
6时序逻辑电路 Sequence Logic Circuits Analysis & Design 6.1时序逻辑电路的基本概念 Basic Concepts of sequence Logic Circuits 6.2同步时序逻辑电路的分析 Analysis of Synchronous sequence Logic Circuits 6.3同步时序逻辑电路的设计 Design of Synchronous Sequence Logic Circuits 6.4异步时序逻辑电路的分析 Analysis of Asynchronous sequence Logic Circuits 6.5典型时序逻辑集成电路
Basic Concepts of sequence Logic Circuits Sequence Logic Circuits Analysis & Design Analysis of Synchronous sequence Logic Circuits Design of Synchronous Sequence Logic Circuits Analysis of Asynchronous sequence Logic Circuits
6.1 Basic Concepts of sequence Logic Circuits 1.Differences of Combinational Circuits and Sequential Circuits(区别) *Combinational Circuits:Output of Circuits is at all times dependent on the input,Having nothing to do with the former states. *Sequential Circuits:The output level depends not only on the present value of inputs,but also on past inputs Stored by Flip-Flop ) 2.The structure of Sequential Circuits(组成) Combinational Circuits Storage Circuits
6.1 Basic Concepts of sequence Logic Circuits 1. Differences of Combinational Circuits and Sequential Circuits(区别 ) Combinational Circuits: Output of Circuits is at all times dependent on the input, Having nothing to do with the former states. Sequential Circuits: The output level depends not only on the present value of inputs, but also on past inputs ( Stored by Flip-Flop ). 2. The structure of Sequential Circuits(组成 ) Combinational Circuits + Storage Circuits
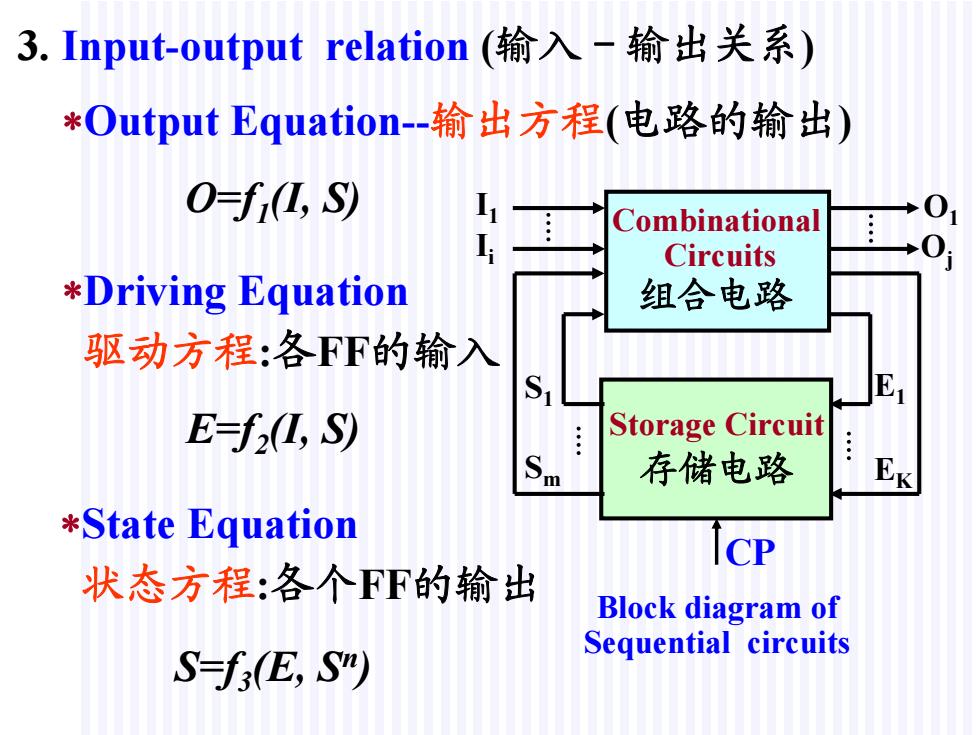
3.nput-output relation(输入-输出关系) *Output Equation-输出方程(电路的输出) O=f (I,S) Combinational Circuits *Driving Equation 组合电路 驱动方程:各FF的输入 S E-f2(I,S) Storage Circuit m 存储电路 E *State Equation CP 状态方程:各个FF的输出 Block diagram of Sequential circuits S-f(E,S")
3. Input-output relation (输入-输出关系) Output Equation-输出方程(电路的输出) Driving Equation 驱动方程:各FF的输入 State Equation 状态方程:各个FF的输出 Storage Circuit 存储电路 E1 EK S1 Sm O1 Oj I1 Ii Combinational Circuits 组合电路 Block diagram of Sequential circuits CP O=f1 (I, S) E=f2 (I, S) S=f3 (E, Sn)
