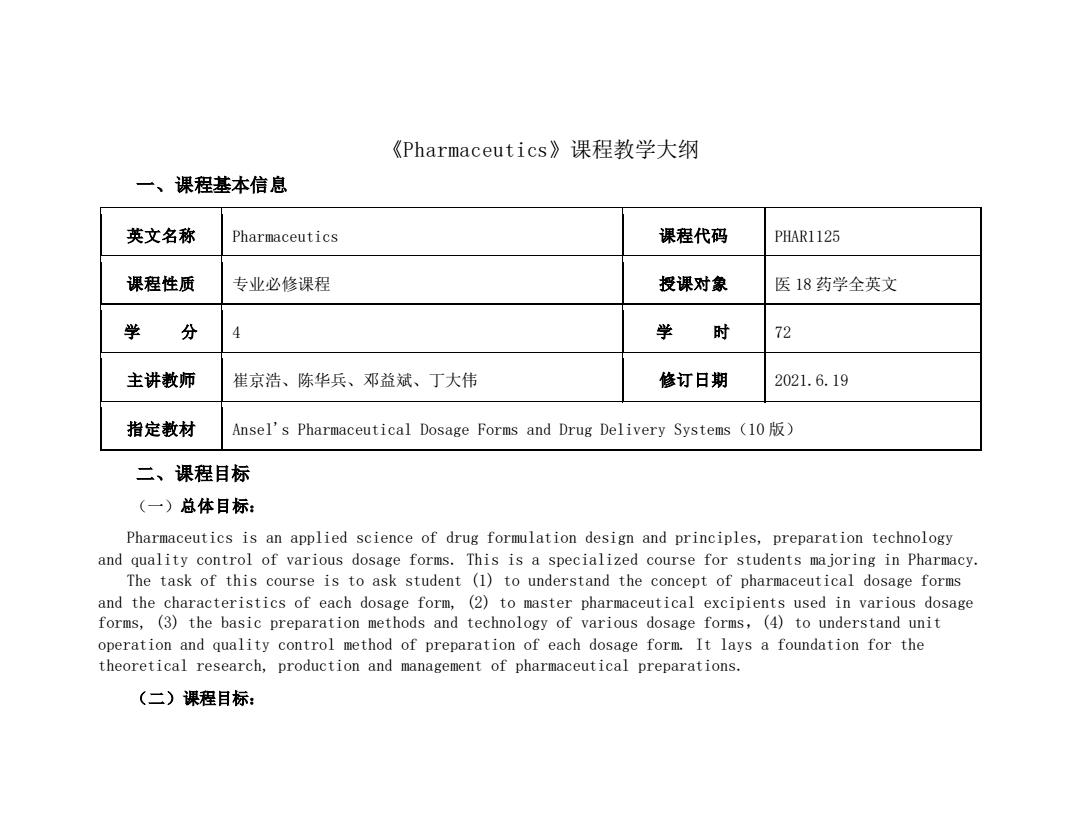
《Pharmaceutics》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Pharmaceutics 课程代码 PHAR1125 课程性质 专业必修课程 授课对象 医18药学全英文 学 分 4 学 时 72 主讲教师 崔京浩、陈华兵、邓益斌、丁大伟 修订日期 2021.6.19 指定教材 Ansel's Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems (10) 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: Pharmaceutics is an applied science of drug formulation design and principles,preparation technology and quality control of various dosage forms.This is a specialized course for students majoring in Pharmacy. The task of this course is to ask student (1)to understand the concept of pharmaceutical dosage forms and the characteristics of each dosage form,(2)to master pharmaceutical excipients used in various dosage forms,(3)the basic preparation methods and technology of various dosage forms,(4)to understand unit operation and quality control method of preparation of each dosage form.It lays a foundation for the theoretical research,production and management of pharmaceutical preparations. (二)课程目标:
《Pharmaceutics》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Pharmaceutics 课程代码 PHAR1125 课程性质 专业必修课程 授课对象 医 18 药学全英文 学 分 4 学 时 72 主讲教师 崔京浩、陈华兵、邓益斌、丁大伟 修订日期 2021.6.19 指定教材 Ansel's Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems(10 版) 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: Pharmaceutics is an applied science of drug formulation design and principles, preparation technology and quality control of various dosage forms. This is a specialized course for students majoring in Pharmacy. The task of this course is to ask student (1) to understand the concept of pharmaceutical dosage forms and the characteristics of each dosage form, (2) to master pharmaceutical excipients used in various dosage forms, (3) the basic preparation methods and technology of various dosage forms,(4) to understand unit operation and quality control method of preparation of each dosage form. It lays a foundation for the theoretical research, production and management of pharmaceutical preparations. (二)课程目标:

课程目标1: 1.1 Introduction to Drugs and Pharmacy Learn the development and purpose of the pharmacopoeia,able to describe the central features of a typical drug monograph,familiar with the concept of pharmaceutical care,understand significant drug regulation and control laws,summarize the Code of Ethics for Pharmacists and Pharmaceutical Scientists. 1.2 New Drug Development and Approval Process Compare and contrast an investigational new drug (IND)application from a new drug application (NDA), differentiate between phase I,phase II,phase III,and phase IV clinical trials,preliminary understand the sources of new drugs. 1.3 Current Good Manufacturing Practices Learn the definition and main contents of cGMP. 1.4 Dosage form design:Pharmaceutical and Formulation Considerations Learn the rationality and properties of preparing various dosage forms,familiar with the content of preformulation research in dosage form design,master the main mechanism of drug degradation and stabilization methods as well as the calculation of drug degradation kinetic parameters,study the pharmaceutical excipients. 1.5 Dosage form design:Biopharmaceutical and Pharmacokinetic Considerations Learn the mechanisms of drug absorption from pharmaceutical dosage forms,interpretation the relationship between drug dissolution and absorption,understand the physicochemical characteristics of a drug that affect its dissolution from various dosage forms. 课程目标2:Solid Dosage Forms and Solid Modified--Release Drug Delivery Systems 2.1 Powders and Granules Differentiate a powder from a granule,explain how a drug's powder particle size influences the pharmaceutical dosage forms which will be used to administer it,define micromeritics and related concepts. 2.2 Capsules
