《Pharmaceutica|Analysis I》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Pharmaceutical Analysis I 课程代码 PHAR1123 课程性质 专业必修课 授课对象 全英药学班 学 分 4 学 时 72 主讲教师 张真庆、汪维鹏、杨霜、李笃信、阮建清 修订日期 2021年6月17日 指定教材 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical analysis/Pharmaceutical Analysis for Small Molecules 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: 药物分析是一门综合性、专业性、实践性和法规性均较强的学科。该课程总体目标是承接基础分析化学在药学研究、药 物生产和临床使用过程中的应用。初步使学生了解药物分析与分析化学的区别,理解药物分析的意义,掌握基本药物分析原 则和原理。该课程为全英文教学,学生的专业英文的掌握也是该课程的目标之一。 (二)课程目标: 课程目标1:掌握基础知识 1.1药物分析相关基本概念
《Pharmaceutical Analysis I》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Pharmaceutical Analysis I 课程代码 PHAR1123 课程性质 专业必修课 授课对象 全英药学班 学 分 4 学 时 72 主讲教师 张真庆、汪维鹏、杨霜、李笃信、阮建清 修订日期 2021 年 6 月 17 日 指定教材 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical analysis/Pharmaceutical Analysis for Small Molecules 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: 药物分析是一门综合性、专业性、实践性和法规性均较强的学科。该课程总体目标是承接基础分析化学在药学研究、药 物生产和临床使用过程中的应用。初步使学生了解药物分析与分析化学的区别,理解药物分析的意义,掌握基本药物分析原 则和原理。该课程为全英文教学,学生的专业英文的掌握也是该课程的目标之一。 (二)课程目标: 课程目标 1:掌握基础知识 1.1 药物分析相关基本概念

1.2药物分析相关国籍法规 1.3药物分析相关基础 课程目标2:掌握基本分析方法原理和仪器 2.1滴定 2.2光谱 2.3色谱 2.4毛细管电泳 2.5质谱 2.6其他分析方法和技术 课程目标3:掌握样品处理方法原则和方式 3.1样品制备 课程目标4:掌握原料药和最终制剂产品的定性定量分析方法、数据处理原则、质量标准制定原则和条目 4.1定性定量方法建立和验证 4.2原料药质量标准制定原则和条目 4.3最终制剂产品质量标准制定原则和条目 课程目标5:掌握生物样品中药物分析流程和方法
1.2 药物分析相关国籍法规 1.3 药物分析相关基础 课程目标 2:掌握基本分析方法原理和仪器 2.1 滴定 2.2 光谱 2.3 色谱 2.4 毛细管电泳 2.5 质谱 2.6 其他分析方法和技术 课程目标 3:掌握样品处理方法原则和方式 3.1 样品制备 课程目标 4:掌握原料药和最终制剂产品的定性定量分析方法、数据处理原则、质量标准制定原则和条目 4.1 定性定量方法建立和验证 4.2 原料药质量标准制定原则和条目 4.3 最终制剂产品质量标准制定原则和条目 课程目标 5:掌握生物样品中药物分析流程和方法

(要求参照《普通高等学校本科专业类教学质量国家标准》,对应各类专业认证标准,注意对毕业要求支撑程度强弱的 描述,与“课程目标对毕业要求的支撑关系表一致)( (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系 表1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 程 课程 目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 标 1.1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 掌握基础知识,包括: 药物分析相关基本概念: 课程 1.2 International Pharmacopoeias,Regulations and Guidelines 药物分析相关国籍法规: 目标 1 药物分析相关基础: Fundamental Chemical Properties,Buffers and pH 1.3 掌握相应专业术语和专业英语,包括: Fundamentals of Pharmaceutical Analysis 听说读写 课程 2.1 Titrimetric Methods 目标 要求掌握各种分析方法的分析原理、仪器原 2 2.2 Introduction to Spectroscopic Methods/UV Spectrophotometry/IR 理等,包括: Spectrophotometry/Atomic Spectrometry
(要求参照《普通高等学校本科专业类教学质量国家标准》,对应各类专业认证标准,注意对毕业要求支撑程度强弱的 描述,与“课程目标对毕业要求的支撑关系表一致)( (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系 表 1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 课程 目标 课程 子目 标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 课程 目标 1 1.1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 掌握基础知识,包括: 药物分析相关基本概念; 药物分析相关国籍法规; 药物分析相关基础; 掌握相应专业术语和专业英语,包括: 听说读写 1.2 International Pharmacopoeias, Regulations and Guidelines 1.3 Fundamental Chemical Properties, Buffers and pH Fundamentals of Pharmaceutical Analysis 课程 目标 2 2.1 Titrimetric Methods 要求掌握各种分析方法的分析原理、仪器原 理等,包括: 2.2 Introduction to Spectroscopic Methods/ UV Spectrophotometry/ IR Spectrophotometry/ Atomic Spectrometry
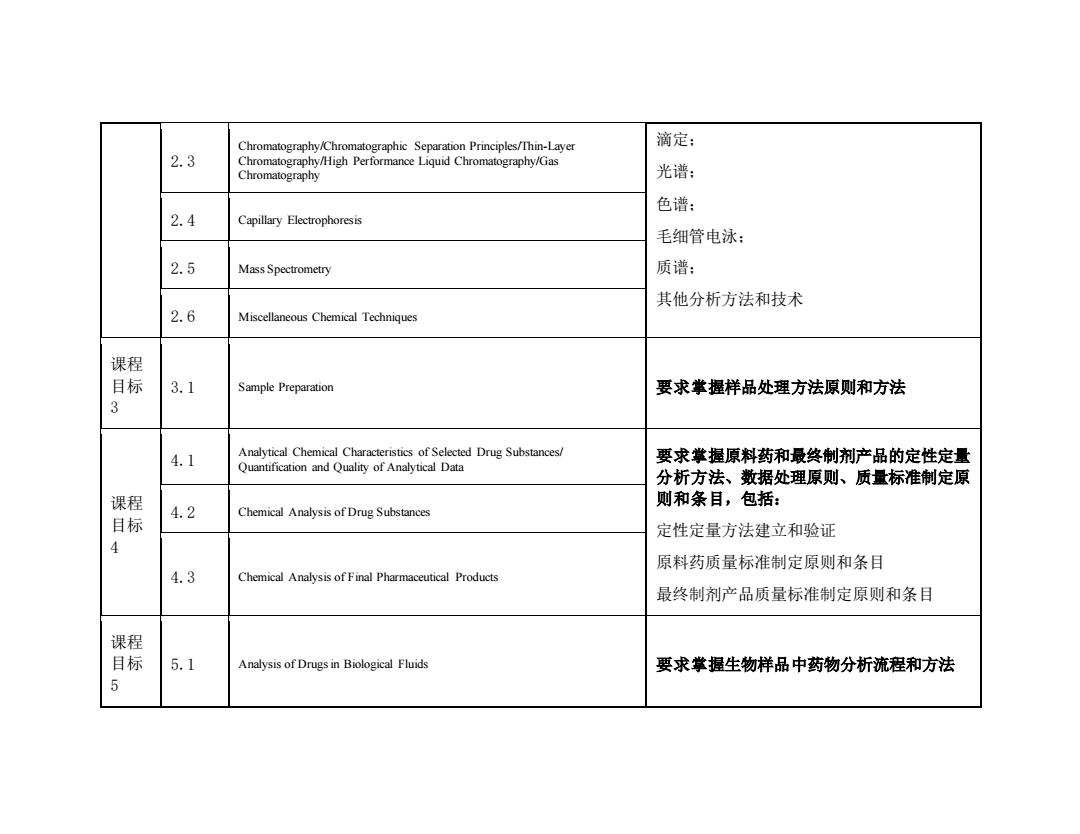
