
Data Communications and Networking Forouzan Fourth Edition Chapter 16 Wireless WANs: Cellular Telephone and Satellite Networks 16.1 CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display
16.1 Chapter 16 Wireless WANs: Cellular Telephone and Satellite Networks Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display

16-1 CELLULAR TELEPHONY Cellular telephony is designed to provide communications between two moving units,called mobile stations (MSs),or between one mobile unit and one stationary unit,often called a land unit. Topics discussed in this section: Frequency-Reuse Principle Transmitting Receiving Roaming First Generation Second Generation Third Generation 16.2
16.2 16-1 CELLULAR TELEPHONY Cellular telephony is designed to provide communications between two moving units, called mobile stations (MSs), or between one mobile unit and one stationary unit, often called a land unit. Frequency-Reuse Principle Transmitting Receiving Roaming First Generation Second Generation Third Generation Topics discussed in this section:
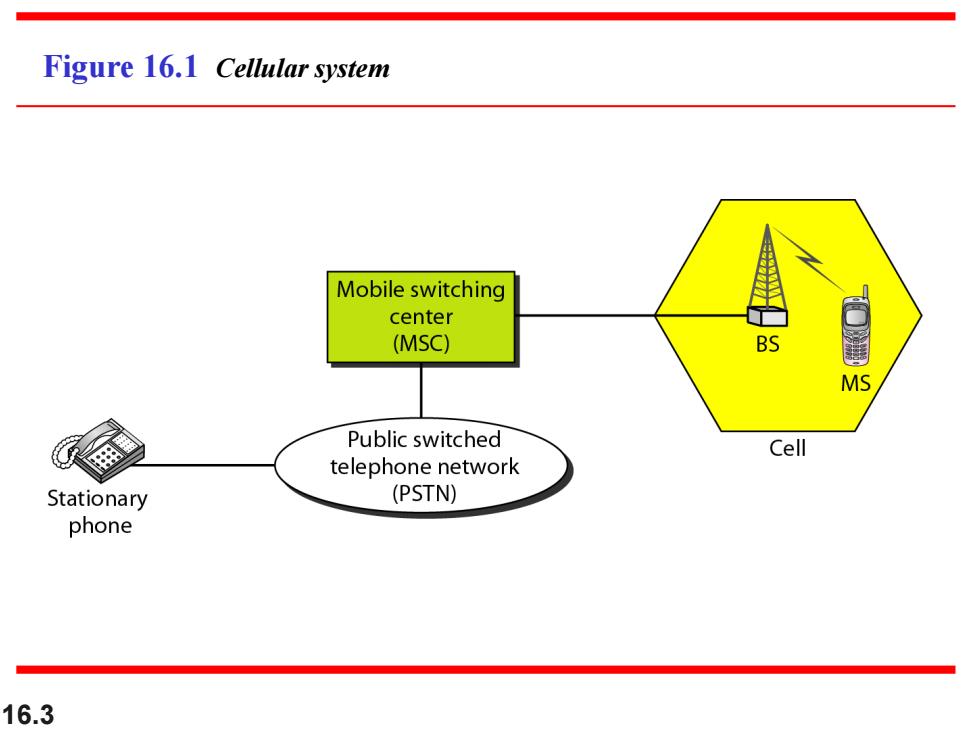