课程目标 1: 1.1 Introduction to Drugs and Pharmacy Learn the development and purpose of the pharmacopoeia, able to describe the central features of a typical drug monograph, familiar with the concept of pharmaceutical care, understand significant drug regulation and control laws, summarize the Code of Ethics for Pharmacists and Pharmaceutical Scientists. 1.2 New Drug Development and Approval Process Compare and contrast an investigational new drug (IND) application from a new drug application (NDA), differentiate between phase I, phase II, phase III, and phase IV clinical trials, preliminary understand the sources of new drugs. 1.3 Current Good Manufacturing Practices Learn the definition and main contents of cGMP. 1.4 Dosage form design: Pharmaceutical and Formulation Considerations Learn the rationality and properties of preparing various dosage forms, familiar with the content of preformulation research in dosage form design, master the main mechanism of drug degradation and stabilization methods as well as the calculation of drug degradation kinetic parameters, study the pharmaceutical excipients. 1.5 Dosage form design: Biopharmaceutical and Pharmacokinetic Considerations Learn the mechanisms of drug absorption from pharmaceutical dosage forms, interpretation the relationship between drug dissolution and absorption, understand the physicochemical characteristics of a drug that affect its dissolution from various dosage forms. 课程目标 2:Solid Dosage Forms and Solid Modified-Release Drug Delivery Systems 2.1 Powders and Granules Differentiate a powder from a granule, explain how a drug’s powder particle size influences the pharmaceutical dosage forms which will be used to administer it, define micromeritics and related concepts. 2.2 Capsules

Differentiate the definition and properties between hard gelatin and soft gelatin capsules,learn the preparation method and quality control of hard capsules. 2.3 Tablets Study the definition and properties of various types of tablet dosage forms,familiar with diverse excipients employed in the tablets,masters the common preparation methods for tablets. Describe quality control standards for tablets,understand the common occurred problems in the preparation of tablets and how to solve them. 2.4 Solid Oral Modified-release Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems Differentiate between the various types of modified-release dosage forms,compare and contrast advantages and disadvantages of them.List physicochemical characteristics of drugs that used as candidates for an extended-release dosage form.Learn some technologies to prepare modified-release dosage forms,such as microencapsulation,ion exchange,and osmotic pump,etc.Understand the significance of the in vitro and in vivo drug release from an extended-release/delayed-release oral dosage form will differ from an oral, film-coated tablet. 课程目标3:Semisolid Dosage Forms,Transdermal Drug Delivery System and Suppositories 3.1 Ointments,Creams,and Gels After learning,the student could differentiate between the various types of ointment bases on the basis of physicochemical properties,list the criteria for the selection of an ointment base to treat a topical affliction.After that,they describe the methods to incorporate (an)active ingredient(s)into an ointment base,explain the difference between an ointment,a cream,and a gel.In addition,the student could compare and contrast an ophthalmic ointment base and a topical ointment base for application to the skin. Furthermore,they could list advantages and disadvantages of administering drugs rectally and vaginally. 3.2 Transdermal Drug Delivery System After learning this part,the student can explain the physicochemical properties of drugs which determine their ability to be incorporated into a transdermal dosage form.After that,they can describe
