《Anatomical Physiology,》-Anatomy课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 Anatomical Physiology 英文名称 -Human Anatomy part 课程代码 PHAR1136 课程性质 大类基础课程 授课对象 药学全英文班 学 分 4.0 学 时 45(39+6) 主讲教师 王悦 修订日期 2021年6月16日 指定教材 吕广明等编著,《人体解剖学》,科学出版社,2016年,第2版 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: 通过学习人体解剖结构等基本医学知识,通过老师的讲授和实验室模型多重感官刺激加强记忆,让学生懂得医学知识的真正意义,并努力通过 学生和老师的共同努力树立正确的人生观、事业观、培养真正的科学人才! (二)课程目标: Human anatomy and physiology mainly talk about the structure of human body.It is characterized by the systematically describe the various organs in the human body on the morphological structure and the main functions,so that students would have a basic understanding of the human body,to lay the foundation for other basic courses.Therefore,it is compulsory and requi red courses for Pharmacy students. (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系
《Anatomical Physiology》-Anatomy 课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Anatomical Physiology -Human Anatomy part 课程代码 PHAR1136 课程性质 大类基础课程 授课对象 药学全英文班 学 分 4.0 学 时 45(39+6) 主讲教师 王悦 修订日期 2021 年 6 月 16 日 指定教材 吕广明等编著,《人体解剖学》,科学出版社,2016 年,第 2 版 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: 通过学习人体解剖结构等基本医学知识,通过老师的讲授和实验室模型多重感官刺激加强记忆,让学生懂得医学知识的真正意义,并努力通过 学生和老师的共同努力树立正确的人生观、事业观、培养真正的科学人才! (二)课程目标: Human anatomy and physiology mainly talk about the structure of human body. It is characterized by the systematically describe the various organs in the human body on the morphological structure and the main functions, so that students would have a basic understanding of the human body, to lay the foundation for other basic courses. Therefore, it is compulsory and requi red courses for Pharmacy students. (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系
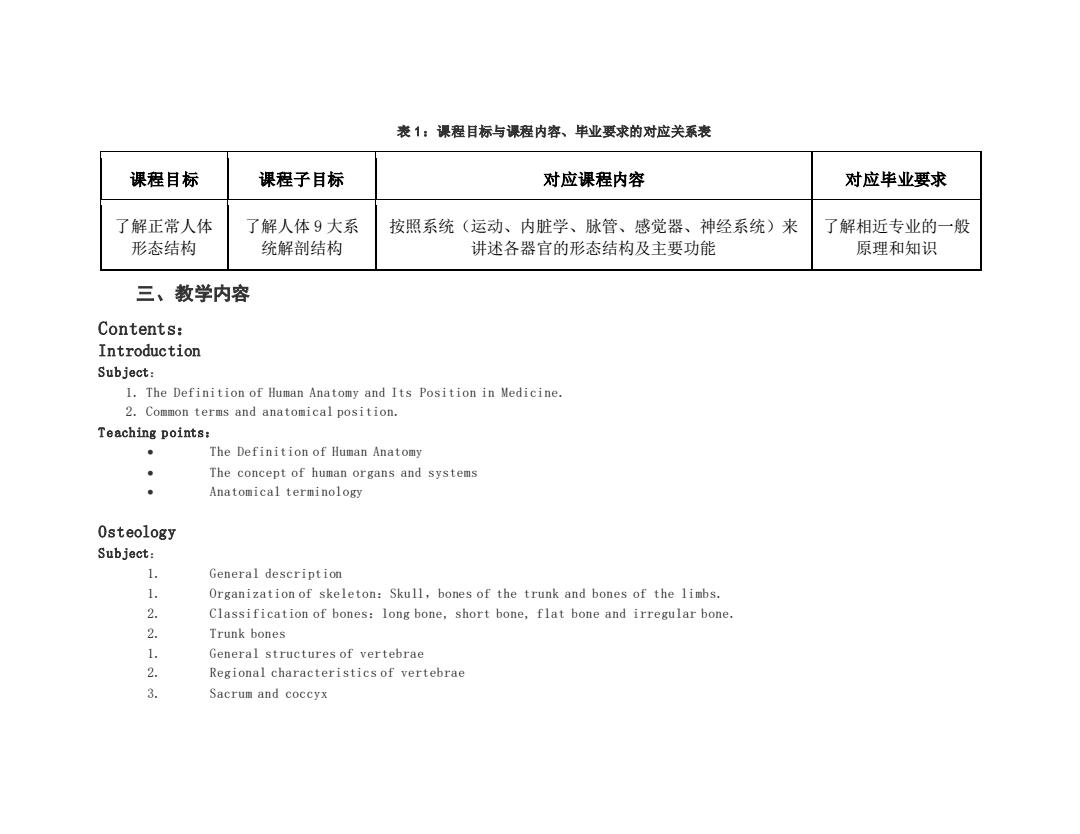
表1:课程目标与课程内容、单业要求的对应关系表 课程目标 课程子目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 了解正常人体 了解人体9大系 按照系统(运动、内脏学、脉管、感觉器、神经系统)来 了解相近专业的一般 形态结构 统解剖结构 讲述各器官的形态结构及主要功能 原理和知识 三、教学内容 Contents: Introduction Subject: 1.The Definition of Human Anatomy and Its Position in Medicine. 2.Common terms and anatomical position. Teaching points: The Definition of Human Anatomy The concept of human organs and systems Anatomical terminology Osteology Subject: 1. General description 1. Organization of skeleton:Skull,bones of the trunk and bones of the limbs. 2. Classification of bones:long bone,short bone,flat bone and irregular bone. 2. Trunk bones 1. General structures of vertebrae 2. Regional characteristics of vertebrae 3. Sacrum and coccyx
表 1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 课程目标 课程子目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 了解正常人体 形态结构 了解人体 9 大系 统解剖结构 按照系统(运动、内脏学、脉管、感觉器、神经系统)来 讲述各器官的形态结构及主要功能 了解相近专业的一般 原理和知识 三、教学内容 Contents: Introduction S u bject: 1. The Definition of Human Anatomy and Its Position in Medicine. 2. Common terms and anatomical position. T e aching p oints: • The Definition of Human Anatomy • The concept of human organs and systems • Anatomical terminology Osteology S u bject: 1. General description 1. Organization of skeleton:Skull,bones of the trunk and bones of the limbs. 2. Classification of bones:long bone, short bone, flat bone and irregular bone. 2. Trunk bones 1. General structures of vertebrae 2. Regional characteristics of vertebrae 3. Sacrum and coccyx

