
How Can Computer Science Help When Your Drinking Water Gets too Salty? Jimmy Lee Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong In collaboration with the International 尖am univecsily Institute for Software Technology UNU-IIST United Nations University International Institute for Sofiware Technology MSC Seminar(January 30,2012) Controlling Salinity in a Potable Water Supply System Using a Constraint Programming Approach Jimmy Lee Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong In collaboration with the International Institute for Software Technology UNU-IIST United Nations University International Istitute for Sofiware Teclmology MSC Seminar (January 30,2012) 1
1 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) How Can Computer Science Help When Your Drinking Water Gets too Salty? Jimmy Lee Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong In collaboration with the International Institute for Software Technology United Nations University MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Controlling Salinity in a Potable Water Supply System Using a Constraint Programming Approach Jimmy Lee Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong In collaboration with the International Institute for Software Technology United Nations University

Outline ·Domain Description Constraint Programming(CP) ·Problem Modelling ·Improvements ·Concluding Remarks MSC Seminar (January 30,2012) Outline ·Domain Description Constraint Programming(CP) 。Problem Modelling 。Improvements 。Concluding Remarks MSC Seminar (January 30,2012) 2
2 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Outline • Domain Description • Constraint Programming (CP) • Problem Modelling • Improvements • Concluding Remarks MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Outline • Domain Description • Constraint Programming (CP) • Problem Modelling • Improvements • Concluding Remarks

Increasing Salinity in Water Salinity is the concentration SOCIO-ECONOMIC of salts in water RIVER INFLOW Decrease of river flow during dry seasons WIND WATER QUALITY Intrusion of sea water TIDE Duration depends on unforeseen factors such as tidal flow and weather conditions MSC Seminar(January 30,2012) The Raw Water System 3
3 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Increasing Salinity in Water • Salinity is the concentration of salts in water • Decrease of river flow during dry seasons • Intrusion of sea water • Duration depends on unforeseen factors such as tidal flow and weather conditions TIDE RIVER INFLOW CURRENT WIND WATER QUALITY SOCIO-ECONOMIC MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) The Raw Water System Pump Station Reservoir C Reservoir E Reservoir B Reservoir A Reservoir D
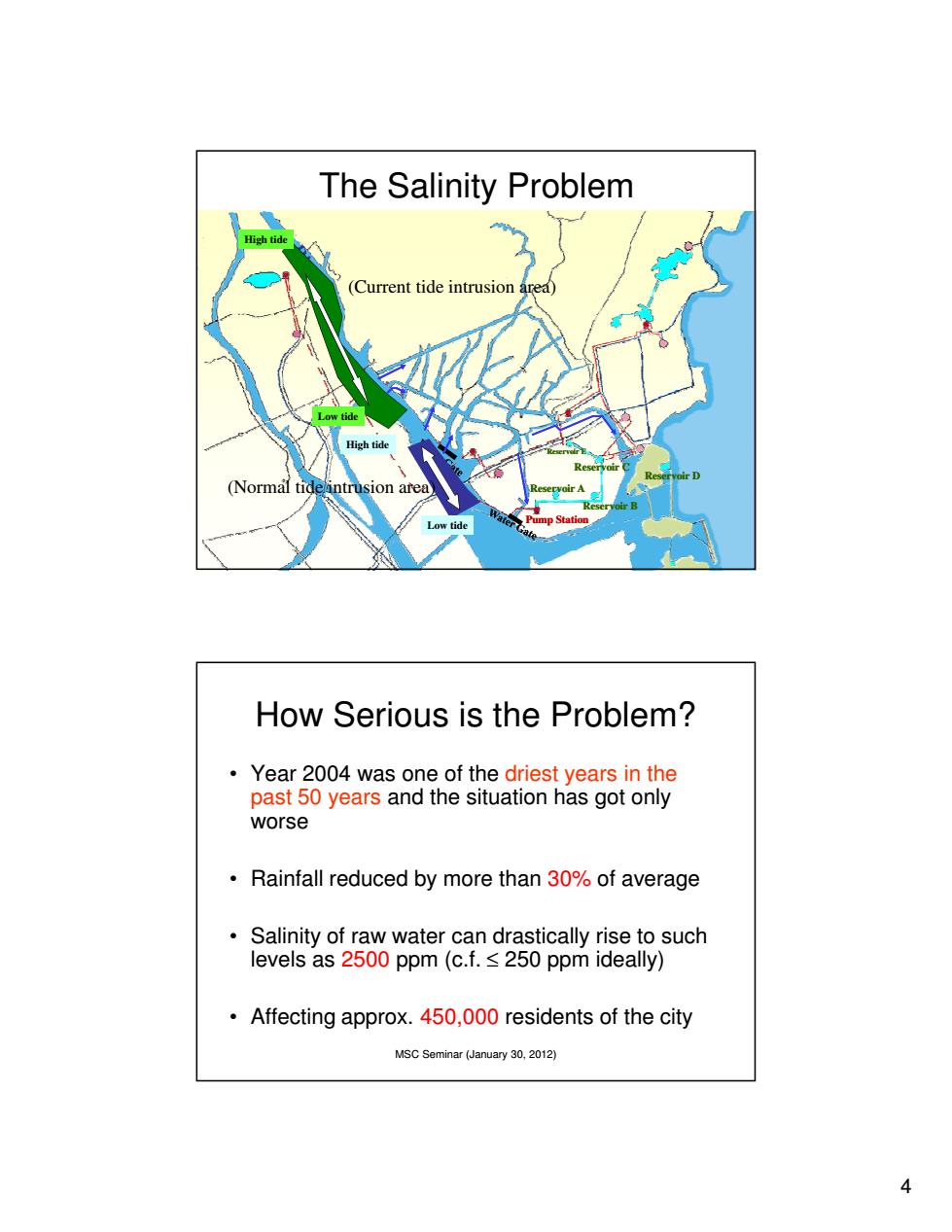
The Salinity Problem High tide (Current tide intrusion ared) Low tide High tide (Normal tide intrusion area) Low tide ump Station How Serious is the Problem? Year 2004 was one of the driest years in the past 50 years and the situation has got only worse Rainfall reduced by more than 30%of average Salinity of raw water can drastically rise to such levels as 2500 ppm(c.f.250 ppm ideally) Affecting approx.450,000 residents of the city MSC Seminar(January 30,2012) 4
