
《国际市场营销学(全英)》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 课程代码:060043 课程名称:国际市场营销学(全英) 英文名称:International Marketing 课程类别:专业必修课 时:48 学 分:3 适用对象:国际贸易本科学士 考核方式:考试 先修课程:国际贸易 二、课程简介 As global economic growth occurs.understanding marketing in all cultures is increasingly important.isa theoretical and practicalcourse,in the interpretation of the basic theory of marketing at the same time,combined with the actual business case analysis InterationalMarketing addresses global issues and describes concepts relevant to all international marketers,regardless of the extent of their international involvement.Not all frms engaged in overseas marketing have a global perspective,nor do they need to. It is with this future that the sixteenth edition of International Marketing is concemed. Emphasis is on the strategic implications of competition in different country markets.An environmentalcultural approach to interational marketing permits a truly global orientation.The text is designed to stimulate curiosity about management practices of companies,large and small,seeking market opportunities outside the home country and to raise the reader's consciousness about the importance of viewing international marketing management strategies from a global perspective.Although this revised edition is infused throughout with a global orientation,export marketing and the operations of smaller companies are also included.Issues specifc to exporting are discussed where strategies applicable to exporting arise,and examples of marketing practices of smaller companies are examined
1 《国际市场营销学(全英)》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 课程代码:060043 课程名称:国际市场营销学(全英) 英文名称:International Marketing 课程类别:专业必修课 学 时:48 学 分:3 适用对象:国际贸易本科学士 考核方式:考试 先修课程:国际贸易 二、课程简介 As global economic growth occurs, understanding marketing in all cultures is increasingly important. This course is a theoretical and practical course, in the interpretation of the basic theory of marketing at the same time, combined with the actual business case analysis. InternationalMarketing addresses global issues and describes concepts relevant to all international marketers, regardless of the extent of their international involvement. Not all frms engaged in overseas marketing have a global perspective, nor do they need to. It is with this future that the sixteenth edition of International Marketing is concerned. Emphasis is on the strategic implications of competition in different country markets. An environmental∕cultural approach to international marketing permits a truly global orientation. The text is designed to stimulate curiosity about management practices of companies, large and small, seeking market opportunities outside the home country and to raise the reader’s consciousness about the importance of viewing international marketing management strategies from a global perspective. Although this revised edition is infused throughout with a global orientation, export marketing and the operations of smaller companies are also included. Issues specifc to exporting are discussed where strategies applicable to exporting arise, and examples of marketing practices of smaller companies are examined

三、课程性质与教学目的 本课程是一门全英课程,是专门针对国际贸易的本科学士开设的一门专业必修 课。 通过本课程的学习,首先,使学生对国际营销的学科体系有一个全面的认识,为 学生进一步学习其它专业知识奠定学科基础,并使之具有较完备、合理的知识结构和 实践能力。其次,使学生能明确理解国际营销特点、作用:弄懂各种概念、范畴等基 本知识:掌握运用各种分析方法。再次,培养学生理论联系实际的能力,在今后的实 际工作和生活中,能将营销学的知识贯穿其中。最后,还要教会学生理论分析,使他 们能够分析社会经济现象的具体营销事例并能以报告的形式给出分析结果和合理化 建议。 