
第5章消化与吸收 Digestion and Absorption 1.概述Introduction 2.摄食Food intake 3.▣腔内消化Digestion in oral cavity 4.胃内消化Digestion in stomach 5.小肠内消化Digestion in small intestine 6.吸收Absorption
第5章 消化与吸收 Digestion and Absorption 1.概述 Introduction 2.摄食 Food intake 3.口腔内消化 Digestion in oral cavity 4.胃内消化 Digestion in stomach 5.小肠内消化 Digestion in small intestine 6.吸 收 Absorption
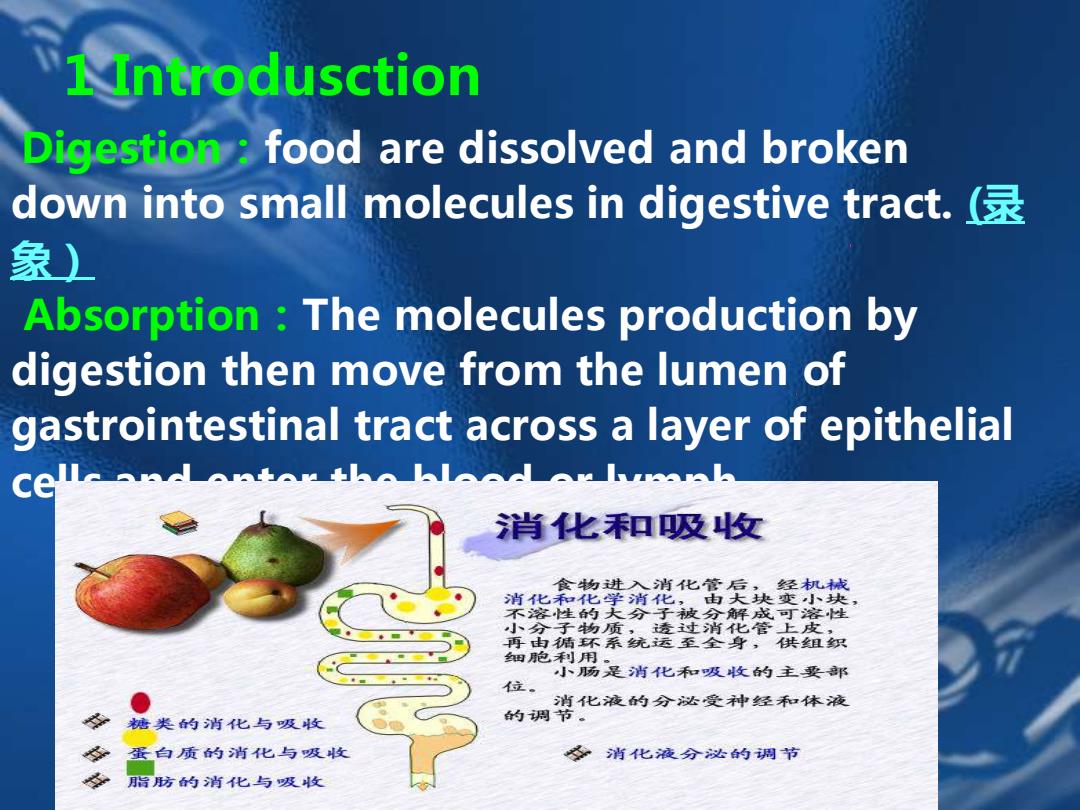
1 Introdusction Digestion food are dissolved and broken down into small molecules in digestive tract. 象) Absorption The molecules production by digestion then move from the lumen of gastrointestinal tract across a layer of epithelial 肖化和吸收 食物进入消化管后,经机械 消化和化学消化,由大块变小块 不溶性的大分子被分解成可溶性 小小分子物质,透过消化管上皮 再由循环系统运至全身,供组织 细胞利用 小肠是消化不和吸收的主要耶 位。 消化液的分达受神经和体液 糖类的消化与吸收 的调节。 蛋白质的消化与吸收 消化液分泌的调节 脂防的消化与吸收
Digestion:food are dissolved and broken down into small molecules in digestive tract. (录 象) Absorption:The molecules production by digestion then move from the lumen of gastrointestinal tract across a layer of epithelial cells and enter the blood or lymph. 1 Introdusction