4 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Pump Station Reservoir C Reservoir E Reservoir B Reservoir A Reservoir D High tide Low tide (Normal tide intrusion area) Low tide High tide (Current tide intrusion area) The Salinity Problem MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) How Serious is the Problem? • Year 2004 was one of the driest years in the past 50 years and the situation has got only worse • Rainfall reduced by more than 30% of average • Salinity of raw water can drastically rise to such levels as 2500 ppm (c.f. ≤ 250 ppm ideally) • Affecting approx. 450,000 residents of the city

Consequence of Salinity The salinity is more a matter of taste (increased content of chloride)than health while it is less than 2000 ppm Salinity level Taste 200-300ppm Very slight saline taste >300-600ppm Noticeable discomfort in taste >600-800ppm Increasing discomfort in taste >800-1000ppm Very strong discomfort in taste >1000-2000ppm Extremely strong discomfort in taste MSC Seminar (January 30,2012) W.H.O.Guidelines Average dietary intake of chloride for human -Ranging from 6 g/day to 12 g/day The consequence is that daily intake of salt from water is usually less than 5%to 10%of total intake from foods No evidence on health effect of prolonged intake of large amounts of chloride in diet -Except in the special case of impaired sodium chloride metabolism,e.g.in congestive heart failure MSC Seminar (January 30,2012) 5