四、教学内容及要求 terThe Scope and Challenge of Intemational Marketing 1.The benefits of international markets 2.The changing face 3.The scope of the intemational marketing task 4.The importance of the self-reference criterion (SRC)in international marketing 5.The increasing importance of global awareness 6.The progression of becoming a global marketer (二)教学内容 Funda woncepts d Demands Section2.What is Marketing?What is International Marketing? Marketing sap叫 ompanies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships tocapture value from customers in retu. International marketing is the performance of business activities designed to plan,price, promote.and direct the flow of a company's goods and services to consumers or users in more than one nation fora profit The difference between international marketing and domestic marketing er'task/B aBu ess goal/Marketing environment n3.TheI The international marketer's task is more complicated than that of the domestic markete because the international marketer must deal with at least two levels of uncontrollable uncertainty instead of one.Uncertainty is created by the uncontrollable elements of all 2
2 三、课程性质与教学目的 本课程是一门全英课程,是专门针对国际贸易的本科学士开设的一门专业必修 课。 通过本课程的学习,首先,使学生对国际营销的学科体系有一个全面的认识,为 学生进一步学习其它专业知识奠定学科基础,并使之具有较完备、合理的知识结构和 实践能力。其次,使学生能明确理解国际营销特点、作用;弄懂各种概念、范畴等基 本知识;掌握运用各种分析方法。再次,培养学生理论联系实际的能力,在今后的实 际工作和生活中,能将营销学的知识贯穿其中。最后,还要教会学生理论分析,使他 们能够分析社会经济现象的具体营销事例并能以报告的形式给出分析结果和合理化 建议。 四、教学内容及要求 Chapter 1 The Scope and Challenge of International Marketing (一)目的与要求 1. The benefits of international markets 2. The changing face of U.S. business 3. The scope of the international marketing task. 4. The importance of the self-reference criterion (SRC) in international marketing 5. The increasing importance of global awareness 6. The progression of becoming a global marketer (二)教学内容 Section1. Fundamental concepts Customer Needs, Wants, and Demands Section2. What is Marketing? What is International Marketing? Marketing is a process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships to capture value from customers in return. International marketing is the performance of business activities designed to plan, price, promote, and direct the flow of a company’s goods and services to consumers or users in more than one nation for a profit. The difference between international marketing and domestic marketing. Country/ Marketer’s task/ Business goal/ Business goal / Marketing environment Section3. The International Marketing Task The international marketer’s task is more complicated than that of the domestic marketer because the international marketer must deal with at least two levels of uncontrollable uncertainty instead of one. Uncertainty is created by the uncontrollable elements of all

business environments,but each foreign country in which a company operates adds its own Section4.Self-Reference Criterion Ethnocentrism SelfReference Criterion (SRC)is an unconscious reference to one's own cultural values, experiences,and knowledge as a basis for decisions. the notion that people in one's own company,culture,or country know best how to do things Both the SRC and ethnocentrism impede the ability to assess a foreign market in its true tion5.Stages of International Marketing Involvement No Direct Foreign Marketing:Infrequent Foreign Marketing;Regular Foreign Marketing. International Marketing:Global Marketing (三)思老与实我 1.掌握书上本章概念。 Needs,wants and demand Market International marketing Domestic environn Foreign environment Self-reference criterion Controllable elements Uncontrollables Global awareness Uncontrollable elements 2.完成本章书后练习题。 (1)What's the structure of the text? (2)"The marketer's task is the same whether applied in Dimebox,Texas,or Dar es Salaam,Tanzania"Discuss (3)How can the increased interest in international marketing on the part of U.S.firms be explained? (4)Discuss the four phases of intemational marketing involvement. (5)Differentiate between a global company and a multinational company. (6)Discuss the three factors necessary to achieve global awareness (7)Define and discuss the idea of global orientation. (四)教学方法与手段 1.教学方法:慕课:课堂讲授:课堂练习:辅导答疑。 2.教学手段:慕课平台:QQ:多媒体教学 Chapter 2 The Global Environment of International Marketing (一)目的与要求 3
