
Diuretic Drugs
Diuretic Drugs

OVERVIEW Drugs inducing a state of increased urine flow are called diuretics.These agents are ion transport inhibitors that decrease the reabsorption of Na+at different sites in the nephron
OVERVIEW ◼ Drugs inducing a state of increased urine flow are called diuretics. These agents are ion transport inhibitors that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at different sites in the nephron

NORMAL REGULATION OF FLUID AND ELECTROLYTES BY THE KIDNEYS Approximately 16-20%of the blood plasma entering the kidneys is filtered from the glomerular capillaries into Bowman's capsule. These include glucose,sodium bicarbonate,amino acids,and other organic solutes,plus electrolytes,such as Na +K+,and CI-
NORMAL REGULATION OF FLUID AND ELECTROLYTES BY THE KIDNEYS ◼ Approximately 16-20% of the blood plasma entering the kidneys is filtered from the glomerular capillaries into Bowman's capsule. ◼ These include glucose, sodium bicarbonate, amino acids, and other organic solutes, plus electrolytes, such as Na +, K +, and CI-

five functional zones The kidney regulates the ionic composition and volume of urine by the reabsorption or secretion of ions and/or water at five functional zones along the nephron,namely the proximal convoluted tubule,the descending loop of Henle,the ascending loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule,and the collecting duct
five functional zones ◼ The kidney regulates the ionic composition and volume of urine by the reabsorption or secretion of ions and/or water at five functional zones along the nephron, namely the proximal convoluted tubule, the descending loop of Henle, the ascending loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule, and the collecting duct
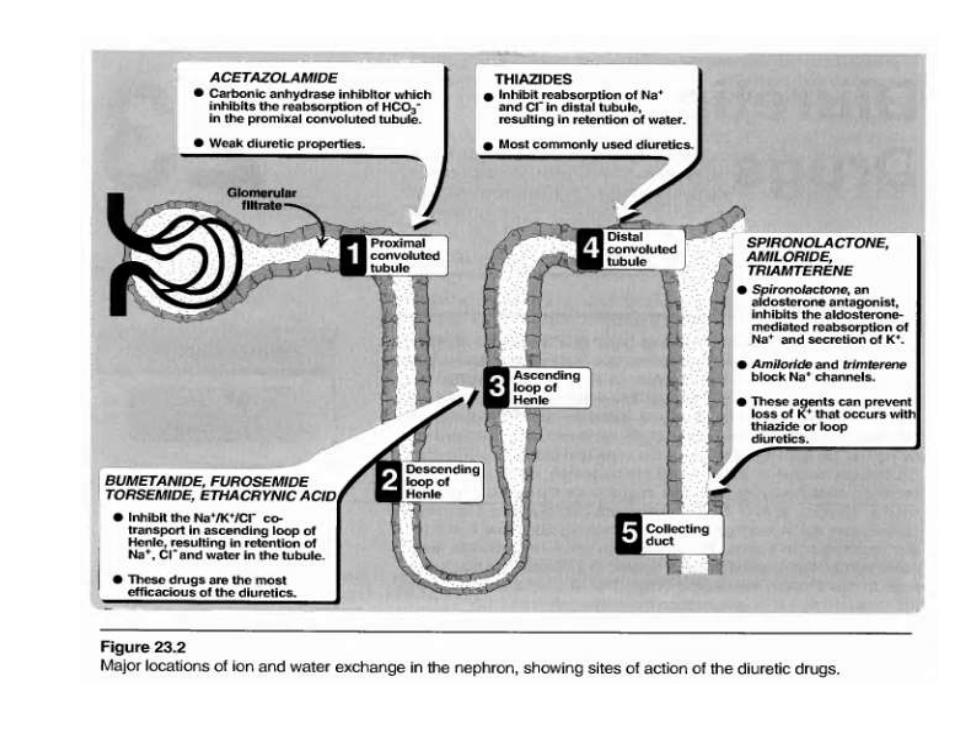
ACETAZOLAMIDE THIAZIDES n the prom Weak diuretic properties. Most commonly used diuretic Glomerular Proximal Distal convoluted SPIRONOLACTONE, convoluted tubule AMILORIDE ubulo TRIAMTERENE ·n loop of Henle 982aa8ca8m thiazide or loop diuretics. BUMETANIDE,FUROSEMIDE TORSEMIDE,ETHACRYNIC ACID ●nh the NaC58e ending loop of Collecting duct Figure 23.2 Major locations of ion and water exchange in the nephron,showing sites of action of the diuretic drugs

Proximal convoluted tubule almost all of the glucose,bicarbonate, amino acids,and other metabolites are reabsorbed.Approximately two thirds of the Na is also reabsorbed in the proximal tubule;chloride and water follow passively to maintain electrical and osmolar equality
Proximal convoluted tubule ◼ almost all of the glucose, bicarbonate, amino acids, and other metabolites are reabsorbed. Approximately two thirds of the Na + is also reabsorbed in the proximal tubule; chloride and water follow passively to maintain electrical and osmolar equality