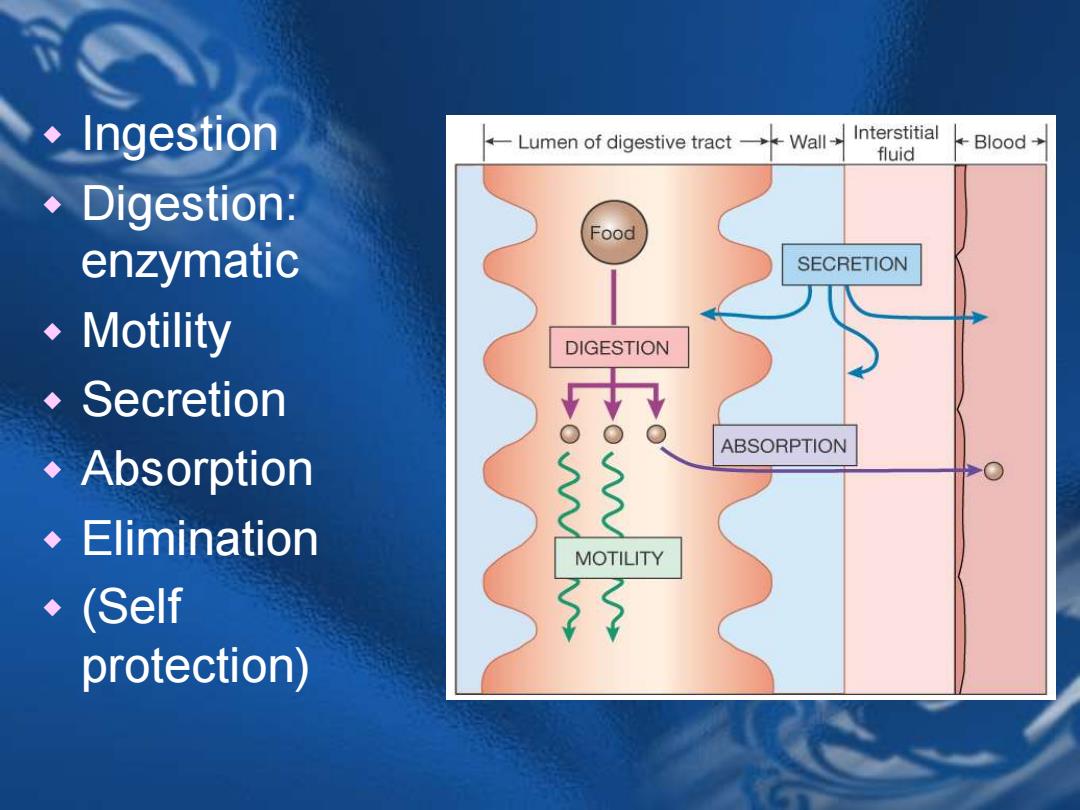
◆Ingestion Lumen of digestive tractWall Interstitial Blood→ fluid Digestion: Food enzymatic SECRETION Motility DIGESTION ◆Secretion ABSORPTION Absorption 33 ◆Elimination MOTILITY (Self protection)
Ingestion Digestion: enzymatic Motility Secretion Absorption Elimination (Self protection)
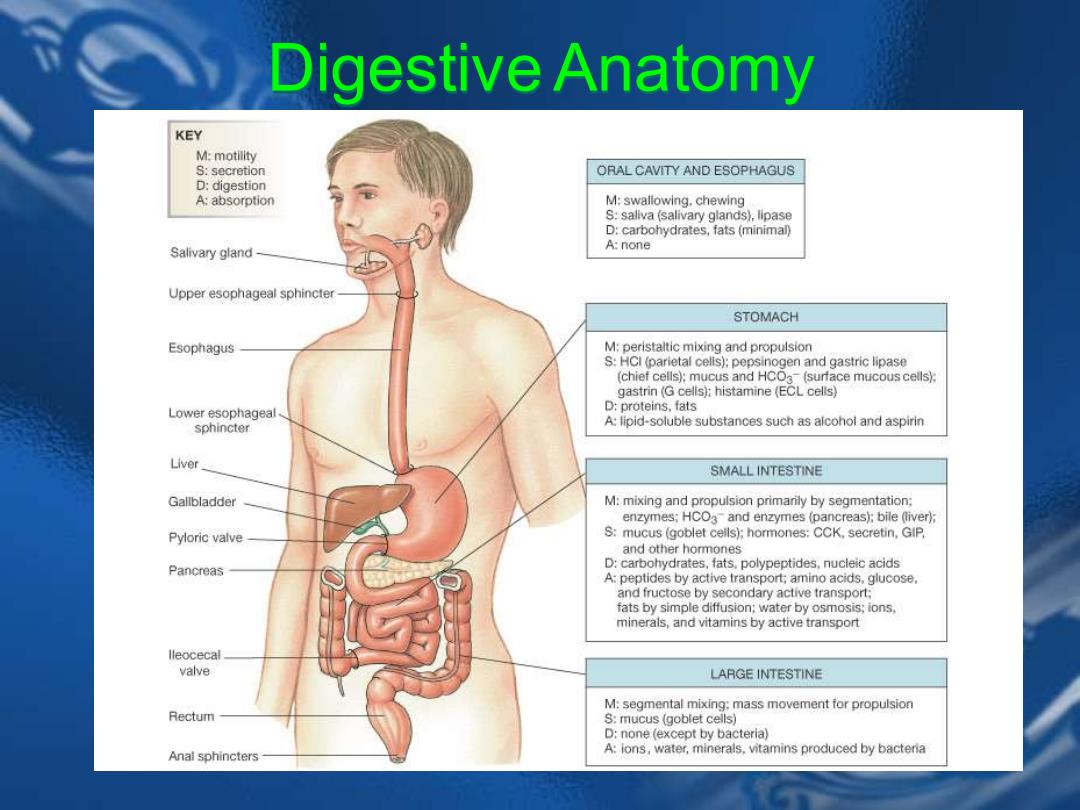
Digestive Anatomy KEY M:motility S:secretion ORAL CAVITY AND ESOPHAGUS D:digestion A:absorption M:swallowing.chewing S:saliva (salivary glands),lipase D:carbohydrates,fats(minimal) Salivary gland A:none Upper esophageal sphincter STOMACH Esophagus M:peristaltic mixing and propulsion S:HCI (parietal cells):pepsinogen and gastric lipase (chief cells):mucus and HCO3-(surface mucous cells): gastrin(G cells):histamine (ECL cells) Lower esophageal D:proteins,fats sphincter A:lipid-soluble substances such as alcohol and aspirin Liver SMALL INTESTINE