4 Ribs:costal bone and costal cartilage 5. Sternum 3. Bones of the limbs Bones of upper limbs:pectoral girdle bones and bones of free upper limbs 2. Bones of lower limbs:pelvic girdle bones and bones of free lower limbs 4. Bones of skull 1. Cranial bones 2. Facial skeleton 3. Whole views of the skull:superior and posterior view of skull;internal and external views of base of the skull. Teaching points: Morphological classification of bones Composition of trunk bones The general morphology and the characteristics of the vertebrae Three parts of the sternum and the concept of the sternal angle The division and composition of upper and lower limb bone the position and morphologic features of clavicle,scapula,humerus,radius,hip bones,femur,tibia,fibula The division and composition of skull bones The tag architecture of internal views of base of the skull and the concept of pterion Arthrology Subject: 1. General description 1. Fibrous joint 2. Cartilaginous joint 3. Synovial joint:general structures,assisting structures,types of the movements 2. Articulations of the trunk 1. Joints of the vertebrae:joints of the vertebral body/vertebral arch 2. The different aspects and movements of Vertebral column 3. The composition of thoracic cage and movements
4. Ribs: costal bone and costal cartilage 5. Sternum 3. Bones of the limbs 1. Bones of upper limbs: pectoral girdle bones and bones of free upper limbs 2. Bones of lower limbs: pelvic girdle bones and bones of free lower limbs 4. Bones of skull 1. Cranial bones 2. Facial skeleton 3. Whole views of the skull: superior and posterior view of skull; internal and external views of base of the skull. T e aching p oints: • Morphological classification of bones • Composition of trunk bones • The general morphology and the characteristics of the vertebrae • Three parts of the sternum and the concept of the sternal angle • The division and composition of upper and lower limb bone • the position and morphologic features of clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, hip bones, femur, tibia, fibula • The division and composition of skull bones • The tag architecture of internal views of base of the skull and the concept of pterion Arthrology S u bject: 1. General description 1. Fibrous joint 2. Cartilaginous joint 3. Synovial joint:general structures, assisting structures, types of the movements 2. Articulations of the trunk 1. Joints of the vertebrae: joints of the vertebral body/vertebral arch 2. The different aspects and movements of Vertebral column 3. The composition of thoracic cage and movements

3. Articulations of the limbs 1. Articulations of upper limbs:pectoral girdle and free upper limbs articulations 2. Articulations of lower limbs:pelvic girdle and free lower limbs articulations 4. articulations of the skull Teaching points: general and assisting Structures of Synovial joint The structure and function of the intervertebral disc The composition of vertebral column (physiological curvatures)and thoracic cage The composition of articulations (shoulder joint,elbow joint,hip joint,knee joint and ankle joint)with their movements Myology Subject: 1. General description 1. Morphology and structure of skeletal muscles 2. The origin,insertion and the action of the muscles 2. Muscles of the trunk 1. Muscles of the back:the superficial and deep layers. 2. Muscles of the thorax 3. Diaphragm 4. Muscles of the abdomen:anterolateral group 3. Muscles of the head and neck 1. Muscles of the head:facial muscles;masticatory muscles 2. Muscles of the neck:superficial group,deep group:suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles 4. Muscles of upper limbs 1. Pectoral girdle Muscles 2. Muscles of brachium:anterior group,posterior group 3. Muscles of forearm:anterior group,posterior group 4. Muscles of hand:Lateral group (thenar muscles),Medial group (hypothenar muscles)and Intermediate group