4.Category of Sequential Circuits(分类) According to the relationship among output O, present state Sm and input I(各变量的关系) *Moore Model(摩尔型电路):O=fi(S") *Mealy Model(米里型电路):O=f2(I,S") According to the clock pulse that control the sequential states(CP对各个触发器的控制) *Synchronous:All FFs in the storage circuits are controlled by a uniform CP source. 同步时序电路:各个FF受同一个CP控制. Asynchronous:No such a uniform CP source. 异步时序电路:各F℉没有统一的CP源
4. Category of Sequential Circuits (分类) ◆According to the relationship among output O, present state Sn and input I (各变量的关系) Moore Model (摩尔型电路): )S(fO n 1 Mealy Model (米里型电路): )S,I(fO n 2 ◆According to the clock pulse that control the sequential states (CP对各个触发器的控制) Synchronous: All FFs in the storage circuits are controlled by a uniform CP source. 同步时序电路:各个FF受同一个CP控制. Asynchronous: No such a uniform CP source. 异步时序电路:各FF没有统一的CP源
6.Description of logic functions(逻辑功能描述) ◆L0 gic Equation(逻辑方程组) *Output Equation(输出方程) *Driving Equation(驱动方程) *State Equation(状态方程) ◆State transition table(状态表) ◆State diagram(状态图) ◆Timing Diagram/Waveform(时序图/波形图)
