
第2章血液 1.体液与内环境 2.血液的组成和理化特性 3.血 浆 4.血细胞及其功能 5.血液凝固 6.血 型
第 2 章 血 液 2.血液的组成和理化特性 4.血 细 胞 及 其 功 能 5.血 液 凝 固 3.血 浆 6.血 型 1.体 液 与 内 环 境
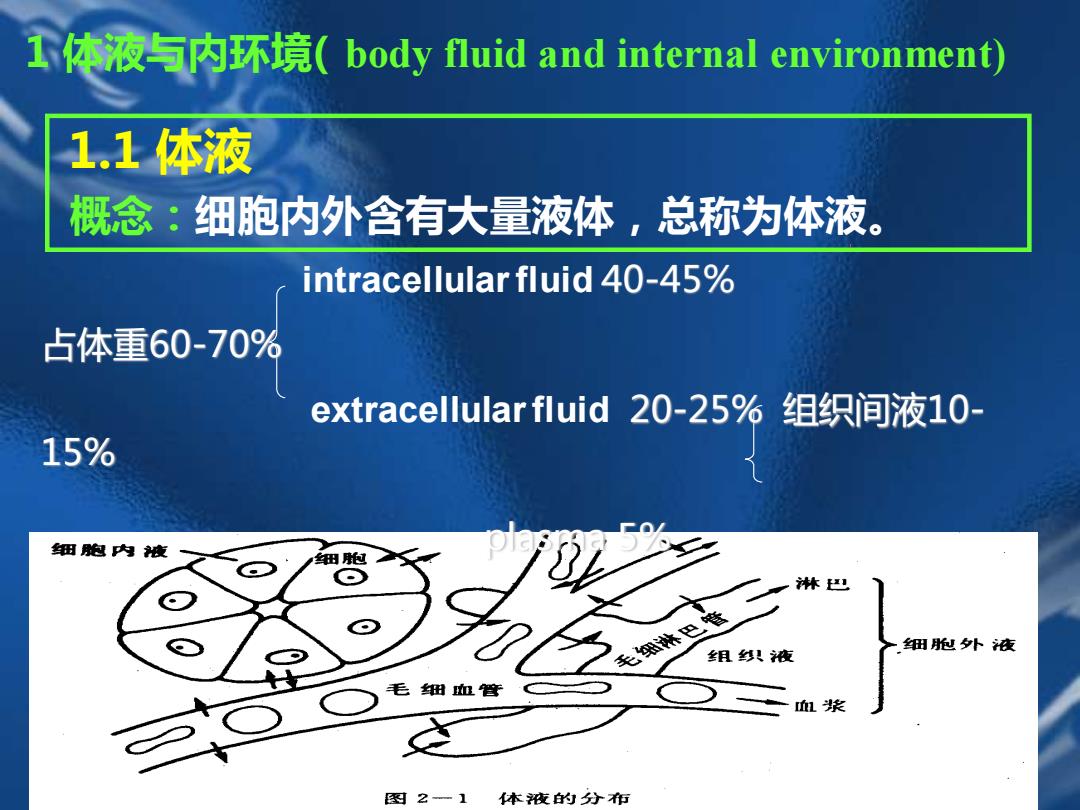
I体液与内环境(body fluid and internal environment) 1.1体液 概念:细胞内外含有大量液体,总称为体液。 intracellular fluid 40-45% 占体重60-70% extracellular fluid20-25%组织间液10- 15% 细胞内夜 细 林巴 毛细巴 组丝织液 细抛外液 毛细血管 血浆 图2一1 本夜的分衔
1.1 体液 概念:细胞内外含有大量液体,总称为体液。 1 体液与内环境( body fluid and internal environment) intracellular fluid 40-45% 占体重60-70% extracellular fluid 20-25% 组织间液10- 15% plasma 5%

