
第一章 8 遥感图像处理基础 1
1 第一章 遥感图像处理基础 UESTC-RSIP

第一颗陆地卫星:1972年,Landsat Multispectral Scanner System(MSS).4个波 段,波谱宽度100nm,像元大小80米。 Dubai January 22,1973 Dubai October 11,2006 Landsat 1 MSS Landsat 7 ETM+bands 4,3,2 2
2 第一颗陆地卫星:1972年, Landsat Multispectral Scanner System (MSS). 4个波 段,波谱宽度100nm,像元大小80米。 Dubai - January 22,1973 Landsat 1 MSS Dubai - October 11, 2006 Landsat 7 ETM+ bands 4, 3, 2 UESTC-RSIP

从遥感图像提取信息 以图像为中心:感兴趣的是地面各种地物的空 间关系。制作地图,提取感兴趣地物,绘制等 高线等。 以数据为中心:感兴趣的是数据本身,如像元 的光谱数据。如高光谱图像测量光谱吸收特性。 3
3 从遥感图像提取信息 以图像为中心:感兴趣的是地面各种地物的空 间关系。制作地图,提取感兴趣地物,绘制等 高线等。 以数据为中心:感兴趣的是数据本身,如像元 的光谱数据。如高光谱图像测量光谱吸收特性。 UESTC-RSIP

Photogrammetry VS Remote Sensing Photogrammetry is the practice of determining the geometric properties of objects from photographic images. Remote sensing refers to the use of aerial sensor or satellite to detect and classify objects on Earth. 4