3 business environments, but each foreign country in which a company operates adds its own Section4. Self-Reference Criterion & Ethnocentrism Self-Reference Criterion (SRC) is an unconscious reference to one’s own cultural values, experiences, and knowledge as a basis for decisions. Ethnocentrism is the notion that people in one’s own company, culture, or country know best how to do things. Both the SRC and ethnocentrism impede the ability to assess a foreign market in its true light. Section5. Stages of International Marketing Involvement No Direct Foreign Marketing; Infrequent Foreign Marketing; Regular Foreign Marketing; International Marketing; Global Marketing (三)思考与实践 1.掌握书上本章概念。 Needs, wants and demand Market International marketing Domestic environment Foreign environment Self-reference criterion Controllable elements Uncontrollables Global awareness Uncontrollable elements 2.完成本章书后练习题。 (1) What’s the structure of the text? (2)“The marketer’s task is the same whether applied in Dimebox, Texas, or Dar es Salaam, Tanzania.” Discuss (3)How can the increased interest in international marketing on the part of U.S. firms be explained? (4)Discuss the four phases of international marketing involvement. (5)Differentiate between a global company and a multinational company. (6)Discuss the three factors necessary to achieve global awareness. (7)Define and discuss the idea of global orientation. (四)教学方法与手段 1.教学方法:慕课;课堂讲授;课堂练习;辅导答疑。 2.教学手段:慕课平台;QQ;多媒体教学。 Chapter 2 The Global Environment of International Marketing (一) 目的与要求

1.The importance of GATT and the World Trade Organization 2.The emergence of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank Group 3.The evolution of the European Union 4.The interrelationships among countries in the region 5.Strategic implications for marketing in the region 6.The size and nature of marketing opportunities in the European/African/Middle East regions 7.The importance of the Bottom-of-the-Pyramid Markets 8.The diversity across the region (二)教学内容 Section 1.GATT WTO Section 2.International Monetary Fund(IMF)and World Bank Group s,Economic and Monetary Union(EMU).Expansion of the European Union FA.NAFTA. Association of Southeast Asian Nations(ASEAN),Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Section 4.Marketing in a Developing Country (三)思老与实践 1.掌握书上本章概念 GATT,Balance of payments;Current account;Protectionism;Nontariff barriers;Tariff Voluntary export restraints (VERs);World Trade Organization (WTO);International Monetary Fund (IMF) 2.完成本章书后练习题 (1)Discuss the globalization of the U.S.economy. (2)enumerate the ways in which a nation can overcome an unfavorable balance of trade (3)Support or refute each of the various arguments commonly used in support of tariffs. such variations in exports? (5)Does widespread unemployment change the economic logic of protectionism? (6)Review the economic effects of major trade imbalances such as those caused by petroleum imports (7)Discuss the main provisions of the Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of 1988