5 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Consequence of Salinity • The salinity is more a matter of taste (increased content of chloride) than health while it is less than 2000 ppm Salinity level Taste 200 - 300 ppm Very slight saline taste >300 - 600 ppm Noticeable discomfort in taste >600 - 800 ppm Increasing discomfort in taste >800 - 1000 ppm Very strong discomfort in taste >1000 - 2000 ppm Extremely strong discomfort in taste MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) W.H.O. Guidelines • Average dietary intake of chloride for human – Ranging from 6 g/day to 12 g/day • The consequence is that daily intake of salt from water is usually less than 5% to 10% of total intake from foods • No evidence on health effect of prolonged intake of large amounts of chloride in diet – Except in the special case of impaired sodium chloride metabolism, e.g. in congestive heart failure

Why not Supply Restriction? ·No health risk Restriction may cause sanitary problem with reduction on people hygiene May increase water duration in pipes,flush some particles,create vacuuming and potentially lead to bacteriological contamination May affect the overall economy of the city May damage International Image of the city MSC Seminar (January 30,2012) Tackling the Problem On the technical/engineering level -Improved monitoring and pumping system -Preparation before the crisis:top-up of reservoirs Leak detection to reduce water loss Technical communication and coordination with related partners when the crisis started A software to optimize the logistical operations, so as to forecast and control the salinity of potable water below a desirable level MSC Seminar (January 30,2012) 6
