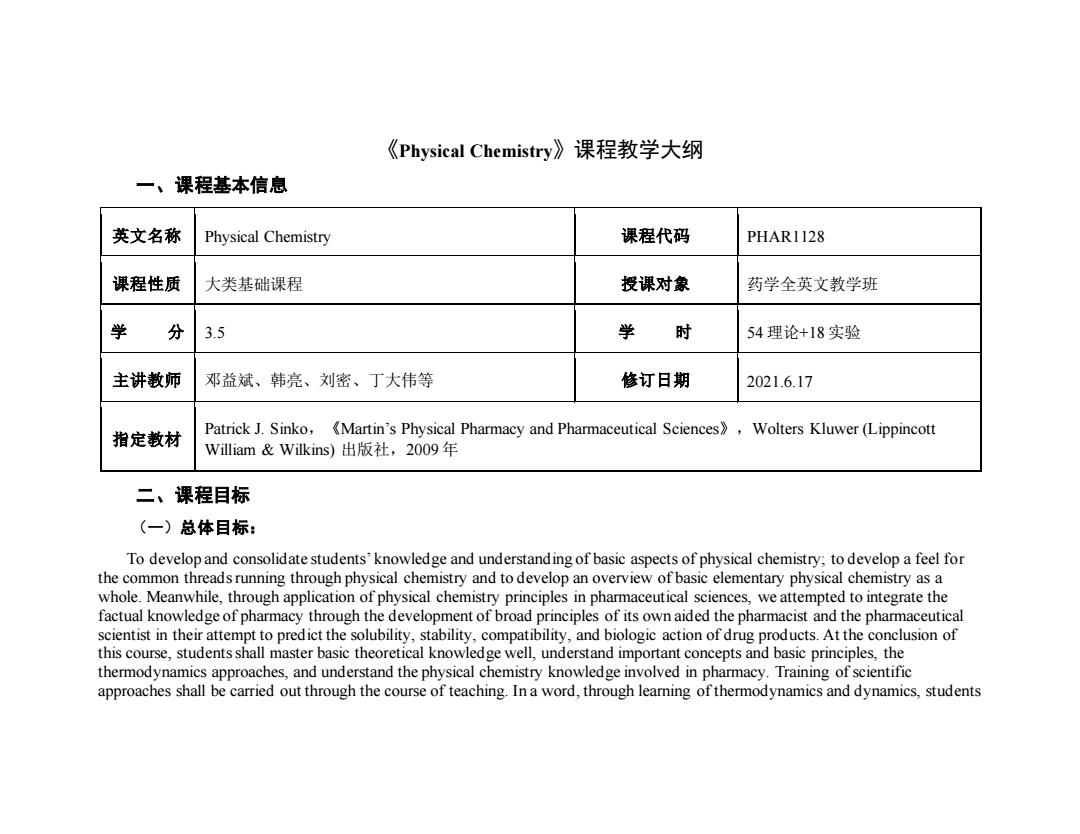
《Physical Chemistry》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Physical Chemistry 课程代码 PHAR1128 课程性质 大类基础课程 授课对象 药学全英文教学班 学 分 3.5 学 时 54理论+18实验 主讲教师 邓益斌、韩亮、刘密、丁大伟等 修订日期 2021.6.17 指定教材 Patrick J.Sinko,(Martin's Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences,Wolters Kluwer(Lippincott William&Wilkins)出版社,2009年 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: To develop and consolidate students'knowledge and understanding of basic aspects of physical chemistry;to develop a feel for the common threads running through physical chemistry and to develop an overview of basic elementary physical chemistry as a whole.Meanwhile,through application of physical chemistry principles in pharmaceutical sciences,we attempted to integrate the factual knowledge of pharmacy through the development of broad principles of its own aided the pharmacist and the pharmaceutical scientist in their attempt to predict the solubility,stability,compatibility,and biologic action of drug products.At the conclusion of this course,students shall master basic theoretical knowledge well,understand important concepts and basic principles,the thermodynamics approaches,and understand the physical chemistry knowledge involved in pharmacy.Training of scientific approaches shall be carried out through the course of teaching.In a word,through learning of thermodynamics and dynamics,students
《Physical Chemistry》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Physical Chemistry 课程代码 PHAR1128 课程性质 大类基础课程 授课对象 药学全英文教学班 学 分 3.5 学 时 54 理论+18 实验 主讲教师 邓益斌、韩亮、刘密、丁大伟等 修订日期 2021.6.17 指定教材 Patrick J. Sinko,《Martin’s Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences》,Wolters Kluwer (Lippincott William & Wilkins) 出版社,2009 年 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: To develop and consolidate students’ knowledge and understanding of basic aspects of physical chemistry; to develop a feel for the common threads running through physical chemistry and to develop an overview of basic elementary physical chemistry as a whole. Meanwhile, through application of physical chemistry principles in pharmaceutical sciences, we attempted to integrate the factual knowledge of pharmacy through the development of broad principles of its own aided the pharmacist and the pharmaceutical scientist in their attempt to predict the solubility, stability, compatibility, and biologic action of drug products. At the conclusion of this course, students shall master basic theoretical knowledge well, understand important concepts and basic principles, the thermodynamics approaches, and understand the physical chemistry knowledge involved in pharmacy. Training of scientific approaches shall be carried out through the course of teaching. In a word, through learning of thermodynamics and dynamics, students

will grasp general methods of inducing and deducing from experimental results,be familiar with methods of concluding theories from hypothesis and understand general scientific approaches ofresolving practical problems through theories and experimental techniques. (二)课程目标: 课程目标l:Master the basic knowledge and basic theories of physical chemistry 1.1 Determine the direction and limit of chemical changes. 1.2 Master the speed and mechanism of chemical reactions. 1.3 Master the relevant knowledge of interface phenomena,colloidal chemistry,powder science and rheology 2:Cultivate theoretical thinking ability and be able to quantitatively describe physical and chemical related problems in common systems. 