
Drugs Affecting Blood
Drugs Affecting Blood

three important dysfunctions of blood thrombosis,bleeding,and anemia. Thrombosis-the formation of an unwanted clot within the blood vessels or heart. ■ Bleeding disorders involving failure of hemostasis are less common than thromboembolic diseases and include hemophilia and vitamin K deficiency. Anemias caused by nutritional deficiencies can be treated with either dietary or pharmaceutical supplementation
three important dysfunctions of blood ◼ thrombosis, bleeding, and anemia. Thrombosis-the formation of an unwanted clot within the blood vessels or heart. ◼ Bleeding disorders involving failure of hemostasis are less common than thromboembolic diseases and include hemophilia and vitamin K deficiency. ◼ Anemias caused by nutritional deficiencies can be treated with either dietary or pharmaceutical supplementation

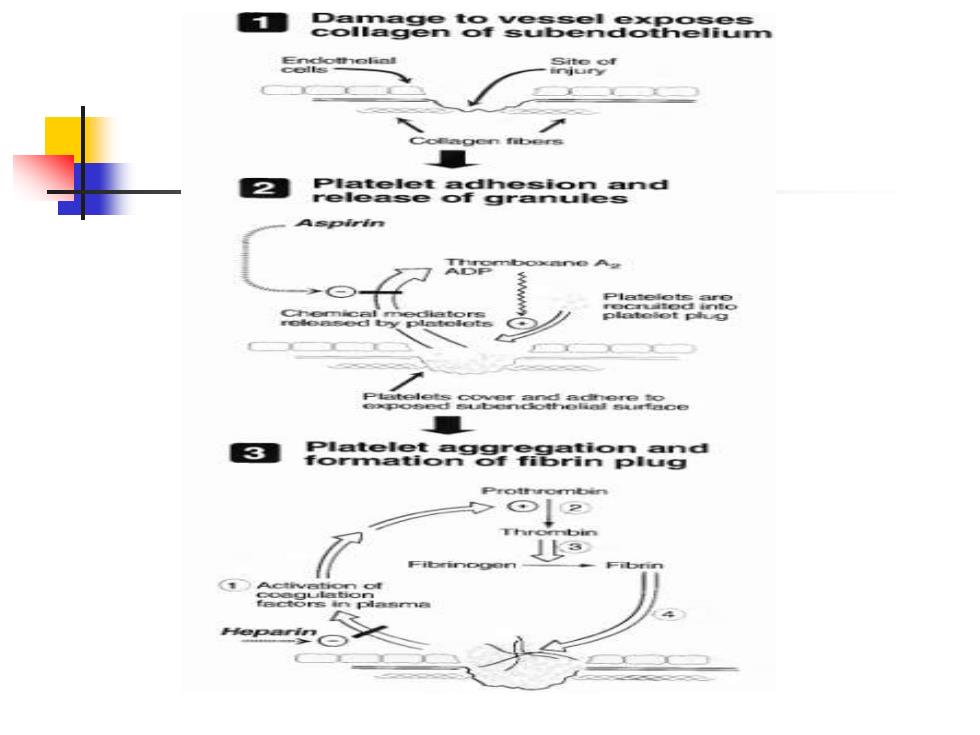
NORMAL RESPONSE TO VASCULAR TRAUMA Physical trauma to the vascular system, such as a puncture or cut,initiates a complex series of interactions between platelets,endothelial cells,and the coagulation cascade.This results in the formation of a platelet-fibrin plug
NORMAL RESPONSE TO VASCULAR TRAUMA ◼ Physical trauma to the vascular system, such as a puncture or cut, initiates a complex series of interactions between platelets, endothelial cells, and the coagulation cascade. This results in the formation of a platelet-fibrin plug

A.Formation of a clot Clot formation requires platelet activation and aggregation,followed by formation of thrombin
A. Formation of a clot ◼ Clot formation requires platelet activation and aggregation, followed by formation of thrombin

Role of platelets Platelets respond to vascular trauma by "activation"processes,which involve three steps:adhesion to the site of injury,release of intracellular granules, and aggregation of the platelets
Role of platelets ◼ Platelets respond to vascular trauma by "activation" processes, which involve three steps: adhesion to the site of injury, release of intracellular granules, and aggregation of the platelets
1雪 Sofomhotol 2 Fereslo spgemsrsna 3通

