《Microbiology&Immunology》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 (2020-2021-2)-PHAR1115-1 英文名称 Microbiology Immunology 课程代码 9WZ15-1 课程性质 专业必修课程 授课对象 2019级药学全英班 学 分 3 学 时 54 郑毅然(9课时)/滕昕辰(9课时)1 主讲教师 应征(9课时)/任洪枫(9课时)王 修订日期 2021/06/17 媛(9课时)/刘密(9课时) Foundations in Microbiology 10曲Edition,.Talaro,Chess主编 指定教材 Kuby Immunology 7th Edition,Owen,Punt,Stranford 二、课程目标(四号黑体) (一)总体目标:(小四号黑体) 《Microbiology&Immunology》是药学英文班专业必修课程。课程以英文为教学媒体, 旨在让学生对微生物与人体免疫学形成整体学科认识,了解学科的发展历史、主要研究领域、 常用技术和应用范围,熟悉学科相关知识体系,为学科专业知识的深入学习和后续药理学相 关课程和酶工程等微生物应用课程的学习打下必要的专业基础。学科教育遵循“三基”(基础 理论、基本知识、基本技能),“五性”(思想性、科学性、启发性、先进性、适用性)的原 则,密切结合药学专业本科的培养目标,选取实用、适合的国际教材和领域最新进展,夯实 学生关于微生物与免疫学的理论基础,提高学生英文听说读写能力,培养学生的拓展思维和 综合学习能力,为提高学生理解、应用药物新技术和研发新药的能力提供支撑。 (二)课程目标: (课程目标规定某一阶段的学生通过课程学习以后,在发展德、智、体、美、劳等方面 期望实现的程度,它是确定课程内容、教学目标和教学方法的基础。)(五号宋体) 该课程的基本任务是使学生掌握微生物学与免疫学的基础理论知识、常用技术及应用, 为进一步学习分子生物学、药理学等课程打下良好基础,同时为未来从事开发研制与人体免 疫系统和微生物有关的药物、药品质量控制与保管等方面做基础知识和技术储备。 课程目标1: 通过学习微生物学,使学生掌握细菌、真菌、病毒等微生物的结构和生物学性状,了解 各类微生物的营养、生长、代谢、遗传与变异和致病机理,了解消毒与灭菌、感染诊治与防
《Microbiology & Immunology》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Microbiology & Immunology 课程代码 (2020-2021-2)-PHAR1115-1 9WZ15-1 课程性质 专业必修课程 授课对象 2019 级药学全英班 学 分 3 学 时 54 主讲教师 郑毅然(9 课时)/滕昕辰(9 课时)/ 应征(9 课时)/王洪枫(9 课时)/王 媛(9 课时)/刘密(9 课时) 修订日期 2021/06/17 指定教材 Foundations in Microbiology 10 th Edition, Talaro, Chess 主编 Kuby Immunology 7 th Edition,Owen,Punt,Stranford 主编 二、课程目标(四号黑体) (一)总体目标:(小四号黑体) 《Microbiology & Immunology》是药学英文班专业必修课程。课程以英文为教学媒体, 旨在让学生对微生物与人体免疫学形成整体学科认识,了解学科的发展历史、主要研究领域、 常用技术和应用范围,熟悉学科相关知识体系,为学科专业知识的深入学习和后续药理学相 关课程和酶工程等微生物应用课程的学习打下必要的专业基础。学科教育遵循“三基”(基础 理论、基本知识、基本技能),“五性”(思想性、科学性、启发性、先进性、适用性)的原 则,密切结合药学专业本科的培养目标,选取实用、适合的国际教材和领域最新进展,夯实 学生关于微生物与免疫学的理论基础,提高学生英文听说读写能力,培养学生的拓展思维和 综合学习能力,为提高学生理解、应用药物新技术和研发新药的能力提供支撑。 (二)课程目标: (课程目标规定某一阶段的学生通过课程学习以后,在发展德、智、体、美、劳等方面 期望实现的程度,它是确定课程内容、教学目标和教学方法的基础。)(五号宋体) 该课程的基本任务是使学生掌握微生物学与免疫学的基础理论知识、常用技术及应用, 为进一步学习分子生物学、药理学等课程打下良好基础,同时为未来从事开发研制与人体免 疫系统和微生物有关的药物、药品质量控制与保管等方面做基础知识和技术储备。 课程目标 1: 通过学习微生物学,使学生掌握细菌、真菌、病毒等微生物的结构和生物学性状,了解 各类微生物的营养、生长、代谢、遗传与变异和致病机理,了解消毒与灭菌、感染诊治与防

护的方法和科学原理,为后续药理学和酶工程等微生物应用课程的学习打下必要的专业知识 基础。 课程目标2: 通过学习免疫学,使学生掌握抗原抗体、免疫分子和免疫细胞的结构特征和生物学功能, 掌握T细胞和B细胞等免疫细胞在机体中的分化发育过程和各细胞亚群的功能,熟悉免疫 应答和超敏反应的科学原理和相关临床免疫学基础知识,了解新型实用免疫学技术,形成基 本的学科素养,为药理学深入学习和新药设计打下理论基础。 课程目标3: 通过对本课程的学习,使学生了解免疫学与微生物学的发展现状和主要待解决问题,了 解微生物及其相关产物在维持生态稳态、污水处理、食品加工、药物制备中的应用,了解免 疫学在肿瘤、自身免疫性疾病和脑神经疾病诊疗中的应用。激发学生对免疫学和微生物学的 兴趣和学科认同感,培养学生在学科领域提出科学问题并进行初步探索的能力,促进学生进 一步参加学科相关的科研和实践工作。 课程目标4: 提高学生英文听说读写能力,使其熟悉免疫学和微生物学中的英文专业术语,培养学生 文献搜索能力、自学能力、综合分析能力、创新思维能力、英文论文写作能力。 (要求参照《普通高等学校本科专业类教学质量国家标准》,对应各类专业认证标准, 注意对毕业要求支撑程度强弱的描述,与“课程目标对毕业要求的支撑关系表一致) (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系(小四号黑体) 表1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表(五号宋体) 课程目标 课程子目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 第一章Microbiology introduction 第二章Microbiology physiology and introduction to immunology 1.1掌握细菌结构、 第十章Basic knowledge of bacteria: 生物学性状、生长 掌握细菌相关药理学 1.掌握微 繁殖、致病机理和 gram-positive and negative cocci I 基本概念和基础理论 生物学相关 防治措施 第十一章Gram-positive and negative 基础知识 cocciII 第十二章Gram-positive and negative cocciIII 1.2掌握真菌结构、 第十三章Fungi 掌握真菌相关药理学 生物学性状、生长