4 1. The importance of GATT and the World Trade Organization 2. The emergence of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank Group 3. The evolution of the European Union 4. The interrelationships among countries in the region 5. Strategic implications for marketing in the region 6. The size and nature of marketing opportunities in the European/African/Middle East regions 7. The importance of the Bottom-of-the-Pyramid Markets 8. The diversity across the region (二)教学内容 Section 1. GATT & WTO Section 2. International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank Group Section 3. Europe and European Integration, The Americas, and Asia Pacific Trade Associations EU Institutions, Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), Expansion of the European Union CFTA, NAFTA, Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Section 4. Marketing in a Developing Country (三)思考与实践 1.掌握书上本章概念。 GATT; Balance of payments; Current account; Protectionism; Nontariff barriers; Tariff; Voluntary export restraints (VERs); World Trade Organization (WTO); International Monetary Fund (IMF) 2.完成本章书后练习题。 (1) Discuss the globalization of the U.S. economy. (2) Enumerate the ways in which a nation can overcome an unfavorable balance of trade. (3) Support or refute each of the various arguments commonly used in support of tariffs. (4) France exports about 18 percent of its gross domestic product, while neighboring Belgium exports 46 percent. What areas of economic policy are likely to be affected by such variations in exports? (5) Does widespread unemployment change the economic logic of protectionism? (6) Review the economic effects of major trade imbalances such as those caused by petroleum imports. (7) Discuss the main provisions of the Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of 1988
(8)The Tokyo Round of GATT emphasized the reduction of nontariff barriers.How does the Uruguay round differ? (9)Discuss the impact of GATS,TRIMs,and TRIPs on global trade. (四)教学方法与手段 教学方法 慕课:课堂讲授:课堂练习:辅导答疑 2.教学手段:慕课平台:QQ:多媒体教学。 (一)目的与要 ter 3 History and Geography:The Foundations of Culture 1.The importance of history and geography in understanding international markets 2.The effects of history on a country's culture 3.The effect of geographic diversity on economic profiles of a country 4.Why marketers geography of a country 5.The economic effects of controlling population growth and aging populations 6.Communication infrastructures are an integral part of international commerce (二)教学内容 Sectionl.The Definitions of Culture Culture is the sum of thevalues,rituals,symbols,beliefs,and thought processes that are leamed,shared by a group of people,and transmitted from generation to generation Orlains nent.rations) Peers】Imitation Origins,Elements,and Consequence of Culture
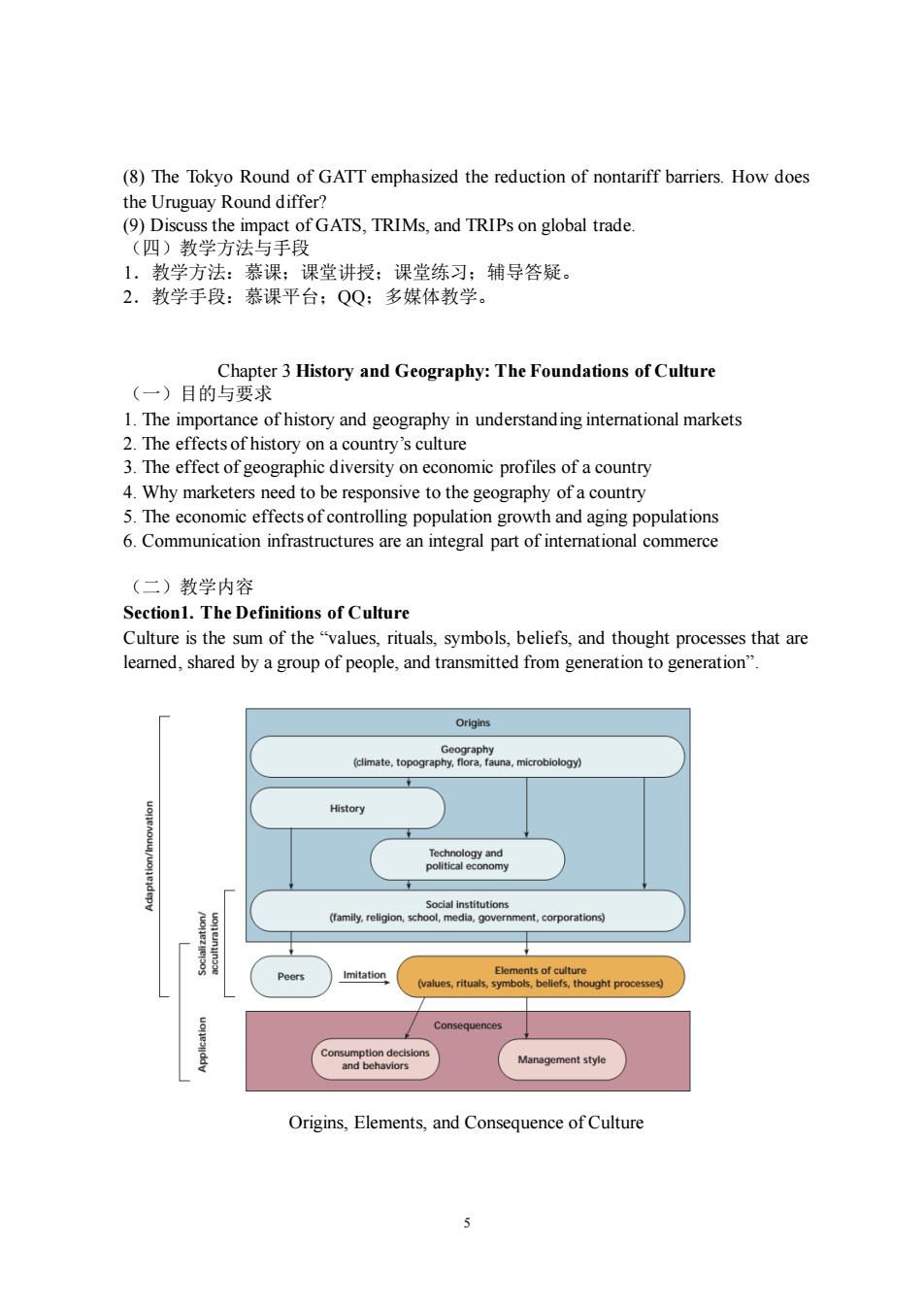
5 (8) The Tokyo Round of GATT emphasized the reduction of nontariff barriers. How does the Uruguay Round differ? (9) Discuss the impact of GATS, TRIMs, and TRIPs on global trade. (四)教学方法与手段 1.教学方法:慕课;课堂讲授;课堂练习;辅导答疑。 2.教学手段:慕课平台;QQ;多媒体教学。 Chapter 3 History and Geography: The Foundations of Culture (一)目的与要求 1. The importance of history and geography in understanding international markets 2. The effects of history on a country’s culture 3. The effect of geographic diversity on economic profiles of a country 4. Why marketers need to be responsive to the geography of a country 5. The economic effects of controlling population growth and aging populations 6. Communication infrastructures are an integral part of international commerce (二)教学内容 Section1. The Definitions of Culture Culture is the sum of the “values, rituals, symbols, beliefs, and thought processes that are learned, shared by a group of people, and transmitted from generation to generation”. Origins, Elements, and Consequence of Culture