6 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) • No health risk • Restriction may cause sanitary problem with reduction on people hygiene • May increase water duration in pipes, flush some particles, create vacuuming and potentially lead to bacteriological contamination • May affect the overall economy of the city • May damage International Image of the city Why not Supply Restriction? MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Tackling the Problem • On the technical/engineering level – Improved monitoring and pumping system – Preparation before the crisis: top-up of reservoirs – Leak detection to reduce water loss • Technical communication and coordination with related partners when the crisis started • A software to optimize the logistical operations, so as to forecast and control the salinity of potable water below a desirable level
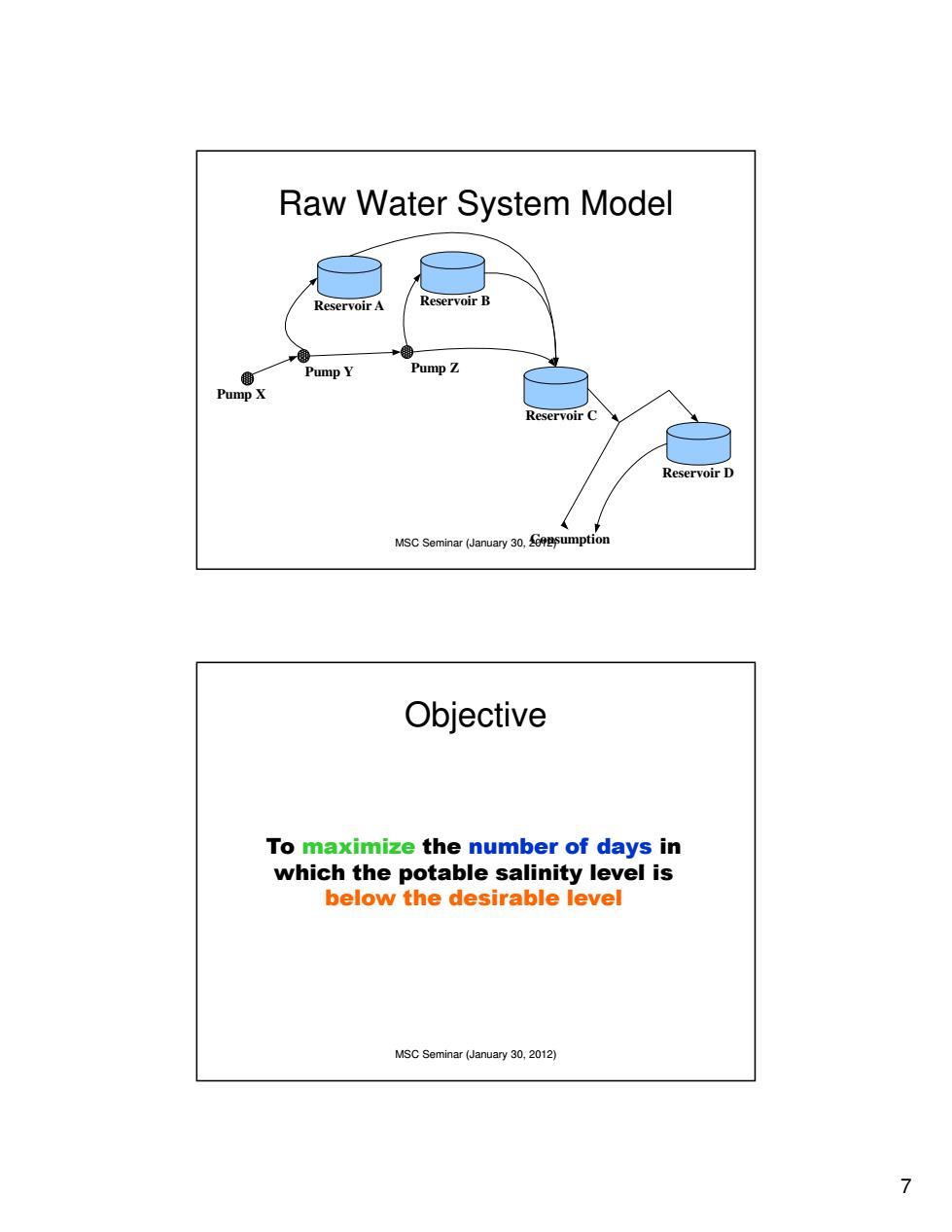
Raw Water System Model Reservoir A Reservoir B PumpY Pump Z PumpX Reservoir C Reservoir D MSC Seminar (January 30,sumption Objective To maximize the number of days in which the potable salinity level is below the desirable level MSC Seminar(January 30,2012) 7
7 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Raw Water System Model Pump X Pump Y Pump Z Reservoir A Reservoir B Reservoir C Reservoir D Consumption MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Objective To maximize the number of days in which the potable salinity level is below the desirable level
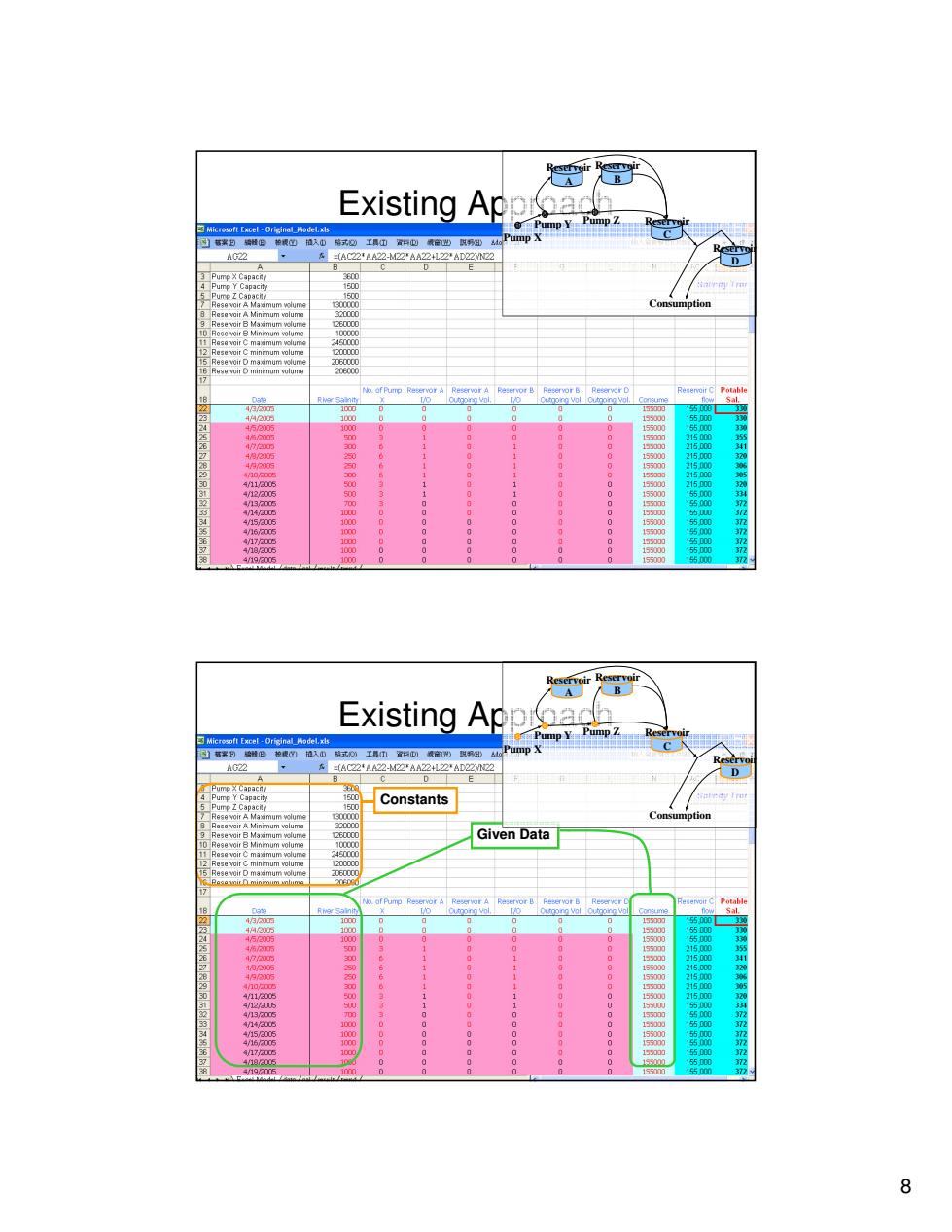