Figure 16.1 Cellular system Mobile switching center (MSC) BS MS Public switched Cell telephone network Stationary (PSTN) phone 16.3
16.3 Figure 16.1 Cellular system

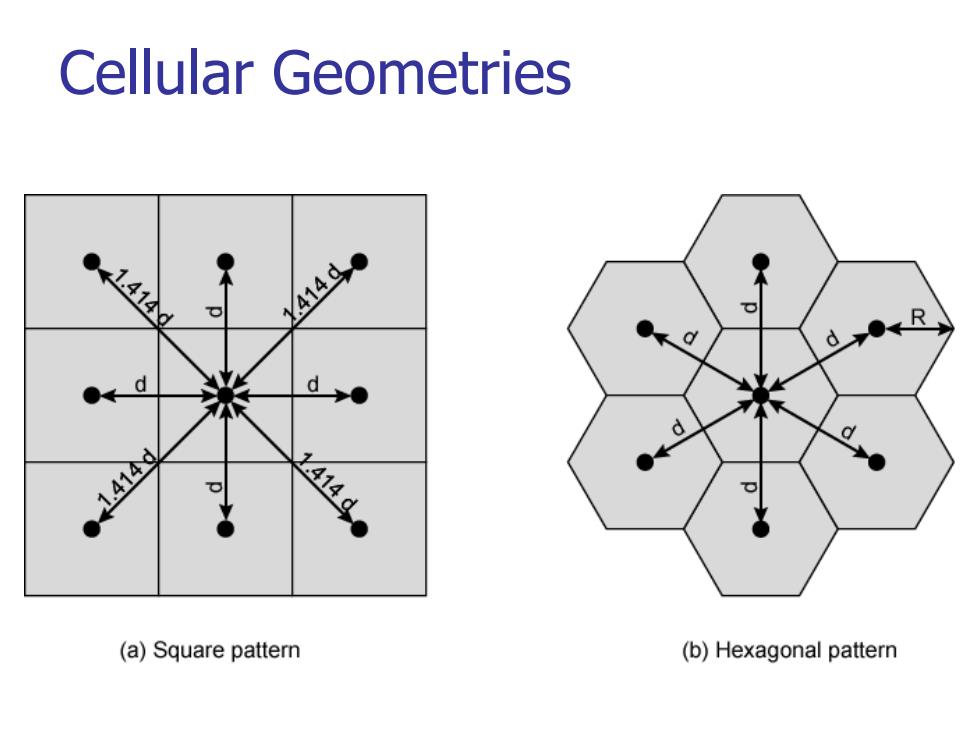
Shape of Cells Square Width dcellhas four neighbors at distance dand four at distance√2d Better if all adjacent antennas equidistant Simplifies choosing and switching to new antenna ■Hexagon(六边形) Provides equidistant antennas Radius defined as radius of circum-circle Distance from center to vertex equals length of side Distance between centers of cells radius R is 3 R Not always precise hexagons Topographical limitations Local signal propagation conditions ■Location of antennas
Shape of Cells Square Width d cell has four neighbors at distance d and four at distance d Better if all adjacent antennas equidistant Simplifies choosing and switching to new antenna Hexagon(六边形) Provides equidistant antennas Radius defined as radius of circum-circle Distance from center to vertex equals length of side Distance between centers of cells radius R is R Not always precise hexagons Topographical limitations Local signal propagation conditions Location of antennas 2 3