护的方法和科学原理,为后续药理学和酶工程等微生物应用课程的学习打下必要的专业知识 基础。 课程目标 2: 通过学习免疫学,使学生掌握抗原抗体、免疫分子和免疫细胞的结构特征和生物学功能, 掌握 T 细胞和 B 细胞等免疫细胞在机体中的分化发育过程和各细胞亚群的功能,熟悉免疫 应答和超敏反应的科学原理和相关临床免疫学基础知识,了解新型实用免疫学技术,形成基 本的学科素养,为药理学深入学习和新药设计打下理论基础。 课程目标 3: 通过对本课程的学习,使学生了解免疫学与微生物学的发展现状和主要待解决问题,了 解微生物及其相关产物在维持生态稳态、污水处理、食品加工、药物制备中的应用,了解免 疫学在肿瘤、自身免疫性疾病和脑神经疾病诊疗中的应用。激发学生对免疫学和微生物学的 兴趣和学科认同感,培养学生在学科领域提出科学问题并进行初步探索的能力,促进学生进 一步参加学科相关的科研和实践工作。 课程目标 4: 提高学生英文听说读写能力,使其熟悉免疫学和微生物学中的英文专业术语,培养学生 文献搜索能力、自学能力、综合分析能力、创新思维能力、英文论文写作能力。 (要求参照《普通高等学校本科专业类教学质量国家标准》,对应各类专业认证标准, 注意对毕业要求支撑程度强弱的描述,与“课程目标对毕业要求的支撑关系表一致) (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系(小四号黑体) 表 1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表(五号宋体) 课程目标 课程子目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 1. 掌 握 微 生物学相关 基础知识 1.1 掌握细菌结构、 生物学性状、生长 繁殖、致病机理和 防治措施 第一章 Microbiology introduction 第二章 Microbiology physiology and introduction to immunology 第十章 Basic knowledge of bacteria: gram-positive and negative cocci Ⅰ 第十一章 Gram-positive and negative cocci II 第十二章 Gram-positive and negative cocci III 掌握细菌相关药理学 基本概念和基础理论 1.2 掌握真菌结构、 生物学性状、生长 第十三章 Fungi 掌握真菌相关药理学
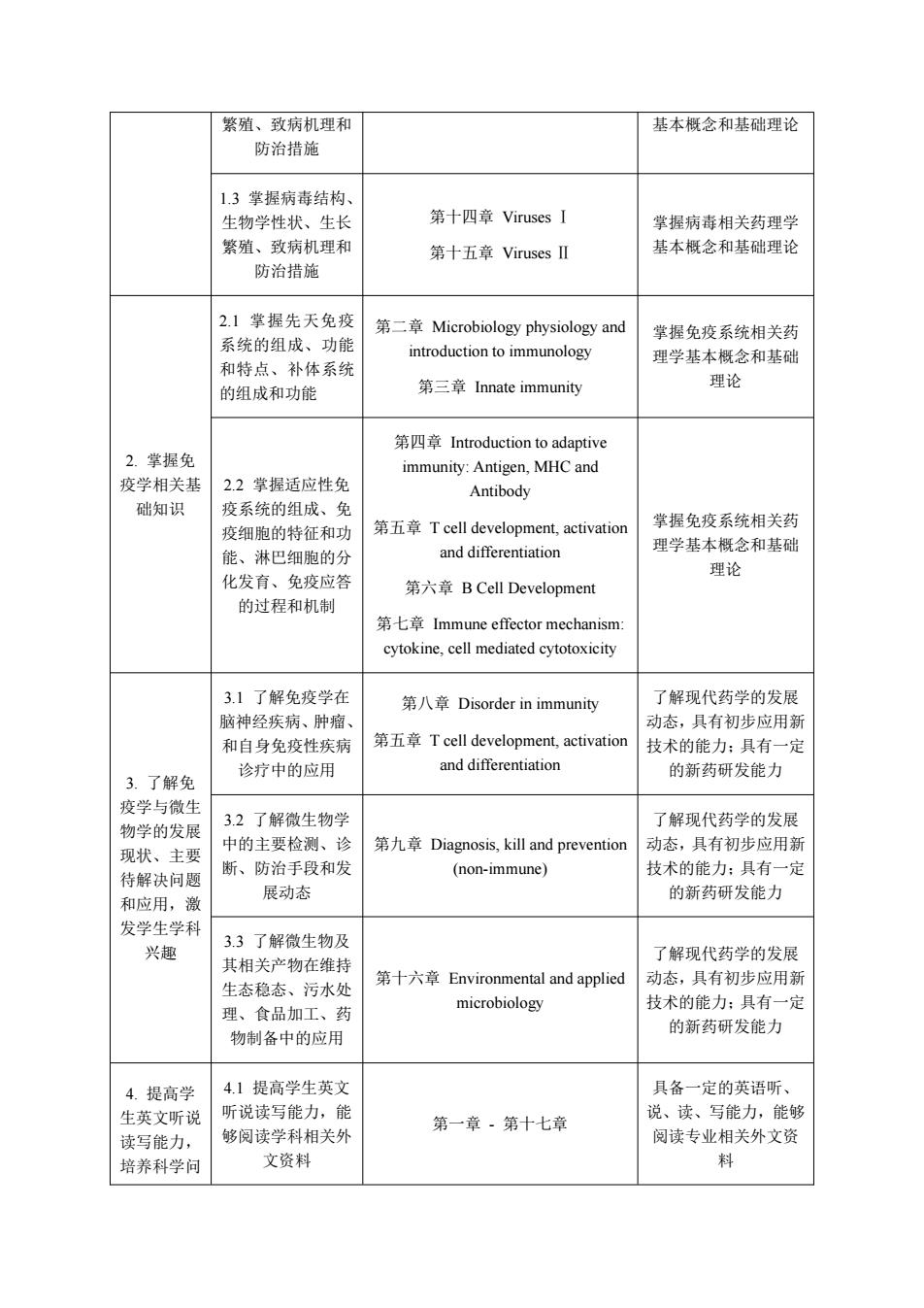
繁殖、致病机理和 基本概念和基础理论 防治措施 1.3掌握病毒结构、 生物学性状、生长 第十四章Viruses I 掌握病毒相关药理学 繁殖、致病机理和 第十五章VirusesⅡ 基本概念和基础理论 防治措施 2.1掌握先天免疫 第二章Microbiology physiology and 掌握免疫系统相关药 系统的组成、功能 introduction to immunology 理学基本概念和基础 和特点、补体系统 第三章nnate immunity 理论 的组成和功能 第四章Introduction to adaptive 2.掌握免 immunity:Antigen,MHC and 疫学相关基 2.2掌握适应性免 Antibody 础知识 疫系统的组成、免 第五章T cell development,.activation 掌握免疫系统相关药 疫细胞的特征和功 能、淋巴细胞的分 and differentiation 理学基本概念和基础 理论 化发育、免疫应答 第六章B Cell Development 的过程和机制 第七章Immune effector mechanism: cytokine,cell mediated cytotoxicity 3.1了解免疫学在 第八章Disorder in immunity 了解现代药学的发展 脑神经疾病、肿瘤、 动态,具有初步应用新 和自身免疫性疾病 第五章T cell development,activation 技术的能力:具有一定 诊疗中的应用 and differentiation 的新药研发能力 3.了解免 疫学与微生 3.2了解微生物学 了解现代药学的发展 物学的发展 中的主要检测、诊 第九章Diagnosis,,kill and prevention 动态,具有初步应用新 现状、主要 断、防治手段和发 (non-immune) 技术的能力:具有一定 待解决问题 展动态 的新药研发能力 和应用,激 发学生学科 兴趣 3.3了解微生物及 其相关产物在维持 了解现代药学的发展 生态稳态、污水处 第十六章Environmental and applied 动态,具有初步应用新 理、食品加工、药 microbiology 技术的能力:具有一定 的新药研发能力 物制备中的应用 4.提高学 4.1提高学生英文 具备一定的英语听、 生英文听说 听说读写能力,能 说、读、写能力,能够 第一章·第十七章 读写能力, 够阅读学科相关外 阅读专业相关外文资 培养科学问 文资料 料
繁殖、致病机理和 防治措施 基本概念和基础理论 1.3 掌握病毒结构、 生物学性状、生长 繁殖、致病机理和 防治措施 第十四章 Viruses Ⅰ 第十五章 Viruses Ⅱ 掌握病毒相关药理学 基本概念和基础理论 2. 掌握免 疫学相关基 础知识 2.1 掌握先天免疫 系统的组成、功能 和特点、补体系统 的组成和功能 第二章 Microbiology physiology and introduction to immunology 第三章 Innate immunity 掌握免疫系统相关药 理学基本概念和基础 理论 2.2 掌握适应性免 疫系统的组成、免 疫细胞的特征和功 能、淋巴细胞的分 化发育、免疫应答 的过程和机制 第四章 Introduction to adaptive immunity: Antigen, MHC and Antibody 第五章 T cell development, activation and differentiation 第六章 B Cell Development 第七章 Immune effector mechanism: cytokine, cell mediated cytotoxicity 掌握免疫系统相关药 理学基本概念和基础 理论 3. 了解免 疫学与微生 物学的发展 现状、主要 待解决问题 和应用,激 发学生学科 兴趣 3.1 了解免疫学在 脑神经疾病、肿瘤、 和自身免疫性疾病 诊疗中的应用 第八章 Disorder in immunity 第五章 T cell development, activation and differentiation 了解现代药学的发展 动态,具有初步应用新 技术的能力;具有一定 的新药研发能力 3.2 了解微生物学 中的主要检测、诊 断、防治手段和发 展动态 第九章 Diagnosis, kill and prevention (non-immune) 了解现代药学的发展 动态,具有初步应用新 技术的能力;具有一定 的新药研发能力 3.3 了解微生物及 其相关产物在维持 生态稳态、污水处 理、食品加工、药 物制备中的应用 第十六章 Environmental and applied microbiology 了解现代药学的发展 动态,具有初步应用新 技术的能力;具有一定 的新药研发能力 4. 提高学 生英文听说 读写能力, 培养科学问 4.1 提高学生英文 听说读写能力,能 够阅读学科相关外 文资料 第一章 - 第十七章 具备一定的英语听、 说、读、写能力,能够 阅读专业相关外文资 料

题的解决能 掌握文献搜索、资料查 力 4.2培养科学问题 的解决能力 第十七章Writing informative essay 询的基本方法,具有一 定的科学研究能力 (大类基础课程、专业教学课程及开放选修课程按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕业 要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。通识教育课程含通识选修课程、新生研讨课程及公共基础课程, 面向专业为工科、师范、医学等有专业认证标准的专业,按照专业认证通用标准填写“对应 毕业要求”栏:面向其他尚未有专业认证标准的专业,按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕 业要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。) 三、教学内容(四号黑体) (具体描述各章节教学目标、教学内容等。实验课程可按实验模块描述) 第-章Microbiology introduction(Yuan Wang) 1.