
CSCI 3160 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Tutorial 5 Chengyu Lin
CSCI 3160 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Tutorial 5 Chengyu Lin

Outline 。Dynamic programming -Chain Matrix Multiplication Longest increasing subsequence (LIS) Goal:help understand the lecture materials further
Outline • Dynamic programming – Chain Matrix Multiplication – Longest increasing subsequence (LIS) • Goal: help understand the lecture materials further
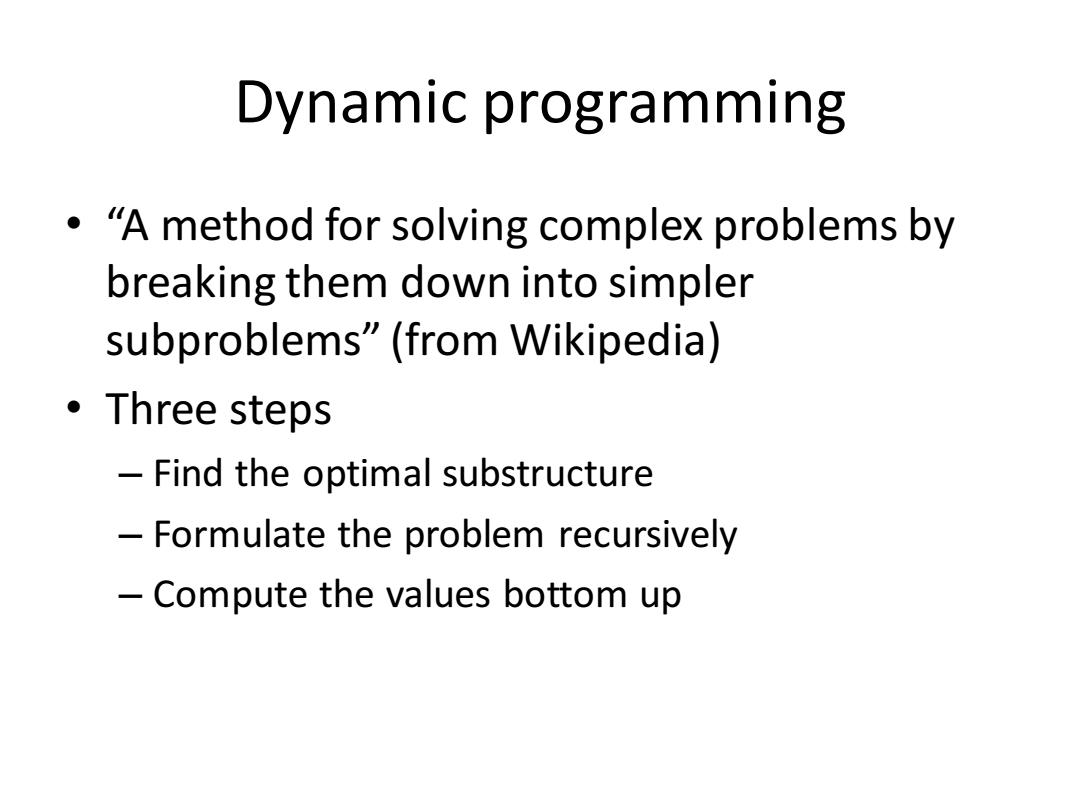
Dynamic programming "A method for solving complex problems by breaking them down into simpler subproblems"(from Wikipedia) ·Three steps Find the optimal substructure Formulate the problem recursively Compute the values bottom up
Dynamic programming • “A method for solving complex problems by breaking them down into simpler subproblems” (from Wikipedia) • Three steps – Find the optimal substructure – Formulate the problem recursively – Compute the values bottom up

Chain Matrix Multiplication You want to multiply N matrices A1,...,A Suppose the cost of multiplying an m-by-n matrix with an n-by-/matrix is mn/. The product is an m-by-/matrix What is the minimum total cost to get the product of the N matrices P=A1...AN?
Chain Matrix Multiplication • You want to multiply N matrices A1 , …, AN • Suppose the cost of multiplying an m-by-n matrix with an n-by-l matrix is mnl. – The product is an m-by-l matrix • What is the minimum total cost to get the product of the N matrices P = A1…AN ?