Cellular Geometries 414④d 414 (a)Square pattern (b)Hexagonal pattern
Cellular Geometries
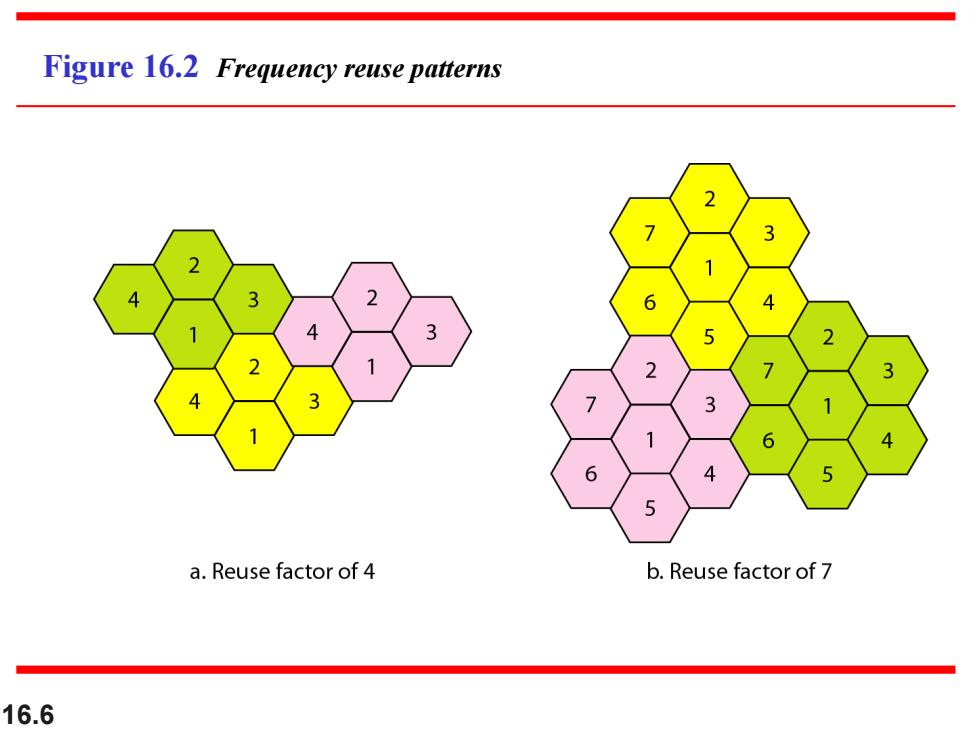
Figure 16.2 Frequency reuse patterns a.Reuse factor of 4 b.Reuse factor of 7 16.6
16.6 Figure 16.2 Frequency reuse patterns

Characterizing Frequency Reuse D minimum distance between centers of cells that use the same band of frequencies(called cochannels,.同波道)(相距最近的同频小 区中心间的距离) ■R=radius of a cel d distance between centers of adjacent cells(d R) ■N=number of cells in repetitioust(重复的)pattern ·Reuse factor Each cell in pattern uses unique band of frequencies Hexagonal cell pattern,following values of N possible ·N=2+J2+(1×J),I,J=0,1,2,3,. Possible values of N are 1,3,4,7,9,12,13,16,19,21,. ■Q=D/R=√3N (称为同频复用比例) ■ D/d =N Q的值越小容量越大;Q值大可以提高传播质量,同频干扰小
Characterizing Frequency Reuse D = minimum distance between centers of cells that use the same band of frequencies (called cochannels,同波道)(相距最近的同频小 区中心间的距离) R = radius of a cell d = distance