2.1 Master the basic research methods of physical chemistry 2.2 Use the principles of physical chemistry to deal with problems in solution chemistry 2.3 The relationship between intramolecular or intermolecular interactions and physicochemical properties in the analysis system 3:Cultivate the ability of scientific thinking and rigorous logical reasoning to enable students to understand the physical and chemical problems involved in pharmaceutical research,and to initially develop their ability to apply physical and chemical principles to solve problems related to drug development 4:Cultivate patriotic dedication and a sense of scientific mission,form a correct personal value orientation and professional ethics,expand scientific research knowledge accumulation and international perspective (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系
will grasp general methods of inducing and deducing from experimental results, be familiar with methods of concluding theories from hypothesis and understand general scientific approaches of resolving practical problems through theories and experimental techniques. (二)课程目标: 课程目标 1:Master the basic knowledge and basic theories of physical chemistry 1.1 Determine the direction and limit of chemical changes. 1.2 Master the speed and mechanism of chemical reactions. 1.3 Master the relevant knowledge of interface phenomena, colloidal chemistry, powder science and rheology. 课程目标 2:Cultivate theoretical thinking ability and be able to quantitatively describe physical and chemical related problems in common systems. 2.1 Master the basic research methods of physical chemistry 2.2 Use the principles of physical chemistry to deal with problems in solution chemistry 2.3 The relationship between intramolecular or intermolecular interactions and physicochemical properties in the analysis system 课程目标 3:Cultivate the ability of scientific thinking and rigorous logical reasoning to enable students to understand the physical and chemical problems involved in pharmaceutical research, and to initially develop their ability to apply physical and chemical principles to solve problems related to drug development 课程目标 4:Cultivate patriotic dedication and a sense of scientific mission, form a correct personal value orientation and professional ethics, expand scientific research knowledge accumulation and international perspective (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系
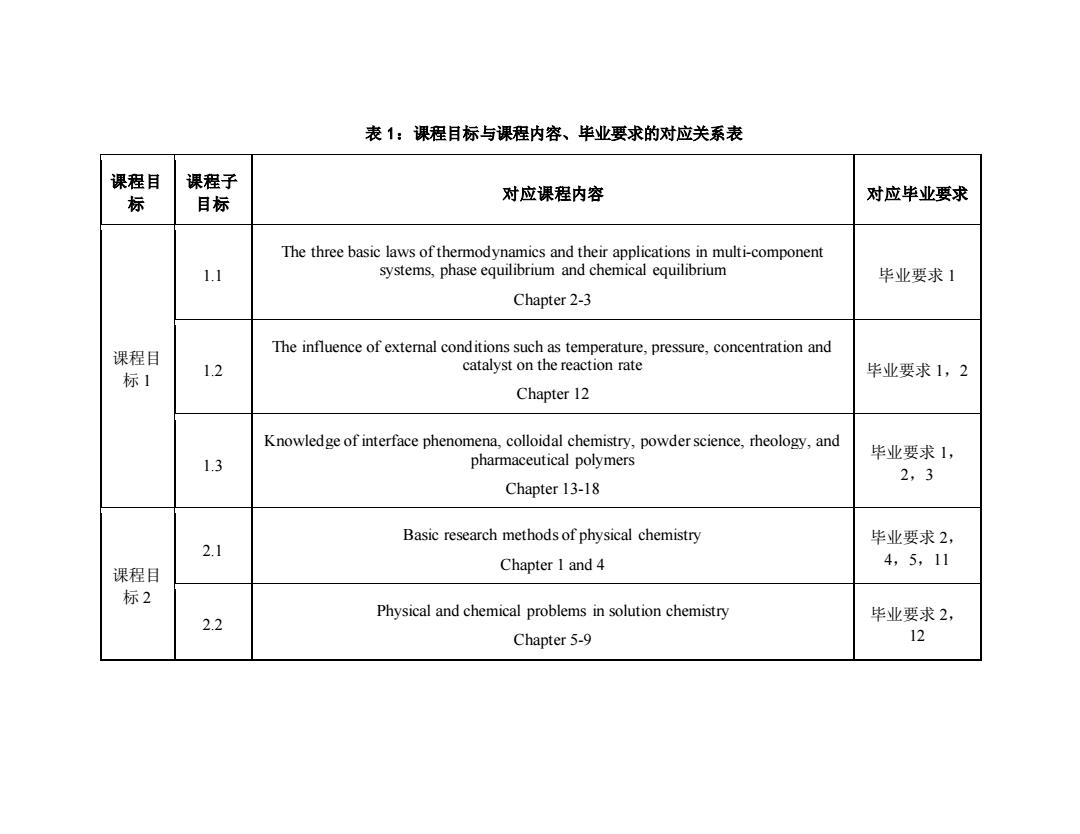
表1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 课程目 课程子 标 目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 The three basic laws of thermodynamics and their applications in multi-component 1.1 systems,phase equilibrium and chemical equilibrium 毕业要求1 Chapter 2-3 课程目 The influence of external conditions such as temperature,pressure,concentration and 1.2 catalyst on the reaction rate 标1 毕业要求1,2 Chapter 12 Knowledge of interface phenomena,colloidal chemistry,powder science,rheology,and 毕业要求1, 1.3 pharmaceutical polymers 2,3 Chapter 13-18 Basic research methods of physical chemistry 毕业要求2, 2.1 4,5,11 课程目 Chapter I and 4 标2 Physical and chemical problems in solution chemistry 2.2 毕业要求2, Chapter 5-9 12
表 1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 课程目 标 课程子 目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 课程目 标 1 1.1 The three basic laws of thermodynamics and their applications in multi-component systems, phase equilibrium and chemical equilibrium Chapter 2-3 毕业要求 1 1.2 The influence of external conditions such as temperature, pressure, concentration and catalyst on the reaction rate Chapter 12 毕业要求 1,2 1.3 Knowledge of interface phenomena, colloidal chemistry, powder science, rheology, and pharmaceutical polymers Chapter 13-18 毕业要求 1, 2,3 课程目 标 2 2.1 Basic research methods of physical chemistry Chapter 1 and 4 毕业要求 2, 4,5,11 2.2 Physical and chemical problems in solution chemistry Chapter 5-9 毕业要求 2, 12