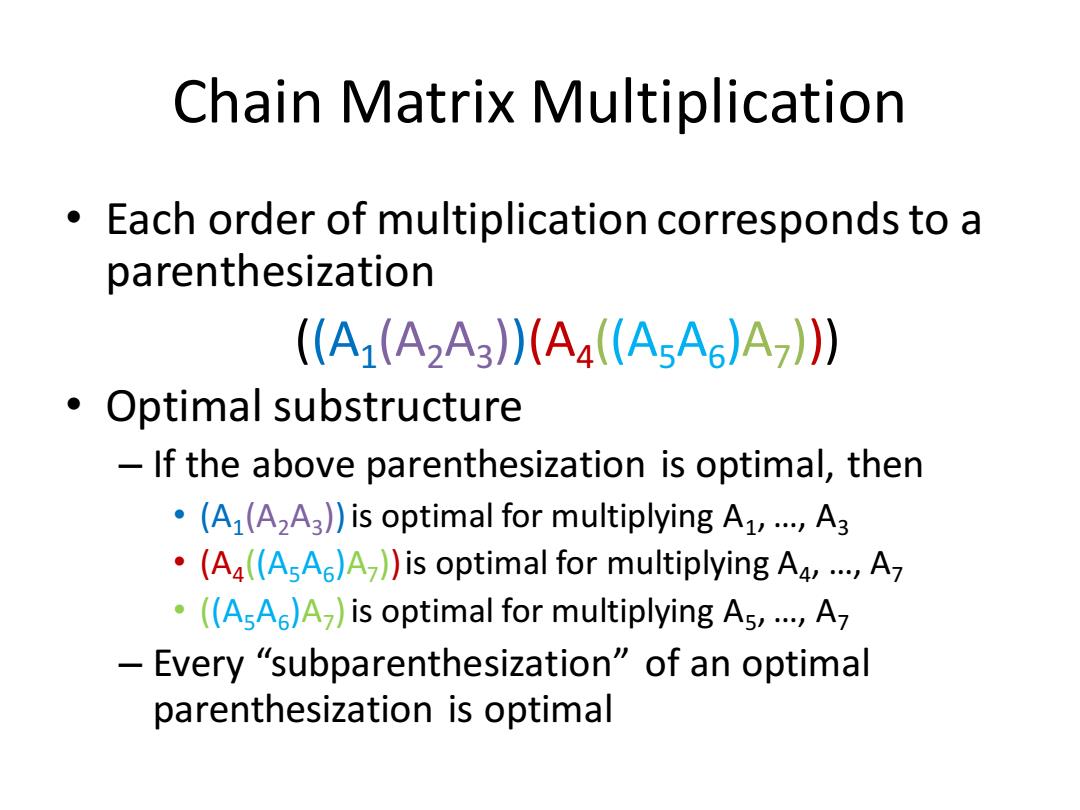
Chain Matrix Multiplication Each order of multiplication corresponds to a parenthesization (A1(A2A3(A4(AsA6)A7) Optimal substructure If the above parenthesization is optimal,then .(A(A2A3))is optimal for multiplying A1,...A3 .(A((AsA )A))is optimal for multiplying Aa,...,A .((AsA)A)is optimal for multiplying As,...,A -Every“"subparenthesization”of an optimal parenthesization is optimal
Chain Matrix Multiplication • Each order of multiplication corresponds to a parenthesization ((A1 (A2A3 ))(A4 ((A5A6 )A7 ))) • Optimal substructure – If the above parenthesization is optimal, then • (A1 (A2A3 )) is optimal for multiplying A1 , …, A3 • (A4 ((A5A6 )A7 )) is optimal for multiplying A4 , …, A7 • ((A5A6 )A7 )is optimal for multiplying A5 , …, A7 – Every “subparenthesization” of an optimal parenthesization is optimal
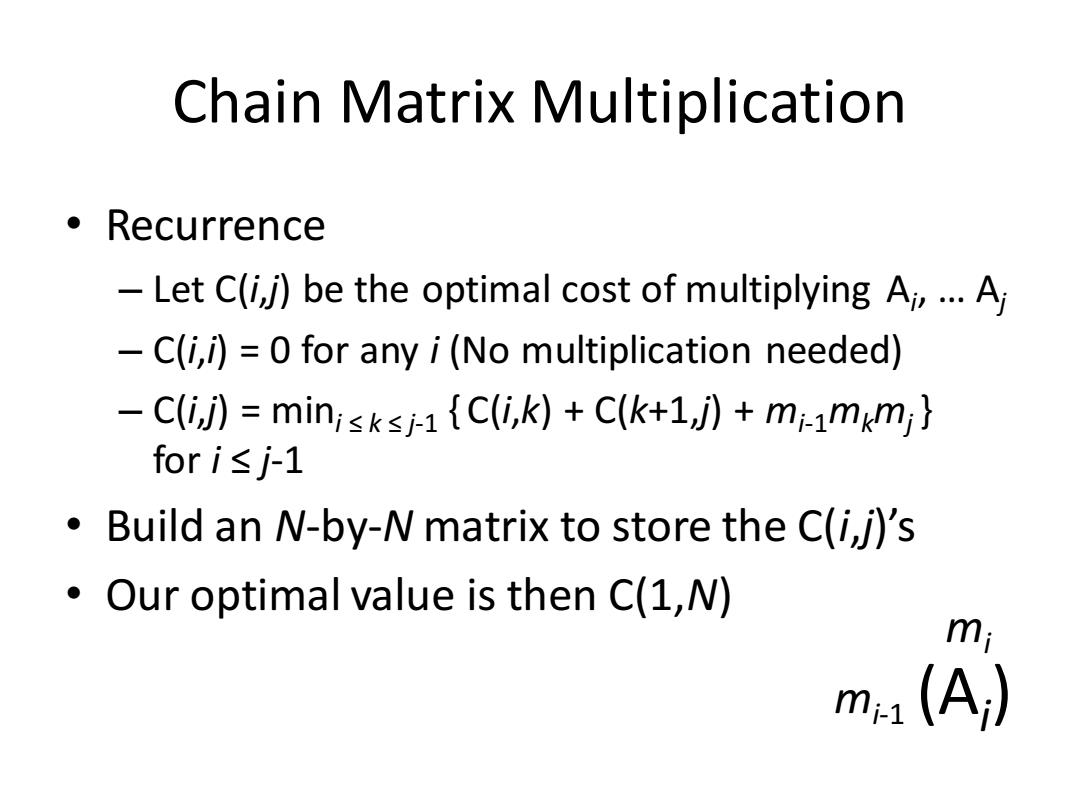
Chain Matrix Multiplication ·Recurrence -Let C(i,j)be the optimal cost of multiplying Ai,...A -C(i,i)=0 for any i(No multiplication needed) -C(i,j)minisksj-1 {C(i,k)+C(k+1,j)+mi-1mkmj} fori≤j-1 Build an N-by-N matrix to store the C(i,j)'s Our optimal value is then C(1,N) mi m1(A)
