
Chapter 9 Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry, UV (紫外吸收光谱分析)
Chapter 9 Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry, UV (紫外吸收光谱分析)

Moleaular absorption Absorbing species UV/Vis We are dealing with electronic transitions. Due to the large number of vibrational and rotational states,the spectra appear as bands
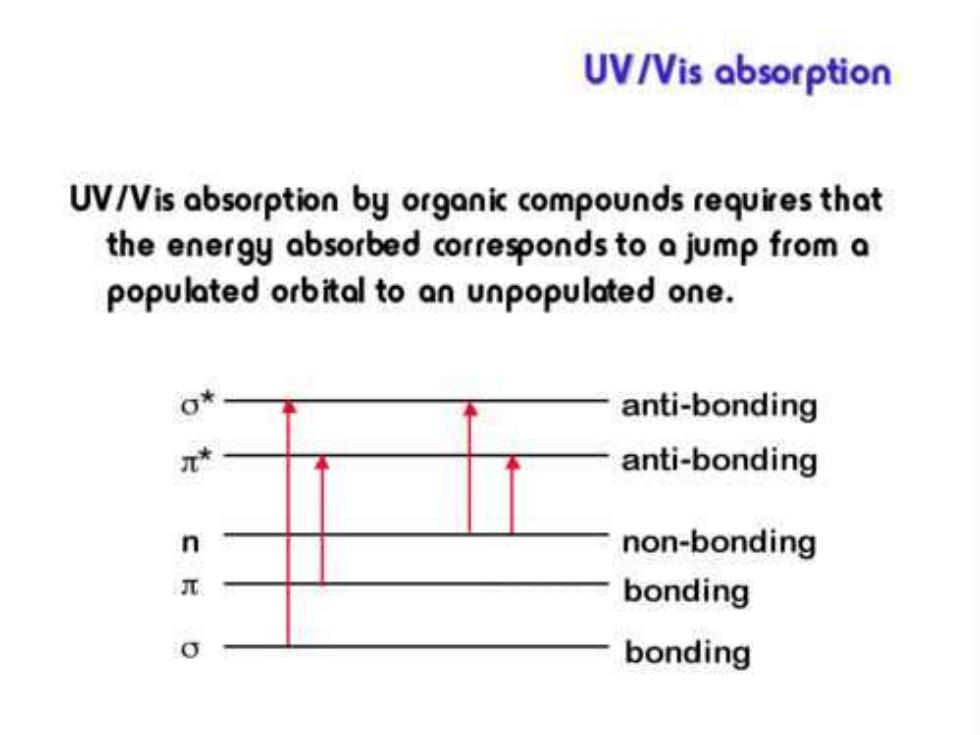
UV/Vis absorption UV/Vis absorption by organic compounds requires that the energy absorbed corresponds to a jump from a populated orbital to an unpopulated one. anti-bonding anti-bonding n non-bonding bonding bonding

Electronic transitions include three kinds of types: ● N→V transitions include →* transitions in saturated organic compounds andππ* transitions in unsaturated compounds. ● N→Q transitions: a kind of transitions arise from the electron excitation from nonbonding orbital to anti-bonding orbital. ● N→R transition: electron is excited to a higher level until it is ionized to molecular ion. ● Charge transfer transitions: charge (electron) transfers between different parts of the compound due to charge redistribution of the compound excited by a radiation
Electronic transitions include three kinds of types: ● N→V transitions include →* transitions in saturated organic compounds andππ* transitions in unsaturated compounds. ● N→Q transitions: a kind of transitions arise from the electron excitation from nonbonding orbital to anti-bonding orbital. ● N→R transition: electron is excited to a higher level until it is ionized to molecular ion. ● Charge transfer transitions: charge (electron) transfers between different parts of the compound due to charge redistribution of the compound excited by a radiation