Differentiate the definition and properties between hard gelatin and soft gelatin capsules, learn the preparation method and quality control of hard capsules. 2.3 Tablets Study the definition and properties of various types of tablet dosage forms, familiar with diverse excipients employed in the tablets, masters the common preparation methods for tablets. Describe quality control standards for tablets, understand the common occurred problems in the preparation of tablets and how to solve them. 2. 4 Solid Oral Modified-release Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems Differentiate between the various types of modified-release dosage forms, compare and contrast advantages and disadvantages of them. List physicochemical characteristics of drugs that used as candidates for an extended-release dosage form. Learn some technologies to prepare modified-release dosage forms, such as microencapsulation, ion exchange, and osmotic pump, etc. Understand the significance of the in vitro and in vivo drug release from an extended-release/delayed-release oral dosage form will differ from an oral, film-coated tablet. 课程目标 3:Semisolid Dosage Forms, Transdermal Drug Delivery System and Suppositories 3.1 Ointments, Creams, and Gels After learning, the student could differentiate between the various types of ointment bases on the basis of physicochemical properties, list the criteria for the selection of an ointment base to treat a topical affliction. After that, they describe the methods to incorporate (an) active ingredient(s) into an ointment base, explain the difference between an ointment, a cream, and a gel. In addition, the student could compare and contrast an ophthalmic ointment base and a topical ointment base for application to the skin. Furthermore, they could list advantages and disadvantages of administering drugs rectally and vaginally. 3.2 Transdermal Drug Delivery System After learning this part, the student can explain the physicochemical properties of drugs which determine their ability to be incorporated into a transdermal dosage form. After that, they can describe

physiological factors of the skin which influence percutaneous absorption.In addition,the student can understand various permeation enhancement strategies for drugs,including chemical and physical methods. Furthermore,they can list the advantages and the disadvantages of transdermal delivery of drugs compared to other forms of drug delivery. 3.3 Suppositories After learning this part,the student can compare and contrast various suppositories dosage forms in terms of physical appearance,size and shape.Understand the advantages and disadvantages of suppository drug deliveryversus oral drug delivery,identify and explain physiologic factors which influence the drug absorption from rectal suppository administration.In addition,they can identify and explain the physicochemical factors of the drug and suppository base as this influence rectal absorption,compare and contrast the various classes of suppository bases.Furthermore,the student is able to describe the three methods of suppository preparation. 课程目标4:Liquid Dosage Forms and Sterile Dosage Forms and Delivery Systems 4.1 Solutions After learning this part,the student can define the various types of oral and topical liquid dosage forms and the advantages and disadvantages of using liquid dosage forms in extemporaneous compounded prescriptions and in patient therapy.After that,they can compare and contrast liquid dosage forms to traditional oral dosage forms,define solubility and describe how different factors increase or decrease solute solubility in a given solvent.Furthermore,the student could evaluate and select a proper solvent and delivery system for a given solute,purpose,and/or patient population. 4.2 Disperse Systems After learning this part,the student can differentiate between a suspension,an emulsion,a gel,and a magma,compare and contrast various disperse systems and list advantages and disadvantages of each system. After that,they can compare and contrast the following emulsification theories:surface tension,oriented-
