
Drugs Used to Treat Epilepsy
Drugs Used to Treat Epilepsy

OVERVIEW OF EPILEPSY Epilepsy is not a single entity;it is a family of different recurrent seizure disorders that have in common the sudden,excessive and disorderly discharge of cerebral neurons
OVERVIEW OF EPILEPSY ◼ Epilepsy is not a single entity; it is a family of different recurrent seizure disorders that have in common the sudden, excessive and disorderly discharge of cerebral neurons

Etiology The neuronal discharge in epilepsy results from the firing of a small population of neurons in some specific area of the brain,referred to as the primary focus. Primary epilepsy Secondary epilepsy
Etiology ◼ The neuronal discharge in epilepsy results from the firing of a small population of neurons in some specific area of the brain, referred to as the primary focus. Primary epilepsy Secondary epilepsy
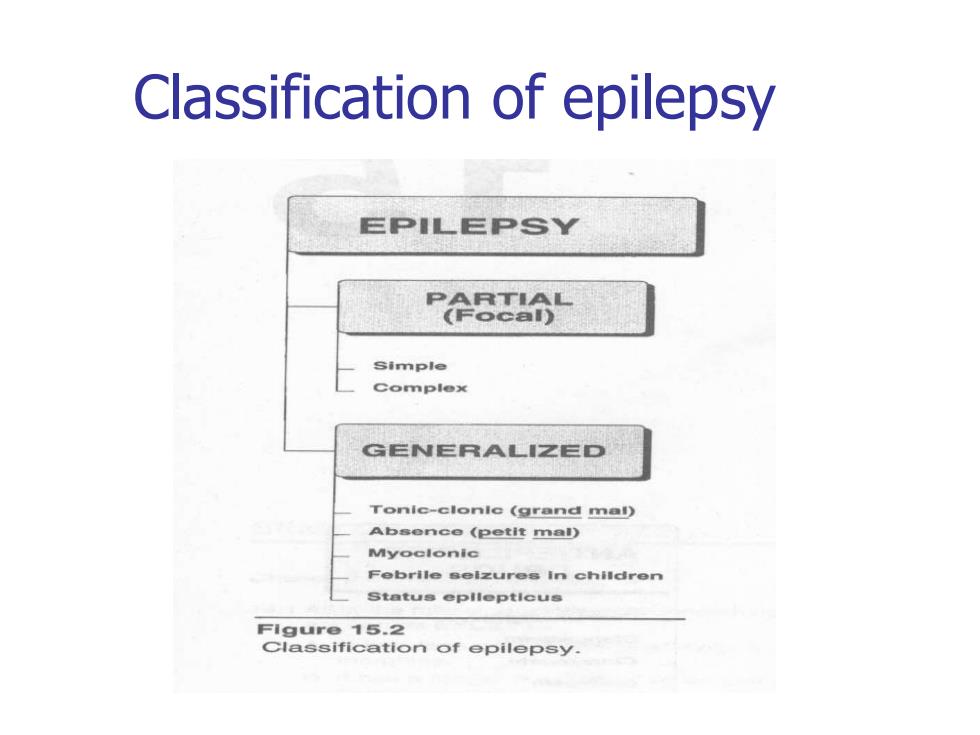
Classification of epilepsy EPIL三PSY P865 Simple Complex GENERALIZED Tonic-clonle(grand mal) Absence (petit mal) Myoclonic Febrlle selzures In children Status epllepticus Figure 15.2 Classification of epilepsy
Classification of epilepsy

Mechanism of action of antiepileptic drugs Drugs that are effective in seizure reduction can either block the initiation of the electrical discharge from the focal area or,more commonly,prevent the spread of the abnormal electrical discharge to adjacent brain areas
Mechanism of action of antiepileptic drugs ◼ Drugs that are effective in seizure reduction can either block the initiation of the electrical discharge from the focal area or, more commonly, prevent the spread of the abnormal electrical discharge to adjacent brain areas

ANTIEPILEPTIC DRUGS Phenytoin is effective in suppressing tonic-clonic and partial seizures,and is a drug of choice for initial therapy, particularly in treating adults
ANTIEPILEPTIC DRUGS ◼ Phenytoin is effective in suppressing tonic-clonic and partial seizures, and is a drug of choice for initial therapy, particularly in treating adults

Mechanism of action Phenytoin stabilizes neuronal membranes to depolarization by decreasing the flux of sodium ions in neurons in the resting state or during depolarization.It also reduces the influx of calcium ions during depolarization and suppresses repetitive firing of neurons
Mechanism of action ◼ Phenytoin stabilizes neuronal membranes to depolarization by decreasing the flux of sodium ions in neurons in the resting state or during depolarization. It also reduces the influx of calcium ions during depolarization and suppresses repetitive firing of neurons


action Phenytoin is not a generalized CNS depressant like the barbiturates,but it does produce some degree of drowsiness and lethargy without progression to hypnosis.Phenytoin reduces the propagation of abnormal impulses in the brain
action ◼ Phenytoin is not a generalized CNS depressant like the barbiturates, but it does produce some degree of drowsiness and lethargy without progression to hypnosis. Phenytoin reduces the propagation of abnormal impulses in the brain

Therapeutic uses Phenytoin is highly effective for all partial seizures(simple and complex), for tonic-clonic seizures,and in the treatment of status epilepticus caused by recurrent tonic-clonic seizures Phenytoin is not effective for absence seizures,which often may worsen if such a patient is treated with this drug
Therapeutic uses ◼ Phenytoin is highly effective for all partial seizures (simple and complex), for tonic-clonic seizures, and in the treatment of status epilepticus caused by recurrent tonic- clonic seizures ◼ Phenytoin is not effective for absence seizures, which often may worsen if such a patient is treated with this drug