6. Description of logic functions (逻辑功能描述) ◆Logic Equation (逻辑方程组) Output Equation (输出方程) Driving Equation (驱动方程) State Equation (状态方程) ◆State transition table (状态表) ◆State diagram (状态图) ◆Timing Diagram/Waveform (时序图/波形图)
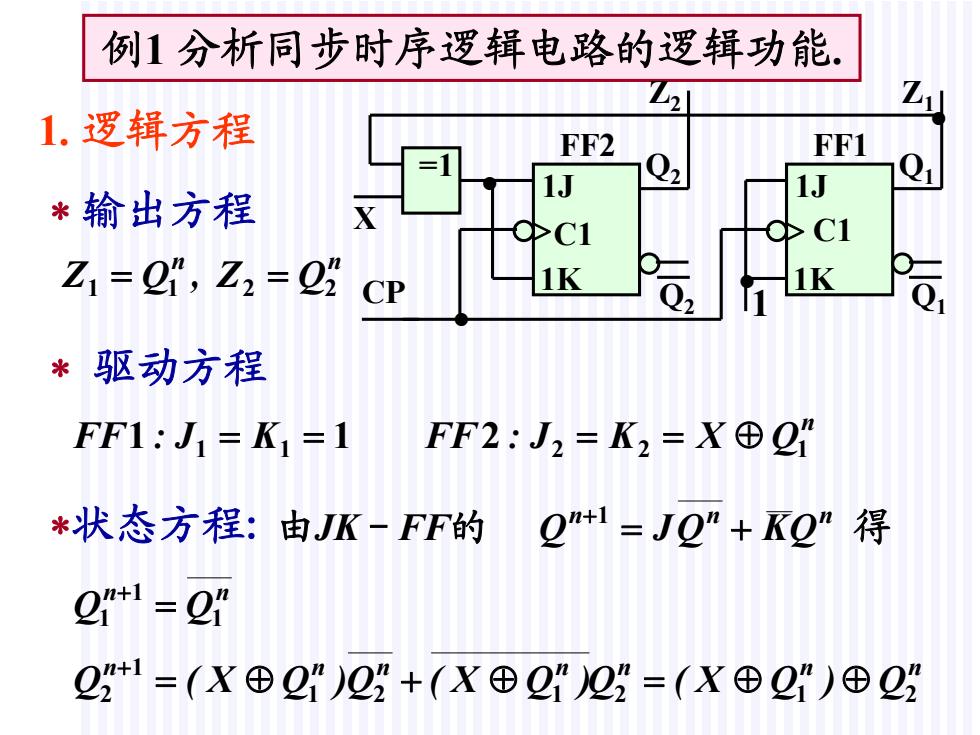
例1分析同步时序逻辑电路的逻辑功能. Z 1.逻辑方程 FF2 FF1 *输出方程 Z1=2",Z2=02 CP 1K 1K *驱动方程 FF1:J1=K1=1 FF2:J2=K2=X⊕Q” *状态方程:由JK-FF的 Q+1=JQ”+K0”得 201=2” 2+1=(X⊕2")2+(X⊕21”22=(X⊕21)⊕22
输出方程 n n QZ,QZ 2211 驱动方程 n KJ:FF 11 22 QXKJ:FF 1 1 2 1 状态方程: 由 的- n1 n QKQJQFFJK n 得 n n QQ 1 1 1 n nn nn nn 21 21 Q)QX(Q)QX(Q)QX(Q 21 1 2 例1 分析同步时序逻辑电路的逻辑功能. 1. 逻辑方程 1J 1K C1 FF2 1J 1K C1 FF1 • • • • Z2 Z1 Q2 Q1 Q2 Q1 X CP =1 1
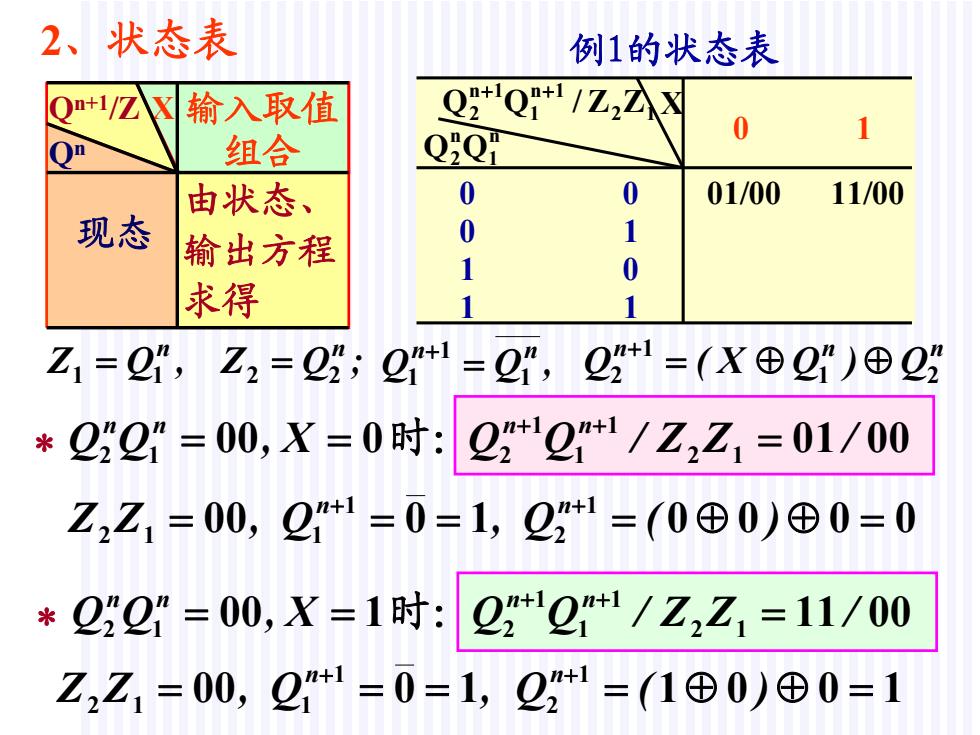
2、状态表 例1的状态表 +1/Z 输入取值 Qg*'Q+'/Z2公☒ 0 组合 Q2Q 由状态、 0 0 01/00 11/00 现态 输出方程 0 1 1 0 求得 1 1 Z1=2”,Z2=22;211=21,22+1=(X⊕2")⊕2 *22”2”=00,X=0时: 221/Z2Z1=01/00 Z2Z1=00,2+1=0=1,221=(0⊕0)⊕0=0 *222”=00,X=1时: 2221/Z2Z1=11/00 Z,Z,=00,0+1=0=1,Q21=(1⊕0)©0=1