between centers of adjacent cells (d = R) N = number of cells in repetitious(重复的) pattern Reuse factor Each cell in pattern uses unique band of frequencies Hexagonal cell pattern, following values of N possible N = I2 + J2 + (I x J), I, J = 0, 1, 2, 3, . Possible values of N are 1, 3, 4, 7, 9, 12, 13, 16, 19, 21, . Q=D/R= (称为同频复用比例) D/d = Q的值越小容量越大;Q值大可以提高传播质量,同频干扰小 3N N
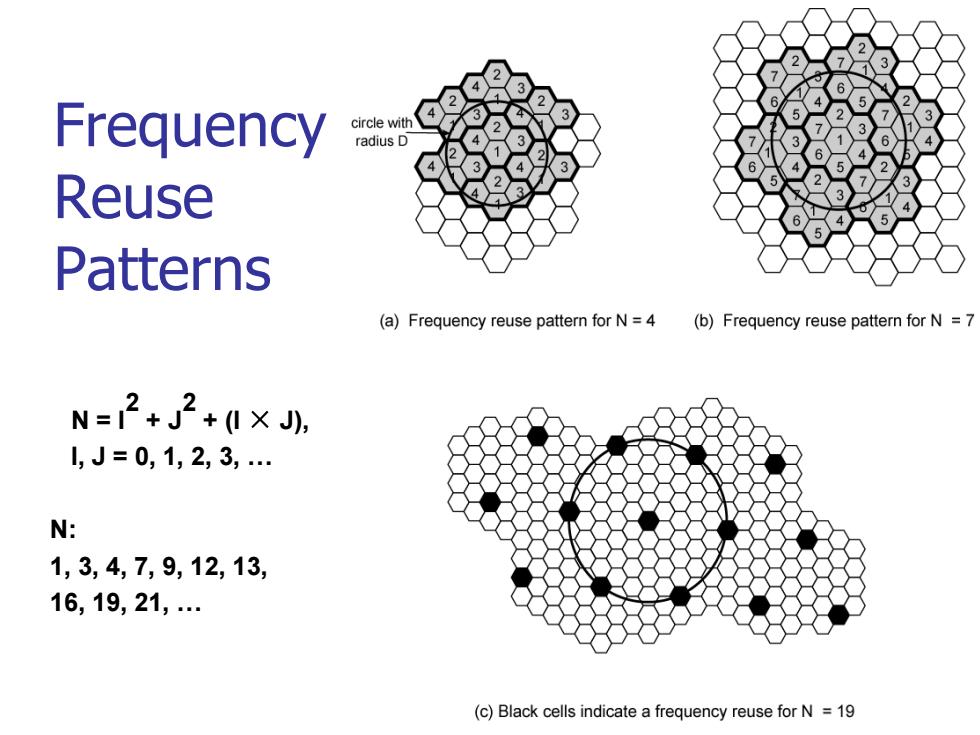
Frequency circle with radius D Reuse Patterns (a)Frequency reuse pattern for N=4 (b)Frequency reuse pattern for N =7 N=2+J2+0×, 1,J=0,1,2,3,. N: 1,3,4,7,9,12,13, 16,19,21, (c)Black cells indicate a frequency reuse for N =19
Frequency Reuse Patterns N = I2 + J2 + (I × J), I, J = 0, 1, 2, 3, . N: 1, 3, 4, 7, 9, 12, 13, 16, 19, 21,
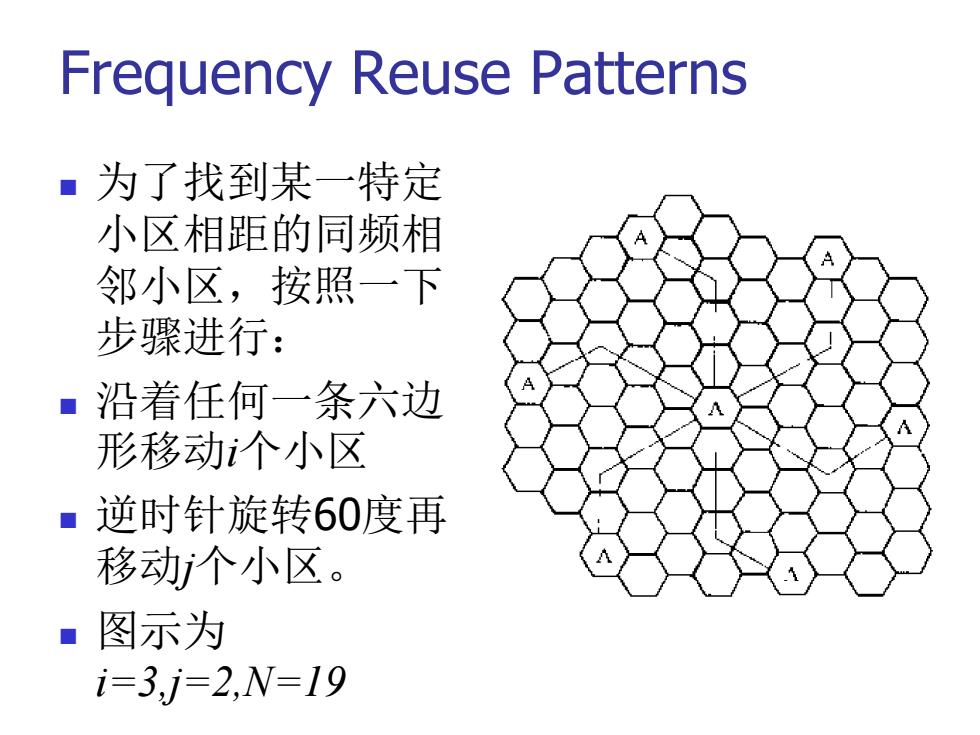
Frequency Reuse Patterns ■为了找到某一特定 小区相距的同频相 邻小区,按照一下 步骤进行: ■沿着任何一条六边 A 形移动个小区 ■逆时针旋转60度再 移动个小区。 ■图示为 i=3,j=2,N=19
Frequency Reuse Patterns 为了找到某一特定 小区相距的同频相 邻小区,按照一下 步骤进行: 沿着任何一条六边 形移动i个小区 逆时针旋转60度再 移动j个小区。 图示为 i=3,j=2,N=19

Note AMPS是一种使用FDMA的模拟移动电话系 统 16.10
16.10 AMPS 是一种使用FDMA的模拟移动电话系 统. Note