
Chapter 10 Endocrine Section1 Introduction Section2 Hypothalamus and Pituitary Section3 Thyroid Section4 Hormones Regulating Ca and P Metabolism Section5 Pancreatic Islets Section6 Adrenal Gland Section7 Gonad gland Section8 Other Endocrine Hormones
Chapter 10 Endocrine Section1 Introduction Section2 Hypothalamus and Pituitary Section3 Thyroid Section4 Hormones Regulating Ca and P Metabolism Section5 Pancreatic Islets Section6 Adrenal Gland Section7 Gonad gland Section8 Other Endocrine Hormones

Section1 Introduction
Section1 Introduction
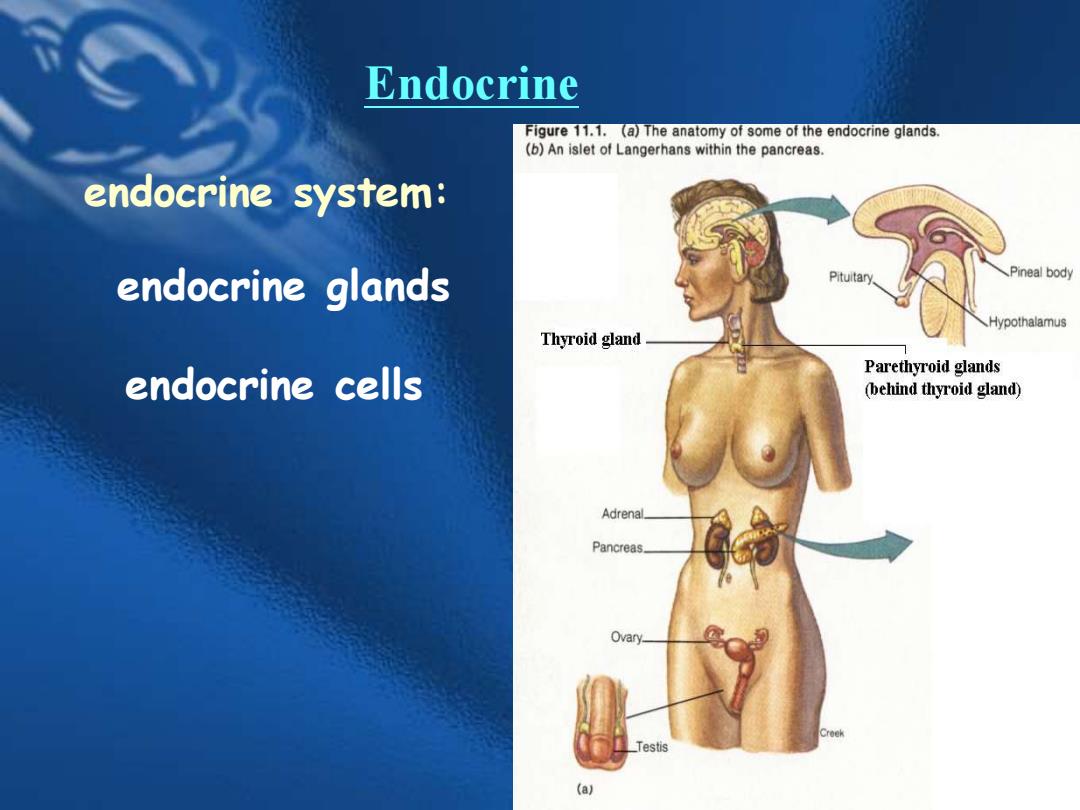
Endocrine Figure 11.1.(a)The anatomy of some of the endocrine glands. (b)An islet of Langerhans within the pancreas. endocrine system: endocrine glands Pituitary. Pineal body Hypothalamus Thyroid gland endocrine cells Parethyroid glands (behind thyroid gland) Adrenal. Pancreas. Ovary. Testis (a
endocrine system: Endocrine endocrine glands endocrine cells