Existing Appac Microsoft Excel-Original_Model.xls Pump Y Pump子fd 福案由培情田轴根心植入山棉式边工具①置山载官出以易出从 AG22 =(AC22*AA22-M22AA22+122'AD22N2☑ D Pump X Capacity mp Consumption A Minimum yalume 2000 3 Reservoir B Maximum wolume 1260000 Reservoir B Minimum volume 206000 15500 82348878908234678 4500 15500 500 0 15500 215000 11 15500 21500 411 666333000000 110 0000 00000 1110000000 40400000000 9000000000000 2150 55 4/18/20 15500 372 419a005 1000 155000 5 372 Reservoir Existing Ap Microsoft Excel-Original Model.xls Pump AG22 =(AC22*A422-M22AA22+L22AD2222 D Constants Reservoir A Maximum wolume 130000 Reservair A Minimum volume 300 um Given Data 1200000 5 Reservoir D maximum wolume 20600 430国 1000 150 4420 1000 15500 23456789010345678 1 /11 415/2a00 66603300000 11000 00000 11000000 00000000000000 000000000000 15 0 5 8
8 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Existing Approach Pump X Pump Y Pump Z Reservoir A Reservoir B Reservoir C Reservoir D Consumption MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Constants Given Data Existing Approach Pump X Pump Y Pump Z Reservoir A Reservoir B Reservoir C Reservoir D Consumption
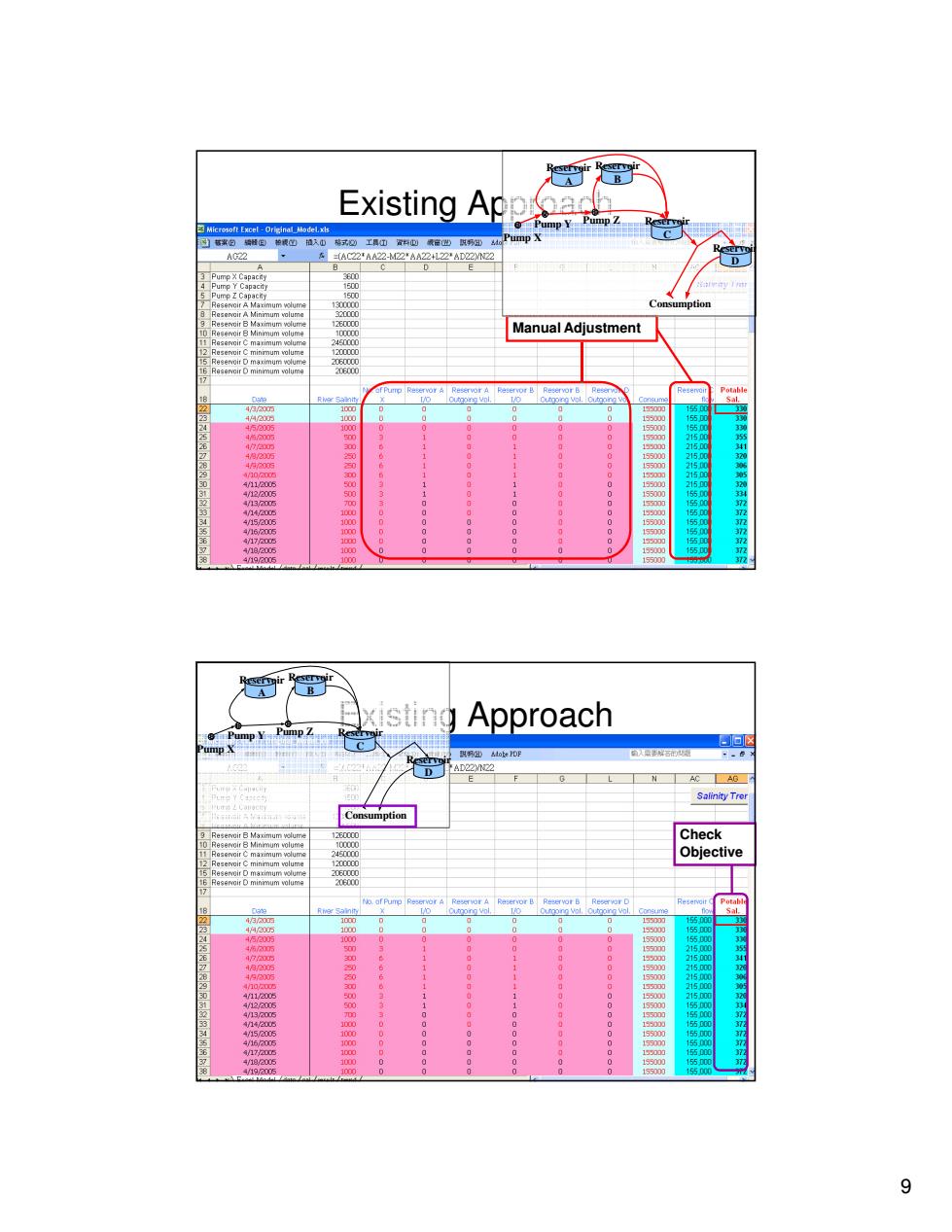
Existing Appa Microsoft Excel-Original_Model.xls ump Y 福案由培情田轴根心植入山棉式边工具①置山载官出以易出从 AG22 =(AC22*AA22-M22AA22+122'AD22N2☑ D Pump X Capacity mp Consumption A Minimum yalume 3 Reservoir B Maximum wolume 1260000 Reservoir B Minimum volume Manual Adjustment 206000 82348878908234678 4500 11 1550 230 411 412 11 1 6666330008 000 000000 11100000 00000000000000 0000000000000 4/18/20 5 372 4/19/a005 1000 15500 B xisting Approach 回☒ AC AG Salinity Trer Consumption mum Check Objective 1200000 5 Reservoir D maximum wolume 20EU000 6 Regervair D minimum volume 430 1000 55 4420 1000 15500 15500 2348678901034578 4/10 1 /11 000 /2005 110000 1 +666333000006 00000 11000000 90000000000000 9000000000000 0 9
