
Chapter11 reproduction Section1 Introduction Section2 Male reproduction Section3 Female reproduction
Chapter11 reproduction Section1 Introduction Section2 Male reproduction Section3 Female reproduction

Section1 Introduction
Section1 Introduction

Reproduction The formation of new living entities, which closely resemble to the parent species. The processes are very complex including production of sperms and ova,sexual intercourse,fertilization,pregnancy, development of fetus and lactation
Reproduction The formation of new living entities, which closely resemble to the parent species. The processes are very complex including production of sperms and ova, sexual intercourse, fertilization, pregnancy, development of fetus and lactation

性成熟和体成熟 性成熟:生殖器官和副性征基本发育完全,具备繁 殖能力,叫性成熟。 初情期:性成熟的开始阶段 体成熟:动物的生长基本结束,并具有成年动物所固 有的形态和结构特点,称体成熟. 影响性成熟的因素 1、动物的种类和品种 2、气候因素 3、营养因素 4、群体因素 繁殖季节 常年繁殖:牛、猪、家兔等 季节性繁殖:马、羊、狗等
繁殖季节 常年繁殖:牛、猪、家兔等 季节性繁殖:马、羊、狗等 性成熟和体成熟 性成熟:生殖器官和副性征基本发育完全,具备繁 殖能力,叫性成熟。 初情期:性成熟的开始阶段 体成熟:动物的生长基本结束,并具有成年动物所固 有的形态和结构特点,称体成熟. 影响性成熟的因素 1、动物的种类和品种 2、气候因素 3、营养因素 4、群体因素

Section2 Male reproduction
Section2 Male reproduction
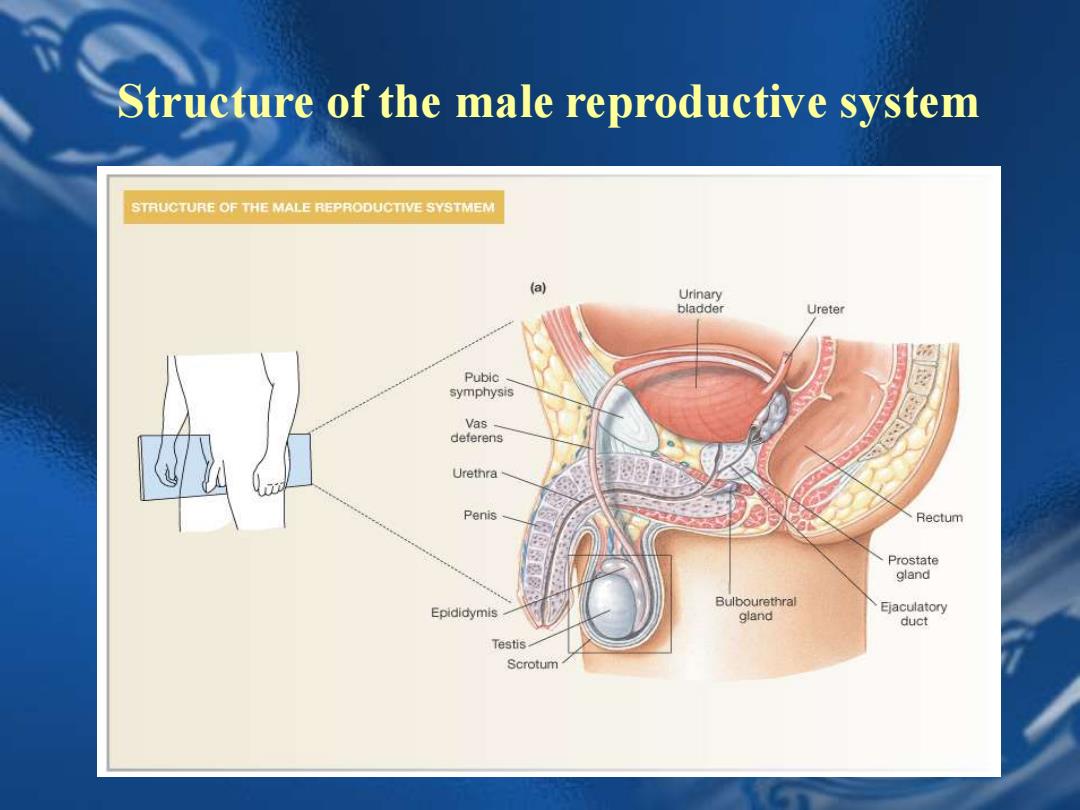
Structure of the male reproductive system STRUCTURE OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTMEM Urinary bladder Ureter Pubic symphysis Vas deferens Urethra Penis Rectum Prostate gland Bulbourethral Epididymis Ejaculatory gland duct Testis Scrotum
Structure of the male reproductive system