physiological factors of the skin which influence percutaneous absorption. In addition, the student can understand various permeation enhancement strategies for drugs, including chemical and physical methods. Furthermore, they can list the advantages and the disadvantages of transdermal delivery of drugs compared to other forms of drug delivery. 3. 3 Suppositories After learning this part, the student can compare and contrast various suppositories dosage forms in terms of physical appearance, size and shape. Understand the advantages and disadvantages of suppository drug deliveryversus oral drug delivery, identify and explain physiologic factors which influence the drug absorption from rectal suppository administration. In addition, they can identify and explain the physicochemical factors of the drug and suppository base as this influence rectal absorption, compare and contrast the various classes of suppository bases. Furthermore, the student is able to describe the three methods of suppository preparation. 课程目标 4:Liquid Dosage Forms and Sterile Dosage Forms and Delivery Systems 4.1 Solutions After learning this part, the student can define the various types of oral and topical liquid dosage forms and the advantages and disadvantages of using liquid dosage forms in extemporaneous compounded prescriptions and in patient therapy. After that, they can compare and contrast liquid dosage forms to traditional oral dosage forms, define solubility and describe how different factors increase or decrease solute solubility in a given solvent. Furthermore, the student could evaluate and select a proper solvent and delivery system for a given solute, purpose, and/or patient population. 4.2 Disperse Systems After learning this part, the student can differentiate between a suspension, an emulsion, a gel, and a magma, compare and contrast various disperse systems and list advantages and disadvantages of each system. After that, they can compare and contrast the following emulsification theories: surface tension, oriented-

wedge,and interfacial film.In addition,the students can define and differentiate the following terms from one another:Lyophobic,Lyophilic,Hydrophobic,Hydrophilic,Amphiphilic,Imbibition,Swelling,Syneresis, Thixotropy,and Xerogel. 4.3 Parenterals After learning this part,the student can list the advantages and disadvantages of parenteral administration,define parenteral administration and list the different parenteral methods of administration.After that,they are able to compare and contrast the risks and benefits of the various parenteral routes,identify the challenges of using nonaqueous vehicles in parenteral products.In addition, the students are asked to define osmolality and osmolarity and explain their relationship with the tonicity of a substance,compare and contrast a small-volume and a large-volume parenteral.Furthermore,they can outline the different methods of sterilization for parenteral products,differentiate between single-and multiple-dose packaging requirements. 4.4 Special solutions and suspensions After learning this part,the student will be able to describe ophthalmic,nasal,and inhalation drug delivery,list drugs which are typically administered by each of these drug delivery systems.Secondly,they can explain the advantages/disadvantages of using one of these drug delivery systems over oral administration.Thirdly,the students are asked to describe the use of the various pharmaceutical ad juvants which are employed in the creation of these dosage forms.Fourthly,they can explain the proper administration of each of these drug delivery systems. 课程目标5:Novel and Advanced Dosage Forms,.Delivery Systems,and Devices 5.1 Radiopharmaceuticals After learning this part,the student can Compare and contrast the three principal types of radioactive decay (i.e.. alpha,beta,gamma),compare and contrast the use of radiopharmaceuticals in diagnostics and therapeutics.After that,they can identify the