Gallbladder M:mixing and propulsion primarily by segmentation: enzymes;HCO3 and enzymes (pancreas):bile(liver); Pyloric valve S:mucus (goblet cells);hormones:CCK,secretin,GIP, and other hormones Pancreas D:carbohydrates,fats,polypeptides.nucleic acids A:peptides by active transport;amino acids,glucose. and fructose by secondary active transport: fats by simple diffusion;water by osmosis;ions, minerals,and vitamins by active transport lleocecal valve LARGE INTESTINE M:segmental mixing:mass movement for propulsion Rectum S:mucus (goblet cells) D:none (except by bacteria) Anal sphincters A:ions,water,minerals.vitamins produced by bacteria
Digestive Anatomy

1.1消化方式(Nays of digestion) 物理消化(physical digestion):通过消化管的运 动,将食物粉碎、搅拌和推进的过程。(录象) 化学消化(chemical digestion):通过消化酶将食 物大分子分解成小分子的过程 微生物消化(microbial digestion):消化道内的微 生物对食糜进行消化而被动物自身利用的过程
1.1 消化方式(Ways of digestion) 物理消化(physical digestion):通过消化管的运 动,将食物粉碎、搅拌和推进的过程。(录象) 化学消化(chemical digestion):通过消化酶将食 物大分子分解成小分子的过程. 微生物消化(microbial digestion) :消化道内的微 生物对食糜进行消化而被动物自身利用的过程