Hormone Definition --chemical substance --is secreted into the internal body fluids by endocrine glands or endocrine cells --has a physiological control effect on other cells of the body Functions: Regulation of metabolism,growth and development,water and electrolyte balance,reproduction ,and behavior,etc
Definition Hormone --chemical substance --is secreted into the internal body fluids by endocrine glands or endocrine cells --has a physiological control effect on other cells of the body Functions: Regulation of metabolism, growth and development, water and electrolyte balance, reproduction ,and behavior, etc
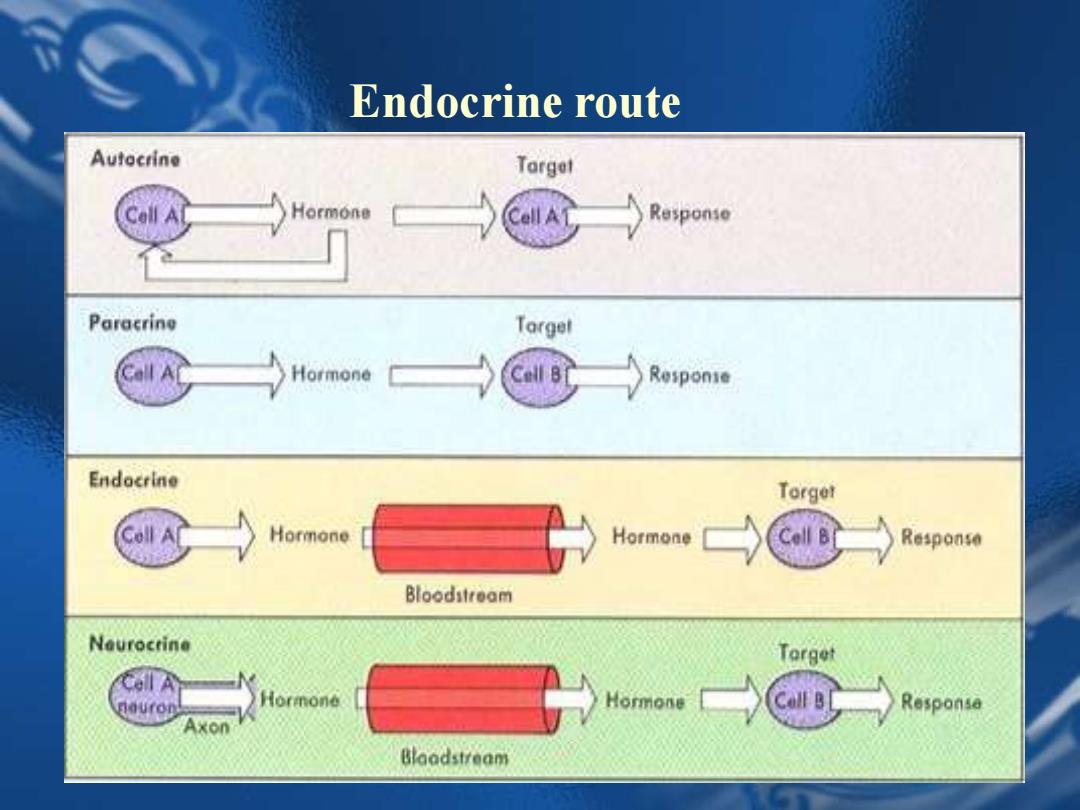
Endocrine route Autocrine Target Hormone Response Paracrine Targel Hormone Response Endocrine Torget Hormone Hormone Response Bloodstream Neurocrine Torget Cell A Responsa Axon Blaadstream
Endocrine route

Classification of hormone 1)Proteins and Polypeptides Insulin,gastrointestinal hormone, 2).Amine hormone:N,NE,T 3)Steroids secreted by the adrenal cortex (cortisol and aldosterone),the ovaries (estrogen and progesterone), the testes (testosterone),and the placenta (estrogen and progesterone)
1) Proteins and Polypeptides Insulin, gastrointestinal hormone, 2). Amine hormone:N, NE, T 3) Steroids secreted by the adrenal cortex (cortisol and aldosterone), the ovaries (estrogen and progesterone), the testes (testosterone), and the placenta (estrogen and progesterone) Classification of hormone

