
Data Communications and Networking Forouzan Fourth Edition 第9章 使用电话网和有线电视网 进行数据传输 9.1 CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display
9.1 第9章 使用电话网和有线电视网 进行数据传输 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display

-1 TELEPHONE NETWORK Telephone networks use circuit switching. The telephone network had its beginnings in the late 1800s. The entire network,which is referred to as the plain old telephone system (POTS),was originally an analog system using analog signals to transmit voice. Topics discussed in this section: Major Components LATAS Signaling Services Provided by Telephone Networks 9.2
9.2 9-1 TELEPHONE NETWORK Telephone networks use circuit switching. The telephone network had its beginnings in the late 1800s. The entire network, which is referred to as the plain old telephone system (POTS), was originally an analog system using analog signals to transmit voice. Major Components LATAs Signaling Services Provided by Telephone Networks Topics discussed in this section:
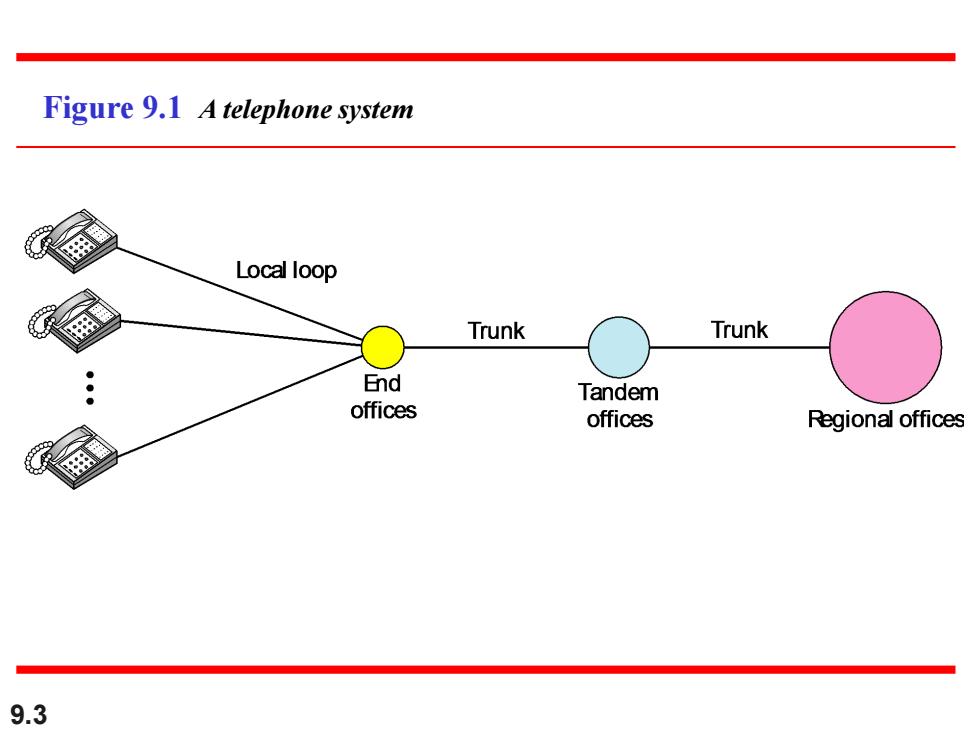