wedge, and interfacial film. In addition, the students can define and differentiate the following terms from one another: Lyophobic, Lyophilic, Hydrophobic, Hydrophilic, Amphiphilic, Imbibition, Swelling, Syneresis, Thixotropy, and Xerogel. 4.3 Parenterals After learning this part, the student can list the advantages and disadvantages of parenteral administration, define parenteral administration and list the different parenteral methods of administration. After that, they are able to compare and contrast the risks and benefits of the various parenteral routes, identify the challenges of using nonaqueous vehicles in parenteral products. In addition, the students are asked to define osmolality and osmolarity and explain their relationship with the tonicity of a substance, compare and contrast a small-volume and a large-volume parenteral. Furthermore, they can outline the different methods of sterilization for parenteral products, differentiate between single- and multiple-dose packaging requirements. 4.4 Special solutions and suspensions After learning this part, the student will be able to describe ophthalmic, nasal, and inhalation drug delivery, list drugs which are typically administered by each of these drug delivery systems. Secondly, they can explain the advantages/disadvantages of using one of these drug delivery systems over oral administration. Thirdly, the students are asked to describe the use of the various pharmaceutical adjuvants which are employed in the creation of these dosage forms. Fourthly, they can explain the proper administration of each of these drug delivery systems. 课程目标 5:Novel and Advanced Dosage Forms, Delivery Systems, and Devices 5.1 Radiopharmaceuticals After learning this part, the student can compare and contrast the three principal types of radioactive decay (i.e., alpha, beta, gamma), compare and contrast the use of radiopharmaceuticals in diagnostics and therapeutics. After that, they can identify the

diagnostic and/or therapeutic role(s)and delivery method(s)for the commonly used radiopharmaceuticals.In addition,the students can describe the concept and therapeutic utility of positron emission tomography (PET). 5.2 Products of Biotechnology After learning this part,the student will be able to differentiate between the various techniques using living organisms in the production or modification of biotechnology drugs.After that,they can describe the classification of products of biotechnology used in clinical practice,provide examples of biotechnology drugs for each classification of biotechnology drug type.Thirdly,the students can summarize important concepts associated with biotechnology product handling,storage,and administration. 5.3 Novel Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Technologies After learning this part,the student will be able to describe the benefits of new,innovative drug delivery systems,mechanisms utilized to develop new,novel dosage forms and list novel drug delivery systems for each topical,oral,vaginal,ophthalmic,and parenteral route.After that,the student is asked to list drugs which are typically administered by each of these drug delivery systems,explain the advantages each novel delivery system may or may not have over traditional oral administration.Thirdly, they can describe the principles of iontophoresis and phonophoresis,and their benefits in advancing topical drug administration.Furthermore,the student can differentiate between liposomes for parenteral administration,and standard parenteral solutions:describe a situation where liposomes for parenteral administration would be the preferred therapeutic dosage form over standard parenteral solutions. (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系(小四号黑体) 表1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表(五号宋体) 课程 理 子目 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求