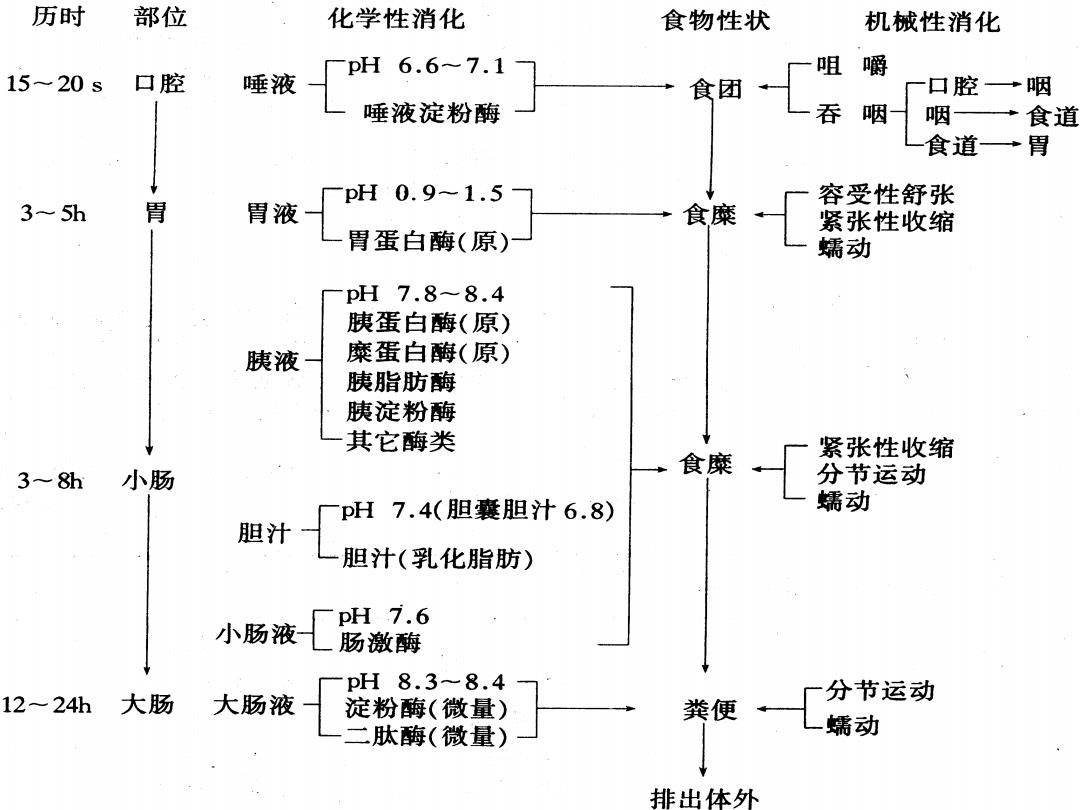
历时 部位 化学性消化 食物性状 机械性消化 H6.6~7.1 咀 嚼 15~20s 口腔 唾液 →食团 口腔→咽 唾液淀粉酶 吞咽 咽→ 食道 食道→胃 胃液 pH0.9-1.5 容受性舒张 3~5h 胃 食糜 紧张性收缩 胃蛋白酶(原) 蠕动 pH7.8~8.4 胰蛋白酶(原) 胰液 糜蛋白酶(原) 胰脂肪酶 胰淀粉酶 其它酶类 紧张性收缩 3~8h 小肠 食糜 分节运动 PH 7.4(胆囊胆汁6.8) 蠕动 胆汁 胆汁(乳化脂肪) 小肠液 pH7.6 肠激酶 pH8.3~8.4 12~24h 大肠 大肠液 分节运动 淀粉酶(微量) 粪便 二 肽酶(微量) 蠕动 排出体外

1,2消化道平滑肌特性(Characteristics of gut smooth muscle) 1.21消化道平滑肌的一般特性 1)兴奋性(Excitability:low,slow contraction 2)伸展性(Extensibility):bigger. 3)紧张性(Tensity):tonic contraction. 4)自动节律性(Automaticity):slow rhythm. 5)敏感性(Sensitivity):sensitive to chemical, stretch and temperature stimuli. 1.2.2电生理特性(electrical characteristics) 静息电位(Resting potential)) 钾离子平衡电位,膜电位值-55~60毫伏
1.2 消化道平滑肌特性(Characteristics of gut smooth muscle) 1.2.1 消化道平滑肌的一般特性 1)兴奋性(Excitability): low, slow contraction 2)伸展性(Extensibility): bigger. 3)紧张性(Tensity) :tonic contraction. 4)自动节律性(Automaticity): slow rhythm. 5)敏感性(Sensitivity):sensitive to chemical, stretch and temperature stimuli. 1.2.2 电生理特性(electrical characteristics) ●静息电位(Resting potential) 钾离子平衡电位,膜电位值-55~60毫伏

