
CSCI 3160 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Chengyu Lin
CSCI 3160 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Chengyu Lin
Approximation algorithms 。Motivation Some (optimization)problems are very hard Unlikely to have efficient polynomial-time algorithms Approximation algorithms -Algorithms to find approximate solutions to optimization problems
Approximation algorithms • Motivation – Some (optimization) problems are very hard – Unlikely to have efficient polynomial-time algorithms • Approximation algorithms – Algorithms to find approximate solutions to optimization problems

Optimization Many problems are actually optimization problems i.e-the task can be naturally rephrased as finding a maximal/minimal solution For example:Vertex Cover problem
Optimization • Many problems are actually optimization problems • i.e – the task can be naturally rephrased as finding a maximal/minimalsolution • For example: Vertex Cover problem
Approximation Algorithm An algorithm that returns near-optimal solutions in polynomial time Approximation Ratio p(n): Define:C*as a optimal solution and C is the solution produced by the approximation algorithm -max (C/C*,C*/C)<=p(n) -Maximization problem:0<C<=C*,thus C*/C shows that C*is larger than c by p(n) Minimization problem:0<C*<=C,thus C/C* shows that C is larger than C*by p(n)
Approximation Algorithm • An algorithm that returns near-optimal solutions in polynomial time • Approximation Ratio ρ(n): – Define: C* as a optimal solution and C is the solution produced by the approximation algorithm – max (C/C*, C*/C) <= ρ(n) – Maximization problem: 0 < C <= C*, thus C*/C shows that C* is larger than C by ρ(n) – Minimization problem: 0 < C* <= C, thus C/C* shows that C is larger than C* by ρ(n)
Techniques A variety of techniques to design and analyze many approximation algorithms for computationally hard problems: Combinatorial algorithms Linear Programming based algorithms Semi-definite Programming based algorithms
Techniques • A variety of techniques to design and analyze many approximation algorithms for computationally hard problems: – Combinatorial algorithms – Linear Programming based algorithms – Semi-definite Programming based algorithms

Vertex Cover 。Definition Given an undirected graph G=V,E),a subset 'V is called a vertex cover of G iff for every edge eeE,e has at least one endpoint incident at V 。Example Vertex Cover
Vertex Cover • Definition – Given an undirected graph 𝐺 = (𝑉, 𝐸),a subset 𝑉′ ⊆ 𝑉 is called a vertex cover of 𝐺 iff for every edge 𝑒 ∈ 𝐸, 𝑒 has at least one endpoint incident at 𝑉′ • Example

Vertex Cover Problem ●Definition: Given an undirected graph G=(V,E),find a vertex cover with minimum size (has the least number of vertices) -This is sometimes called cardinality vertex cover More generalization: Given an undirected graph G=(V,E),and a cost function on vertices c:V>Q+ -Find a minimum cost vertex cover
Vertex Cover Problem • Definition: – Given an undirected graph G=(V,E), find a vertex cover with minimum size (has the least number of vertices) – This is sometimes called cardinality vertex cover • More generalization: – Given an undirected graph G=(V,E), and a cost function on vertices c: V → Q+ – Find a minimum cost vertex cover
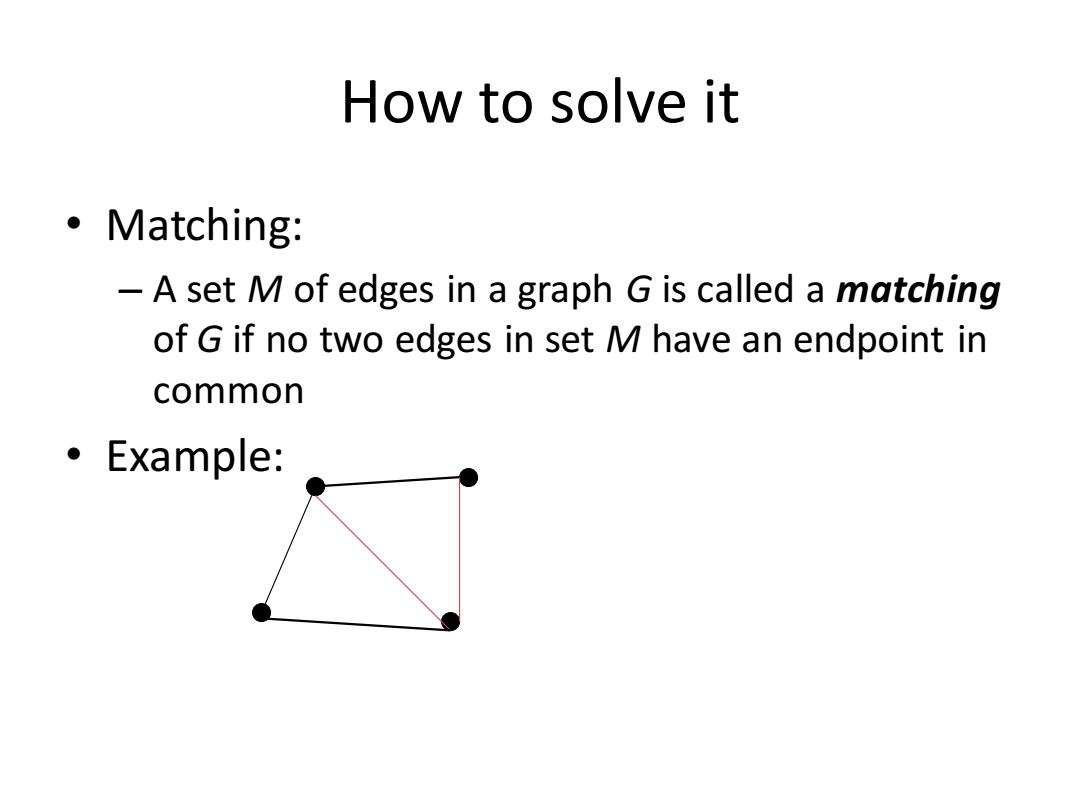
How to solve it 。Matching: -A set M of edges in a graph G is called a matching of G if no two edges in set M have an endpoint in common 。Example:
How to solve it • Matching: – A set M of edges in a graph G is called a matching of G if no two edges in set M have an endpoint in common • Example:

How to solve it(cont. 。Maximum Matching: -A matching of G with the greatest number of edges 。Maximal Matching: -A matching which is not contained in any larger matching Note:Any maximum matching is certainly maximal,but not the reverse
How to solve it(cont.) • Maximum Matching: – A matching of G with the greatest number of edges • Maximal Matching: – A matching which is not contained in any larger matching • Note: Any maximum matching is certainly maximal, but not the reverse
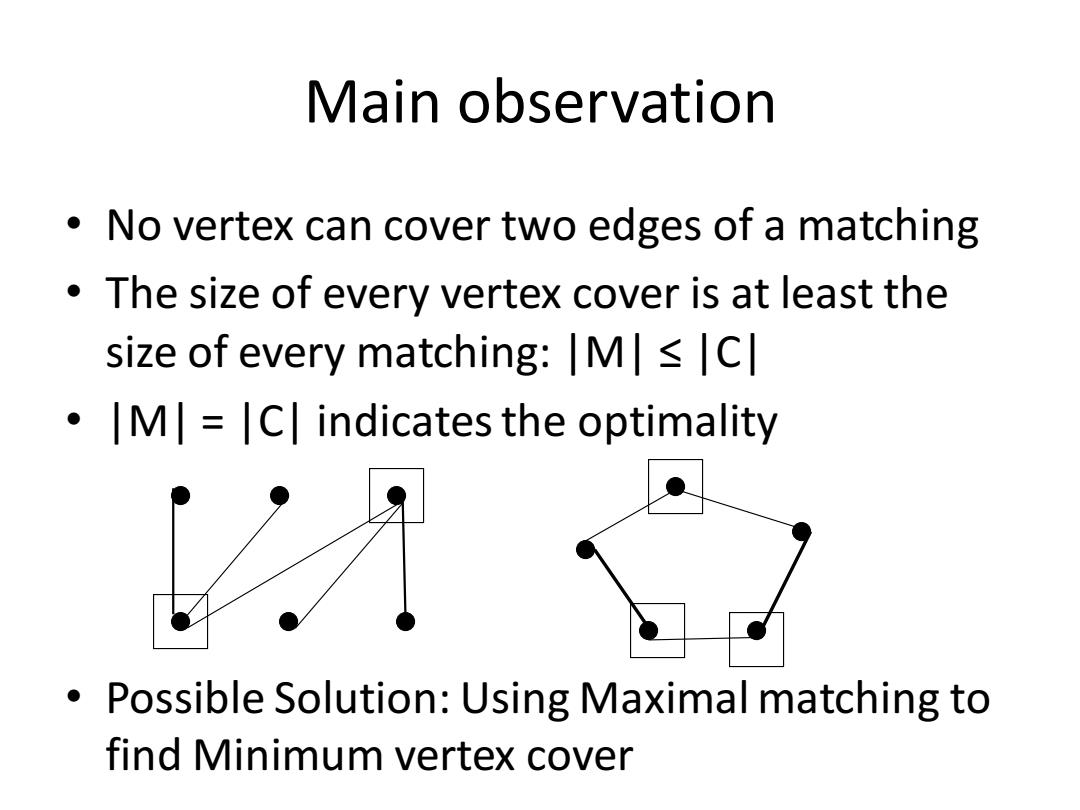
Main observation No vertex can cover two edges of a matching The size of every vertex cover is at least the size of every matching:M<C .M=C indicates the optimality Possible Solution:Using Maximal matching to find Minimum vertex cover
Main observation • No vertex can cover two edges of a matching • The size of every vertex cover is at least the size of every matching: |M| ≤ |C| • |M| = |C| indicates the optimality • Possible Solution: Using Maximal matching to find Minimum vertex cover