Chromatography/Chromatographic Separation Principles/Thin-Layer 滴定: 2.3 Chromatography/High Performance Liquid Chromatography/Gas Chromatography 光谱: 色谱: 2.4 Capillary Electrophoresis 毛细管电泳: 2.5 Mass Spectrometry 质谱: 其他分析方法和技术 2.6 Miscellaneous Chemical Techniques 课程 目标 3.1 Sample Preparation 要求掌握样品处理方法原则和方法 3 4.1 Analytical Chemical Characteristics of Selected Drug Substances/ 要求掌握原料药和最终制剂产品的定性定量 Quantification and Quality of Analytical Data 分析方法、数据处理原则、质量标准制定原 课程 则和条目,包括: Chemical Analysis of Drug Substances 目标 4.2 定性定量方法建立和验证 4 原料药质量标准制定原则和条目 4.3 Chemical Analysis of Final Pharmaceutical Products 最终制剂产品质量标准制定原则和条目 课程 目标 5.1 Analysis of Drugs in Biological Fluids 要求掌握生物样品中药物分析流程和方法 5
2.3 Chromatography/Chromatographic Separation Principles/Thin-Layer Chromatography/High Performance Liquid Chromatography/Gas Chromatography 滴定; 光谱; 色谱; 毛细管电泳; 质谱; 其他分析方法和技术 2.4 Capillary Electrophoresis 2.5 Mass Spectrometry 2.6 Miscellaneous Chemical Techniques 课程 目标 3 3.1 Sample Preparation 要求掌握样品处理方法原则和方法 课程 目标 4 4.1 Analytical Chemical Characteristics of Selected Drug Substances/ Quantification and Quality of Analytical Data 要求掌握原料药和最终制剂产品的定性定量 分析方法、数据处理原则、质量标准制定原 则和条目,包括: 定性定量方法建立和验证 原料药质量标准制定原则和条目 最终制剂产品质量标准制定原则和条目 4.2 Chemical Analysis of Drug Substances 4.3 Chemical Analysis of Final Pharmaceutical Products 课程 目标 5 5.1 Analysis of Drugs in Biological Fluids 要求掌握生物样品中药物分析流程和方法

(大类基础课程、专业教学课程及开放选修课程按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕业要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。 通识教育课程含通识选修课程、新生研讨课程及公共基础课程,面向专业为工科、师范、医学等有专业认证标准的专业,按 照专业认证通用标准填写“对应毕业要求”栏:面向其他尚未有专业认证标准的专业,按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕 业要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。) 三、教学内容 (具体描述各章节教学目标、教学内容等。实验课程可按实验模块描述) Chapter 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1. 教学目标 This chapter briefly reviews the life of medical products and the manufacture of medical products according to interational regulations and guidelines.Based on this review the major areas and usage of pharmaceutical analysis are identified. 2. 教学重难点 The quality control system. 3. 教学内容 Contents 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1.2 The Life of Medicines 1.3 The Quality of Medical Products 1.4 Summary Problems: 1. The concept of drug? 2. What's the main function of excipients? 3. What are the means of QA.QC and GMP?
(大类基础课程、专业教学课程及开放选修课程按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕业要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。 通识教育课程含通识选修课程、新生研讨课程及公共基础课程,面向专业为工科、师范、医学等有专业认证标准的专业,按 照专业认证通用标准填写“对应毕业要求”栏;面向其他尚未有专业认证标准的专业,按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕 业要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。) 三、教学内容 (具体描述各章节教学目标、教学内容等。实验课程可按实验模块描述) Chapter 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1. 教学目标 This chapter briefly reviews the life of medical products and the manufacture of medical products according to international regulations and guidelines. Based on this review the major areas and usage of pharmaceutical analysis are identified. 2. 教学重难点 The quality control system. 3. 教学内容 Contents 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1.2 The Life of Medicines 1.3 The Quality of Medical Products 1.4 Summary Problems: 1. The concept of drug? 2. What’s the main function of excipients? 3. What are the means of QA,QC and GMP?