4 Photogrammetry VS Remote Sensing Photogrammetry is the practice of determining the geometric properties of objects from photographic images. Remote sensing refers to the use of aerial sensor or satellite to detect and classify objects on Earth. UESTC-RSIP
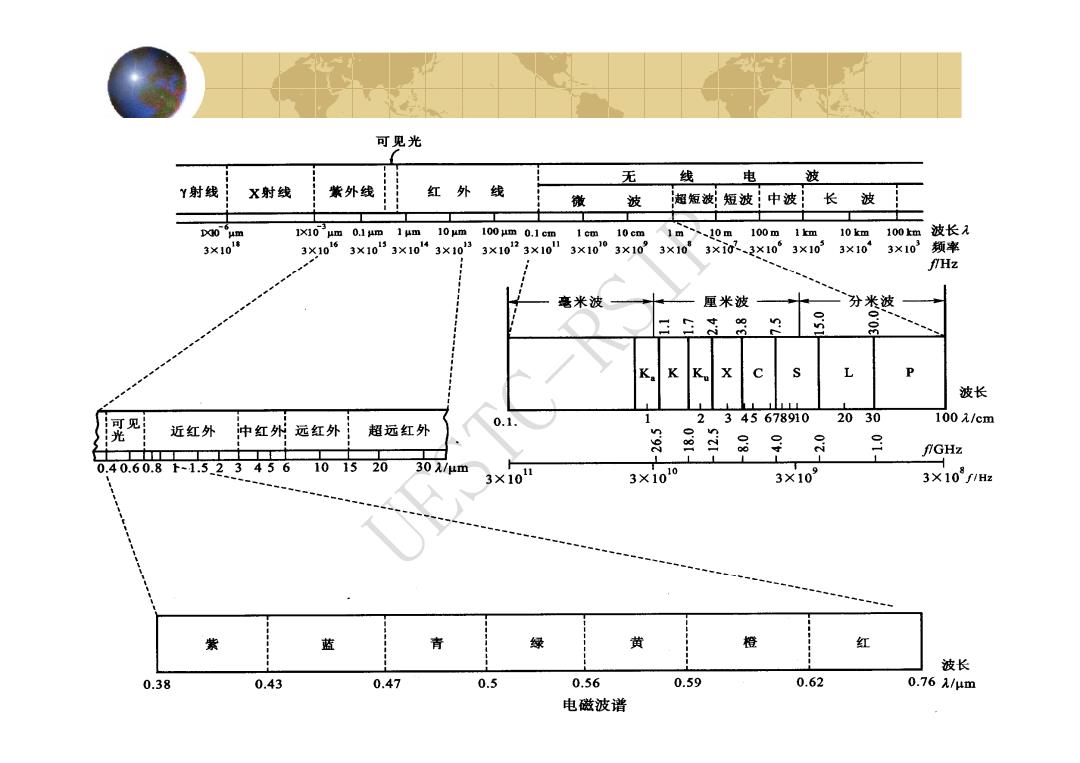
可见光 无 线 电 波 Y射线 X射线 紫外线 红外线 微 波 超短波;短波!中波 长波 D0 um 1um 10 um 100 jm 0.1 cm 1 cm 10cm 1m、、10m 100m1m 10km :100km波长 3×101塘 3X106 3×1053×10“3×1033×1023×10 3×1010 310” 3×10 3×i0、3×10 3×103 3×10 3×103频率 fHz 毫米波 厘米波 分米波 n K K X P 波长 可见 0.1. 1 2345678910 2030 100元/cm 光 近红外 中红外远红外 1 超远红外 n 9 二 fGHz 0.40.60.8下-1.523456 101520 30λ/μm 3×10 3×1010 3×109 3×10f1H 紫 蓝 青 绿 黄 橙 红 波长 0.38 0.43 0.47 0.5 0.56 0.59 0.62 0.761/μm 电磁波谱
5 UESTC-RSIP