* : anti-bond orbital
* : anti-bond orbital

UV/Vis absorption n->o*transitions The compound must contain atoms with unshared electron pairs. Compounds containing O,S,N and halogens can absorb via this type of transition. Absorptions are typically in the 150-250 nm region and are not very intense
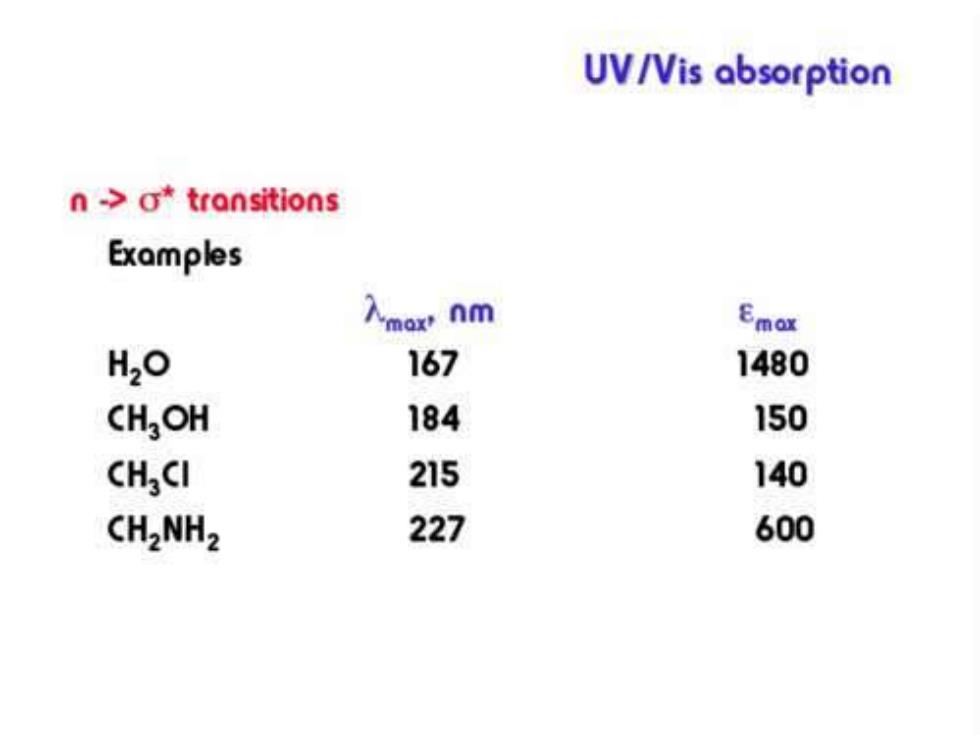
UV/Vis absorption n ->o*transitions Examples 入mox nm Emox H2O 167 1480 CHOH 184 150 CHCI 215 140 CH2NH2 227 600