Section2.Geography and Global Markets Geography (broadly defined here to include climate,topography,flora,fauna,and microbiology)has influenced history,technology,economics,our social institutions. en the boy-to-girl birth ratio,and,yes,our ways of thinking influences manifest themselves in our deepest cultural alues developed through the millennia. (Climate and Topography 2Geography,Nature Economic Growth Social Responsibility&Environmental Management ④Resources Section3.Populations Necessary to know about: rural/urban population shifts /rates of growth /age levels /population control /population aging /wo ortage and immigration 2Population Control Issues 3Population Decline and Aging 4The Population Structure 二)甲老与空 掌握本章概念 Culture Geography Climate and Topography Social Responsibility Environmental Management 2.完成本章书后练习。 ational marketing? (3)Some say the global environment is a global issue rather than a national one.What doesthis mean? (4)Pick a country and show how employment and topography affect marketing within the market characteristics,distribution systems,and the state of the economy."Comment (6)The world population pattern is shifting from rural to urban areas.Discuss the marketing ramifications. (7Select a country with a stable population and one witha rapidly growing population Contrast the marketing implications of these two situations (四)教学方法与手段 1.教学方法:慕课:课堂讲授:课堂练习:辅导答疑。 6
6 Section2. Geography and Global Markets Geography (broadly defined here to include climate, topography, flora, fauna, and microbiology) has influenced history, technology, economics, our social institutions, perhaps even the boy-to-girl birth ratio, and, yes, our ways of thinking. Geographical influences manifest themselves in our deepest cultural values developed through the millennia. ①Climate and Topography ②Geography, Nature & Economic Growth ③Social Responsibility & Environmental Management ④Resources Section3. Populations Necessary to know about: rural/urban population shifts /rates of growth /age levels /population control /population decline and aging /worker shortage and immigration ① Global Population Trends ②Population Control Issues ③Population Decline and Aging ④The Population Structure (三)思考与实践 1.掌握本章概念. Culture Geography Climate and Topography Social Responsibility Environmental Management 2.完成本章书后练习。 (1)Why study geography in international marketing? (2)How does an understanding of history help an international marketer (3)Some say the global environment is a global issue rather than a national one. What does this mean? (4)Pick a country and show how employment and topography affect marketing within the country. (5)The marketer “should also examine the more complex effect of geography on general market characteristics, distribution systems, and the state of the economy.” Comment (6)The world population pattern is shifting from rural to urban areas. Discuss the marketing ramifications. (7)Select a country with a stable population and one with a rapidly growing population. Contrast the marketing implications of these two situations. (四)教学方法与手段 1.教学方法:慕课;课堂讲授;课堂练习;辅导答疑

2.教学手段:慕课平台:QQ:多媒体教学。 Chapter 4 Cultural Dynamics in Assessing Global Markets (一)目的与要求 The origins of cul nd its consequences (二)教学内容 Section1.A CASE EQUITIES AND Ebay-CULTURE GETS IN THE WAY Section2.Culture's Pervasive Impac es or d influences culture Italy.Even diseases are influe ed h pre sto f by British,wines by France and ach r in 1 nd lu an in Exhibit 4.2 Patterns of Consumption(annual per capita) and Dried Country (ka Wine (S) Tobacco (S ance 021 370 228 438 Netherlands 153610 4.8 38 490 50 43 3.1 305 Discussion:Why there are no Starbucks in Italy? Section3. Culture's Social Institutions Social institu including family,religion,school,the media,government,and corporations all ct culture and vility are interpreted erythhoidefne deceney ,0 1.Family behavior varies across the world