大气窗口(Atmospheric window) 由于大气层的反射、散射和吸收作用, 使得太阳辐射的各波段受到衰减的作用 轻重不同,因而各波段的透射率也各不 相同。受到大气衰减作用较轻、透射率 较高的波段叫大气窗口。 6
6 大气窗口(Atmospheric window) 由于大气层的反射、散射和吸收作用, 使得太阳辐射的各波段受到衰减的作用 轻重不同,因而各波段的透射率也各不 相同。受到大气衰减作用较轻、透射率 较高的波段叫大气窗口。 UESTC-RSIP
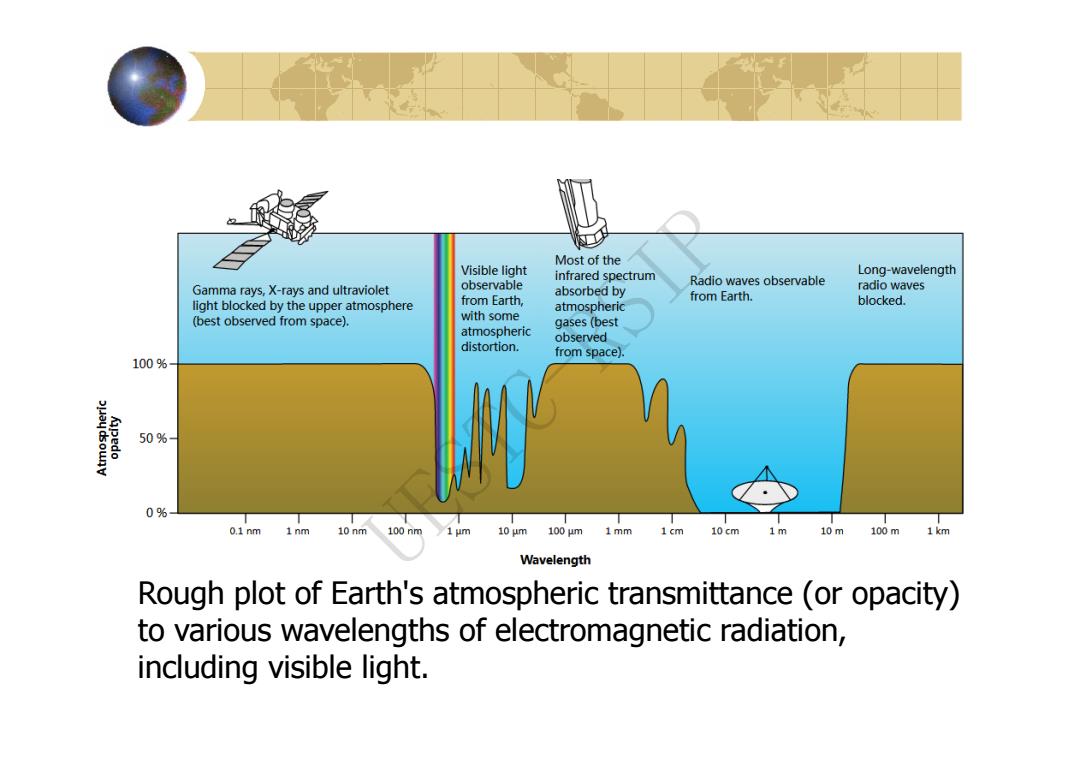
Most of the Visible light infrared spectrum Long-wavelength observable Radio waves observable Gamma rays,X-rays and ultraviolet absorbed by radio waves from Earth, from Earth. light blocked by the upper atmosphere atmospheric blocked. (best observed from space). with some gases (best atmospheric observed distortion. from space). 100% 50% 0% 0.1nm 1nm 10nm 100nm 10 um 100um 1mm 1cm 10cm 1m 10m 100m 1km Wavelength Rough plot of Earth's atmospheric transmittance (or opacity) to various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light