1.2内环境与内环境稳态(Internal Environment and Hemeostasis 外环境:(External Environment) 机体整体直接接触和生活的环境 (外界、大气环境) 内环境(Internal Environment) 细胞直接接触和生活的环境。(extracellular fluid) 稳态(homeostasis) concept 内环境的成分和理化因素保持相对稳定的状态
1.2 内环境与内环境稳态( Internal Environment and Hemeostasis ) 外环境:(External Environment) 内环境(Internal Environment ) 机体整体直接接触和生活的环境。(外界、大气环境) 细胞直接接触和生活的环境。(extracellular fluid) 稳态(homeostasis) concept: 内环境的成分和理化因素保持相对稳定的状态

稳态的含义:Including two meaning (1)relatively stable (2)the control process maintaining the constant conditions of internal environments ①指细胞外液的成分和理化因素在一定水平上是 恒定的; ②指这个恒定状态并不是固定不变的,是一个动 态平衡,在微小波动中保持相对恒定
稳态的含义: Including two meaning: (1) relatively stable (2) the control process maintaining the constant conditions of internal environments ①指细胞外液的成分和理化因素在一定水平上是 恒定的; ②指这个恒定状态并不是固定不变的,是一个动 态平衡,在微小波动中保持相对恒定

稳态的实现:How can homeostsis be maintained? 茬整体是在神经体液机制调节下,通过各器官系统 的活动而实现的 All of the organs and tissues perform function to help maintain these constant conditions. 稳态的意义(Function): 维持细胞、器官、 系统乃至整体的正常功能及生命 活动的必要条件。若破坏内环境稳定,机体将发生疾 病
稳态的实现:How can homeostsis be maintained? 在整体是在神经体液机制调节下,通过各器官系统 的活动而实现的。 All of the organs and tissues perform function to help maintain these constant conditions. 稳态的意义(Function): 维持细胞、器官、系统乃至整体的正常功能及生命 活动的必要条件。若破坏内环境稳定,机体将发生疾 病

2血液的组成与理化特性 (Components and properties of blood) 2.1 Components of blood Plasma(血浆) 血液的组成 血液的主要组成可概括如下: Blood cells: 白蛋白 血浆蛋白 球蛋白 水(91%一92% 纤维蛋白原 Red blood cells 血浆 50%-60%】 电解质 Na+.K+.Ca2.Mg? HCO".Ci“.HPOi.SOi 溶质《8%一9%】 White blood cells 营养物质 液 小分子有机物 代谢终产物 激素 红细能 气体:O2.C0 Platelets(血小板) 血细胞 40%-50%6 白细胞 血小板
由血细胞和血浆组成。血浆包括: ① 晶体物质溶液 水、电解质、小分子、 有机化合物、气体 ② 血浆蛋白 白蛋白、球蛋白、纤维蛋白原 血液的组成 2 血液的组成与理化特性 (Components and properties of blood) 2.1 Components of blood Plasma(血浆) Blood cells: Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets (血小板)
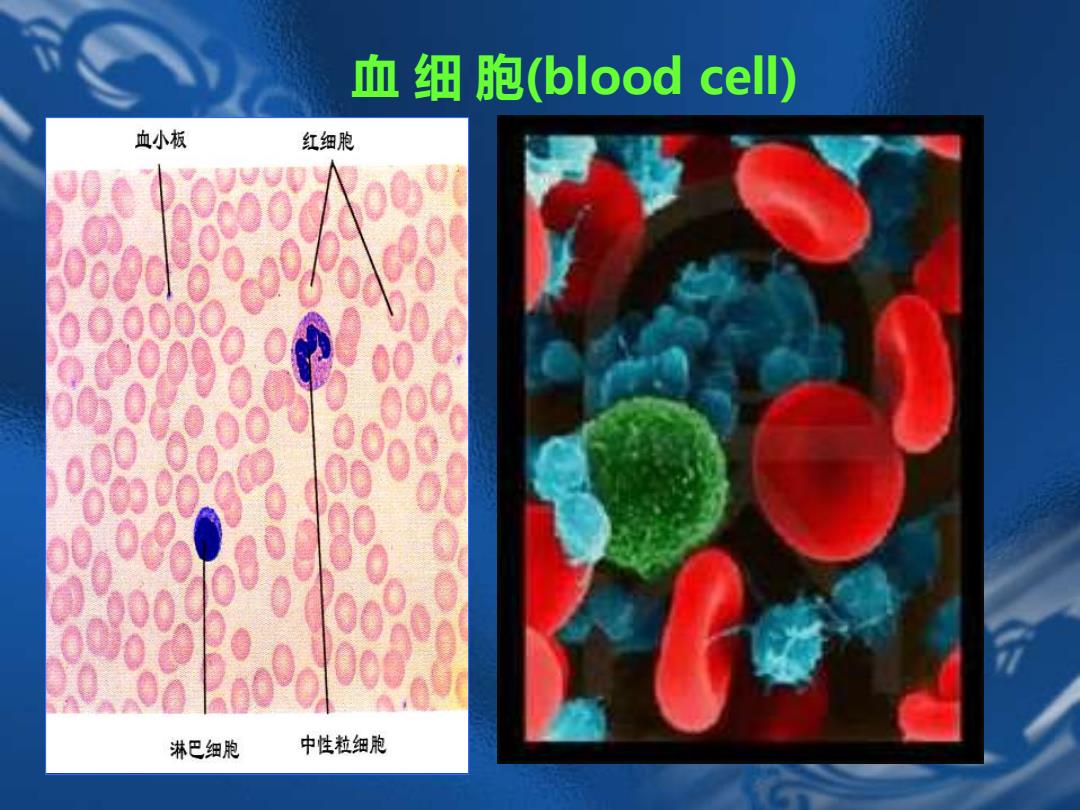
血细胞(blood cell) 血小板 红细胞 000 00000 6000 0 00000 00 00 淋巴细胞 中性粒细胞
血 细 胞(blood cell)

