
Composite Materials LIU Jing
Composite Materials LIU Jing

Types of Materials Natural vs.Synthesized
Types of Materials Natural vs. Synthesized
Types of Materials Structural vs.Functional
Types of Materials Structural vs. Functional

Types of Materials Building materials Electronic materials Environmental materials Energy materials Biomedical materials Automotive materials Aerospace materials 000
Types of Materials Building materials Electronic materials Environmental materials Energy materials Biomedical materials Automotive materials Aerospace materials …

Types of Materials Polymer Metal Ceramic Van der Waals force Metallic lonic covalent
Types of Materials Polymer Metal Ceramic Van der Waals force Metallic Ionic & covalent

Types of Materials Polymer Metal Ceramic Melting/working LOw Moderate temperature High Young's LOW Moderate modulus High Toughness Moderate High Low Density LOW High Moderate Electric conductivity High LOw
Types of Materials Polymer Metal Ceramic Melting/working temperature Low Moderate High Young’s modulus Low Moderate High Toughness Moderate High Low Density Low High Moderate Electric conductivity Low High Low … … … …

Definition of Composites "Composites are materials that consist of two or more phases generally exhibiting properties that superior to either of the single components." -B.Terry and G.Jones,Metal Matrix Composites
Definition of Composites “Composites are materials that consist of two or more phases generally exhibiting properties that superior to either of the -B. Terry and G. Jones, Metal Matrix Composites single components

Metals Fe,Al,Ni,Ti,Cu,etc Strong,stiff,dense,tough Co/WC Kevlar/Al Ceramics Polymer C,Al,O,SiC +Carbon/resin← Epoxy resin,PP,PU, Hard,stiff,light, etc high melting sic/C Composites Easily formed,soft, light SiO2/AI Car tyre Glass reinforced Car tyre polyester Glass Toughened Rubber Inorganic Polystyrene Elastomers Hard,stiff,transparent High extensions
Metals Fe, Al, Ni, Ti, Cu, etc Strong, stiff, dense, tough Rubber Elastomers High extensions Polymer Epoxy resin, PP, PU, etc Easily formed, soft, light Ceramics C, Al2O3 , SiC Hard, stiff, light, high melting Glass Inorganic Hard, stiff, transparent Composites Co/WC Kevlar/Al Carbon/resin SiO2 /Al Car tyre Toughened Polystyrene Glass reinforced polyester Car tyre SiC/C

Why composites? Composites enable a unique combination of properties The property can be made to vary continuously over a range
Why composites? • Composites enable a unique combination of properties • The property can be made to vary continuously over a range
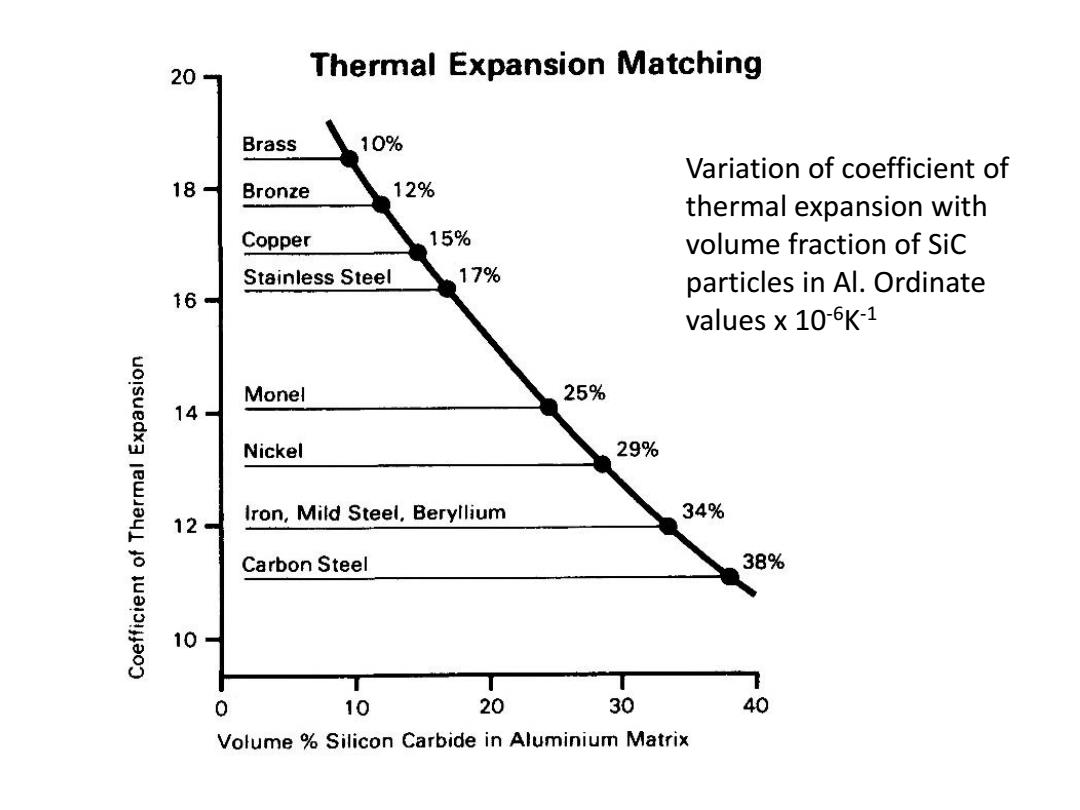
20 Thermal Expansion Matching Brass 10% Variation of coefficient of 18 Bronze 12% thermal expansion with Copper 15% volume fraction of Sic Stainless Steel 17% particles in Al.Ordinate 16 values x 10-6K-1 uolsuedx3 Monel 25% 14- Nickel 29% 12- Iron,Mild Steel,Beryllium 34% 6 Carbon Steel 38% 10 7 0 10 20 30 40 Volume Silicon Carbide in Aluminium Matrix
Variation of coefficient of thermal expansion with volume fraction of SiC particles in Al. Ordinate values x 10-6K -1