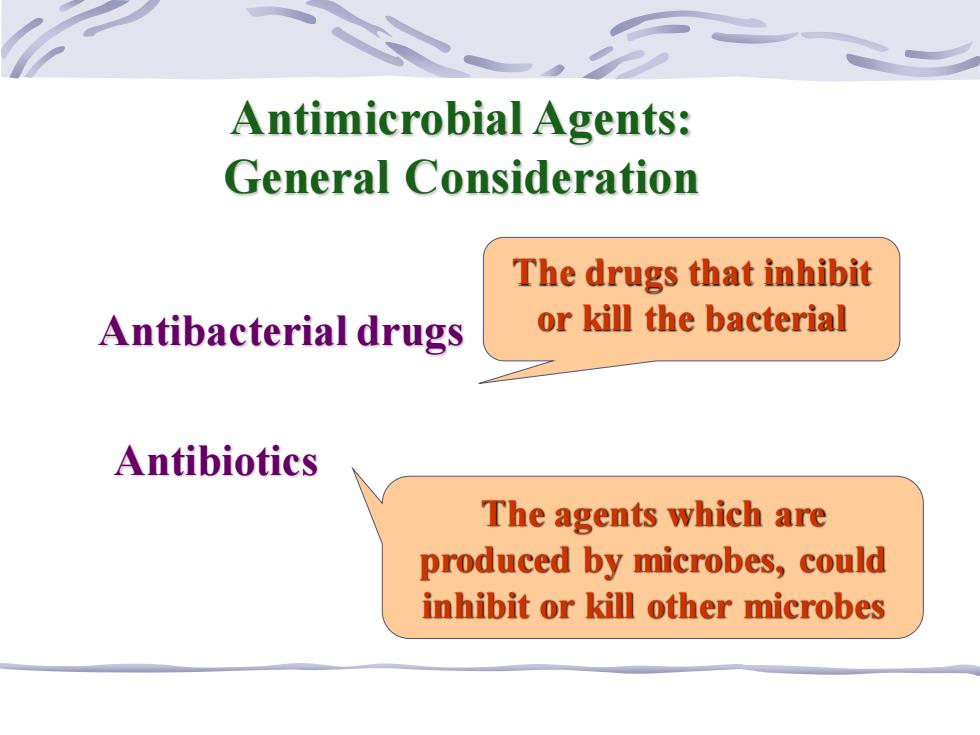
。 Antimicrobial Agents: General Consideration The drugs that inhibit Antibacterial drugs or kill the bacterial Antibiotics The agents which are produced by microbes,could inhibit or kill other microbes
Antimicrobial Agents: General Consideration Antibiotics Antibacterial drugs The drugs that inhibit or kill the bacterial The agents which are produced by microbes, could inhibit or kill other microbes
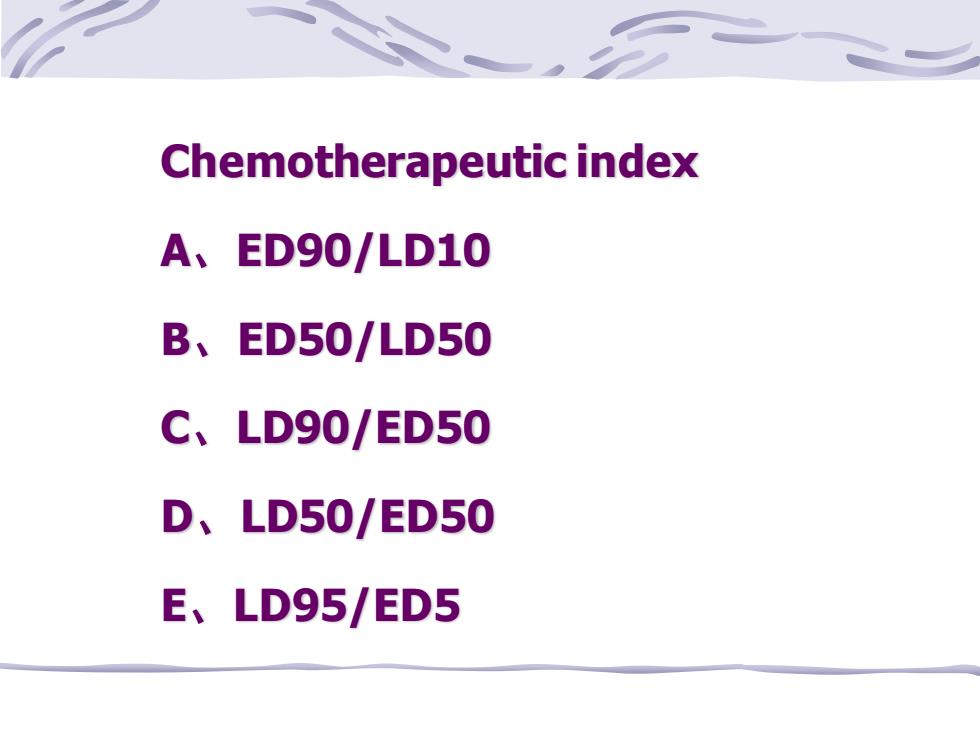
Chemotherapeutic index A、ED90/LD10 B、ED50/LD50 C、LD90/ED50 D、LD50/ED50 E、LD95/ED5
Chemotherapeutic index A、ED90/LD10 B、ED50/LD50 C、LD90/ED50 D、LD50/ED50 E、LD95/ED5