UV/Vis absorption n->*and>*transitions For a orbital to be available,there must be some degree of unsaturation. multiple bonds and resonance structures These result in some of the most intense absorptions (200-700 nm region). As the degree of unsaturation increases,you typically see a shift to higher
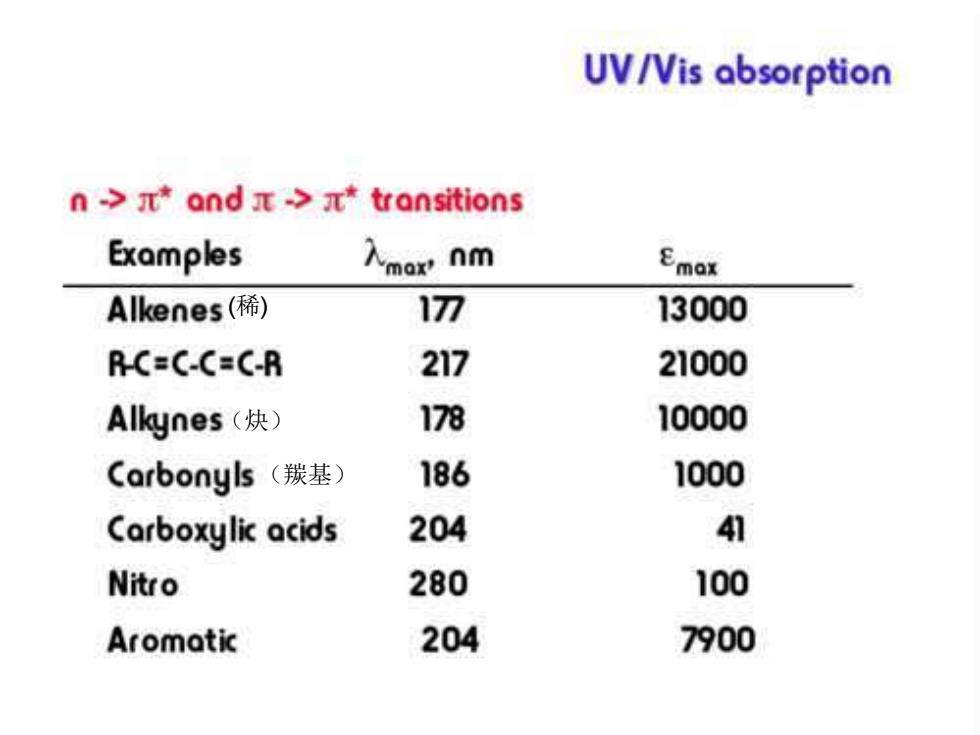
(稀) (炔) (羰基)
(稀) (炔) (羰基)
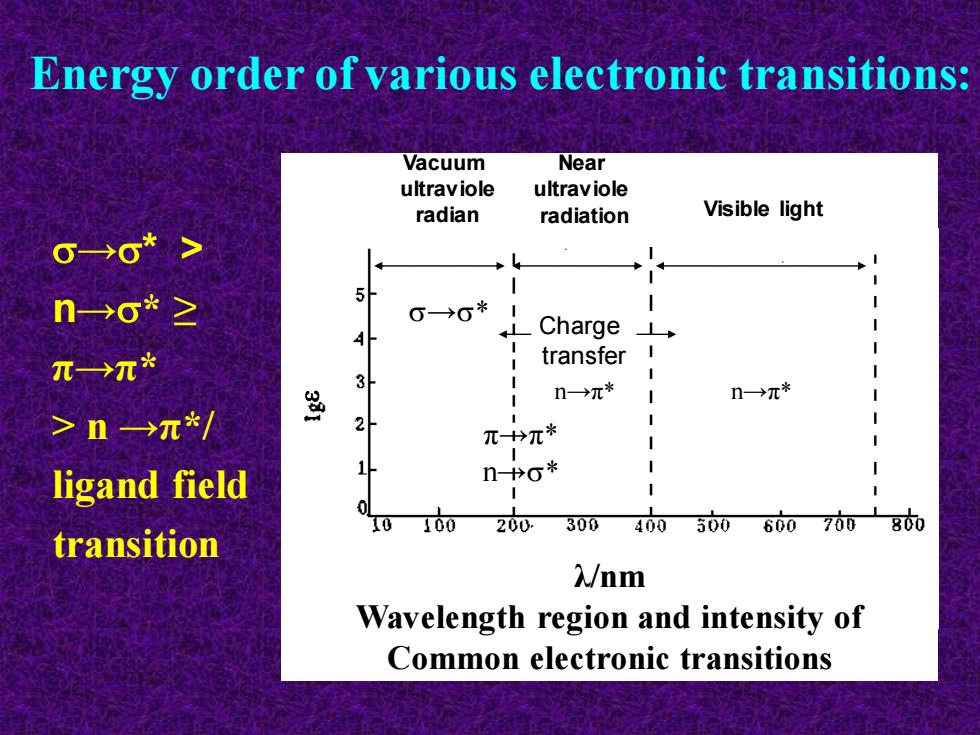
→* > n→* ≥ π→π* > n →π*/ ligand field transition Energy order of various electronic transitions: Vacuum ultraviole radian Near ultraviole radiation Visible light →* π→π* n→* n→π* n→π* Charge transfer λ/nm Wavelength region and intensity of Common electronic transitions
→* > n→* ≥ π→π* > n →π*/ ligand field transition Energy order of various electronic transitions: Vacuum ultraviole radian Near ultraviole radiation Visible light →* π→π* n→* n→π* n→π* Charge transfer λ/nm Wavelength region and intensity of Common electronic transitions