教学目标 To understand the basic concepts of microbe and microbiology To understand the methods,goals and advantages of microbiology studying To understand the scope of microbes and general characteristics and cell structures of microorganisms To know about the relationship between microbes and human 2.教学重难点 2.1.教学重点 General classification of microorganisms Cell structures of different microbes 2.2教学难点 The similarity and difference of the cell structures and organelles functions of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells The general methods to investigate and study microbes 3.教学内容 3.1.Introduction of microbe and microbiology Definition of microbe and microbiology General Characteristics of Microorganisms and Their applications The Cellular Organization of Microorganisms Microbial Dimensions Human Use of Microorganisms
题的解决能 力 4.2 培养科学问题 的解决能力 第十七章 Writing informative essay 掌握文献搜索、资料查 询的基本方法,具有一 定的科学研究能力 (大类基础课程、专业教学课程及开放选修课程按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕业 要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。通识教育课程含通识选修课程、新生研讨课程及公共基础课程, 面向专业为工科、师范、医学等有专业认证标准的专业,按照专业认证通用标准填写“对应 毕业要求”栏;面向其他尚未有专业认证标准的专业,按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕 业要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。) 三、教学内容(四号黑体) (具体描述各章节教学目标、教学内容等。实验课程可按实验模块描述) 第一章 Microbiology introduction (Yuan Wang) 1.教学目标 • To understand the basic concepts of microbe and microbiology • To understand the methods, goals and advantages of microbiology studying • To understand the scope of microbes and general characteristics and cell structures of microorganisms • To know about the relationship between microbes and human 2.教学重难点 2.1.教学重点 • General classification of microorganisms • Cell structures of different microbes 2.2.教学难点 • The similarity and difference of the cell structures and organelles functions of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells • The general methods to investigate and study microbes 3.教学内容 3.1. Introduction of microbe and microbiology • Definition of microbe and microbiology • General Characteristics of Microorganisms and Their applications • The Cellular Organization of Microorganisms • Microbial Dimensions • Human Use of Microorganisms

General classification of Microorganisms Microbial Roles in Infectious Diseases Evolution of Microorganisms Methods of Microbial Investigation 3.2.Prokaryotic Cells and Microorganisms Prokaryotic Profiles:The Bacteria and Archaea The Structure of a Generalized Bacterial Cell Cell Extensions and Surface Structures:Flagellum,Fimbriae and Pili,Bacterial Surface Coating,or Glycocalyx The Cell Envelope,Structure of Cell Walls,The Gram-Positive Cell Wall, Gram-negative Cell Wall Cell Membrane Structure Bacterial Internal Structure:Cell Cytoplasm (Chromosomes and Plasmids,Ribosomes. inclusions,Cytoskeleton,bacterial endospore ·Bacterial Shapes ·Other Prokaryotes 3.3.Eukaryotic Cells and Microorganisms External Structures:Cilia and Flagella,The Glycocalyx,Cell Wall,Cytoplasmic Membrane Internal Structures:Nucleus Internal Structures:Endoplasmic Reticulum,Golgi Apparatus,Mitochondria. Chloroplasts Ribosomes:Protein Synthesizers Cytoskeleton Eukaryotic-Prokaryotic Comparisons Fungi:Organization of Microscopic Fungi,Reproductive Strategies and Spore Formation Protists:Algae,Protozoa The Parasitic Helminths 4.教学方法 4.1.多媒体教学 Examples of common microbes and their sizes comparation Illustrations of cellular organelles and unique structures of microbes Work on problems with students together to emphasize the basic principles covered in the chapter 4.2.互动教学