Mechanism of action Polymyxin B-lactam Polyenes Vancomycin Azoles Cell wall Quinolones DNA← THF A 505 50S 60 DHFA Rifampin Plasma membrane Tetracyclines TMP Aminoglycosides Sulfonamides PABA Macrolides Chloramphenicol Lincomycin
Mechanism of action Quinolones -lactam Vancomycin DNA Plasma membrane PABA DHF A THF A 50S 50S 50S 30S 30S 30S mRNA Rifampin TMP Sulfonamides

The mechanism of Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents: A.Production of inactivator B.Decreased porins of bacterial outer membrane C.Modification of target sites D.Increased permeability of bacterial outer membrane E.Decreased efflux pump
The mechanism of Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents: A. Production of inactivator B. Decreased porins of bacterial outer membrane C. Modification of target sites D. Increased permeability of bacterial outer membrane E. Decreased efflux pump

一Lactam Antibiotics Penicillins Cephalosporins Monobactams Carbapenems Beta-Lactam inhibitors
β-Lactam Antibiotics Penicillins Cephalosporins Monobactams Carbapenems Beta-Lactam inhibitors

Section 1 Penicillins
Section 1 Penicillins
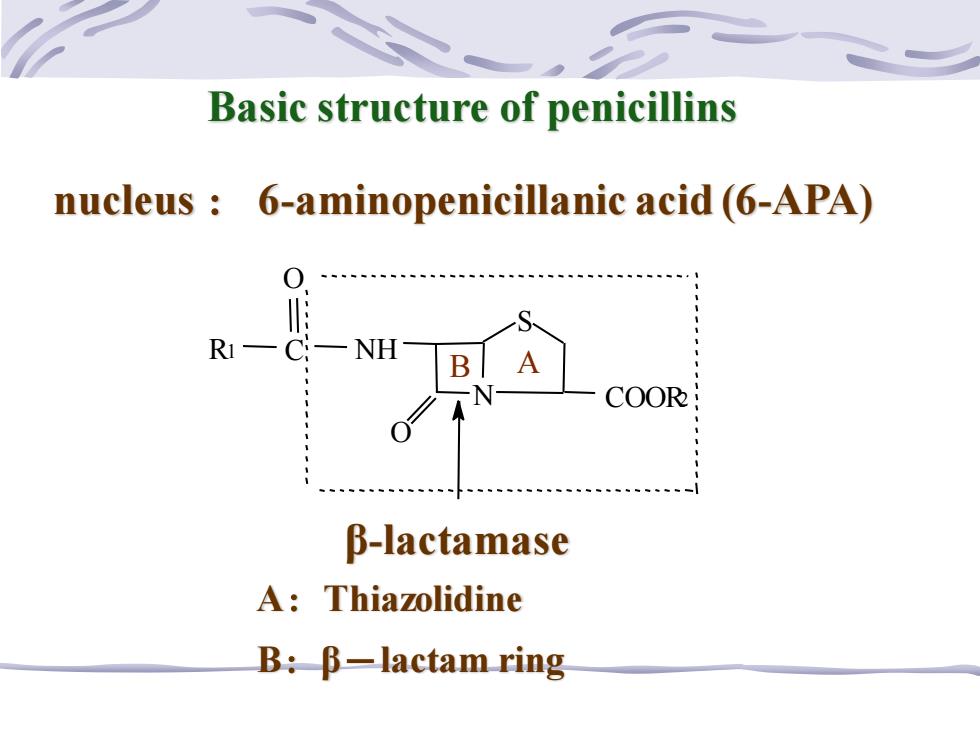
Basic structure of penicillins nucleus 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) R1—C NH A COOR B-lactamase A:Thiazolidine B:B-lactam ring
β-lactamase nucleus : 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) B:β-lactam ring N S COOR2 O R1 C NH O B A A:Thiazolidine Basic structure of penicillins

、 Natrural penicillin 【Pharmacokinetics】 冬 intramuscular or intravenous therapy distribute to most tissues and serosa-lined cavities, low concentrations appear in cerebrospinal fluid Penicillin G is excreted by the kidneys
一、Natrural penicillin 【 Pharmacokinetics 】 ❖ intramuscular or intravenous therapy ❖ distribute to most tissues and serosa-lined cavities, low concentrations appear in cerebrospinal fluid ❖ Penicillin G is excreted by the kidneys

【Antibacterial activity】 Gram-positive coccus Gram-negative coccus Gram-positive bacilli Helicoids
【 Antibacterial activity 】 Gram-positive coccus Gram-negative coccus Gram-positive bacilli Helicoids

Gram positive coccus: staphylococci-Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epidermidis streptococcus-Streptococcus hemolyticus Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus viridans
Gram positive coccus: staphylococci-Staphylococcus aureus、 Staphylococcus epidermidis streptococcus-Streptococcus hemolyticus、 Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus viridans