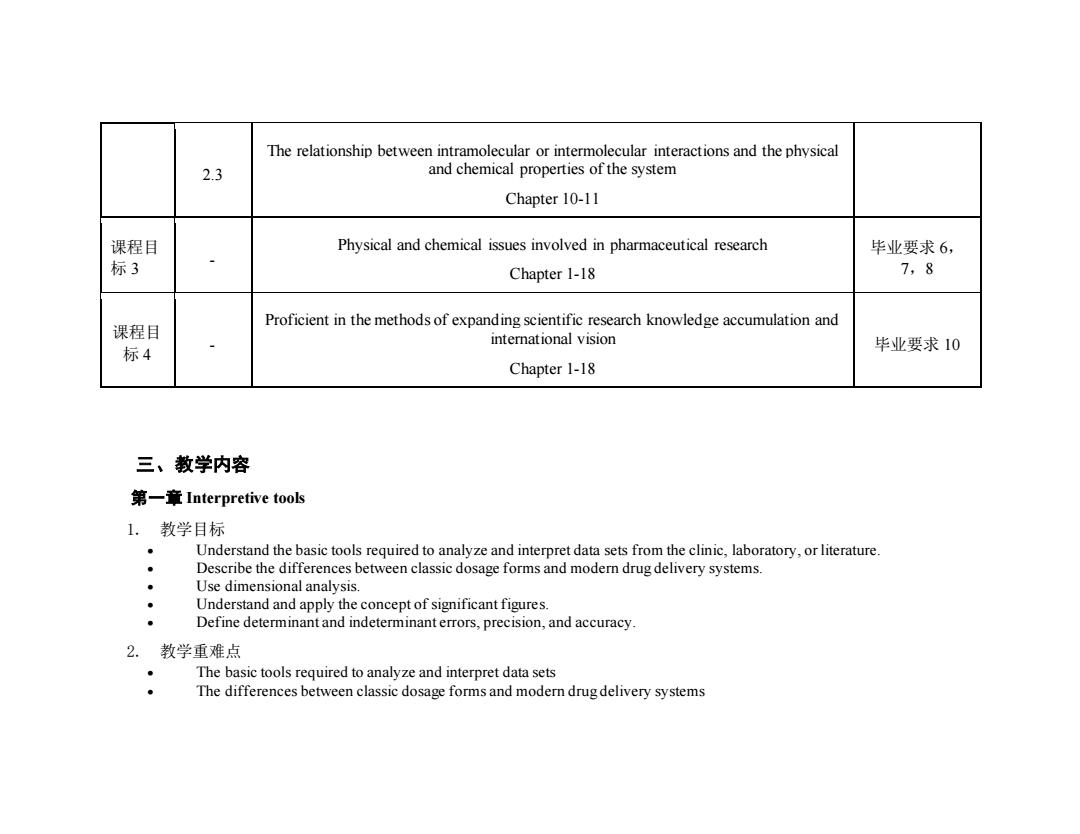
The relationship between intramolecular or intermolecular interactions and the physical 2.3 and chemical properties of the system Chapter 10-11 课程目 Physical and chemical issues involved in pharmaceutical research 毕业要求6, 标3 Chapter 1-18 7,8 Proficient in the methods of expanding scientific research knowledge accumulation and 课程目 international vision 标4 毕业要求10 Chapter 1-18 三、教学内容 第一章Interpretive tools 1.教学目标 Understand the basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets from the clinic,laboratory,or literature. Describe the differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems. Use dimensional analysis. Understand and apply the concept of significant figures. Define determinant and indeterminant errors,precision,and accuracy. 2.教学重难点 The basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets The differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems
2.3 The relationship between intramolecular or intermolecular interactions and the physical and chemical properties of the system Chapter 10-11 课程目 标 3 - Physical and chemical issues involved in pharmaceutical research Chapter 1-18 毕业要求 6, 7,8 课程目 标 4 - Proficient in the methods of expanding scientific research knowledge accumulation and international vision Chapter 1-18 毕业要求 10 三、教学内容 第一章 Interpretive tools 1. 教学目标 • Understand the basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets from the clinic, laboratory, or literature. • Describe the differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems. • Use dimensional analysis. • Understand and apply the concept of significant figures. • Define determinant and indeterminant errors, precision, and accuracy. 2. 教学重难点 • The basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets • The differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems

3.教学内容 Introduction Physical chemistry,physical pharmacy,pharmaceutical technology Measurements,data,propagation of uncertainty Data analysis tools,dimensional analysis,significant figures,data types Error and describing variability Determinate errors,indeterminate errors,precision and accuracy Descriptive statistics Central tendency:mean,median,modes,variability:measures of dispersion Visualizing results:graphic,methods,lines Linear regression analysis 4.教学方法 Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods Interactive teaching 5.教学评价 课后问题:Textbook,Chapter 1,PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE:1-4,1-5,1-7,1-l2 第二章States of Matter 1.教学目标 Understand the nature of the intra-and intermolecular forces; Understand the intermolecular forces and the states of matters; ● Be able to perform calculations:ideal gas law,molecular weights,vapor pressure,boiling points,kinetic molecular theory,van der Waals real gases,the Clausius-Clapeyron equation,heats of fusion and melting points,phase rule equation; Understand phase rule and use it for phase analysis. 2.教学重难点 The concept of physical chemistry and its research focus; The method to learn physical chemistry;
3. 教学内容 • Introduction Physical chemistry, physical pharmacy, pharmaceutical technology • Measurements, data, propagation of uncertainty Data analysis tools, dimensional analysis, significant figures, data types • Error and describing variability Determinate errors, indeterminate errors, precision and accuracy • Descriptive statistics Central tendency: mean, median, modes, variability: measures of dispersion • Visualizing results: graphic, methods, lines Linear regression analysis 4. 教学方法 • Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods • Interactive teaching 5. 