3. Articulations of the limbs 1. Articulations of upper limbs: pectoral girdle and free upper limbs articulations 2. Articulations of lower limbs: pelvic girdle and free lower limbs articulations 4. articulations of the skull T e aching p oints: • general and assisting Structures of Synovial joint • The structure and function of the intervertebral disc • The composition of vertebral column (physiological curvatures) and thoracic cage • The composition of articulations (shoulder joint, elbow joint, hip joint, knee joint and ankle joint) with their movements M y ology S u bject: 1. General description 1. Morphology and structure of skeletal muscles 2. The origin, insertion and the action of the muscles 2. Muscles of the trunk 1. Muscles of the back: the superficial and deep layers. 2. Muscles of the thorax 3. Diaphragm 4. Muscles of the abdomen: anterolateral group 3. Muscles of the head and neck 1. Muscles of the head: facial muscles; masticatory muscles 2. Muscles of the neck: superficial group, deep group; suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles 4. Muscles of upper limbs 1. Pectoral girdle Muscles 2. Muscles of brachium: anterior group, posterior group 3. Muscles of forearm: anterior group, posterior group 4. Muscles of hand: Lateral group (thenar muscles), Medial group (hypothenar muscles) and Intermediate group

5.muscles of the lower limbs 1. Muscles of the hip:Anterior group,Posterior group 2. Muscles of the thigh:Anterior group,Medial group and Posterior group 3. Muscles of the calf:Anterior group,Lateral group and Posterior group Teaching points: Morphology and structure of skeletal muscles The component parts of trunk muscles The effect of trapezius,latissimus dorsi and erector spinae The effect of pectoralis major,intercostales externi/interni muscles The location,effect and three hiatuses of the diaphragm The name and effect of anterolateral group muscles the component of masticatory muscles The location and effect of sternocleidomastoid:the structure of scalene hiatus The location and effect of deltoid The location and effect of Biceps brachii,triceps The location and effect of Gluteus maximus,quadriceps,calf triceps Digestive System Subject: 1. Digestive tract 1. The mouth:regions of the mouth,lips,cheeks,palate,teeth,tongue and salivary glands 2. Pharynx:the position,form,three portions and the important structures. Esophagus:the position,form and narrows. 4. Stomach:the position,form and parts 5. Small intestine:Duodenum jejunum and ileum 6. Large intestine:Cecum,appendix,colon,rectum and anal canal 2. Digestive gland 1. Liver:the form,position and extrahepatic biliary duct 2. Pancreas
5. muscles of the lower limbs 1. Muscles of the hip: Anterior group, Posterior group 2. Muscles of the thigh: Anterior group, Medial group and Posterior group 3. Muscles of the calf: Anterior group, Lateral group and Posterior group T e aching p oints: • Morphology and structure of skeletal muscles • The component parts of trunk muscles • The effect of trapezius, latissimus dorsi and erector spinae • The effect of pectoralis major, intercostales externi/interni muscles • The location, effect and three hiatuses of the diaphragm • The name and effect of anterolateral group muscles • the component of masticatory muscles • The location and effect of sternocleidomastoid; the structure of scalene hiatus • The location and effect of deltoid • The location and effect of Biceps brachii, triceps • The location and effect of Gluteus maximus, quadriceps, calf triceps Digestive System S u bject: 1. Digestive tract 1. The mouth:regions of the mouth, lips, cheeks, palate, teeth, tongue and salivary glands 2. Pharynx: the position, form, three portions and the important structures. 3. Esophagus: the position, form and narrows. 4. Stomach: the position, form and parts 5. Small intestine: Duodenum jejunum and ileum 6. Large intestine: Cecum, appendix, colon, rectum and anal canal 2. Digestive gland 1. Liver: the form, position and extrahepatic biliary duct 2. Pancreas

