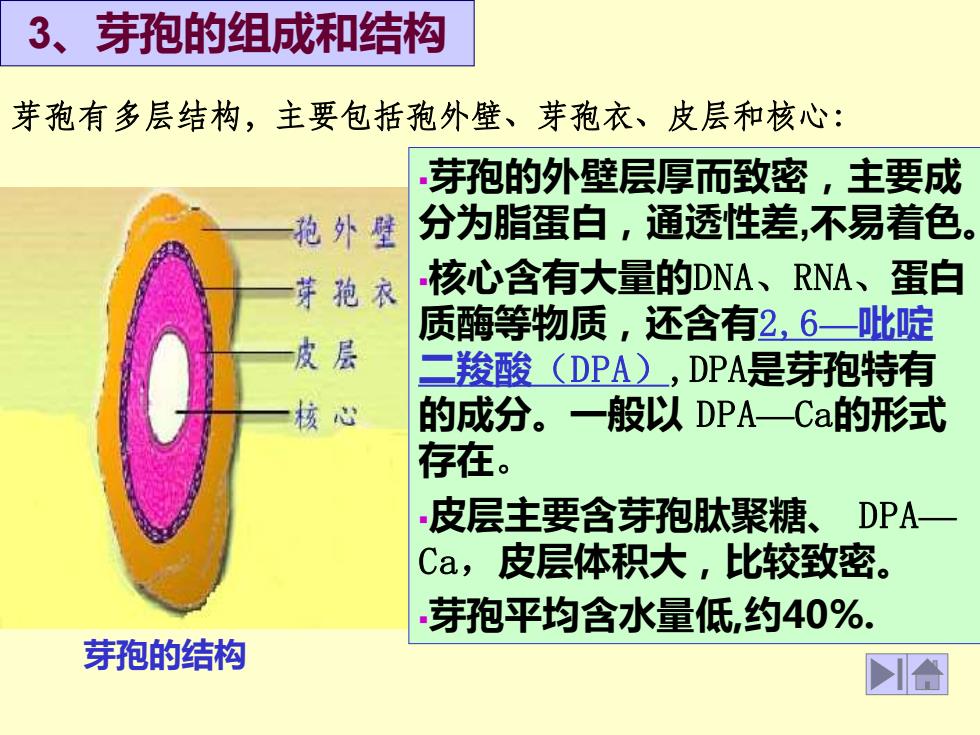
芽孢的结构 ▪芽孢的外壁层厚而致密,主要成 分为脂蛋白,通透性差,不易着色。 ▪核心含有大量的DNA、RNA、蛋白 质酶等物质,还含有2,6—吡啶 二羧酸(DPA),DPA是芽孢特有 的成分。一般以 DPA—Ca的形式 存在。 ▪皮层主要含芽孢肽聚糖、 DPA— Ca,皮层体积大,比较致密。 ▪芽孢平均含水量低,约40%. 3、芽孢的组成和结构 芽孢有多层结构,主要包括孢外壁、芽孢衣、皮层和核心:
芽孢的结构 ▪芽孢的外壁层厚而致密,主要成 分为脂蛋白,通透性差,不易着色。 ▪核心含有大量的DNA、RNA、蛋白 质酶等物质,还含有2,6—吡啶 二羧酸(DPA),DPA是芽孢特有 的成分。一般以 DPA—Ca的形式 存在。 ▪皮层主要含芽孢肽聚糖、 DPA— Ca,皮层体积大,比较致密。 ▪芽孢平均含水量低,约40%. 3、芽孢的组成和结构 芽孢有多层结构,主要包括孢外壁、芽孢衣、皮层和核心:

EXOSPORIUM SPORE COAT CORTEX DNA CORE WALL 备

Figure . Electron micrograph of a bacterial endospore. The spore has a core wall of unique peptidoglycan surrounded by several layers, including the cortex, the spore coat and the exosporium. The dehydrated core contains the bacterial chromosome and a few ribosomes and enzymes to jump-start protein synthesis and metabolism during germination
Figure . Electron micrograph of a bacterial endospore. The spore has a core wall of unique peptidoglycan surrounded by several layers, including the cortex, the spore coat and the exosporium. The dehydrated core contains the bacterial chromosome and a few ribosomes and enzymes to jump-start protein synthesis and metabolism during germination

轴丝形成 形成前芽孢 前芽孢隔膜形成 前芽孢发育成熟 芽孢形成 芽孢囊裂解 4、芽孢的形成过程
轴丝形成 形成前芽孢 前芽孢隔膜形成 前芽孢发育成熟 芽孢形成 芽孢囊裂解 4、芽孢的形成过程

★1、对高温、干燥、辐射、化学药物 有强大的抵抗力。 ★2、含水量低、壁厚而致密,通透性 差,不易着色,折光性强。 ★3、芽胞内新陈代谢几乎停止,处于 休眠状态,但保持潜在萌发力。 ★4、一个芽孢萌发只产生一个营养状 态的细胞。 5、芽孢的特性
★1、对高温、干燥、辐射、化学药物 有强大的抵抗力。 ★2、含水量低、壁厚而致密,通透性 差,不易着色,折光性强。 ★3、芽胞内新陈代谢几乎停止,处于 休眠状态,但保持潜在萌发力。 ★4、一个芽孢萌发只产生一个营养状 态的细胞。 5、芽孢的特性

Property Vegetative cells Endospores Surface coats Typical Gram-positive murein cell wall polymer Thick spore coat, cortex, and peptidoglycan core wall Microscopic appearance Nonrefractile Refractile Calcium dipicolinic acid Absent Present in core Cytoplasmic water activity High Very low Enzymatic activity Present Absent Macromolecular synthesis Present Absent Heat resistance Low High Resistance to chemicals and acids Low High Radiation resistance Low High Sensitivity to lysozyme Sensitive Resistant Sensitivity to dyes and staining Sensitive Resistant Table. Differences between endospores and vegetative cells
Property Vegetative cells Endospores Surface coats Typical Gram-positive murein cell wall polymer Thick spore coat, cortex, and peptidoglycan core wall Microscopic appearance Nonrefractile Refractile Calcium dipicolinic acid Absent Present in core Cytoplasmic water activity High Very low Enzymatic activity Present Absent Macromolecular synthesis Present Absent Heat resistance Low High Resistance to chemicals and acids Low High Radiation resistance Low High Sensitivity to lysozyme Sensitive Resistant Sensitivity to dyes and staining Sensitive Resistant Table. Differences between endospores and vegetative cells