Rough plot of Earth's atmospheric transmittance (or opacity) to various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. UESTC-RSIP
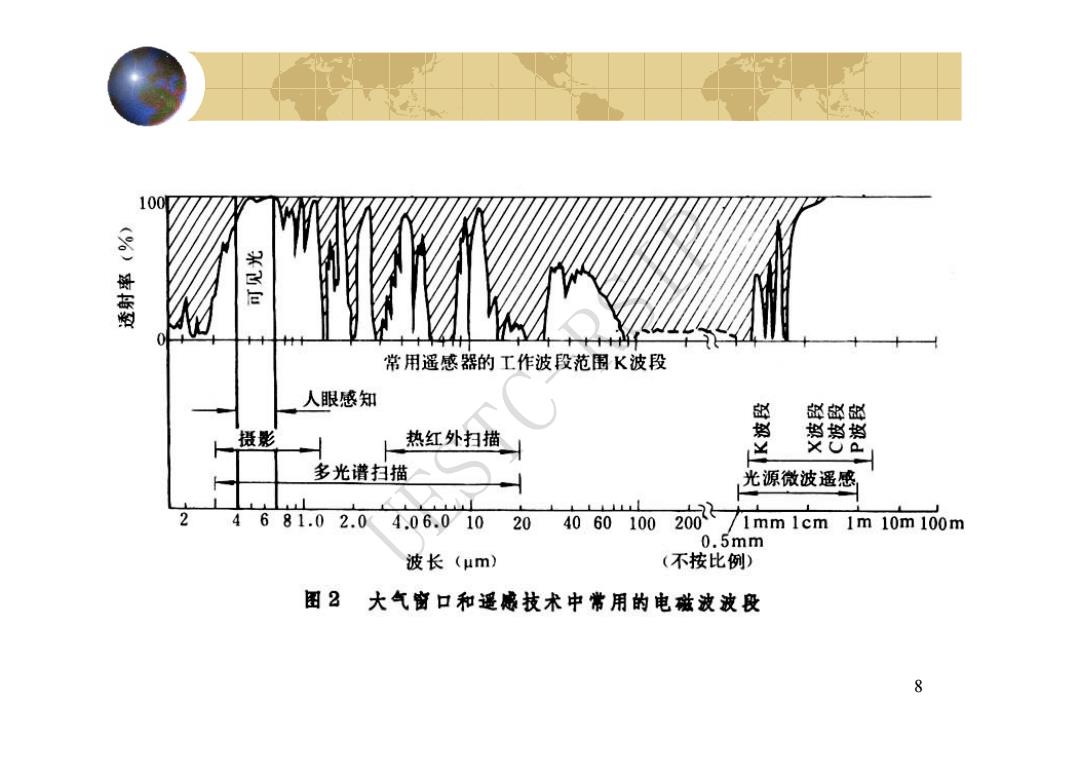
100M (0)溪有型 常用遥感器的工作波段范围K波段 人眼感知 部卧的 人 摄影 热红外扫描 判肖挡 安 多光谱扫描 光源微波遥感 2 4681.0 2.0 4.06.01020 4060 100 201 1mm 1cm 1m10m100m 0.5mm 波长(μm) (不按比例) 图2大气前口和遥感技术中常用的电磁波波段 8
8 UESTC-RSIP
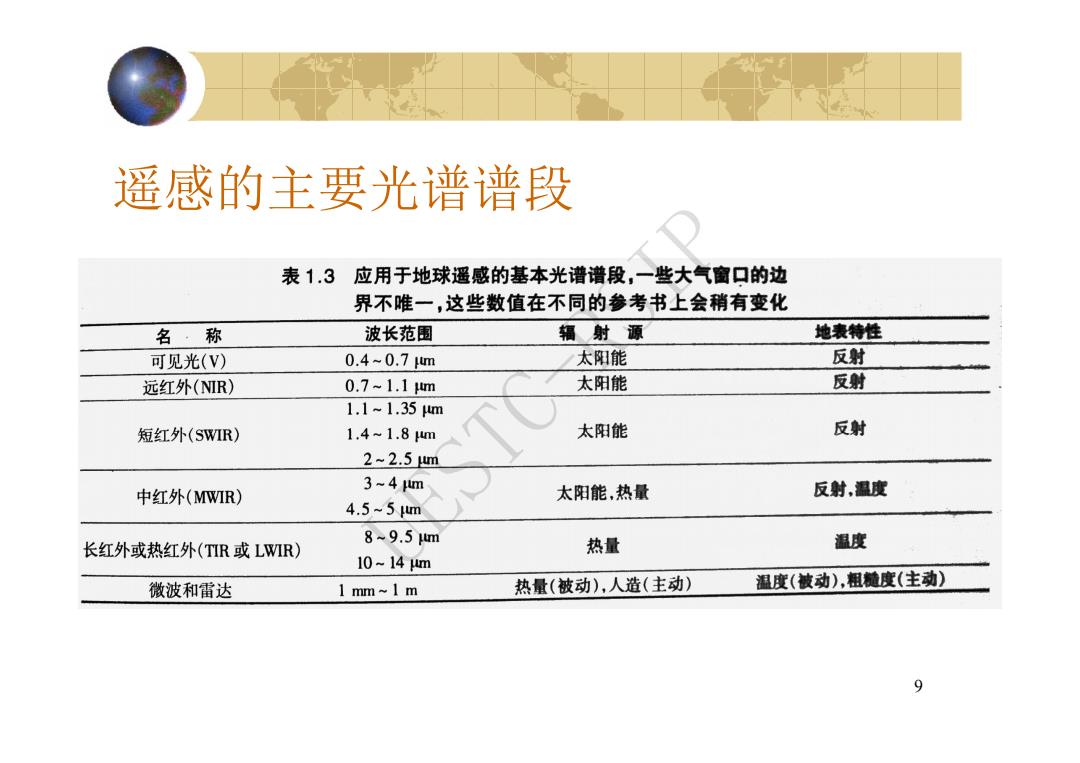
遥感的主要光谱谱段 表1.3应用于地球遥感的基本光谱谱段,一些大气窗口的边 界不唯一,这些数值在不同的参考书上会稍有变化 名·称 波长范围 辐射源 地表特性 可见光(V) 0.4-0.7m 太阳能 反射 远红外(NIR) 0.7~1.1m 太阳能 反射 1.1~1.35m 短红外(SWIR) 1.4~1.8wm 太阳能 反射 2~2.5wm 3-4m 中红外(MWIR) 太阳能,热量 反射,温度 4.5~5wm 8~9.5m 长红外或热红外(TR或LWIR) 热量 温度 10-14m 微波和雷达 1 mm~1 m 热量(被动),人造(主动) 温度(被动),粗髓度(主动) 9
9 遥感的主要光谱谱段 UESTC-RSIP
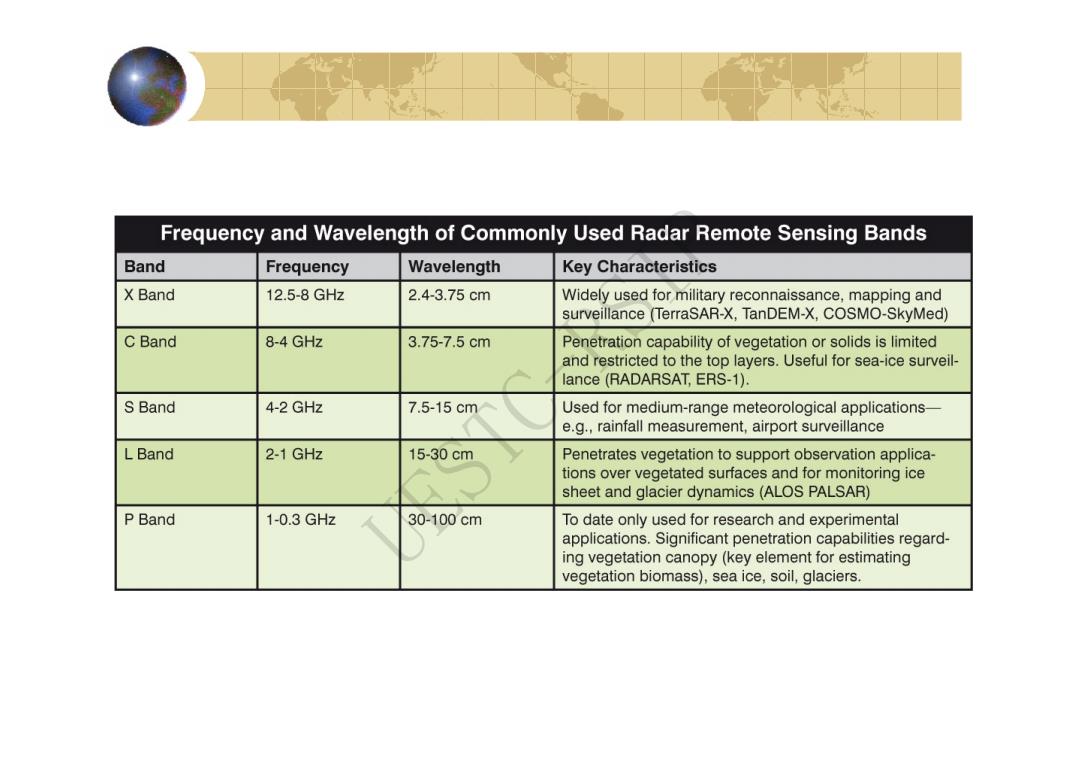
Frequency and Wavelength of Commonly Used Radar Remote Sensing Bands Band Frequency Wavelength Key Characteristics X Band 12.5-8GHz 2.4-3.75cm Widely used for military reconnaissance,mapping and surveillance (TerraSAR-X,TanDEM-X,COSMO-SkyMed) C Band 8-4 GHz 3.75-7.5cm Penetration capability of vegetation or solids is limited and restricted to the top layers.Useful for sea-ice surveil- lance(RADARSAT,ERS-1). S Band 4-2 GHz 7.5-15cm Used for medium-range meteorological applications- e.g.,rainfall measurement,airport surveillance L Band 2-1 GHz 15-30cm Penetrates vegetation to support observation applica- tions over vegetated surfaces and for monitoring ice sheet and glacier dynamics(ALOS PALSAR) P Band 1-0.3GHz 30-100cm To date only used for research and experimental applications.Significant penetration capabilities regard- ing vegetation canopy(key element for estimating vegetation biomass),sea ice,soil,glaciers
UESTC-RSIP