Teaching points: The Composition of Digestive System,the partition of upper and lower digestive tract. The morphology of teeth The position and opening of parotid,submandibular and sublingual gland The position,parts and connection of pharynx The position of esophagus,the narrows and their meanings in clinic The position,form and parts of stomach The parts of small intestine,the parts and morphology of duodenum. The parts and morphology of large intestine The position of cecum and appendix;McBurney's point The parts of colon The position and morphology of rectum and anal canal ● The position and form of liver The structure of extrahepatic biliary duct The position and parts of pancreas Respiratory system Subject: 1 Nose 1. External nose 2. Nasal cavity Paranasal Sinuses 2. Larynx 1. Laryngeal cartilage:Thyroid cartilage,cricoid cartilage,epiglottis cartilage,arytenoid cartilage 2. Laryngeal cavity 3. Trachea and bronchi w The position and form of lungs 5. Pleura and mediastinum:the concepts of chest,pleura and pleural cavity:division of parietal pleura;pleural recesses:mediastinum
T e aching p oints: • The Composition of Digestive System, the partition of upper and lower digestive tract. • The morphology of teeth • The position and opening of parotid, submandibular and sublingual gland • The position, parts and connection of pharynx • The position of esophagus, the narrows and their meanings in clinic • The position, form and parts of stomach • The parts of small intestine, the parts and morphology of duodenum. • The parts and morphology of large intestine • The position of cecum and appendix; McBurney’s point • The parts of colon • The position and morphology of rectum and anal canal • The position and form of liver • The structure of extrahepatic biliary duct • The position and parts of pancreas Respiratory system S u bject: 1. Nose 1. External nose 2. Nasal cavity 3. Paranasal Sinuses 2. Larynx 1. Laryngeal cartilage: Thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, epiglottis cartilage, arytenoid cartilage 2. Laryngeal cavity 3. Trachea and bronchi 4. The position and form of lungs 5. Pleura and mediastinum: the concepts of chest, pleura and pleural cavity; division of parietal pleura; pleural recesses; mediastinum

Teaching points: The Composition of respiratory system,the partition of upper and lower respiratory tracts. The position and opening of paranasal sinuses The position and the cartilages framework of larynx:laryngeal cavity The position of trachea,the partition of left and right principal bronchus The position,morphology and shape of lungs The concepts of pleura and pleura cavity The division of pleura and costodiaphragmatic recess Urinary System Subject: Kidneys 1. The position,form and structure of kidney 2. Renal capsule:fibrous capsule,fatty capsule and renal fascia 2. Ureters 3. Urinary bladder 1. The position and shape of bladder 2. Trigone of bladder 4. Urethra Teaching points: The Composition of respiratory system The position and morphology of kidney Renal capsule The position of ureters the position and morphology of bladder The parts of urethra in males Reproductive System Subject:
T e aching p oints: • The Composition of respiratory system, the partition of upper and lower respiratory tracts. • The position and opening of paranasal sinuses • The position and the cartilages framework of larynx; laryngeal cavity • The position of trachea, the partition of left and right principal bronchus • The position, morphology and shape of lungs • The concepts of pleura and pleura cavity • The division of pleura and costodiaphragmatic recess Urinary System S u bject: 1. Kidneys 1. The position, form and structure of kidney 2. Renal capsule: fibrous capsule, fatty capsule and renal fascia 2. Ureters 3. Urinary bladder 1. The position and shape of bladder 2. Trigone of bladder 4. Urethra T e aching p oints: • The Composition of respiratory system • The position and morphology of kidney • Renal capsule • The position of ureters • the position and morphology of bladder • The parts of urethra in males Reproductive System S u bject:

1. Internal reproductive organs in males 1. Testis,epididymis,ductus deferens and ejaculatory ducts 2. Seminal vesicles,prostate,bulbourethral glands 2. External reproductive organs in males 1. Scrotum and penis 2. Male urethra 3. Internal reproductive organs in females 1 Ovaries,uterine tubes,uterus,and vagina 4. External reproductive organs in females 1. Mons pubis,labia majora,labia minora,vaginal vestibule,clitoris and bulb of the vestibule 2. Greater vestibular (Bartholin's)glands Teaching points: The composition of male reproductive system The position and morphology of testis and epididymis The morphologic features of ductus deferens The position and parts of spermatic cord The position and morphology of prostate The composition of female reproductive system The position and morphology of ovaries The position and parts of uterine tubes The position and morphology of uterus The opening of female urethra and vagina Cardiovascular system Subject: 1. General Description ( Components of the cardiovascular system 2. Circulatory routes 2. Heart
1. Internal reproductive organs in males 1. Testis, epididymis, ductus deferens and ejaculatory ducts 2. Seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands 2. External reproductive organs in males 1. Scrotum and penis 2. Male urethra 3. Internal reproductive organs in females 1. Ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina 4. External reproductive organs in females 1. Mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, vaginal vestibule, clitoris and bulb of the vestibule 2. Greater vestibular (Bartholin’s) glands T e aching p oints: • The composition of male reproductive system • The position and morphology of testis and epididymis • The morphologic features of ductus deferens • The position and parts of spermatic cord • The position and morphology of prostate • The composition of female reproductive system • The position and morphology of ovaries • The position and parts of uterine tubes • The position and morphology of uterus • The opening of female urethra and vagina Cardiovascular system S u bject: 1. General Description 1. Components of the cardiovascular system 2. Circulatory routes 2. Heart

1)Location,shape and structure of the heart 2. Chambers of the heart:atrium and ventricle 3. Conduction system of the heart:SA node,AV node,bundle of His and Purkinje fibers 4. Coronary Circulation:arteries and veins 3.Artery 1. Arteries of the pulmonary circulation 2. Arteries of the systemic circulation:Aorta,arteries of the head and neck,arteries of the upper limbs,arteries of the chest,arteries of the abdominal region,arteries of the pelvic arteries,arteries of the lower limbs 4.Vein 1. Superior vena cava system:the veins of head and neck,the veins of the upper limbs and veins of the chest 2. Inferior vena cava system:the veins of the lower limbs,veins of the pelvis and the veins of the abdominal region 3. Hepatic portal system 5.Lymphatic system 1)General description 2) Lymph and lymphatic vessels:lymphatic Capillary,Iymphatic vessels,lymphatic trunks and lymphatic ducts 3) Lymph Nodes 4)Spleen and thymus Teaching points The composition of cardiovascular system The concepts of systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation The position,form of the heart:structure of heart chambers The structure and effect of Conduction system of the heart The arising,main trunks and distribution of left/right coronary arteries The location and opening of coronary sinus The arising,distribution and branches of aorta The distribution and branches of common carotid artery. The branches of external carotid artery and subclavian artery. The artery trunks of upper and lower limbs