Testis(睾丸) 1.Spermatogenesis 2.Endocrine functions Seminiferous tubule 输出小管 曲细精管 输精管 曲细情管间 直细精管 的结缔组织 黎丸网 白膜 椭膜整层 附跟管 帕膜脏层 鞘膜腔 Sertoli cell Leydig cell 图11-1案丸及附将的结构
Testis(睾丸) 1. Spermatogenesis 2. Endocrine functions
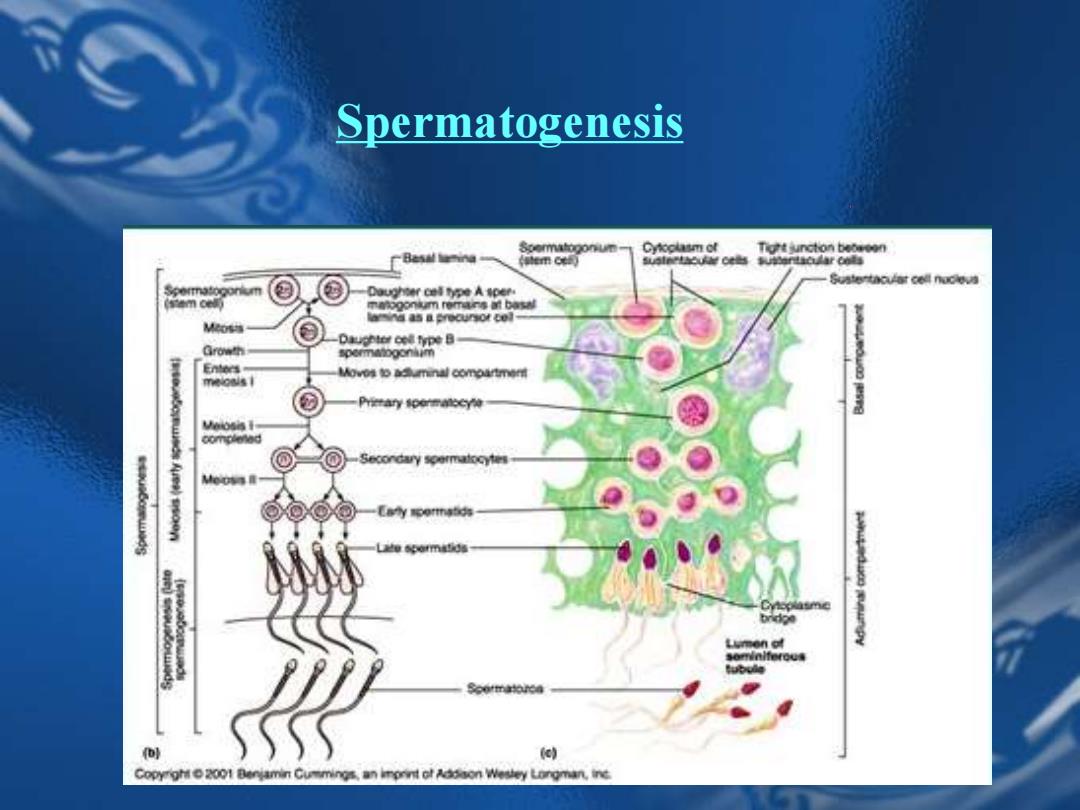
Spermatogenesis Cyoclasm ot T1可t junction beceeen e用ct】 ustrtAoUM ce当nearcnt Sustertaculat cell nocleva 0aC时行eA0e o0 nium rem4rs解6aW and as a precursor col 0集er cel type B spommogoniim Moves to Beuminal compartment Prierary soermaceyi Copyright 2001 Benjamin Cummings,an iprint of Addon Wesley Longman,inc
Spermatogenesis

Endocrine functions of testis 1.Androgens:testosterone 1)Maintenance of spermatogenesis 2)Stimulation of development of genitalia. 3)Development and maintenance of the male secondary sexual characteristics. 4)Maintenance of libido. 5)Effect on metabolism. Testosterone increases anabolism of protein,especially that in muscle and genitalia,and causes growth of the bones in the thickness,deposition of calcium salts as well enhancement of production of red cells
Endocrine functions of testis 1.Androgens: testosterone 1) Maintenance of spermatogenesis 2) Stimulation of development of genitalia. 3) Development and maintenance of the male secondary sexual characteristics. 4) Maintenance of libido. 5) Effect on metabolism. Testosterone increases anabolism of protein, especially that in muscle and genitalia, and causes growth of the bones in the thickness, deposition of calcium salts as well enhancement of production of red cells

2 Inhibin Inhibin has a strong direct effect on the anterior pituitary gland in inhibiting FSH secretion and a light effect on the hypothalamus in inhibiting GnRH secretion. These automatic feedback mechanisms can maintain a normal speed of spermatiogenesis,which is required for male reproduction function
2 Inhibin Inhibin has a strong direct effect on the anterior pituitary gland in inhibiting FSH secretion and a light effect on the hypothalamus in inhibiting GnRH secretion. These automatic feedback mechanisms can maintain a normal speed of spermatiogenesis, which is required for male reproduction function