7 2.教学手段:慕课平台;QQ;多媒体教学。 Chapter 4 Cultural Dynamics in Assessing Global Markets (一)目的与要求 1. The importance of culture to an international marketer 2. The origins of culture 3. The elements of culture 4. The impact of cultural borrowing 5. The strategy of planned change and its consequences (二)教学内容 Section1. A CASE EQUITIES AND Ebay –CULTURE GETS IN THE WAY Section2. Culture’s Pervasive Impact Consumption of different types of food influences culture Chocolate by Swiss, seafood by Japanese preference, beef by British, wines by France and Italy,Even diseases are influenced by culture stomach cancer in Japan, and lung cancer in Spain Discussion: Why there are no Starbucks in Italy? Section3. Culture’s Social Institutions Social institutions including family, religion, school, the media, government, and corporations all affect culture The family, social classes, group behavior, age groups, and how societies define decency and civility are interpreted differently within every culture 1. Family behavior varies across the world

acy late Media(magazin the I fluences . lture and behavior ofadultcizens eg. the F of $800 given to women as a .Coporations nfuenecure via the products they market,MTV Section4.Culture's Social Institutions 1.Cultural Values 2.Rituals 3.Symbols 4.Beliefs 5.Thought Processes (三)思考与实践 1.掌握书上本章概念。 Social institutions Cultural values Rituals Linguistic distance Cultural sensitivity Cultural borrowing Cultural congruence Planned change 2.完成本章书后练习题。 (1 )What role does the marketer play as a change agent? (2)Discuss the three cultural change strategies a foreign marketer can pursue. (3)"Culture is pervasive in all marketing activities."Discuss. (4)What is the importance of cultural empathy to foreign marketers?How do they acquire cultural empathy? (5 )Why should a foreign marketer be concerned with the study of culture? (6)"Members of a society borrow from other cultures tosolve problems that they face in common."What does this mean?What is the significance to marketing? (7)"For the inexperienced marketer,thesimilar-but-different'aspect of culture creates an illusion of similarity that usually doesnot exist."Discuss and give examples (8)Social institutions affect culture and marketing in a variety of ways.Discuss,giving examples
8 2. Religious value systems differ across the world 3. School and education, and literacy rates 4. Media (magazines, TV, the Internet) influences culture and behavior 5. Government policies influence the thinking and behaviors citizens of adult citizens, e.g., the French government offers new “birth bonuses” of $800 given to women as an incentive to increase family size 6. Corporations influence culture via the products they market, e.g., MTV Section4. Culture’s Social Institutions 1. Cultural Values 2. Rituals 3. Symbols 4.Beliefs 5. Thought Processes (三)思考与实践 1.掌握书上本章概念。 Social institutions Cultural values Rituals Linguistic distance Cultural sensitivity Cultural borrowing Cultural congruence Planned change 2.完成本章书后练习题。 (1)What role does the marketer play as a change agent? (2)Discuss the three cultural change strategies a foreign marketer can pursue. (3)“Culture is pervasive in all marketing activities.” Discuss. (4) What is the importance of cultural empathy to foreign marketers? How do they acquire cultural empathy? (5)Why should a foreign marketer be concerned with the study of culture? (6) “Members of a society borrow from other cultures to solve problems that they face in common.” What does this mean? What is the significance to marketing? (7)“For the inexperienced marketer, the ‘similar-but-different’ aspect of culture creates an illusion of similarity that usually does not exist.” Discuss and give examples. (8) Social institutions affect culture and marketing in a variety of ways. Discuss, giving examples