1) Location, shape and structure of the heart 2. Chambers of the heart: atrium and ventricle 3. Conduction system of the heart: SA node, AV node, bundle of His and Purkinje fibers 4. Coronary Circulation: arteries and veins 3. Artery 1. Arteries of the pulmonary circulation 2. Arteries of the systemic circulation: Aorta, arteries of the head and neck, arteries of the upper limbs, arteries of the chest, arteries of the abdominal region, arteries of the pelvic arteries, arteries of th e lower limbs 4. Vein 1. Superior vena cava system: the veins of head and neck, the veins of the upper limbs and veins of the chest 2. Inferior vena cava system: the veins of the lower limbs, veins of the pelvis and the veins of the abdominal region 3. Hepatic portal system 5. Lymphatic system 1) General description 2) Lymph and lymphatic vessels: lymphatic Capillary, lymphatic vessels, lymphatic trunks and lymphatic ducts 3) Lymph Nodes 4) Spleen and thymus T e aching p oints • The composition of cardiovascular system • The concepts of systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation • The position, form of the heart; structure of heart chambers • The structure and effect of Conduction system of the heart • The arising, main trunks and distribution of left/right coronary arteries • The location and opening of coronary sinus • The arising, distribution and branches of aorta • The distribution and branches of common carotid artery. • The branches of external carotid artery and subclavian arter y. • The artery trunks of upper and lower limbs

The composition and distribution of superior vena cava,inferior vena cava and brachiocephalic vein The branches of hepatic portal vein The organization of lymphatic system and lymphatic vessels The arising,distribution and receiving range of thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct The position and forms of spleen Visual Organ Subject: I.Eyeball 1. Walls of eyeball:Fibrous tunic,vascular tunic and retina 2. Internal structure and refractive media of eye:aqueous humor,lens and vitreous body. 2.associated structures of the eye 1)Eyelids,conjunctiva,the lacrimal organ and extrinsic eye muscles. Teaching points: The three layers of tunics in eyeball,and the parts and morphology respectively. The composition and effect of the internal structures. Where are the aqueous humor secretes from and drains in? The structure of lacrimal organ. The effect of extrinsic eye muscles. Vestibulocochlear Organ Subject: 1.External ear 1. Auricle 2. External auditory meatus 2.Middle ear 1. Tympanic cavity:walls of the tympanic cavity:auditory ossicles 2. Auditory tube (Eustachian tube)
• The composition and distribution of superior vena cava, inferior vena cava and brachiocephalic vein • The branches of hepatic portal vein • The organization of lymphatic system and lymphatic vessels • The arising, distribution and receiving range of thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct • The position and forms of spleen Visual Organ S u bject: 1. Eyeball 1. Walls of eyeball: Fibrous tunic, vascular tunic and retina 2. Internal structure and refractive media of eye: aqueous humor, lens and vitreous body. 2. associated structures of the eye 1) Eyelids, conjunctiva, the lacrimal organ and extrinsic eye muscles. T e aching p oints: • The three layers of tunics in eyeball, and the parts and morphology respectively. • The composition and effect of the internal structures. • Where are the aqueous humor secretes from and drains in? • The structure of lacrimal organ. • The effect of extrinsic eye muscles. Vestibulocochlear Organ S u bject: 1. External ear 1. Auricle 2. External auditory meatus 2. Middle ear 1. Tympanic cavity: walls of the tympanic cavity; auditory ossicles 2. Auditory tube (Eustachian tube)