12 X 1n1 1n2 ZZ/QQ n 1 n 2QQ 例1的状态表 Qn+1/Z 由状态、 输出方程 求得 Qn 现态 X 输入取值 组合 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 2、状态表 01/00 11/00 ,QQn n1 1 1 n nn Q)QX(Q 21 1 2 ;QZ,QZ n n 2211 12 nn X,QQ 0 00 时: Z Z 00, 12 Q , n 10 1 1 0000 1 2 )(Qn 0001 12 1 1 1 2 /ZZ/QQ nn 12 nn X,QQ 1 00 时: Z Z 00, 12 Q , n 10 1 1 1001 1 2 )(Qn 0011 12 1 1 1 2 /ZZ/QQ nn
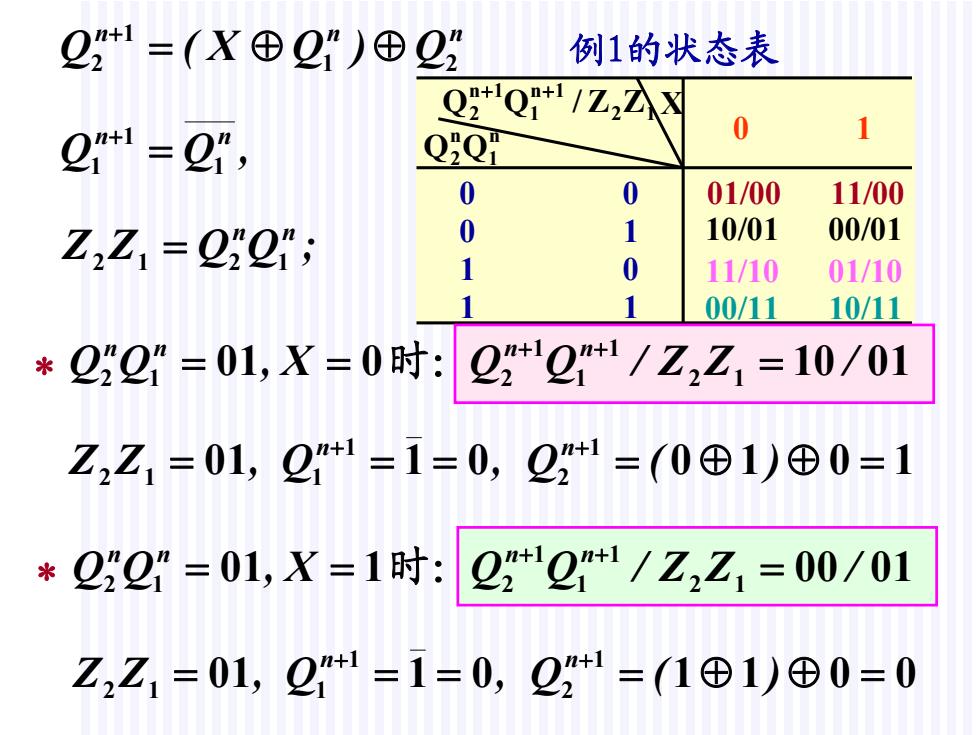
21=(X⊕21")⊕2 例1的状态表 Q+'Q'/z2公X 21=21, 0 Q2QT 0 0 01/00 11/00 Z2Z1=2221", 0 1 10/01 00/01 11/10 01/10 1 00/11 10/11 *222”=01,X=0时: 221/Z2Z1=10/01 Z2Z1=01,2"1=1=0,21=(0⊕1)⊕0=1 *222”=01,X=1时: 22'21/Z2Z1=00/01 Z2Z1=01,21=1=0,221=(1⊕1)⊕0=0
12 X 1n1 1n2 ZZ/QQ n 1 n 2QQ 例1的状态表 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 01/00 11/00 QQ , n n1 1 1 n n n 1 Q)QX(Q 2 1 2 ;QQZZ nn 1212 12 nn X,QQ 0 01 时: Z Z 01, 12 Q , n 01 1 1 1010 1 2 )(Qn 0110 12 1 1 1 2 /ZZ/QQ nn 12 nn X,QQ 1 01 时: Z Z 01, 12 Q , n 01 1 1 0011 1 2 )(Qn 0100 12 1 1 1 2 /ZZ/QQ nn 10/01 00/01 11/10 01/10 00/11 10/11