4. How to assure the safty,protection and well being of the consumer or patient? 5. What requirements should be met before certifying a batch the QP? 6. The significance of the control of drugs'quality 4. 教学方法 课堂教授结合提问 5. 教学评价 期中考试 Chapter 2 International Pharmacopoeias,Regulations and Guidelines 1. 教学目标 This chapter reviews a number of laws,guidelines and regulations important in the pharmaceutical production and thus also for the subject pharmaceutical analysis.The manufacture of drugs is international and therefore this chapter focuses on interational affairs.But also national laws,guidelines,and regulations are important for manufacturers in order to fulfil the requirements of the relevant authorities.All these laws,guidelines and regulations are subject to regular updates and the latest edition should therefore always be consulted. 2. 教学重难点 The concepts of marketing authorization and manufacturing authorization 3. 教学内容 Contents 2.1 Overview of Legislation 2.2 Legislation and Regulations for Industrial Production 2.3 Life Time of Drugs and Drug Substances 2.4 Pharmacopoeias 2.5 International Harmonization
4. How to assure the safty,protection and well being of the consumer or patient? 5. What requirements should be met before certifying a batch the QP? 6. The significance of the control of drugs’ quality ? 4. 教学方法 课堂教授结合提问 5. 教学评价 期中考试 Chapter 2 International Pharmacopoeias, Regulations and Guidelines 1. 教学目标 This chapter reviews a number of laws, guidelines and regulations important in the pharmaceutical production and thus also for the subject pharmaceutical analysis. The manufacture of drugs is international and therefore this chapter focuses on international affairs. But also national laws, guidelines, and regulations are important for manufacturers in order to fulfil the requirements of the relevant authorities. All these laws, guidelines and regulations are subject to regular updates and the latest edition should therefore always be consulted. 2. 教学重难点 The concepts of marketing authorization and manufacturing authorization 3. 教学内容 Contents 2.1 Overview of Legislation 2.2 Legislation and Regulations for Industrial Production 2.3 Life Time of Drugs and Drug Substances 2.4 Pharmacopoeias 2.5 International Harmonization

2.5.1 International Conference on Harmonization 2.5.2 Pharmacopoeial Discussion Group 2.6 Legislation and Regulations for Pharmacy Production 2.7 Summary Problems: 1. What's applicable for Proprietary Medicinal Products? 2. What's the situation the marketing authorization may be withdrawn before the expiration by the Ministry of Health? 3. What's the detail information of the raw materials before production should be controlled? 4. What's the main elements of the GMP/GLP regulations? 5. What are the ICH guidelines of important relevance for the pharmaceutical analysis? 教学方法 课堂教授结合提问 5. 教学评价 期中考试 Chapter 3 Fundamental Chemical Properties,Buffers and pH 1. Chemical analysis is an important part of the quality assessment of drugs.A deeper understanding of the analytical method requires knowledge about both the analytical technique and the chemical properties of the analytes.Therefore a basic knowledge of a number of physicochemical properties of molecules is needed to be able to understand and further develop analytical chemical methods.For example,knowledge of spectroscopic principles and techniques is needed when the choice of the detection technique for a given separation method is made;and knowledge of pH and pKa values is important for the design of many sample preparation techniques.Spectroscopic techniques are treated in separate chapters,and this chapter discusses some important physicochemical and chemical properties of drug substances and focuses on how to utilize the information in an analytical chemical context. 2. 教学重难点