• General classification of Microorganisms • Microbial Roles in Infectious Diseases • Evolution of Microorganisms • Methods of Microbial Investigation 3.2. Prokaryotic Cells and Microorganisms • Prokaryotic Profiles: The Bacteria and Archaea • The Structure of a Generalized Bacterial Cell • Cell Extensions and Surface Structures: Flagellum, Fimbriae and Pili, Bacterial Surface Coating, or Glycocalyx • The Cell Envelope, Structure of Cell Walls, The Gram-Positive Cell Wall, Gram-negative Cell Wall • Cell Membrane Structure • Bacterial Internal Structure: Cell Cytoplasm (Chromosomes and Plasmids, Ribosomes, inclusions, Cytoskeleton, bacterial endospore • Bacterial Shapes • Other Prokaryotes 3.3. Eukaryotic Cells and Microorganisms • External Structures: Cilia and Flagella, The Glycocalyx, Cell Wall, Cytoplasmic Membrane • Internal Structures: Nucleus • Internal Structures: Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts • Ribosomes: Protein Synthesizers • Cytoskeleton • Eukaryotic-Prokaryotic Comparisons • Fungi: Organization of Microscopic Fungi, Reproductive Strategies and Spore Formation • Protists: Algae, Protozoa • The Parasitic Helminths 4.教学方法 4.1.多媒体教学 • Examples of common microbes and their sizes comparation • Illustrations of cellular organelles and unique structures of microbes • Work on problems with students together to emphasize the basic principles covered in the chapter 4.2.互动教学

Strat the lesson with some quick questions to give rise the interest of students,then followed by introducing basic concepts Discuss the complicated knowledge points Solve problems together with students 5.教学评价 Review and answer the following questions What are the basic characteristics of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? What the cellular makeup of microorganisms and their size range?and indicate how viruses differ from cellular microbes. What is the generalized anatomy of bacterial cells? What is the structure and functions of cell walls?and what is the role of peptidoglycan? Review the major differences and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 第二章Microbiology physiology and introduction to immunology(Yuan Wang) 1教学目标 To understand and grasp the microbial(bacterial)growth and metabolism To understand and grasp the principles of bacterial genetics To understand the basic functions and constitutes of immune system 2.教学重难点 2.1.教学重点 Bacterial population growth Bacterial DNA replication Basic concepts of immunology and immune system 2.2.教学难点: The process and enzymes involved in bacterial DNA replication The relationship of immune organs,cells and molecules of immune system 3教学内容 3.1.Microbial Nutrition,Growth,and Metabolism Forms,Sources,and Functions of Essential Nutrients Environmental Factors That Influence Microbes ·Microbial Growth The Basis of Population Growth:Binary Fission Bacterial Cell Cycle The Rate of Population Growth