Role of fibrin Local stimulation of the coagulation cascade by factors released from the injured tissue and platelets results in the formation of thrombin (Factor II). In turn,thrombin,a serine protease, catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin,which is incorporated into the plug
Role of fibrin ◼ Local stimulation of the coagulation cascade by factors released from the injured tissue and platelets results in the formation of thrombin (Factor II). In turn, thrombin, a serine protease, catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, which is incorporated into the plug

Thrombus versus embolus A clot that adheres to a vessel wall is called a thrombus,whereas an intravascular clot that floats within the blood is termed an embolus.Thus,a detached thrombus becomes an embolus
Thrombus versus embolus ◼ A clot that adheres to a vessel wall is called a thrombus, whereas an intravascular clot that floats within the blood is termed an embolus. Thus, a detached thrombus becomes an embolus

Fibrinolysis During platelet plug formation,the fibrinolytic pathway is locally activated. Plasminogen is enzymatically processed to plasmin(fibrinolysin)by plasminogen activators present in the tissue.Plasmin interferes in clot propagation and dissolves the fibrin network as wounds heal
Fibrinolysis ◼ During platelet plug formation, the fibrinolytic pathway is locally activated. Plasminogen is enzymatically processed to plasmin (fibrinolysin) by plasminogen activators present in the tissue. Plasmin interferes in clot propagation and dissolves the fibrin network as wounds heal
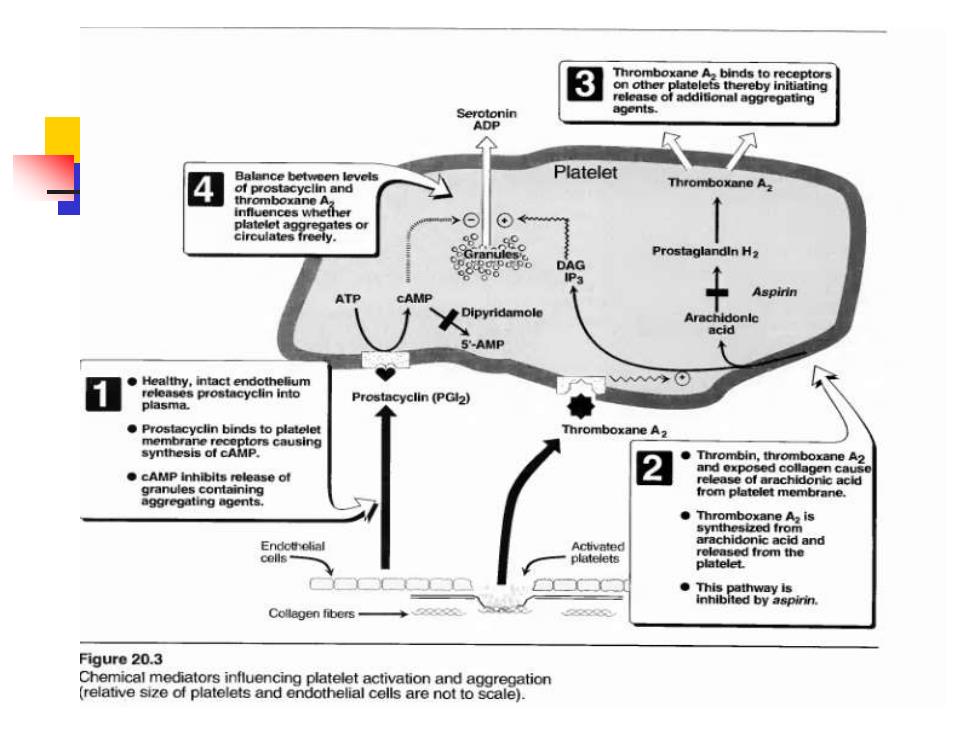
3 release of additional aggregating agents. Platelet Thromboxane nces whether olatelet ag ates or Aspirin Dipyridamole -AMP e Healthy,intact endothelium releases prostacyclin into cyclin (PGl2) piasma. hromboxane A2 synthesis of cAMP.s causing cAMP inhibits release of granules containing hnd exposed collagen cause from platelet aggregating agents. ·memb8rRh5 Endcthelial Activated arachidonic acid and platelets released from the platelet. Collagen fibers- Figure 20.3 Chemical mediators influencing platelet activation and aggregation (relative size of platelets and endothelial cells are not to scale)