
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
Treatment of Parkinson’s disease

Overview of CNS Act presynaptically by influencing the production,storage,or termination of action of neurotransmitters. Other agents may activate or block postsynaptic receptor
Overview of CNS • Act presynaptically by influencing the production, storage, or termination of action of neurotransmitters. • Other agents may activate or block postsynaptic receptor
Neurotransmission in the CNS Similar to autonomic nervous system The circuitry of the CNS is much more complex than the autonomic nervous system Contains powerful networks of inhibitory neurons that are constantly active More than 10 neurotransmitters
Neurotransmission in the CNS • Similar to autonomic nervous system • The circuitry of the CNS is much more complex than the autonomic nervous system • Contains powerful networks of inhibitory neurons that are constantly active • More than 10 neurotransmitters

Synaptic potentials Receptors at most synapses are coupled to ion channels. Depolarization or hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane,depending on the specific ions that move and the direction
Synaptic potentials • Receptors at most synapses are coupled to ion channels. • Depolarization or hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane, depending on the specific ions that move and the direction

Excitatory pathways Excitatory postsynaptic potential(EPSP) are generated by the following 1.stimulation of an excitatory neuron causes the release of neurotransmitter molecules 2.The influx of Na+causes a weak depolarization 3.Pass a threshold,and an all-or-none action potential is generated
Excitatory pathways • Excitatory postsynaptic potential(EPSP) are generated by the following 1. stimulation of an excitatory neuron causes the release of neurotransmitter molecules 2. The influx of Na+ causes a weak depolarization 3. Pass a threshold, and an all-or-none action potential is generated

Inhibitory pathways Results in a hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane.Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP)are 1.releases neurons releases neurotransmitter molecules, such as y-aminobutyric acid (GABA)or glycine.Increase in the permeability of specific ions,such as,potassium and chloride ions 2.the influx of chloride and efflux of potassium cause a weak hyperpolarization or IPSP that moves the postsynaptic potential away from its firing threshold
Inhibitory pathways • Results in a hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) are 1. releases neurons releases neurotransmitter molecules, such as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) or glycine. Increase in the permeability of specific ions, such as, potassium and chloride ions 2. the influx of chloride and efflux of potassium cause a weak hyperpolarization or IPSP that moves the postsynaptic potential away from its firing threshold

Overview of parkinson's disease Parkinson's disease(PD)is a progressive disorder of the nervous system.With an annual incidence of approximately 20 new cases per 100,000 people. PD is generally age-specific;it is estimated that approximately 1%of the population over age 60 has PD
Overview of parkinson’s disease • Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive disorder of the nervous system. With an annual incidence of approximately 20 new cases per 100,000 people. • PD is generally age-specific; it is estimated that approximately 1% of the population over age 60 has PD
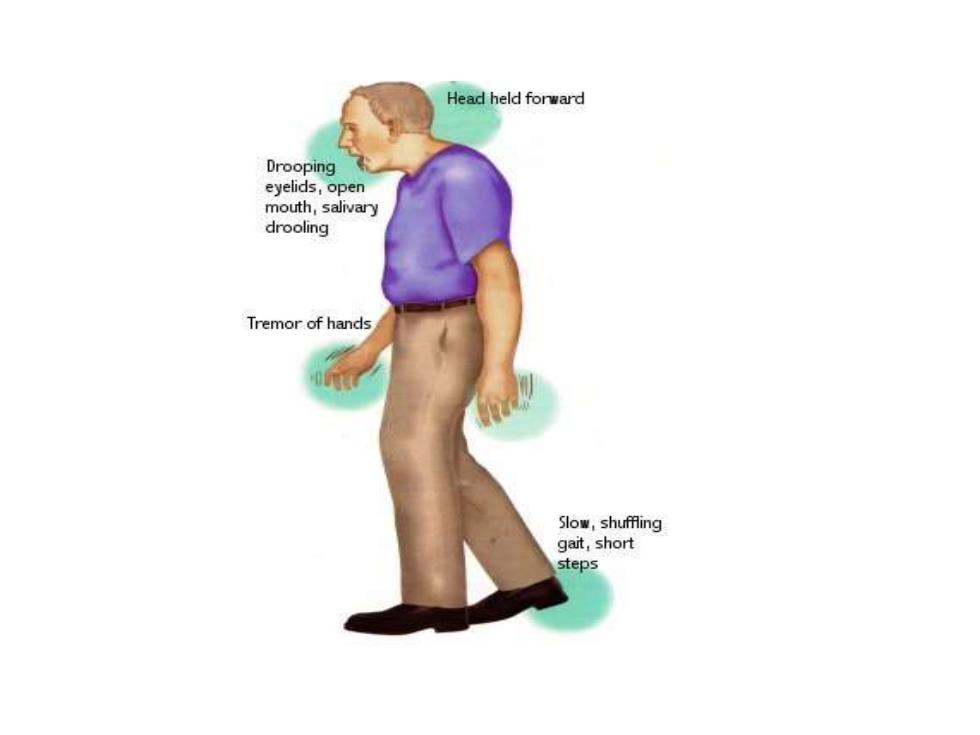
Head held forward Drooping eyelids,open mouth,salivary drooling Tremor of hands Slow,shuffing gait,short steps

Etiology Is correlated with a reduction in the activity of inhibitory dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and corpus striatum
Etiology • Is correlated with a reduction in the activity of inhibitory dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and corpus striatum

Ventricles Thalamus Fronta cortex Substantia Nigra Striatum Hypothalamu -dopamine pathway Brainstem =dopamine pathway Cross-section of the human brain showing the substantia nigra,the region affected by Parkinson's disease
Cross-section of the human brain showing the substantia nigra, the region affected by Parkinson's disease