Acid secretory system The proximal tubule is the site of the organic acid and base secretory systems The secretory system secretes a variety of organic acids(such as uric acid, some antibiotics,diuretics)from the blood-stream into the proximal tubule's lumen.Most diuretic drugs are delivered to the tubular fluid via this system
Acid secretory system ◼ The proximal tubule is the site of the organic acid and base secretory systems ◼ The secretory system secretes a variety of organic acids (such as uric acid, some antibiotics, diuretics) from the blood- stream into the proximal tubule's lumen. Most diuretic drugs are delivered to the tubular fluid via this system
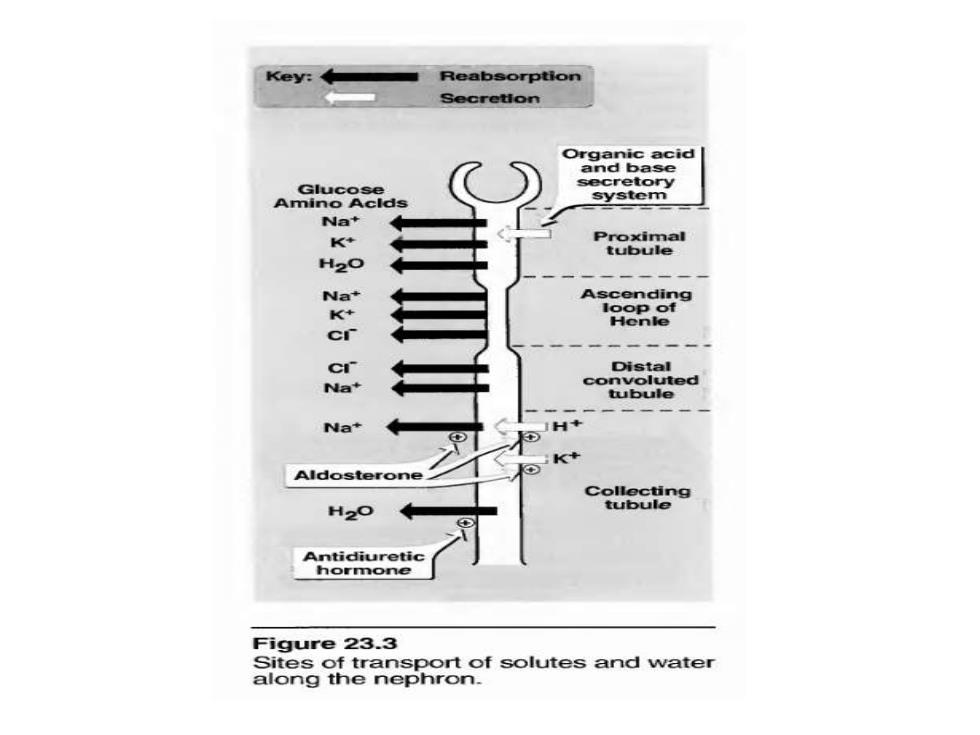
Key: Reabsorption Secretion Organic acid ind base Glucose etory Amino Aclds Na' K Na cr Distal Na' convoluted tubule Na+ Aldosterone ollecting H20 tubule Antidiuretic hormone Figure 23.3 Sites of transport of solutes and water along the nephron

Descending loop of Henle The remaining filtrate,which is isotonic, next enters the descending limb of the loop of Henle and passes into the medulla of the kidney.The osmolarity increases along the descending portion of the loop of Henle because of the countercurrent mechanism.This results in a tubular fluid with a three-fold increase in salt concentration
Descending loop of Henle ◼ The remaining filtrate, which is isotonic, next enters the descending limb of the loop of Henle and passes into the medulla of the kidney. The osmolarity increases along the descending portion of the loop of Henle because of the countercurrent mechanism. This results in a tubular fluid with a three-fold increase in salt concentration

Ascending loop of Henle impermeable to water. Active reabsorption of Na +K and CI-is mediated by a Na+/K+/2CI-cotransporter. Mg +and Ca +enter the interstitial fluid via the paracellular pathway. a diluting region of the nephron. Approximately 25-30%of the tubular sodium chloride returns to the interstitial fluid,thus helping to maintain the fluid's high osmolarity
Ascending loop of Henle ◼ impermeable to water. ◼ Active reabsorption of Na +, K + and CI- is mediated by a Na+/K+/2CI - cotransporter. Mg ++ and Ca ++ enter the interstitial fluid via the paracellular pathway. ◼ a diluting region of the nephron. Approximately 25-30% of the tubular sodium chloride returns to the interstitial fluid, thus helping to maintain the fluid's high osmolarity