教学评价 课后问题:Textbook, Chapter 1, PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE: 1–4, 1-5, 1-7, 1-12 第二章 States of Matter 1. 教学目标 • Understand the nature of the intra- and intermolecular forces; • Understand the intermolecular forces and the states of matters; • Be able to perform calculations: ideal gas law, molecular weights, vapor pressure, boiling points, kinetic molecular theory, van der Waals real gases, the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, heats of fusion and melting points, phase rule equation; • Understand phase rule and use it for phase analysis. 2. 教学重难点 • The concept of physical chemistry and its research focus; • The method to learn physical chemistry;

Data analysis and graphic presentation of results. 3. 教学内容 Bonding forces between molecules The nature of the intra-and intermolecular forces The gaseous state Idea gas equation,PV=nRT ·The liquid state Clausius-Clapeyron equation:heat of vaporization Solids and the crystalline state Polymorphism,melting and heat of fusion The liquid crystalline state Structure and the properties ● The supercritical fluid state Thermal analysis,Karl Fisher method,Vapor sorption/desorption analysis Phase equilibria and the phase rule The phase rule,F-C-P+2,phase diagram,single-component system,Two-component systems,solid dispersion,three-component systems,triangular diagram. 4.教学方法 Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods Interactive teaching 5.教学评价 课后问题:Textbook,Chapter2,PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE 第三章Thermodynamics 1.教学目标 Understand the theory of thermodynamics and its use for describing energy-related changes in reactions Understand the first law of thermodynamics and its use; Understand the second law of thermodynamics and its use;
• Data analysis and graphic presentation of results. 3. 教学内容 • Bonding forces between molecules • The nature of the intra- and intermolecular forces • The gaseous state Idea gas equation, PV=nRT • The liquid state Clausius-Clapeyron equation: heat of vaporization • Solids and the crystalline state Polymorphism, melting and heat of fusion • The liquid crystalline state Structure and the properties • The supercritical fluid state • Thermal analysis, Karl Fisher method, Vapor sorption/desorption analysis • Phase equilibria and the phase rule The phase rule, F=C-P+2, phase diagram, single-component system, Two-component systems, solid dispersion, three-component systems, triangular diagram. 4. 教学方法 • Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods • Interactive teaching 5. 教学评价 课后问题:Textbook, Chapter 2, PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE 第三章 Thermodynamics 1. 教学目标 • Understand the theory of thermodynamics and its use for describing energy-related changes in reactions • Understand the first law of thermodynamics and its use; • Understand the second law of thermodynamics and its use;

Understand the third law of thermodynamics and its use; Define and calculate free energy functions and apply them to pharmaceutically relevant issues; Understand the basic principles of the impact of thermodynamics on pharmaceutically relevant applications; Define the chemical potential and equilibrium processes. 2.教学重难点 The concepts of law of three laws of thermodynamic; Describe different processes using first-law equations; The heat changes accompanying isothermal chemical reactions at constant pressure or volume. The Efficiency of a Heat engine Entropy and calculation of the entropy change in isothermal process or at constant pressure Helmholtz Energy and Gibbs Energy 3.