Figure 9.1 A telephone system Local loop Trunk Trunk End Tandem offices offices Regional offices 9.3
9.3 Figure 9.1 A telephone system

Note LATA:Local access and transport area ● LATA可以是一个城市地区或者大城市 提供LATA内部服务被称为本地交换电信 公司(local exchange carriers,LEC) ● 1996年以后,有多个运营商可以提供 LATA内部服务. 9.4
9.4 LATA: Local access and transport area LATA可以是一个城市地区或者大城市 提供LATA内部服务被称为本地交换电信 公司(local exchange carriers,LEC) 1996年以后,有多个运营商可以提供 LATA内部服务. Note
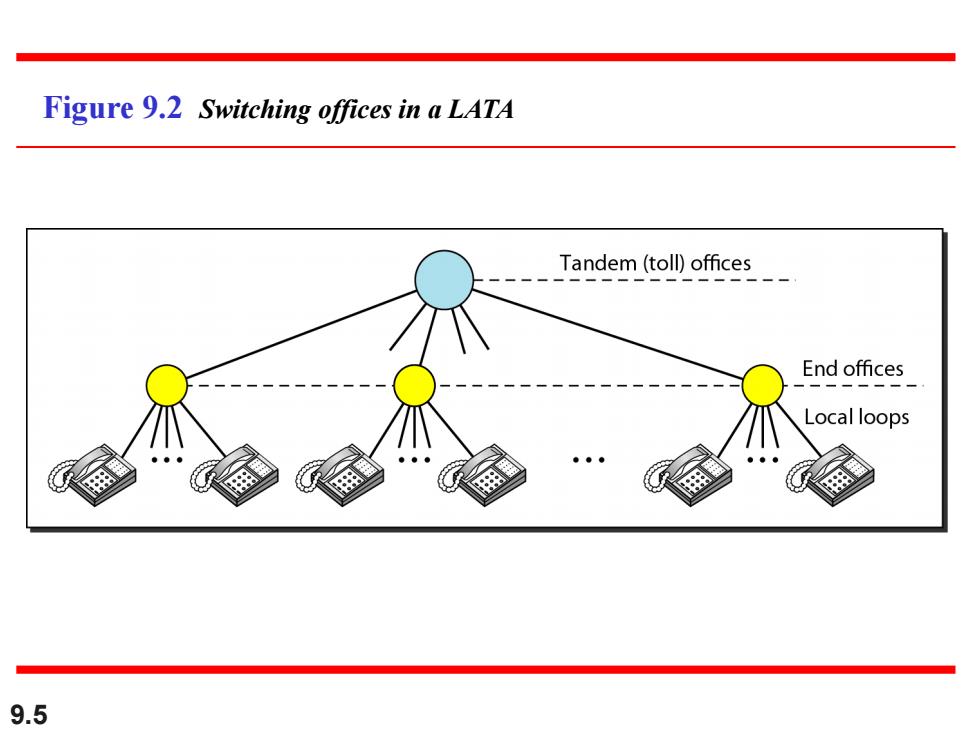
Figure 9.2 Switching offices in a LATA Tandem (toll)offices_ End offices Local loops 9.5
9.5 Figure 9.2 Switching offices in a LATA
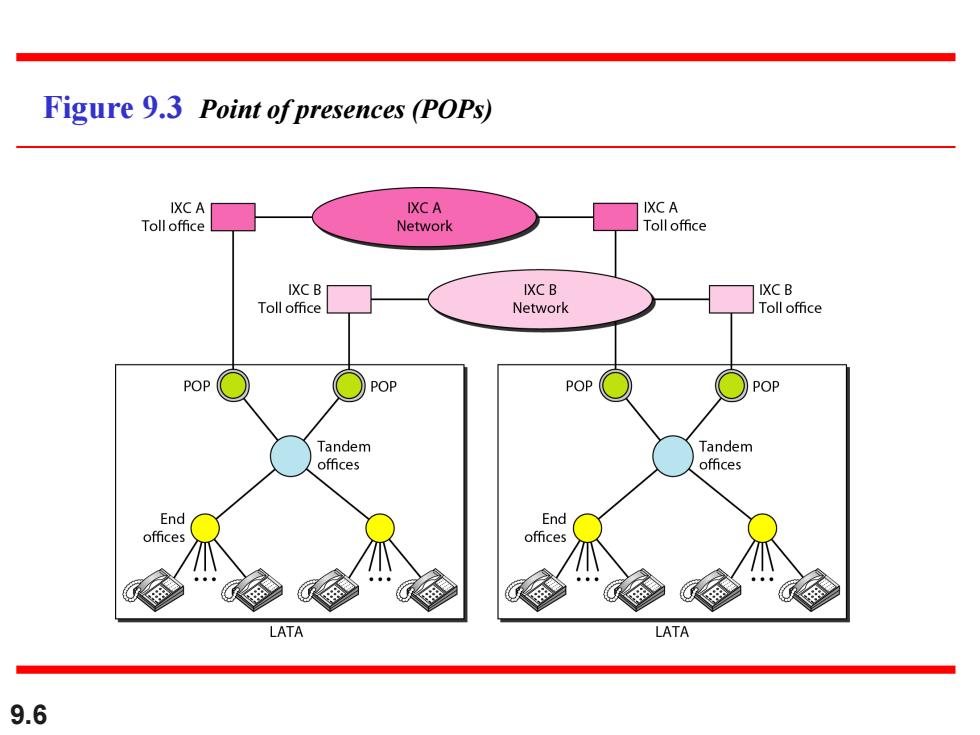
Figure 9.3 Point ofpresences (POPs) IXCA IXCA IXCA Toll office Network Toll office IXC B IXC B IXC B Toll office Network Toll office POP POP POP Tandem Tandem offices offices End End offces offces LATA LATA 9.6
9.6 Figure 9.3 Point of presences (POPs)

Note The tasks of data transfer and signaling are separated in modern telephone networks:data transfer is done by one network,.signaling(信令)by another. 9.7