• Strat the lesson with some quick questions to give rise the interest of students, then followed by introducing basic concepts • Discuss the complicated knowledge points • Solve problems together with students 5.教学评价 Review and answer the following questions • What are the basic characteristics of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? • What the cellular makeup of microorganisms and their size range? and indicate how viruses differ from cellular microbes. • What is the generalized anatomy of bacterial cells? • What is the structure and functions of cell walls? and what is the role of peptidoglycan? • Review the major differences and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 第二章 Microbiology physiology and introduction to immunology (Yuan Wang) 1.教学目标 • To understand and grasp the microbial(bacterial) growth and metabolism • To understand and grasp the principles of bacterial genetics • To understand the basic functions and constitutes of immune system 2.教学重难点 2.1.教学重点 • Bacterial population growth • Bacterial DNA replication • Basic concepts of immunology and immune system 2.2.教学难点: • The process and enzymes involved in bacterial DNA replication • The relationship of immune organs, cells and molecules of immune system 3.教学内容 3.1. Microbial Nutrition, Growth, and Metabolism • Forms, Sources, and Functions of Essential Nutrients • Environmental Factors That Influence Microbes • Microbial Growth • The Basis of Population Growth: Binary Fission • Bacterial Cell Cycle • The Rate of Population Growth

Determinants of Population Growth Introduction to Metabolism and Enzymes Fermentation 3.2.Microbial Genetics The process of DNA replication in prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic Transcription and Translation Operon:A Model for Inducible Gene Regulation in Bacteria Mutations,Categories of Mutations,Repair of Mutations DNA Recombination in Bacteria The Genetics of Animal Viruses Genetic Engineering:Technical Aspects of Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning 3.3.Introduction to immunology Concept of immunology and immune system Basic function of immune system Constitutes of immune system Concept of immune response,types and features of immune response Applications of immunology Organs and tissues in immune system Cells and molecules in immune system 4.教学方法 4.1.多媒体教学 Examples and explanation of certain phenomenon involving the bacterial growth and metabolism Illustrations of bacterial growth,fermentation,nutrients and DNA replication Use cartoons to describe the functions and concepts of immune system 4.2.互动教学 Discuss the COVID-19 infection case to introduce the immunology concepts and functions Discuss the complicated knowledge points Solve problems together with students 5.教学评价 Review and answer the following questions What is microbial growth?Explain the stages in the bacterial cell cycle and binary fission. What is an operon?Describe the functions of regulators,promoters,and operators
• Determinants of Population Growth • Introduction to Metabolism and Enzymes • Fermentation 3.2. Microbial Genetics • The process of DNA replication in prokaryotic cells • Eukaryotic Transcription and Translation • Operon: A Model for Inducible Gene Regulation in Bacteria • Mutations, Categories of Mutations, Repair of Mutations • DNA Recombination in Bacteria • The Genetics of Animal Viruses • Genetic Engineering: Technical Aspects of Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning 3.3. Introduction to immunology • Concept of immunology and immune system • Basic function of immune system • Constitutes of immune system • Concept of immune response, types and features of immune response • Applications of immunology • Organs and tissues in immune system • Cells and molecules in immune system 4.教学方法 4.1.多媒体教学 • Examples and explanation of certain phenomenon involving the bacterial growth and metabolism • Illustrations of bacterial growth, fermentation, nutrients and DNA replication • Use cartoons to describe the functions and concepts of immune system 4.2.互动教学 • Discuss the COVID-19 infection case to introduce the immunology concepts and functions • Discuss the complicated knowledge points • Solve problems together with students 5.教学评价 Review and answer the following questions • What is microbial growth? Explain the stages in the bacterial cell cycle and binary fission. • What is an operon? Describe the functions of regulators, promoters, and operators

Compare conjugation,transformation,and transduction on the basis of general method, donor,and recipient. What is the basic function of immune system? Can you list the important molecules which play function in immune responses?And can you differentiate them which are cell surface molecules and which of them are secreted proteins? 第三章Innate immunity(Yuan Wang) 1.教学目标 To understand the principles of host defense and immune responses To understand the process and functions of innate immunity(inflammation, phagocytosis,interferons) To understand and grasp the function and mechanism of complement system 2教学重难点 2.1.教学重点 3 activation pathways of complement system Functions of complement system 2.2.教学难点 The procedures of complement activation The regulation mechanisms of complement activation 3教学内容 3.1.Introduction to host defense and innate immunity The characteristics of basic host defenses Introduction of three lines of host defense First line of host defense:different barriers'components,structure and functions Introduction of innate and acquired immunity The organs,tissues and cells'in innate immune system Leukocytes'functions and mechanism in innate immunity 3.2.Innate immunity-Inflammation,Phagocytosis,Interferon The Inflammatory Response and its features The process and stages of Inflammation Inflammatory Mediators,their functions and mechanisms Phagocytosis:Phagocytes,Phases Interferon:Types,roles and mechanisms 3.3.Innate immunity-Complement
• Compare conjugation, transformation, and transduction on the basis of general method, donor, and recipient. • What is the basic function of immune system? • Can you list the important molecules which play function in immune responses? And can you differentiate them which are cell surface molecules and which of them are secreted proteins? 第三章 Innate immunity (Yuan Wang) 1.教学目标 • To understand the principles of host defense and immune responses • To understand the process and functions of innate immunity (inflammation, phagocytosis, interferons) • To understand and grasp the function and mechanism of complement system 2.教学重难点 2.1.教学重点 • 3 activation pathways of complement system • Functions of complement system 2.2.教学难点 • The procedures of complement activation • The regulation mechanisms of complement activation 3.教学内容 3.1. Introduction to host defense and innate immunity • The characteristics of basic host defenses • Introduction of three lines of host defense • First line of host defense: different barriers’ components, structure and functions • Introduction of innate and acquired immunity • The organs, tissues and cells’ in innate immune system • Leukocytes’ functions and mechanism in innate immunity 3.2. Innate immunity-Inflammation, Phagocytosis, Interferon • The Inflammatory Response and its features • The process and stages of Inflammation • Inflammatory Mediators, their functions and mechanisms • Phagocytosis: Phagocytes, Phases • Interferon: Types, roles and mechanisms 3.3. Innate immunity-Complement