Chain Matrix Multiplication • Recurrence – Let C(i,j) be the optimal cost of multiplying Ai , … Aj – C(i,i) = 0 for any i (No multiplication needed) – C(i,j) = mini ≤ k ≤ j-1 { C(i,k) + C(k+1,j) + mi-1mkmj } for i ≤ j-1 • Build an N-by-N matrix to store the C(i,j)’s • Our optimal value is then C(1,N) (Ai ) mi mi-1

Example Let A1 be a 5-by-20 matrix,A,be a 20-by-10 matrix,Aa be a 10-by-3 matrix,Aa be a 3-by-2 matrix -m0=5,m1=20,m2=10,m3=3,m4=2 i八j 1 2 3 4 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0
Example • Let A1 be a 5-by-20 matrix, A2 be a 20-by-10 matrix, A3 be a 10-by-3 matrix, A4 be a 3-by-2 matrix – m0 = 5, m1 = 20, m2 = 10, m3 = 3, m4 = 2 i \ j 1 2 3 4 1 0 2 - 0 3 - - 0 4 - - - 0

Example 。m0=5,m1=20,m2=10,m3=3,m4=2 ● C(1,2)=C(1,1)+C(2,2)+mom1m2=5·20·10 =1000 C(2,3)=,C(3,4)=· i八j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 2 0 3 0 4 0
