
Chapter ELEVEN Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy NMR
Chapter ELEVEN Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy NMR

核磁共振原理 核磁共振波谱议 化学位移和核磁共振图谱 图谱解析 教学要求:理解核磁共振波谱法的基本原理及仪器 主要部件的功能;理解化学位移产生的原因及影 响因素;利用核磁共振波谱能正确解析简单化合 物结构
核磁共振原理 核磁共振波谱议 化学位移和核磁共振图谱 图谱解析 教学要求:理解核磁共振波谱法的基本原理及仪器 主要部件的功能;理解化学位移产生的原因及影 响因素;利用核磁共振波谱能正确解析简单化合 物结构

§11-1 Principle of NMR Radio wave: 无线电波 Radio frequency: 射频
§11-1 Principle of NMR Radio wave: 无线电波 Radio frequency: 射频
射频电 磁辐射
射频电 磁辐射

Theory:Quantum Treatment ■ Energies of nuclear spin states are quantized: Nuclear Spin Quantum Number (I) where I=0.毫.1,1是,etc Three Groups of Nuclei: 1.I=0 -non-spinning nuclei,no magnetic moment,even pt&no -examples:12C,160 2. I=主 -spherical spinning charge with magnetic moment -examples:13C.iH 3. I>2 -non-spherica/spinning charge with magnetic moment -examples:2H,14N

More Quantum Numbers All nuclear spin states are degenerate unless in a uniform magnetic field ■Where they split into2I+⊥states Defined by Magnetic Quantum Numbers(m): m=I,I-1,I-2.-I So,for I=0:m=O(only 1 state)NMR inactive forI=m=±垃(2 states) NMR ACTIVE
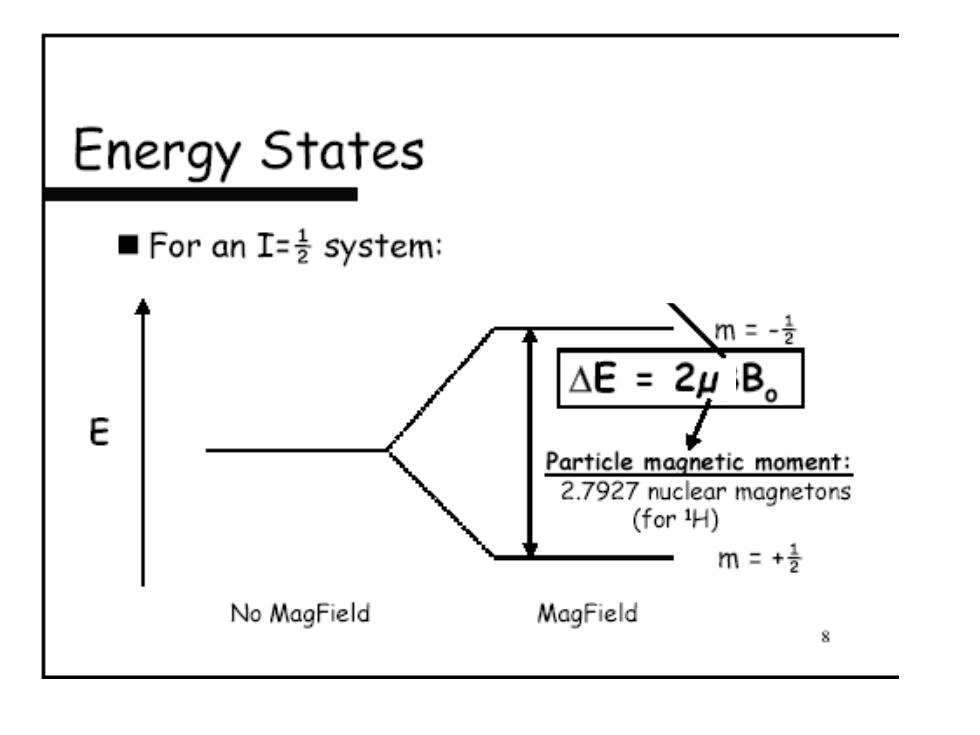
Energy States ■For an I=system: 八m:- △E= 2B。 E Particle magnetic moment: 2.7927 nuclear magnetons (for H) m三+ No MagField MagField 8
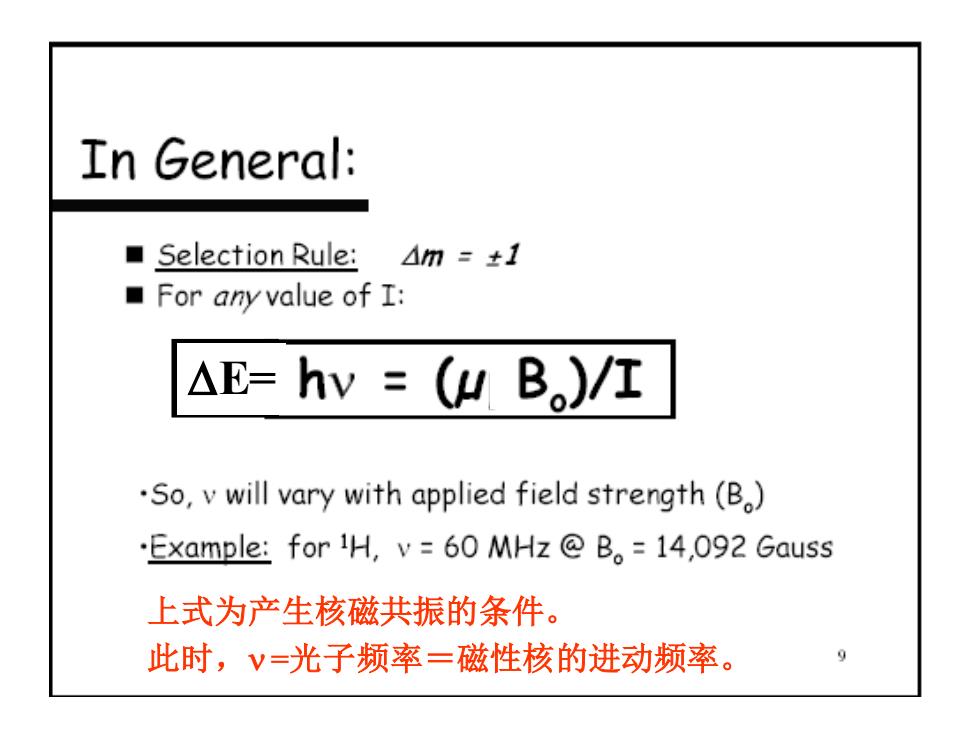
DE= 上式为产生核磁共振的条件。 此时, =光子频率=磁性核的进动频率
DE= 上式为产生核磁共振的条件。 此时, =光子频率=磁性核的进动频率
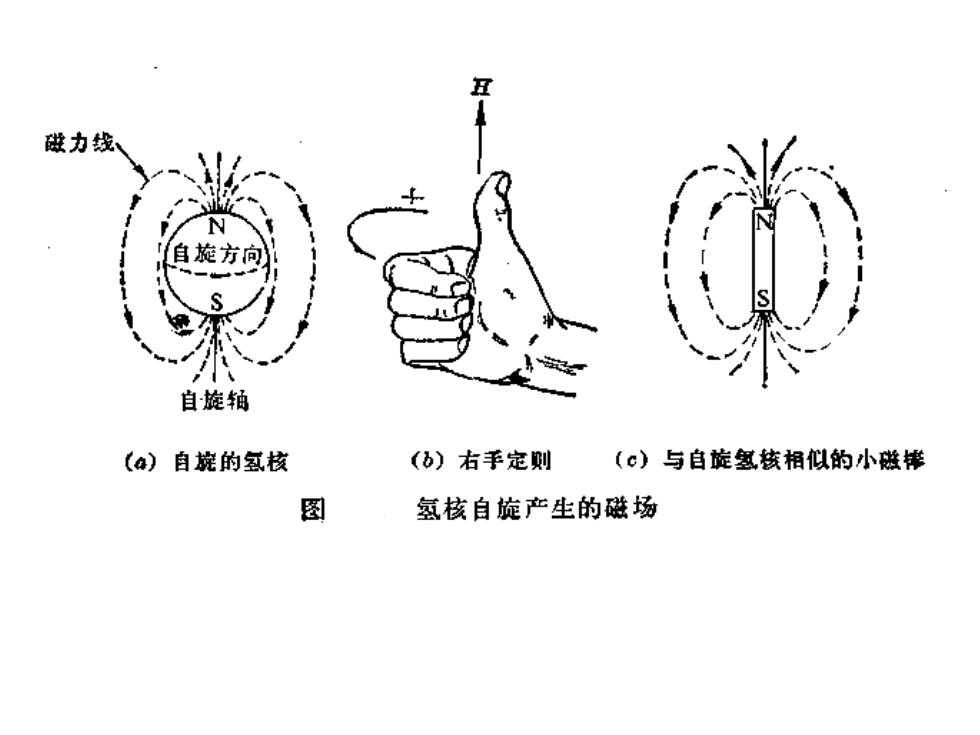
丑 做力线、 自旋方向 自旋轲 (4)自婉的氢核 (b)右手定则 (c)与自旋氢核相似的小磁棒 图 氢核自旋产生的磁场

Where 0 is velocity of spinning nuclear, 0 is precession frequency or Larmor frequency(进动频率, 拉摩尔频率), B0 is applied magnetic field intensity, is magnetogyric ratio(or gyromagnetic ratio). B0
Where 0 is velocity of spinning nuclear, 0 is precession frequency or Larmor frequency(进动频率, 拉摩尔频率), B0 is applied magnetic field intensity, is magnetogyric ratio(or gyromagnetic ratio). B0