Complement introduction:components,terms,and features Complement activation pathways:classic,MB-lectin and alternative pathways Complement functions:cytosis,opsonization,immune complex clearance,inflammatory mediators,involvement in acquired immune responses Complement activation regulation 4教学方法 4.1.多媒体教学 Examples and explanation of certain inflammations Introduce the story how the complement system was found and investigated by scientist to heighten the curiosity and interest of students 4.2.互动教学 Draw the schematic diagram with students to better understand the cascade of complement activation Discuss the complicated knowledge points Solve problems together with students 5教学评价 Review and answer the following questions: What is the difference between innate and acquired immunity?What are the general characteristics of each? How does the immune system distinguish self from foreign cells and particles? What is the cascade in the 3 complement activation pathways? What are the basic functions of complement system? How the complement activation is regulated? 第四章Adaptive immunity:Antigen,.MHC and Antibody(Yiran Zheng) 1.教学目标 Know the similarities and differences between innate and adaptive immune system Grasp the definition of antigens,factors contributing to antigenicity,the different types of antigens and their respective function Know the structure and function of MHC molecules Understand the origin of diversity for MHC molecules and the biological significance for such diversity Know the endogenous and exogenous antigen presentation pathways and understand the different function the two antigen presentation pathways Know the structure of antibodies.main classes of antibodies and their characteristic structure and function
• Complement introduction: components, terms, and features • Complement activation pathways: classic, MB-lectin and alternative pathways • Complement functions: cytosis, opsonization, immune complex clearance, inflammatory mediators, involvement in acquired immune responses • Complement activation regulation 4.教学方法 4.1.多媒体教学 • Examples and explanation of certain inflammations • Introduce the story how the complement system was found and investigated by scientist to heighten the curiosity and interest of students 4.2.互动教学 • Draw the schematic diagram with students to better understand the cascade of complement activation • Discuss the complicated knowledge points • Solve problems together with students 5.教学评价 Review and answer the following questions: • What is the difference between innate and acquired immunity? What are the general characteristics of each? • How does the immune system distinguish self from foreign cells and particles? • What is the cascade in the 3 complement activation pathways? • What are the basic functions of complement system? • How the complement activation is regulated? 第四章 Adaptive immunity: Antigen, MHC and Antibody (Yiran Zheng) 1.教学目标 • Know the similarities and differences between innate and adaptive immune system • Grasp the definition of antigens, factors contributing to antigenicity, the different types of antigens and their respective function • Know the structure and function of MHC molecules • Understand the origin of diversity for MHC molecules and the biological significance for such diversity • Know the endogenous and exogenous antigen presentation pathways and understand the different function the two antigen presentation pathways • Know the structure of antibodies, main classes of antibodies and their characteristic structure and function