Example • m0 = 5, m1 = 20, m2 = 10, m3 = 3, m4 = 2 • C(1,2) = C(1,1) + C(2,2) + m0m1m2 = 5 · 20 · 10 = 1000 • C(2,3) = , C(3,4) = . i \ j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 2 - 0 3 - - 0 4 - - - 0
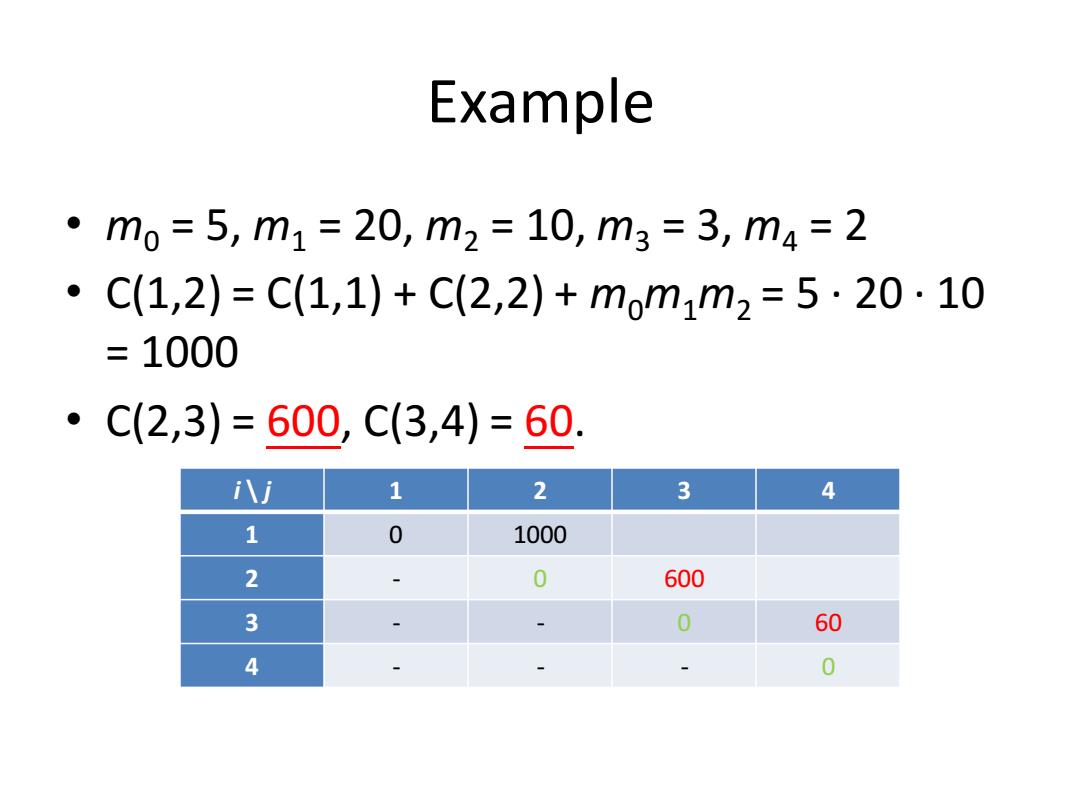
Example 。m0=5,m1=20,m2=10,m3=3,m4=2 0 C(1,2)=C(1,1)+C(2,2)+mom1m2=5·20·10 =1000 C(2,3)=600,C(3,4)=60. i八j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 2 0 600 3 0 60 4 0
Example • m0 = 5, m1 = 20, m2 = 10, m3 = 3, m4 = 2 • C(1,2) = C(1,1) + C(2,2) + m0m1m2 = 5 · 20 · 10 = 1000 • C(2,3) = 600, C(3,4) = 60. i \ j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 2 - 0 600 3 - - 0 60 4 - - - 0

Example 。m0=5,m1=20,m2=10,m3=3,m4=2 ·C(1,3)=min{C(1,1)+C(2,3)+mom1m3 C(1,2)+C(3,3)+mom2m3} =min{0+600+300,1000+0+150}=900 i八j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 900 2 0 600 3 0 60 4 0
Example • m0 = 5, m1 = 20, m2 = 10, m3 = 3, m4 = 2 • C(1,3) = min { C(1,1) + C(2,3) + m0m1m3 , C(1,2) + C(3,3) + m0m2m3 } = min { 0 + 600 + 300, 1000 + 0 + 150 } = 900 i \ j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 900 2 - 0 600 3 - - 0 60 4 - - - 0