基本电节律(basic electrical waves,慢波电 位.slow wave spontaneous,slow and recurring depolarization. Intesity:5~15mVTime:1~4s Frequency stomac-5/min intestin:10/min 动作电位(Action potential,,spike) ● 当慢波电位超过一定临界值时,可触发一个或多个 动作电位。 动作电位的数目越多,肌肉收缩的幅度就越大
●基本电节律(basic electrical waves,慢波电 位,slow wave) spontaneous, slow and recurring depolarization. Intesity:5~15mV,Time:1~4s Frequency:stomac-5/min;intestin:10/min ●动作电位(Action potential, spike) 当慢波电位超过一定临界值时,可触发一个或多个 动作电位。 动作电位的数目越多,肌肉收缩的幅度就越大
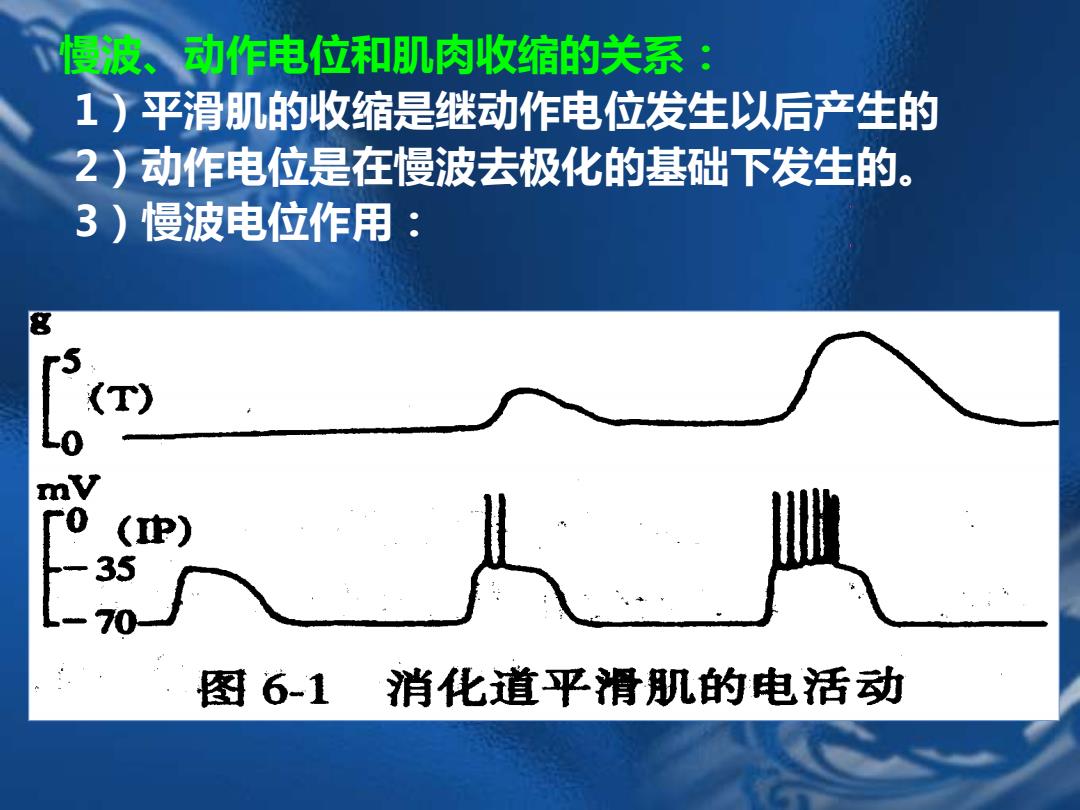
慢波、动作电位和肌肉收缩的关系 1)平滑肌的收缩是继动作电位发生以后产生的 2)动作电位是在慢波去极化的基础下发生的。 3)慢波电位作用: (T) 0 ) 35 70 图6-1 消化道平滑肌的电活动
慢波、动作电位和肌肉收缩的关系: 1)平滑肌的收缩是继动作电位发生以后产生的 2)动作电位是在慢波去极化的基础下发生的。 3)慢波电位作用:

1.3胃肠道机能的调节 1.3.1胃肠道的神经调节 1.3.1.1外来神经:交感神经和副交感神经 交感神经 抑制胃肠运动和消化液分泌。 副交感神经 兴奋胃肠运动和消化液分泌
1.3.1 胃肠道的神经调节 1.3.1.1 外来神经:交感神经和副交感神经 交感神经 抑制胃肠运动和消化液分泌。 副交感神经 兴奋胃肠运动和消化液分泌。 1.3 胃肠道机能的调节