2.5.1 International Conference on Harmonization 2.5.2 Pharmacopoeial Discussion Group 2.6 Legislation and Regulations for Pharmacy Production 2.7 Summary Problems: 1. What’s applicable for Proprietary Medicinal Products? 2. What’s the situation the marketing authorization may be withdrawn before the expiration by the Ministry of Health? 3. What’s the detail information of the raw materials before production should be controlled? 4. What’s the main elements of the GMP/GLP regulations? 5. What are the ICH guidelines of important relevance for the pharmaceutical analysis? 4. 教学方法 课堂教授结合提问 5. 教学评价 期中考试 Chapter 3 Fundamental Chemical Properties, Buffers and pH 1. 教学目标 Chemical analysis is an important part of the quality assessment of drugs. A deeper understanding of the analytical method requires knowledge about both the analytical technique and the chemical properties of the analytes. Therefore a basic knowledge of a number of physicochemical properties of molecules is needed to be able to understand and further develop analytical chemical methods. For example, knowledge of spectroscopic principles and techniques is needed when the choice of the detection technique for a given separation method is made; and knowledge of pH and pKa values is important for the design of many sample preparation techniques. Spectroscopic techniques are treated in separate chapters, and this chapter discusses some important physicochemical and chemical properties of drug substances and focuses on how to utilize the information in an analytical chemical context. 2. 教学重难点

The concepts of pH and pKa 3. 教学内容 Contents 3.1 pH and pKa 3.2 Partition 3.3 Stereochemistry 3.4 Stability Testing 3.5 Summary Problems: 1. What are the means of pH,pKa and pKb? 2. What is called a buffer system and the purpose? 3. What's the typical pKa values of following functional groups,such as R-COOH,R-NH2,R-OH and R-SO2OH? 4. What's the influence of the ions? 5. How isomers can be divided into several groups? 6. How long the drug substances are fairly stable? 4. 教学方法 课堂教授结合提问 5. 教学评价 期中考试 Chapter 4 Fundamentals of Pharmaceutical Analysis
The concepts of pH and pKa 3. 教学内容 Contents 3.1 pH and pKa 3.2 Partition 3.3 Stereochemistry 3.4 Stability Testing 3.5 Summary Problems: 1. What are the means of pH,pKa and pKb? 2. What is called a buffer system and the purpose? 3. What’s the typical pKa values of following functional groups,such as R-COOH,R-NH2,R-OH and R-SO2OH? 4. What’s the influence of the ions? 5. How isomers can be divided into several groups? 6. How long the drug substances are fairly stable? 4. 教学方法 课堂教授结合提问 5. 教学评价 期中考试 Chapter 4 Fundamentals of Pharmaceutical Analysis