(9)"Markets are the result of the three-way interaction of a marketer's efforts,economic conditions,and all other elements of the culture."Comment. (10)What are some particularly troublesome problems caused by language in foreign marketing?Discuss. (11)Defend the proposition that a multinational corporation has no responsibility for the product's safety,performance,and so forth (四)教学方法与手段 1.教学方法:慕课:课堂讲授:课堂练习:辅导答疑。 2.教学手段:慕课平台:QQ:多媒体教学。 Chapter 5 Culture,Management Style,and Business Systems (一)目的与要求 1.The necessity for adapting to cultural differences 2.How and why agement styles vary around the world 3.The extent and implications of gender bias in other countries 4.The importance of cultural differences in business ethics 5.The differences between relationship-oriented and information-oriented cultures (二)教学内容 Sectionl.Ada Required adaptation:Degree of adaptation Section2.Cultural Imperatives,Electives and Exclusives Cultural imperatives:business customs and expectations that must be met,conformed, recognized and accommodated if relationships are to be successful Cultural electives:areas of behavior or to customs that cultural aliens may wish to conform to or participate in but that are not required Cultural exclusives:customs or beh avior patterns reserved exclusively for the locals and from which the foreigner is barred and must not participate Section3.Differences in Management Styles Around the Workd Authority and ion Ma
9 (9)“Markets are the result of the three-way interaction of a marketer’s efforts, economic conditions, and all other elements of the culture.” Comment. (10) What are some particularly troublesome problems caused by language in foreign marketing? Discuss. (11) Defend the proposition that a multinational corporation has no responsibility for the consequences of an innovation beyond the direct effects of the innovation, such as the product’s safety, performance, and so forth. (四)教学方法与手段 1.教学方法:慕课;课堂讲授;课堂练习;辅导答疑。 2.教学手段:慕课平台;QQ;多媒体教学。 Chapter 5 Culture, Management Style, and Business Systems (一)目的与要求 1. The necessity for adapting to cultural differences 2. How and why management styles vary around the world 3. The extent and implications of gender bias in other countries 4. The importance of cultural differences in business ethics 5. The differences between relationship-oriented and information-oriented cultures (二)教学内容 Section1. Adaptation Required adaptation; Degree of adaptation Section2. Cultural Imperatives, Electives and Exclusives Cultural imperatives: business customs and expectations that must be met, conformed, recognized and accommodated if relationships are to be successful Cultural electives: areas of behavior or to customs that cultural aliens may wish to conform to or participate in but that are not required Cultural exclusives: customs or behavior patterns reserved exclusively for the locals and from which the foreigner is barred and must not participate Section3. Differences in Management Styles Around the World 1. Authority and Decision Making 2. Management Objectives and Aspirations 3. Differences in Communication Styles

Exhibit 5.2 kground of Latin Americar English (UK) French North American(US) Scandinavian erman Eopia P-Time M-Tim Section4.Gender Bias Section 5.Business Ethics (1)Utilitariar ethics nd.who are the peru (2)Rights of the parties Doseggee (3)Justice or fairness (三)思考与实践 1.掌握书上本章概念 Cultural imperative:Cultural elective:Cultural exclusive:Silent languages:Monochronic time(M-time);Polychronic time(P-time);Bribery;Lubrication;Subornation 2.完成本章书后练习题。 (1)"More than tolerance of an alien culture is required;there is a need for affirmative 10
10 4. Formality and Tempo 5. P-Time versus M-Time 6. Negotiations Emphasis 7. Market Orientation Section4. Gender Bias Section 5. Business Ethics (三)思考与实践 1.掌握书上本章概念。 Cultural imperative; Cultural elective; Cultural exclusive; Silent languages; Monochronic time (M-time); Polychronic time (P-time); Bribery; Lubrication; Subornation 2.完成本章书后练习题。 (1) “More than tolerance of an alien culture is required; there is a need for affirmative