diagnostic and/or therapeutic role(s) and delivery method(s) for the commonly used radiopharmaceuticals. In addition, the students can describe the concept and therapeutic utility of positron emission tomography (PET). 5.2 Products of Biotechnology After learning this part, the student will be able to differentiate between the various techniques using living organisms in the production or modification of biotechnology drugs. After that, they can describe the classification of products of biotechnology used in clinical practice, provide examples of biotechnology drugs for each classification of biotechnology drug type. Thirdly, the students can summarize important concepts associated with biotechnology product handling, storage, and administration. 5. 3 Novel Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Technologies After learning this part, the student will be able to describe the benefits of new, innovative drug delivery systems, mechanisms utilized to develop new, novel dosage forms and list novel drug delivery systems for each topical, oral, vaginal, ophthalmic, and parenteral route. After that, the student is asked to list drugs which are typically administered by each of these drug delivery systems, explain the advantages each novel delivery system may or may not have over traditional oral administration. Thirdly, they can describe the principles of iontophoresis and phonophoresis, and their benefits in advancing topical drug administration. Furthermore, the student can differentiate between liposomes for parenteral administration, and standard parenteral solutions; describe a situation where liposomes for parenteral administration would be the preferred therapeutic dosage form over standard parenteral solutions. (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系(小四号黑体) 表 1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 (五号宋体) 课 程 课程 子目 标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求
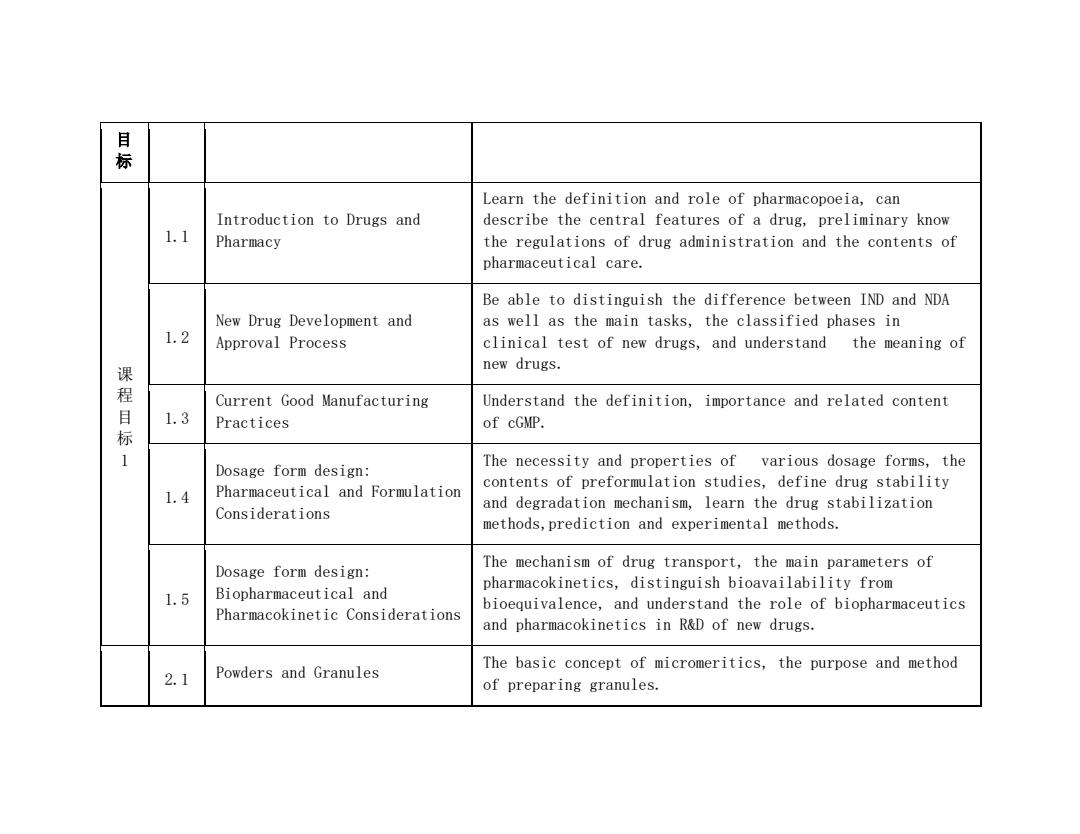
绿 Learn the definition and role of pharmacopoeia,can Introduction to Drugs and describe the central features of a drug,preliminary know 1.1 Pharmacy the regulations of drug administration and the contents of pharmaceutical care. Be able to distinguish the difference between IND and NDA New Drug Development and as well as the main tasks,the classified phases in 1.2 Approval Process clinical test of new drugs,and understand the meaning of new drugs. Current Good Manufacturing Understand the definition,importance and related content 目标 1.3 Practices of cGMP. Dosage form design: The necessity and properties of various dosage forms,the Pharmaceutical and Formulation contents of preformulation studies,define drug stability 1.4 and degradation mechanism,learn the drug stabilization Considerations methods,prediction and experimental methods. Dosage form design: The mechanism of drug transport,the main parameters of pharmacokinetics,distinguish bioavailability from 1.5 Biopharmaceutical and bioequivalence,and understand the role of biopharmaceutics Pharmacokinetic Considerations and pharmacokinetics in R&D of new drugs. The basic concept of micromeritics,the purpose and method 2.1 Powders and Granules of preparing granules
目 标 课 程 目 标 1 1.1 Introduction to Drugs and Pharmacy Learn the definition and role of pharmacopoeia, can describe the central features of a drug, preliminary know the regulations of drug administration and the contents of pharmaceutical care. 1.2 New Drug Development and Approval Process Be able to distinguish the difference between IND and NDA as well as the main tasks, the classified phases in clinical test of new drugs, and understand the meaning of new drugs. 1.3 Current Good Manufacturing Practices Understand the definition, importance and related content of cGMP. 1.4 Dosage form design: Pharmaceutical and Formulation Considerations The necessity and properties of various dosage forms, the contents of preformulation studies, define drug stability and degradation mechanism, learn the drug stabilization methods,prediction and experimental methods. 1.5 Dosage form design: Biopharmaceutical and Pharmacokinetic Considerations The mechanism of drug transport, the main parameters of pharmacokinetics, distinguish bioavailability from bioequivalence, and understand the role of biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics in R&D of new drugs. 2.1 Powders and Granules The basic concept of micromeritics, the purpose and method of preparing granules

The concept,characteristics,preparation method and 2.2 Capsules quality control of capsules. 课程 Concept,characteristics,common excipients,preparation Tablets 2.3 methods and quality control standards of tablets. 标 Solid Oral Modified-release Define various types of modified-release dosage forms and 2.4 Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery characteristics,and learn how to prepare and quality Systems control. Differentiate between the various types of semisolid bases 3.1 Ointments, Creams,and Gels on the basis of physicochemical properties. 课程 Transdermal Drug Delivery Definition and characteristics of transdermal drug delivery 3.2 system,factors affecting transdermal drug absorption and System methods of enhancing drug absorption. 标3 Definition and characteristics of rectal 3.3 Suppositories suppositories,routes of drug absorption,common bases, preparation methods and quality control criteria. Definition and determination method of drug solubility, commonly used medicinal solvents,definition and 课程目 4.1 Solutions characteristics of commonly used liquid preparations, including syrup,elixir,tincture:method of drug extraction
课 程 目 标 2 2.2 Capsules The concept, characteristics, preparation method and quality control of capsules. 2.3 Tablets Concept, characteristics, common excipients, preparation methods and quality control standards of tablets. 2.4 Solid Oral Modified-release Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems Define various types of modified-release dosage forms and characteristics,and learn how to prepare and quality control. 课 程 目 标 3 3.1 Ointments, Creams, and Gels Differentiate between the various types of semisolid bases on the basis of physicochemical properties. 3.2 Transdermal Drug Delivery System Definition and characteristics of transdermal drug delivery system, factors affecting transdermal drug absorption and methods of enhancing drug absorption. 3.3 Suppositories Definition and characteristics of rectal suppositories,routes of drug absorption, common bases, preparation methods and quality control criteria. 课 程 目 4.1 Solutions Definition and determination method of drug solubility, commonly used medicinal solvents, definition and characteristics of commonly used liquid preparations, including syrup, elixir, tincture;method of drug extraction
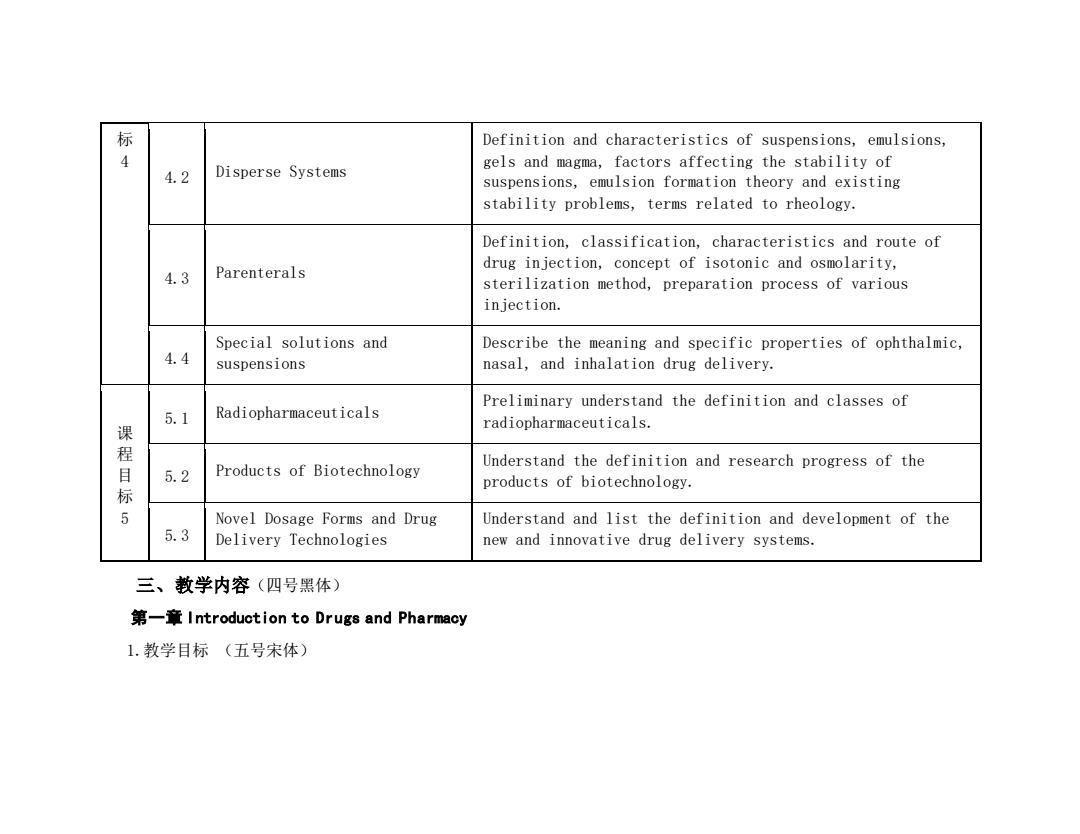
标 Definition and characteristics of suspensions,emulsions, gels and magma,factors affecting the stability of 4.2 Disperse Systems suspensions,emulsion formation theory and existing stability problems,terms related to rheology. Definition,classification,characteristics and route of drug injection,concept of isotonic and osmolarity, 4.3 Parenterals sterilization method,preparation process of various injection. Special solutions and Describe the meaning and specific properties of ophthalmic, 4.4 suspensions nasal,and inhalation drug delivery. Preliminary understand the definition and classes of 5.1 Radiopharmaceuticals radiopharmaceuticals. 课程目标 Products of Biotechnology Understand the definition and research progress of the 5.2 products of biotechnology. Novel Dosage Forms and Drug Understand and list the definition and development of the 5.3 Delivery Technologies new and innovative drug delivery systems. 三、教学内容(四号黑体) 第一章Introduction to Drugs and Pharmacy 1.教学目标(五号宋体)