9 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Manual Adjustment Existing Approach Pump X Pump Y Pump Z Reservoir A Reservoir B Reservoir C Reservoir D Consumption MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Existing Approach Check Objective Pump X Pump Y Pump Z Reservoir A Reservoir B Reservoir C Reservoir D Consumption
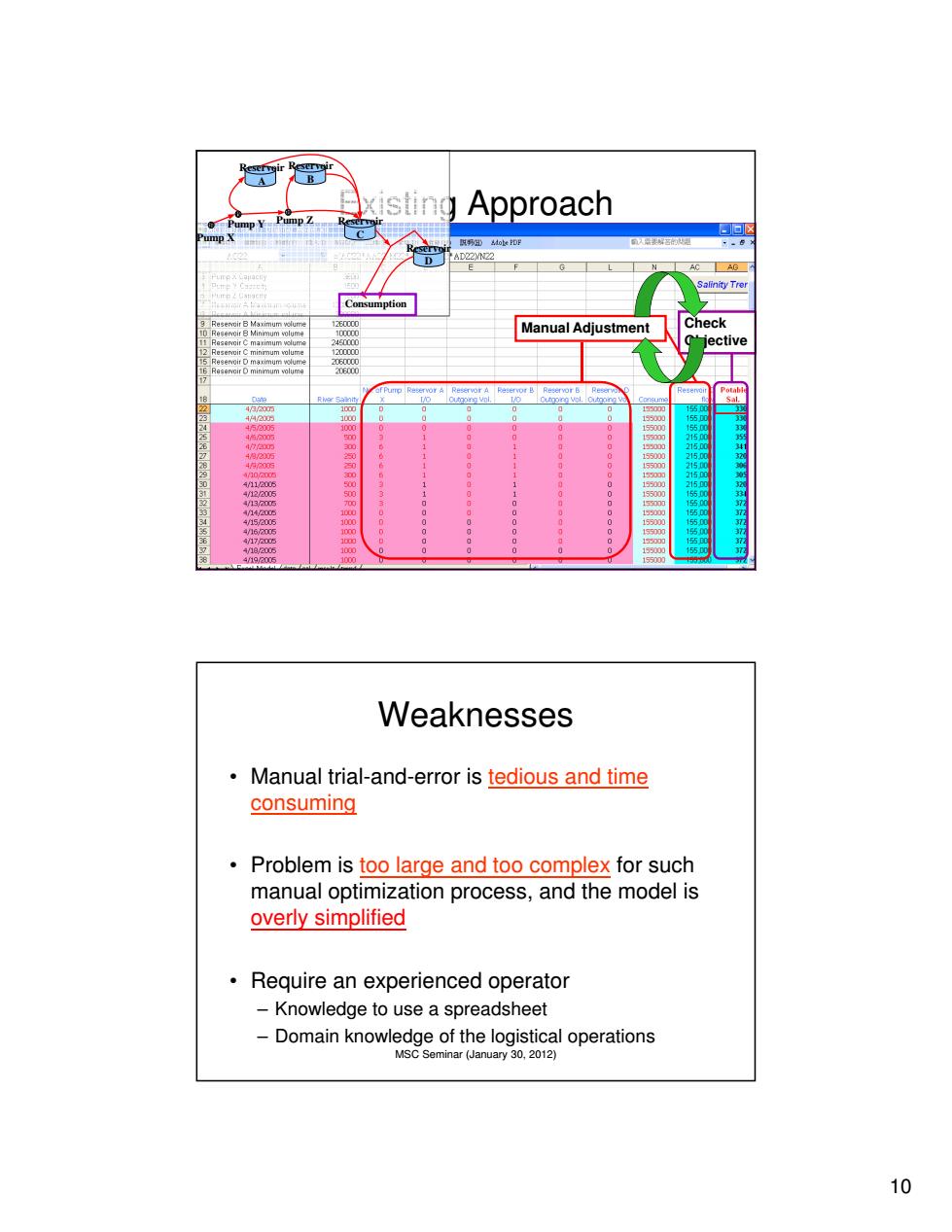
xisting Approach 照易知oe扣明 - D G AC AG Salinity Trer Consumption Reservoir B Maximum wolume 12E0000 Check Reservoir B Minimum volume Manual Adjustment ective olume 206000 45/005 100 0 0 2150 4887890023467 2150 4/112005 1 4/12,2005 0 3300 00000 0000000000000 900000000000 1550 00o 000 55 419a005 1000 15500 Weaknesses Manual trial-and-error is tedious and time consuming Problem is too large and too complex for such manual optimization process,and the model is overly simplified Require an experienced operator -Knowledge to use a spreadsheet Domain knowledge of the logistical operations MSC Seminar (January 30,2012) 10
10 MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Check Objective Manual Adjustment Existing Approach Pump X Pump Y Pump Z Reservoir A Reservoir B Reservoir C Reservoir D Consumption MSC Seminar (January 30, 2012) Weaknesses • Manual trial-and-error is tedious and time consuming • Problem is too large and too complex for such manual optimization process, and the model is overly simplified • Require an experienced operator – Knowledge to use a spreadsheet – Domain knowledge of the logistical operations