1. 教学目标 This chapter discusses the basics of pharmaceutical analysis,including the different types of calculations related to pharmaceutical analysis.The chapter also includes a review of simple laboratory equipment,how to make solutions and dilutions,how to calibrate analytical methods,and how to use simple statistics on the analytical data.The chapter concludes with a list of important terms and concepts in pharmaceutical analysis.It is important that you read carefully through this chapter before proceeding to the subsequent chapters.Important terms should be learned. 2. 教学重难点 Presentation of analytical data 3. 教学内容 Contents 4.1 What is a Pharmaceutical (Chemical)Analysis? 4.2 How to Specify Quantities and Concentrations? 4.3 Basic Laboratory Equipment 4.3.1 The Analytical Balance 4.3.2 Pipettes 4.3.3 Volumetric Flasks 4.3.4 Burettes 4.4 How to Make Solutions and Dilutions 4.5 Calibration of Analytical Methods 4.6 Errors,Accuracy,and Precision 4.6.1 Systematic and Random Errors 4.6.2 Accuracy and Precision 4.7 Statistics 4.7.1 Mean Value and Standard Deviation 4.7.2 Confidence Intervals 4.7.3 Comparison of Means with a t-Test 4.7.4 Q-Test to Reject Outliers
1. 教学目标 This chapter discusses the basics of pharmaceutical analysis, including the different types of calculations related to pharmaceutical analysis. The chapter also includes a review of simple laboratory equipment, how to make solutions and dilutions, how to calibrate analytical methods, and how to use simple statistics on the analytical data. The chapter concludes with a list of important terms and concepts in pharmaceutical analysis. It is important that you read carefully through this chapter before proceeding to the subsequent chapters. Important terms should be learned. 2. 教学重难点 Presentation of analytical data 3. 教学内容 Contents 4.1 What is a Pharmaceutical (Chemical) Analysis? 4.2 How to Specify Quantities and Concentrations? 4.3 Basic Laboratory Equipment 4.3.1 The Analytical Balance 4.3.2 Pipettes 4.3.3 Volumetric Flasks 4.3.4 Burettes 4.4 How to Make Solutions and Dilutions 4.5 Calibration of Analytical Methods 4.6 Errors, Accuracy, and Precision 4.6.1 Systematic and Random Errors 4.6.2 Accuracy and Precision 4.7 Statistics 4.7.1 Mean Value and Standard Deviation 4.7.2 Confidence Intervals 4.7.3 Comparison of Means with a t-Test 4.7.4 Q-Test to Reject Outliers

4.7.5 Linear Regression with the Method of Least Squares 4.7.6 How to Present an Analytical Result 4.8 Some Words and Concepts 4.8.1 Analysis and Determination 4.8.2 Sample Replicates and Measuring Replicates 4.8.3 Interference 4.8.4 Blind Samples Problems: 1. What is a Pharmaceutical (Chemical)Analysis? 2. What should be ensured of sample preparation? 3. How to Specify Quantities and Concentrations? 4. How to calculate concentration in terms of ppm? 5. What are the considerations for the use of the analytical balance? 6. What are the considerations for the use of the pipettes? 7. What are the means of the temperature on pipettes,volumetric flasks and burettes? 4. 教学方法 课堂教授结合提问 5. 教学评价 期中考试 Chapter 5 Titrimetric Methods 1. 教学目标
4.7.5 Linear Regression with the Method of Least Squares 4.7.6 How to Present an Analytical Result 4.8 Some Words and Concepts 4.8.1 Analysis and Determination 4.8.2 Sample Replicates and Measuring Replicates 4.8.3 Interference 4.8.4 Blind Samples Problems: 1. What is a Pharmaceutical (Chemical) Analysis? 2. What should be ensured of sample preparation? 3. How to Specify Quantities and Concentrations? 4. How to calculate concentration in terms of ppm? 5. What are the considerations for the use of the analytical balance? 6. What are the considerations for the use of the pipettes? 7. What are the means of the temperature on pipettes,volumetric flasks and burettes? 4. 教学方法 课堂教授结合提问 5. 教学评价 期中考试 Chapter 5 Titrimetric Methods 1. 教学目标