标 4 4.2 Disperse Systems Definition and characteristics of suspensions, emulsions, gels and magma, factors affecting the stability of suspensions, emulsion formation theory and existing stability problems, terms related to rheology. 4.3 Parenterals Definition, classification, characteristics and route of drug injection, concept of isotonic and osmolarity, sterilization method, preparation process of various injection. 4.4 Special solutions and suspensions Describe the meaning and specific properties of ophthalmic, nasal, and inhalation drug delivery. 课 程 目 标 5 5.1 Radiopharmaceuticals Preliminary understand the definition and classes of radiopharmaceuticals. 5.2 Products of Biotechnology Understand the definition and research progress of the products of biotechnology. 5.3 Novel Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Technologies Understand and list the definition and development of the new and innovative drug delivery systems. 三、教学内容(四号黑体) 第一章 Introduction to Drugs and Pharmacy 1.教学目标 (五号宋体)

Define the pharmacy,pharmaceutics and pharmacopoeia,the contents of pharmaceutical care,the ethical code for pharmaceutical researchers,understand the regulations and laws related to drug administration. 2.教学重难点 教学重点:Definition of pharmaceutics,pharmacopoeia,l pharmaceutical care. 教学难点:The regulations and laws related to drug administration,pharmaceutical care. 3.教学内容 (1)The heritage of pharmacy,(2)Drug standards,(3)Drug regulation and control,(4)The pharmacist's contemporary role,(5)Code of ethics for pharmacists of the American Pharmacists Association,(6)Code of ethics of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists. 4.教学方法 (1)Teaching method:Relevant concepts and theoretical framework. (2)Discussion method:The use of heuristic teaching. 5.教学评价 Quick summary test and discuss selected frequently asked questions. 第二章New Drug Deve lopment and Approval Process 1.教学目标(五号宋体) Define an investigational new drug (IND)application from a new drug application (NDA),understand the differences between phase I,phase II,phase III,and phase IV clinical trials,International Conference on Harmonization (ICH)of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. 2.教学重难点
Define the pharmacy, pharmaceutics and pharmacopoeia, the contents of pharmaceutical care, the ethical code for pharmaceutical researchers,understand the regulations and laws related to drug administration. 2.教学重难点 教学重点:Definition of pharmaceutics, pharmacopoeia, pharmaceutical care. 教学难点:The regulations and laws related to drug administration, pharmaceutical care. 3.教学内容 (1) The heritage of pharmacy, (2) Drug standards, (3) Drug regulation and control, (4) The pharmacist's contemporary role, (5) Code of ethics for pharmacists of the American Pharmacists Association, (6) Code of ethics of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists. 4.教学方法 (1) Teaching method: Relevant concepts and theoretical framework. (2) Discussion method: The use of heuristic teaching. 5.教学评价 Quick summary test and discuss selected frequently asked questions. 第二章 New Drug Development and Approval Process 1.教学目标 (五号宋体) Define an investigational new drug (IND) application from a new drug application (NDA), understand the differences between phase I, phase II, phase III, and phase IV clinical trials,International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. 2.教学重难点