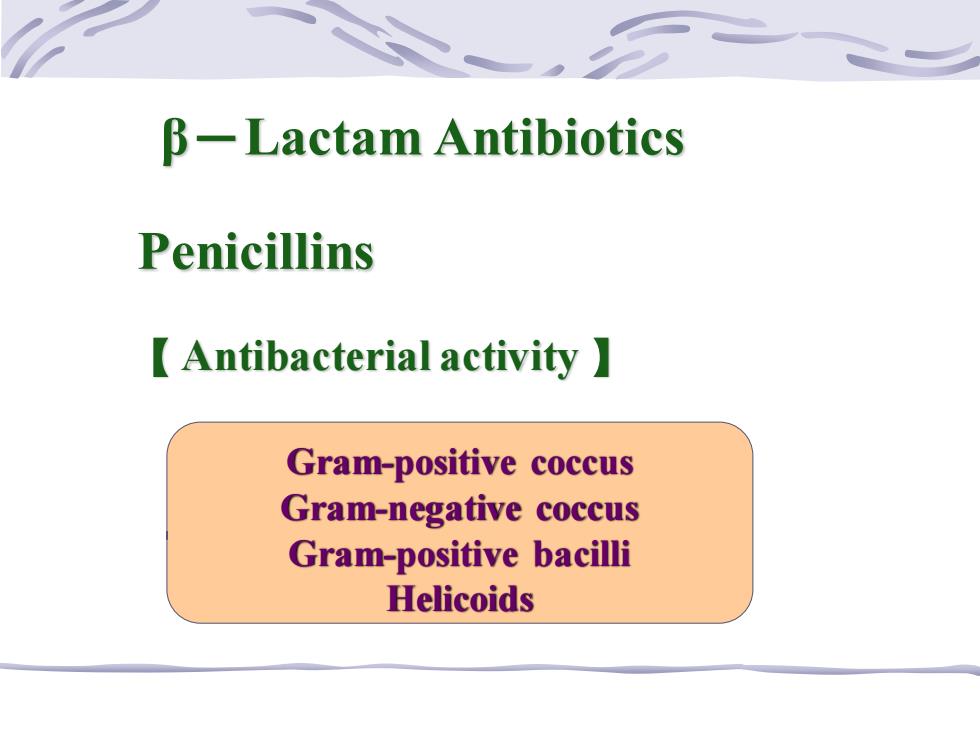
B-Lactam Antibiotics Penicillins 【Antibacterial activity】 Gram-positive coccus Gram-negative coccus Gram-positive bacilli Helicoids
β-Lactam Antibiotics 【 Antibacterial activity 】 Penicillins Gram-positive coccus Gram-negative coccus Gram-positive bacilli Helicoids

Semisynthetic penicillin Penicillinase-resistant penicillin(Oxacillin (1)They kill penicillinase-producing staphylococci (2)They can't kill Methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Semisynthetic penicillin Penicillinase-resistant penicillin( Oxacillin ) (1) They kill penicillinase-producing staphylococci (2) They can’t kill Methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)

Extended spectrum penicillins (Ampicillin) (1)They are more effective against gram-negative bacilli (2)They can not kill pseudomonas aeruginosa Antipseudomonal penicillins Carbenicillin Piperacillin
Extended spectrum penicillins (Ampicillin) (1)They are more effective against gram-negative bacilli (2)They can not kill pseudomonas aeruginosa Antipseudomonal penicillins Carbenicillin Piperacillin
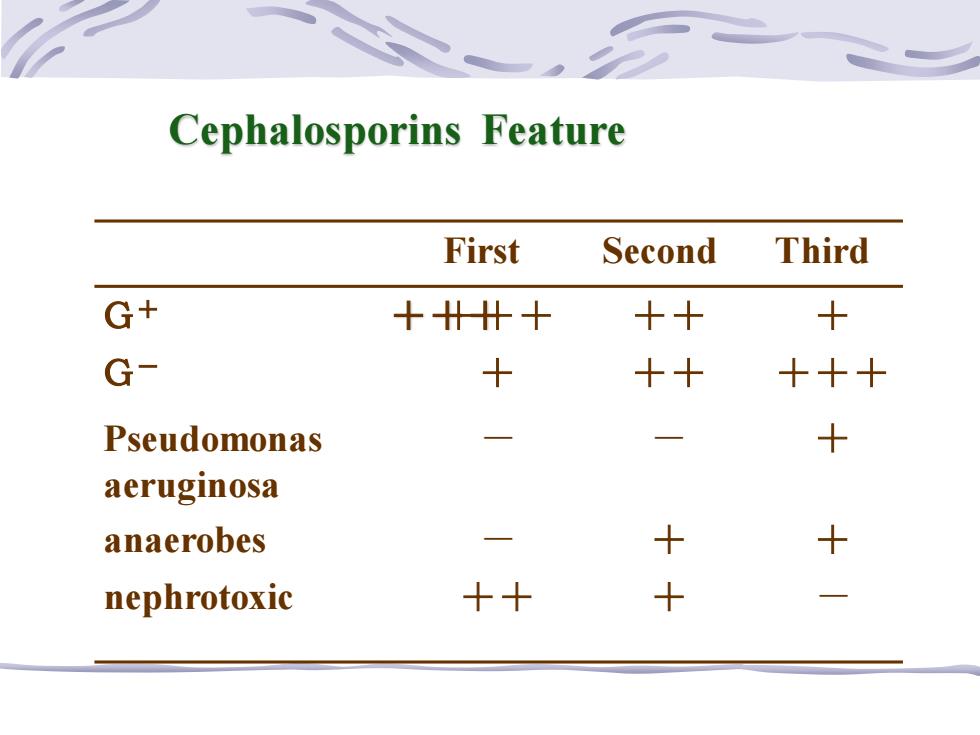
Cephalosporins Feature First Second Third G+ ++ +十 + G- + 十十 十十十 Pseudomonas 一 + aeruginosa anaerobes 一 + + nephrotoxic +十 +
Cephalosporins Feature +++ First Second Third G+ +++ ++ + G- + ++ +++ Pseudomonas aeruginosa - - + anaerobes - + + nephrotoxic ++ + -