Properties of the hormone effect 1.Specificity The special feature of the the target cells is the presence of receptors which can "attract"and interact with the hormone. Receptor Secreting cell Target cell Not a target cell(no receptors)
Properties of the hormone effect 1. Specificity The special feature of the the target cells is the presence of receptors which can “attract” and interact with the hormone

Properties of the hormone effect 2.Signal Transmission The role of the hormones is to transit the regulatory signals from the control (endocrine)system to the target cells (organs or glands). It could enhance or inhibit 6壁结 some function of the target. 乳头体 3.Highly active 神整垂体 ADH
Properties of the hormone effect 2. Signal Transmission The role of the hormones is to transit the regulatory signals from the control (endocrine) system to the target cells (organs or glands). 3.Highly active It could enhance or inhibit some function of the target
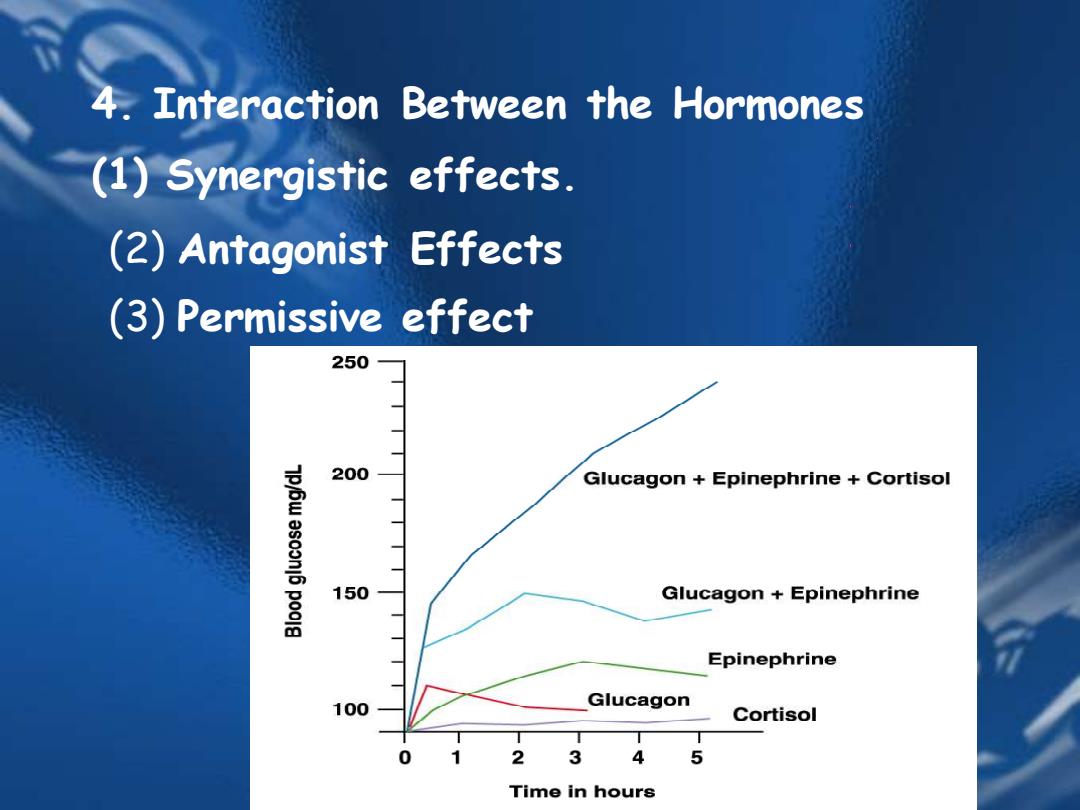
4.Interaction Between the Hormones (1)Synergistic effects. (2)Antagonist Effects (3)Permissive effect 250 200 Glucagon Epinephrine Cortisol 150 Glucagon Epinephrine Epinephrine 100 Glucagon Cortisol 0 1 2 3 4 5 Time in hours
4. Interaction Between the Hormones (1) Synergistic effects. (2) Antagonist Effects (3) Permissive effect

5.Rhythmicity of hormone resection 25 060 5 Lunch Dinner Sleep Breakfast ■■T Noon 4 PM 8 PM Mid- 4AM 8AM Noon night
5. Rhythmicity of hormone resection