教学内容 The first law of thermodynamics Internal energy (E),AE=Q+W,isothermal and adiabatic processes,work of expansion against a constant pressure,maximum work,changes of state at constant pressure. Thermochemistry Heat of formation,heat of reaction from bond energies,heat of neutralization The second law of thermodynamics The efficiency of a heat engine,entropy,entropy and disorder The third law of thermodynamics Absolute entropies Free energy functions and applications Maximum net work,criteria of equilibrium and spontaneity,fugacity,open system,chemical potential,Clausius-Clapeyron equation,activity,standard free energy and the equilibrium constant 4.教学方法 Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods Interactive teaching 5.教学评价 课后问题:Textbook,Chapter3,PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE
• Understand the third law of thermodynamics and its use; • Define and calculate free energy functions and apply them to pharmaceutically relevant issues; • Understand the basic principles of the impact of thermodynamics on pharmaceutically relevant applications; • Define the chemical potential and equilibrium processes. 2. 教学重难点 • The concepts of law of three laws of thermodynamic; • Describe different processes using first-law equations; • The heat changes accompanying isothermal chemical reactions at constant pressure or volume. • The Efficiency of a Heat engine • Entropy and calculation of the entropy change in isothermal process or at constant pressure • Helmholtz Energy and Gibbs Energy 3. 教学内容 • The first law of thermodynamics Internal energy (E), ΔE = Q + W, isothermal and adiabatic processes, work of expansion against a constant pressure, maximum work, changes of state at constant pressure. • Thermochemistry Heat of formation, heat of reaction from bond energies, heat of neutralization • The second law of thermodynamics The efficiency of a heat engine, entropy, entropy and disorder • The third law of thermodynamics Absolute entropies • Free energy functions and applications Maximum net work, criteria of equilibrium and spontaneity, fugacity, open system, chemical potential, Clausius-Clapeyron equation, activity, standard free energy and the equilibrium constant 4. 教学方法 • Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods • Interactive teaching 5. 教学评价 课后问题:Textbook, Chapter 3, PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE

第四章Determination of the physical properties of molecules 1.教学目标 Understand the nature of intra-and intermolecular forces that are involved in stabilizing molecular and physical structures. Understand the differences in the energetics of these forces and their relevance to different molecules. Understand the differences in energies between the vibrational,translational,and rotational levels and define their meaning. Understand the differences between atomic and molecular spectroscopic techniques and the information they provide. 2.教学重难点 The nature of intra-and intermolecular forces that are involved in stabilizing molecular and physical structures; The differences between atomic and molecular spectroscopic techniques and the information they provide; The differences in energies between the vibrational,translational,and rotational levels. 3.教学内容 Molecular structure,energy,and resulting physical properties Dielectric constant and induced polarization Permanent dipole moment of polar molecules Electromagnetic radiation Atomic and molecular spectra Ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry,fluorescence and phosphorescence,infrared spectroscopy,electron paramagnetic and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy,refractive index and molar refraction,optical rotation,optical rotatory dispersion,circular dichroism,electron and neutron scattering and emission spectroscopy 4.教学方法 Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods Interactive teaching 5.教学评价 课后问题:Textbook,Chapter4,PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE
第四章 Determination of the physical properties of molecules 1. 教学目标 • Understand the nature of intra- and intermolecular forces that are involved in stabilizing molecular and physical structures. • Understand the differences in the energetics of these forces and their relevance to different molecules. • Understand the differences in energies between the vibrational, translational, and rotational levels and define their meaning. • Understand the differences between atomic and molecular spectroscopic techniques and the information they provide. 2. 教学重难点 • The nature of intra- and intermolecular forces that are involved in stabilizing molecular and physical structures; • The differences between atomic and molecular spectroscopic techniques and the information they provide; • The differences in energies between the vibrational, translational, and rotational levels. 3. 教学内容 • Molecular structure, energy, and resulting physical properties • Dielectric constant and induced polarization • Permanent dipole moment of polar molecules • Electromagnetic radiation • Atomic and molecular spectra Ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry, fluorescence and phosphorescence, infrared spectroscopy, electron paramagnetic and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, refractive index and molar refraction, optical rotation, optical rotatory dispersion, circular dichroism, electron and neutron scattering and emission spectroscopy. 4. 教学方法 • Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods • Interactive teaching 5. 教学评价 课后问题:Textbook, Chapter 4, PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE

第五章Nonelectrolytes 1.教学目标 Identify and describe the four colligative properties of nonelectrolytes in solution. Understand the various types of pharmaceutical solutions. Calculate molarity,normality,molality,mole fraction,and percentage expressions. Calculate equivalent weights. Define ideal and real solutions using Raoult's and Henry's laws. Calculate vapor pressure lowering,boiling point elevation,freezing point lowering,and pressure for solutions of nonelectrolytes. 2.教学重难点 The basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets The differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems 3.教学内容 Physical properties of substances and solutions Colligative properties,additive properties,constitutive properties,type of solutions Concentration expressions Molarity and normality,molality,mole fraction,percentage expressions,conversion equations for concentration terms Equivalent weights Ideal and real solutions escaping tendency,Raoult's law,real solutions,Henry's law,distillation of binary mixtures Colligative properties Lowering of the vapor pressure,elevation of the boiling point,depression of the freezing point,osmotic pressure,measureme nt of osmotic pressure,van't Hoff and Morse equations for osmotic pressure,thermodynamics of osmotic pressure and vapor pressure lowering Molecular weight determination Choice of colligative properties 4.教学方法
第五章 Nonelectrolytes 1. 教学目标 • Identify and describe the four colligative properties of nonelectrolytes in solution. • Understand the various types of pharmaceutical solutions. • Calculate molarity, normality, molality, mole fraction, and percentage expressions. • Calculate equivalent weights. • Define ideal and real solutions using Raoult’s and Henry’s laws. • Calculate vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point lowering, and pressure for solutions of nonelectrolytes. 2. 教学重难点 • The basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets • The differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems 3. 