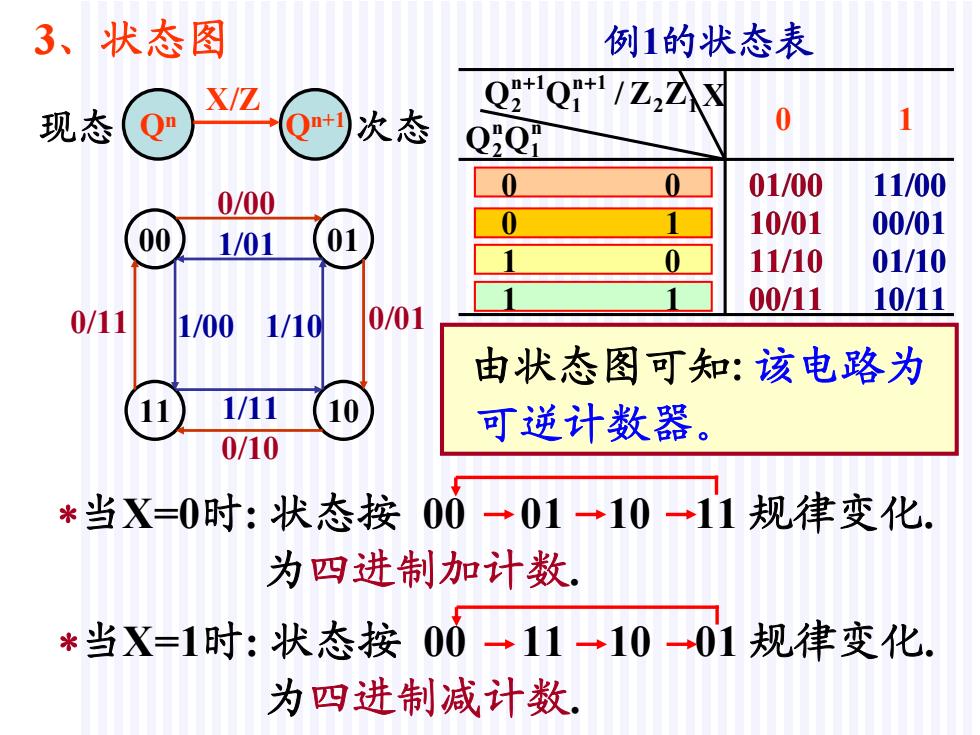
3、状态图 例1的状态表 X/Z 现态 Qn 次态 0 QZQ 0 01/00 11/00 0/00 0 00 1 10/01 00/01 1/01 0 11/10 01/10 00/11 10/11 0/11 1/00 1/10 0/01 由状态图可知:该电路为 1/11 可逆计数器。 0/10 *当X=0时:状态按00一01→10一11规律变化. 为四进制加计数。 *当X=1时:状态按00一11一10-01规律变化. 为四进制减计数
01/00 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 12 X 1n1 1n2 ZZ/QQ n 1 n 2QQ 例1的状态表 10/01 11/10 00/11 11/00 00/01 01/10 10/11 00 01 11 10 01/00 3、状态图 现态 Qn Qn+1 次态 X/Z 0/00 0/01 0/10 0/11 1/00 1/11 1/10 1/01 10/01 11/10 00/11 11/00 00/01 01/10 10/11 由状态图可知:该电路为 可逆计数器。 当X=0时: 状态按 00 01 10 11 规律变化. 为四进制加计数. 当X=1时: 状态按 00 11 10 01 规律变化. 为四进制减计数
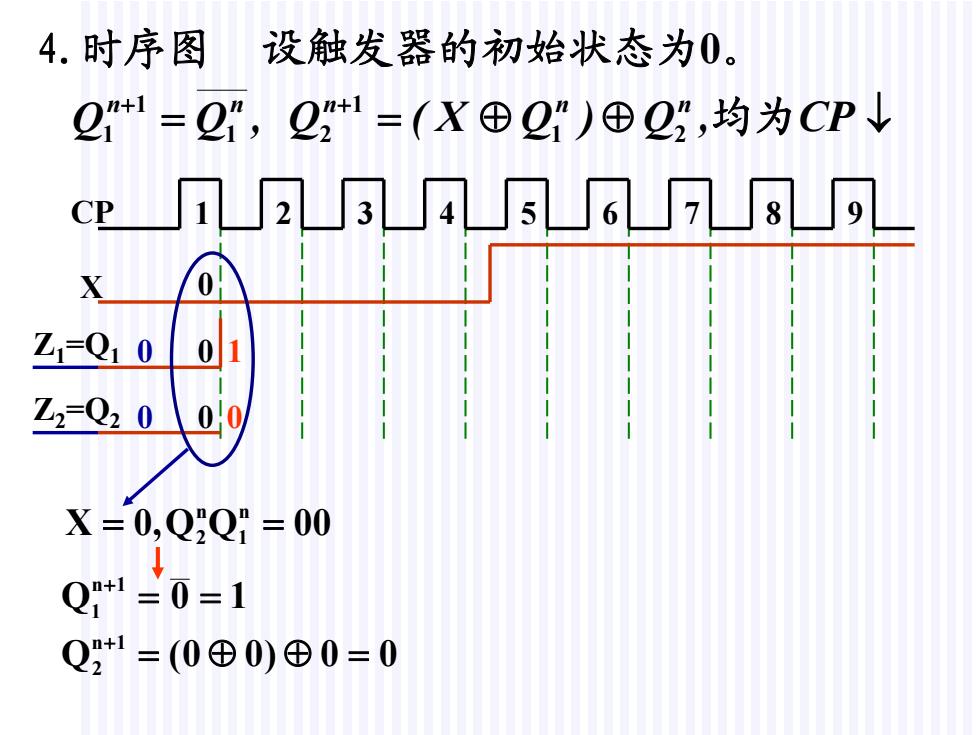
4.时序图 设触发器的初始状态为0。 21=2,221=(X⊕2")⊕22,均为CP↓ 73456789 CP Z=Q10 01 Z2-Q20 00 X=0,QQ1=00 ↓ Q*1=0=1 Q:1=(0⊕0)⊕0=0
4.时序图 CP 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 X Z1 =Q1 Z2 =Q2 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 00QQ,0X n1 n 2 00)00(Q 10Q 1n 2 1n 1 QQ , n n1 1 1 CP,Q)QX(Q2n 1 1n 2n 均为 设触发器的初始状态为0