比容(hematocric): n 每100毫升血液被离心压紧的血 1信 细胞所占的容积,称为红细胞比容 或红细胞压积(PCV) man 40-50% woman 37-48% baby 55% 临 严重腹泻或大面积烧伤时→血浆量↓→红细胞 床 比容↑ 贫血→红细胞↓→红细胞比容↓
比容(hematocric): 每100毫升血液被离心压紧的血 细胞所占的容积,称为红细胞比容 或红细胞压积(PCV) 。 man: 40-50% woman: 37-48% baby:55% 临 床 严重腹泻或大面积烧伤时→血浆量↓→红细胞 比容↑ 贫血→红细胞↓→红细胞比容↓

血浆(plasma) Constituents: Vater:90~92%, Proteins:6~8% Inorganic constituents(无机盐):1% Nutrients:glucose,amino acid,lipids ,vit Waste products: Dissolved gas:02 &CO2 Hormones
血浆(plasma) Constituents: Water: 90~92%, Proteins:6~8% Inorganic constituents(无机盐):1% Nutrients:glucose,amino acid, lipids ,vit Waste products: Dissolved gas:O2 &CO2 Hormones

Proteins 1.Albumin(白蛋白)porduced by liver, most important in maintain of Colloid osmotic pressure 2.Glubulin(球蛋白):肝脏合成。免疾扰体 3.Fibrinogen(纤维蛋白原):produced by liver important in clotting 非蛋白含氮化合物(NPN) 主要包括:尿素、尿酸、肌酐、肌酸、 氨基酸、氨和胆 红素等
1.Albumin(白蛋白):porduced by liver, most important in maintain of Colloid osmotic pressure 2.Glubulin(球蛋白) :肝脏合成。免疫抗体 3.Fibrinogen(纤维蛋白原) :produced by liver important in clotting 非蛋白含氮化合物(NPN) 主要包括:尿素、尿酸、肌酐、肌酸、氨基酸、氨和胆 红素等。 Proteins