教学内容 • Physical properties of substances and solutions Colligative properties, additive properties, constitutive properties, type of solutions • Concentration expressions Molarity and normality, molality, mole fraction, percentage expressions, conversion equations for concentration terms • Equivalent weights • Ideal and real solutions escaping tendency, Raoult’s law, real solutions, Henry’s law, distillation of binary mixtures • Colligative properties Lowering of the vapor pressure, elevation of the boiling point, depression of the freezing point, osmotic pressure, measureme nt of osmotic pressure, van’t Hoff and Morse equations for osmotic pressure, thermodynamics of osmotic pressure and vapor pressure lowering • Molecular weight determination Choice of colligative properties 4. 教学方法

Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods Interactive teaching 5.教学评价 课后间题:Textbook,Chapter5,PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE 第六章Electrolyte solutions 1.教学目标 Understand the important properties of solutions of electrolytes. Understand and apply Faraday's law and electrolytic conductance. Calculate the conductance of solutions,the equivalent conductance,and the equivalent conductance of electrolytes. Compare and contrast the colligative properties of electrolytic solutions and concentrated solutions of nonelectrolytes. Apply the Arrhenius theory of electrolytic dissociation. Understand the differences between osmolality and osmolarity 2.教学重难点 The basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets The differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems 3.教学内容 Properties of solutions of electrolytes Electrolysis,electrolytic conductance,measuring the conductance of solutions,equivalent conductance,equivalent conductance of strong and weak electrolytes,colligative properties of electrolytic solutions and concentrated solutions of nonelectrolytes Theory of electrolytic dissociation Drug and ionization,degree of dissociation Theory of strong electrolytes Activity and activity coefficients,activity of solvent,reference state,standard state,ionic strength,Debye-Hueckel theory Coefficients for expressing colligative properties The L value,osmotic coefficient,osmolality 4.教学方法
• Giving lecture by Multimedia teaching methods • Interactive teaching 5. 教学评价 课后问题:Textbook, Chapter 5, PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR STUDENT USE 第六章 Electrolyte solutions 1. 教学目标 • Understand the important properties of solutions of electrolytes. • Understand and apply Faraday’s law and electrolytic conductance. • Calculate the conductance of solutions, the equivalent conductance, and the equivalent conductance of electrolytes. • Compare and contrast the colligative properties of electrolytic solutions and concentrated solutions of nonelectrolytes. • Apply the Arrhenius theory of electrolytic dissociation. • Understand the differences between osmolality and osmolarity 2. 教学重难点 • The basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets • The differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems 3. 教学内容 • Properties of solutions of electrolytes Electrolysis, electrolytic conductance, measuring the conductance of solutions, equivalent conductance, equivalent conductanc e of strong and weak electrolytes, colligative properties of electrolytic solutions and concentrated solutions of nonelectrolytes • Theory of electrolytic dissociation Drug and ionization, degree of dissociation • Theory of strong electrolytes Activity and activity coefficients, activity of solvent, reference state, standard state, ionic strength, Debye-Hueckel theory • Coefficients for expressing colligative properties The L value, osmotic coefficient, osmolality 4. 教学方法