2教学重难点 The difference between innate and adaptive immune system and why we need both systems The structural and functional difference between MHC class I and class II molecules The characteristic structure and function of the five main classes of antibodies 3.教学内容 3.1.Overview of adaptive immunity Similarities and differences between innate and adaptive immune system 3.2.Antigens and antigenicity Definitions of antigen,antigenicity,immunogen,immunogenicity and epitope The origin of antigens Factors affecting antigenicity (size,complexity and molecular shape)and their applications in inducing immune responses The structure and function of different types of antigens such as hapten,alloantigen, superantigen,allergen and autoantigen 3.3.The Major Histocompatibility Complex(MHC)and antigen presentation Structure and function of MHC Class I and Class II molecules Expression pattern of MHC molecules The origin of diversity of MHC molecules Antigen presenting cells The endogenous pathway of antigen processing and presentation The exogenous pathway of antigen processing and presentation 3.4.Antibody The structure of antibodies (light chains,heavy chains,complementarity-determining region) The structure.function.distribution and relative abundance of the five major classes of antibodies(IgG,IgA,IgM,IgD,IgE) 4.教学方法 4.1.Multimedia PowerPoint slides for content display Video clip about adaptive immune system Video clip about antibody structure 4.2.Teacher-student interaction On-screen multiple-choices quiz at the end of each section during the class Discussion about the roles of MHC molecules the potential outcome during a virus pandemic 5.教学评价 课后问题
2.教学重难点 • The difference between innate and adaptive immune system and why we need both systems • The structural and functional difference between MHC class I and class II molecules • The characteristic structure and function of the five main classes of antibodies 3.教学内容 3.1. Overview of adaptive immunity • Similarities and differences between innate and adaptive immune system 3.2. Antigens and antigenicity • Definitions of antigen, antigenicity, immunogen, immunogenicity and epitope • The origin of antigens • Factors affecting antigenicity (size, complexity and molecular shape) and their applications in inducing immune responses • The structure and function of different types of antigens such as hapten, alloantigen, superantigen, allergen and autoantigen 3.3. The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) and antigen presentation • Structure and function of MHC Class I and Class II molecules • Expression pattern of MHC molecules • The origin of diversity of MHC molecules • Antigen presenting cells • The endogenous pathway of antigen processing and presentation • The exogenous pathway of antigen processing and presentation 3.4. Antibody • The structure of antibodies (light chains, heavy chains, complementarity-determining region) • The structure, function, distribution and relative abundance of the five major classes of antibodies (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE) 4.教学方法 4.1. Multimedia • PowerPoint slides for content display • Video clip about adaptive immune system • Video clip about antibody structure 4.2. Teacher-student interaction • On-screen multiple-choices quiz at the end of each section during the class • Discussion about the roles of MHC molecules the potential outcome during a virus pandemic 5.教学评价 课后问题