Other B-lactams antibiotics Carbapenems Imipenem cilastatin B-lactamase inhibitors Clavulanic acid +Amoxicillin
Imipenem + cilastatin Clavulanic acid + Amoxicillin Other β-lactams antibiotics Carbapenems β-lactamase inhibitors

Chapter 37 Macrolides Lincomycins Polypeptide antibiotics
Macrolides Lincomycins Polypeptide antibiotics Chapter 37

Macrolides Erythromycin Clarithromycin Azithromycin
Macrolides Erythromycin Clarithromycin Azithromycin

Erythromycin (Pharmacokinetics 1.Erythromycin base is destroyed by gastric acid 2.It distributes well to all body fluids including prostatic fluid,but it does not enter the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 3.Erythromycin is extensively metabolized and is excreted in the bile,and only 5%is excreted in the urine
一、Erythromycin 【Pharmacokinetics】 1. Erythromycin base is destroyed by gastric acid 2. It distributes well to all body fluids including prostatic fluid ,but it does not enter the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 3. Erythromycin is extensively metabolized and is excreted in the bile, and only 5% is excreted in the urine

【Antibacterial activity】 1.Erythromycin is bacteriostatic 2.It is effective against gram-positive organisms 3.It is active against some gram-negative organisms 4.Mycoplasma,Chlamydozoan,Legionella and campylobacteria are susceptible
【Antibacterial activity 】 1. Erythromycin is bacteriostatic 2. It is effective against gram-positive organisms 3. It is active against some gram-negative organisms 4. Mycoplasma, Chlamydozoan, Legionella and campylobacteria are susceptible
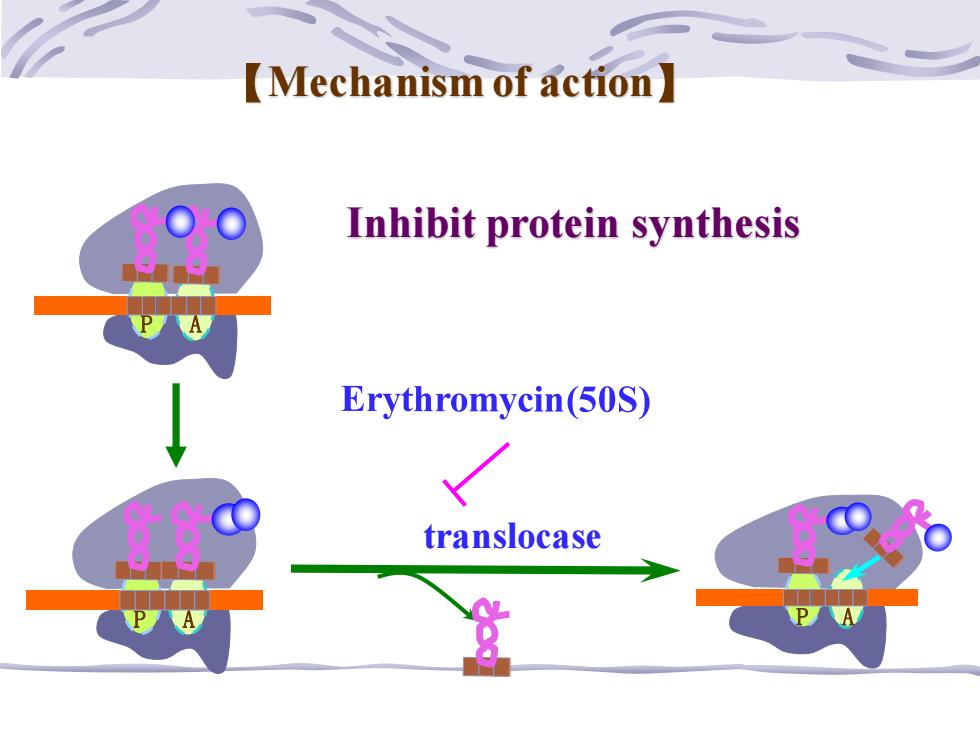
Mechanism of action】 Inhibit protein synthesis Erythromycin(50S) translocase
P A P A P A translocase Inhibit protein synthesis 【Mechanism of action】