9.7 The tasks of data transfer and signaling are separated in modern telephone networks: data transfer is done by one network, signaling(信令) by another. Note
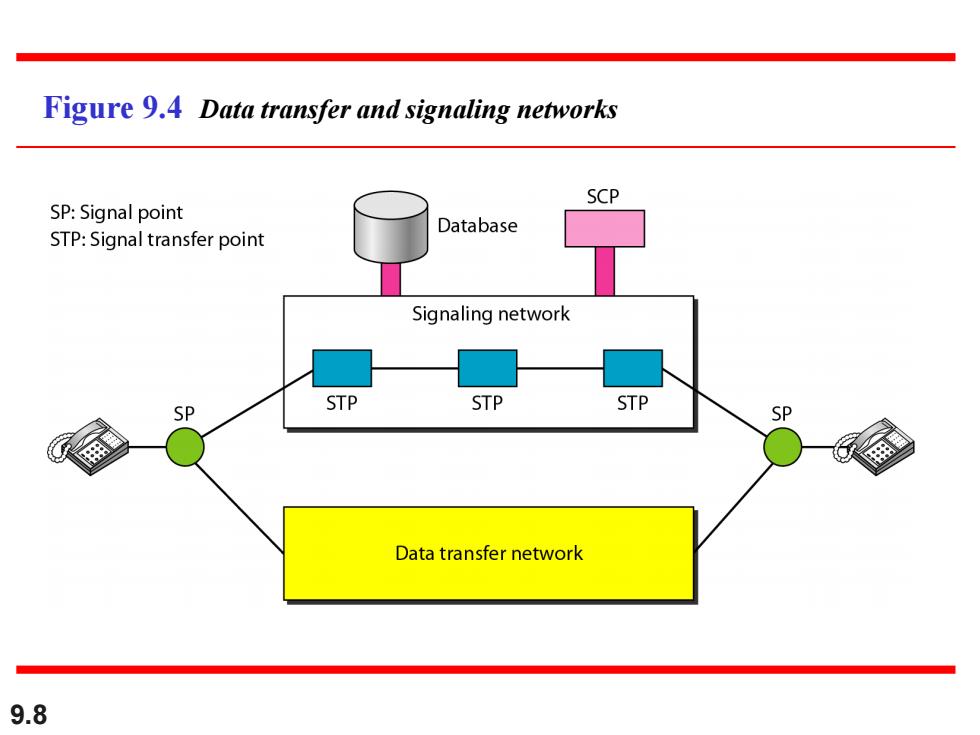
Figure 9.4 Data transfer and signaling networks SCP SP:Signal point Database STP:Signal transfer point Signaling network SP STP STP STP Data transfer network 9.8
9.8 Figure 9.4 Data transfer and signaling networks
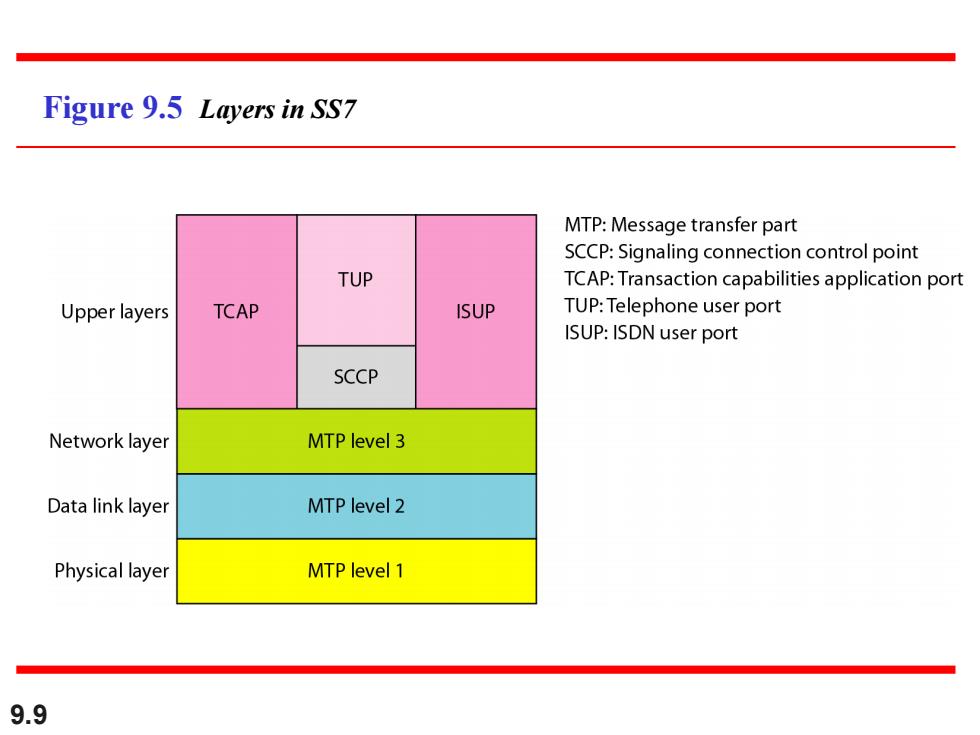
Figure 9.5 Layers in SS7 MTP:Message transfer part SCCP:Signaling connection control point TUP TCAP:Transaction capabilities application port Upper layers TCAP ISUP TUP:Telephone user port ISUP:ISDN user port SCCP Network layer MTP level 3 Data link layer MTP level 2 Physical layer MTP level 1 9.9
9.9 Figure 9.5 Layers in SS7

9-2电话调制解调器 传统的电话线路可以传送颜率范围是 300~3300Hz的信号,提供给信号的带宽是3000Hz。 整个颜率范围用于传输语音,在不丢失可识别性的 情况下,有一些干扰和失真是可以接受的。 本节过论的主题 调制解调器标准 9.10
9.10 9-2 电话调制解调器 传 统 的 电 话 线 路 可 以 传 送 频 率 范 围 是 300~3300Hz的信号,提供给信号的带宽是3000Hz。 整个频率范围用于传输语音,在不丢失可识别性的 情况下,有一些干扰和失真是可以接受的。 调制解调器标准 本节讨论的主题: