
4-2 Membrane Transport Outline Principles of membrane transport; Passive transport and active transport; Two main classes of membrane transport proteins:carriers and channels: The ion transport systems; Endocytosis and phagocytosis:cellular uptake of macromolecules and particles. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Principles of membrane transport 1.The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier.It allows for separation and exchange of materials across the plasma membrane. 2.The protein-free lipid bilayers are highly impermeable to ions. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
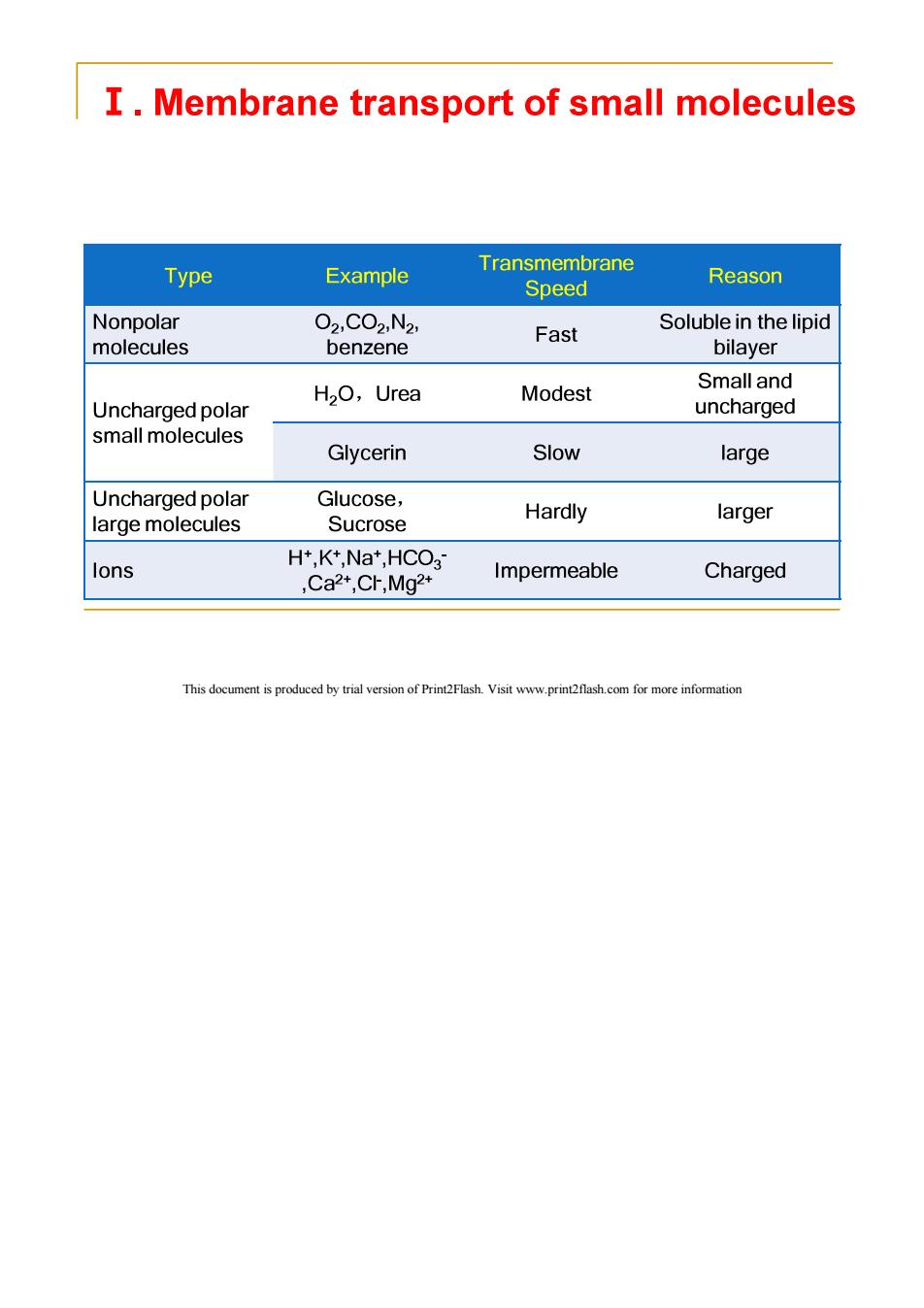
I.Membrane transport of small molecules Type Example Transmembrane Speed Reason Nonpolar O2,C02,N2, Fast Soluble in the lipid molecules benzene bilayer Small and H2O,Urea Modest Uncharged polar uncharged small molecules Glycerin Slow large Uncharged polar Glucose, large molecules Sucrose Hardly larger H+,K+,Na*,HCO3 lons Ca2+,CF,Mg2+ Impermeable Charged This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

The relative permeability of a synthetic lipid bilayer to different classes of molecules. 03 HYDROPHOBIC CO2 MOLECULES N2 If uncharged solutes are small enough, benzene they can move down their concentration SMALL gradients directly across the lipid bilayer by UNCHARGED H2O POLAR urea simple diffusion. MOLECULES glycerol Most solutes can move across the LARGE glucose membrane only if there is a membrane UNCHARGED POLAR sucrose transport protein to transfer them. MOLECULES Passive transport,in the same direction H',Na" HCO K' as a concentration gradient. IONS Ca2,CI Mg2+ Active transport,is mediated by carrier proteins,against a electrochemical gradient, require an input of energy. synthetic lipid bilayer This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

1.Simple diffusion (passive diffusion) 简单扩散(被动扩散) The concentration differs between both sides of membrane; Low molecular weight,fat-soluble; Does not require membrane transport proteins. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
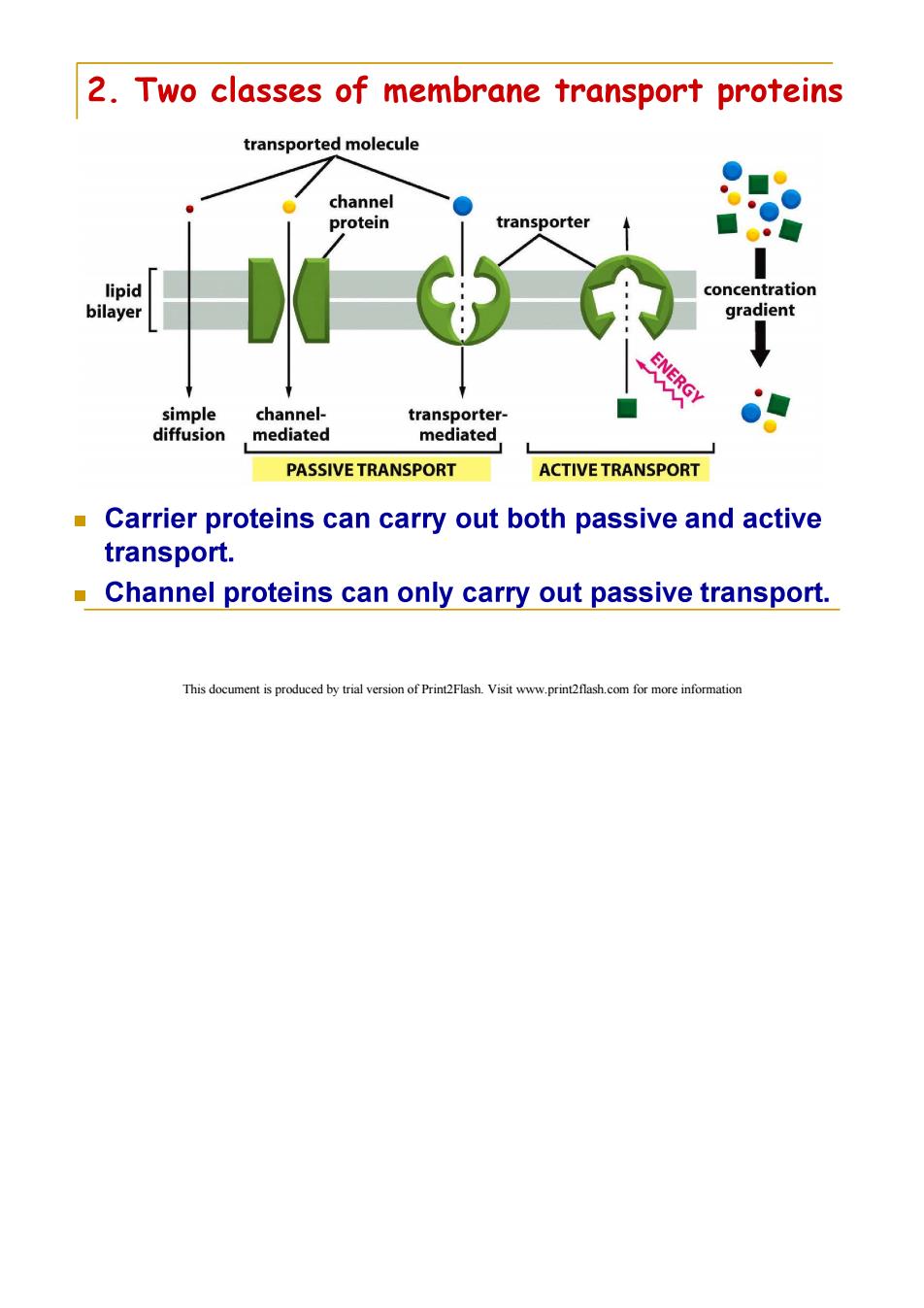
2.Two classes of membrane transport proteins transported molecule channel protein transporter lipid concentration bilayer gradient simple channel- transporter- diffusion mediated mediated PASSIVE TRANSPORT ACTIVE TRANSPORT Carrier proteins can carry out both passive and active transport. Channel proteins can only carry out passive transport. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Carrier Proteins solute stateA state B OUTSIDE lipid concentration bilayer gradient INSIDE transporter mediating solute-binding site passive transport Carrier proteins bind one or more solute molecules on one side of the membrane and then undergo a conformational change that transfer the solute to the other side of the membrane. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Carrier Proteins Carrier protein-mediated: Facilitated diffusion: 1)Bind with solute specifically and change the conformation; 2)Diffusion rate is influenced by the concentration gradient and the number of carrier protein; 3)Downhill,does not need ATP. Active transport: 1)Uphill,need ATP; 2)The carrier has the specificity and variability. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
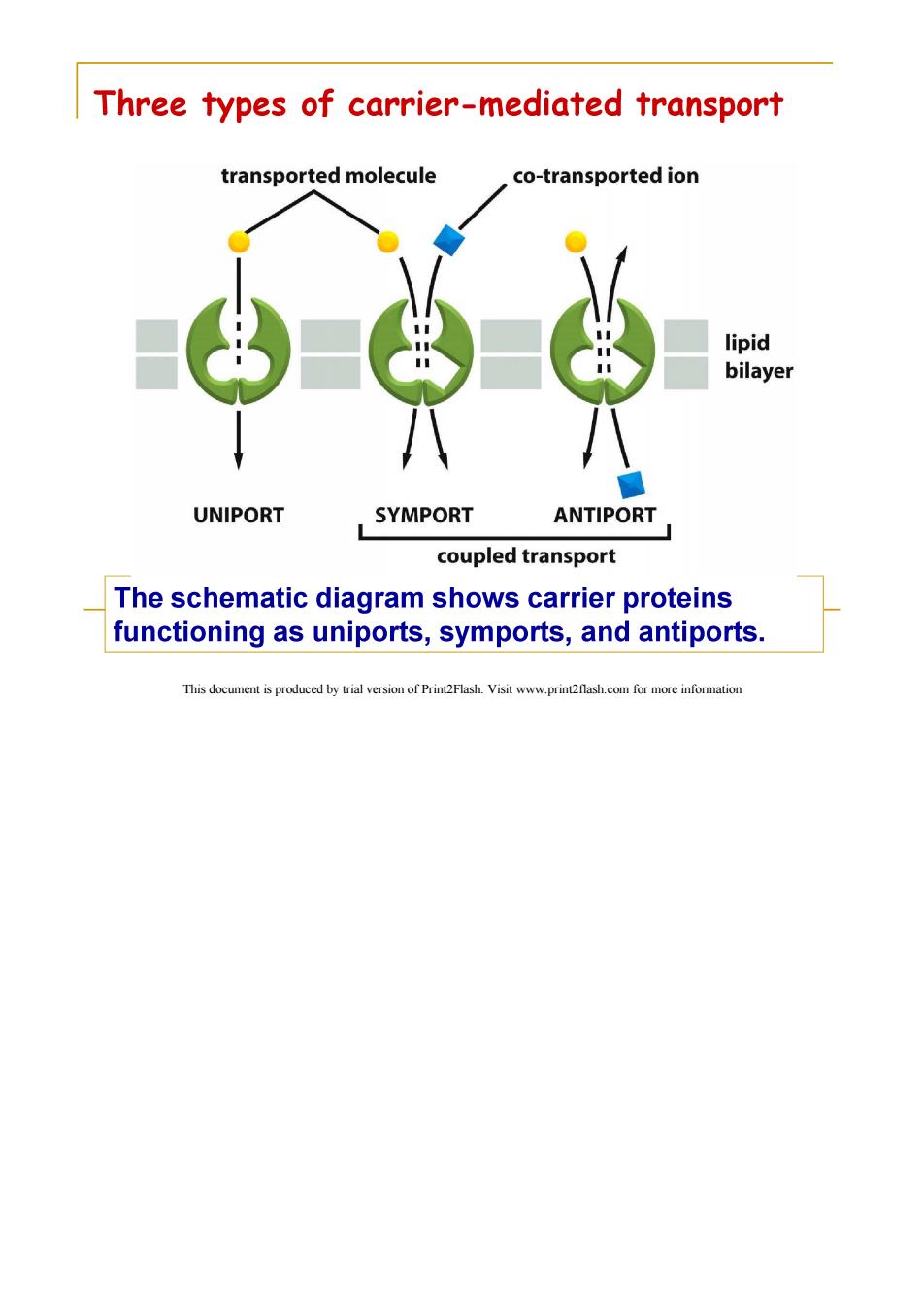
Three types of carrier-mediated transport transported molecule co-transported ion lipid bilayer UNIPORT SYMPORT ANTIPORT coupled transport The schematic diagram shows carrier proteins functioning as uniports,symports,and antiports. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
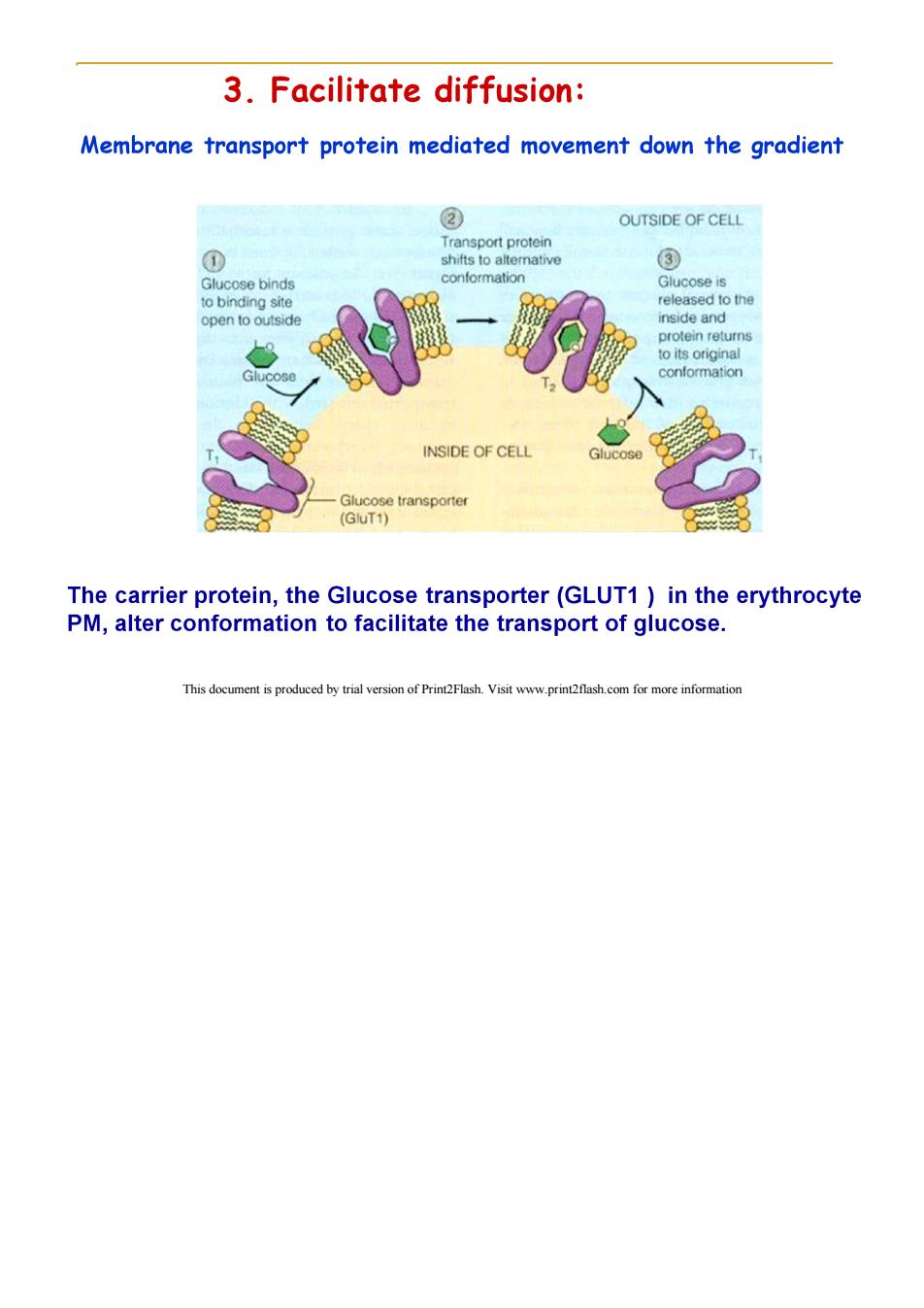
3.Facilitate diffusion: Membrane transport protein mediated movement down the gradient ② OUTSIDE OF CELL Transport protein ① shifts to altemative ③ Glucose binds conformation Glucose is to binding site released to the open to outside inside and protein returns to its original Glucose conformation INSIDE OF CELL Glucose Glucose transporter (GluT1) The carrier protein,the Glucose transporter(GLUT1 )in the erythrocyte PM,alter conformation to facilitate the transport of glucose. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information