
Medical Genetics Chapter 8 Genetics of Common Disorders with Complex Inheritance This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Medical Genetics Outline Multifactorial inheritance; Qualitative and quantitative traits; Genetic analysis of qualitative disease traits; Determining the relative contributions of genes and environment to complex disease; Genetic analysis of quantitative traits. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
Medical Genetics 1.Multifactorial inheritance Multifactorial/complex inheritance result from complex interactions between a number of genetic and environmental factors. o many different genes(major gene,minor gene), many environmental factors. o gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interactions. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Medical Genetics 2.Qualitative and quantitative traits ◆( Qualitative traits:a genetic disease that is either present or absent is referred to as a discrete or qualitative trait;one has the disease or not. Quantitative traits:measurable physiological or biochemical quantities such as height,blood pressure,serum cholesterol concentration,and body mass index(a measure of obesity)that underlie many common and devastating illnesses in the population. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Medical Genetics 2.1 Genetic Analysis of Qualitative Disease Traits Familial aggregation:affected individuals may cluster in families. Concordance and discordance:when two related individuals in a family have the same disease,they are said to be concordant for the disorder.Conversely,when only one member of the pair of relatives is affected and the other is not, the relatives are discordant for the disease. genocopy phenocopy This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Medical Genetics Measuring familial aggregation in qualitative traits ① Relative Risk入r Prevalence of the disease in the 入= relatives of an affected person Prevalence of the disease in the general population The value of Ar is a measure of familial aggregation that depends both on the risk of the disease's recurrence in the family and on the population prevalence; ◆the larger入ris,the greater is the familial aggregation. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Medical Genetics ◆ Measuring familial aggregation in qualitative traits ① Relative Risk入r ② Case-control studies: Patients with a disease(the cases)are compared with suitably chosen individuals without the disease(the controls),with respect to family history of disease(as well as other factors,such as environmental exposures, occupation,geographical location,parity,and previous illnesses). This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Medical Genetics 2.2 Determining the relative contributions of genes and environment to complex disease ◆ Concordance and allele sharing among relatives Unrelated family member controls ◆Twin studies This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
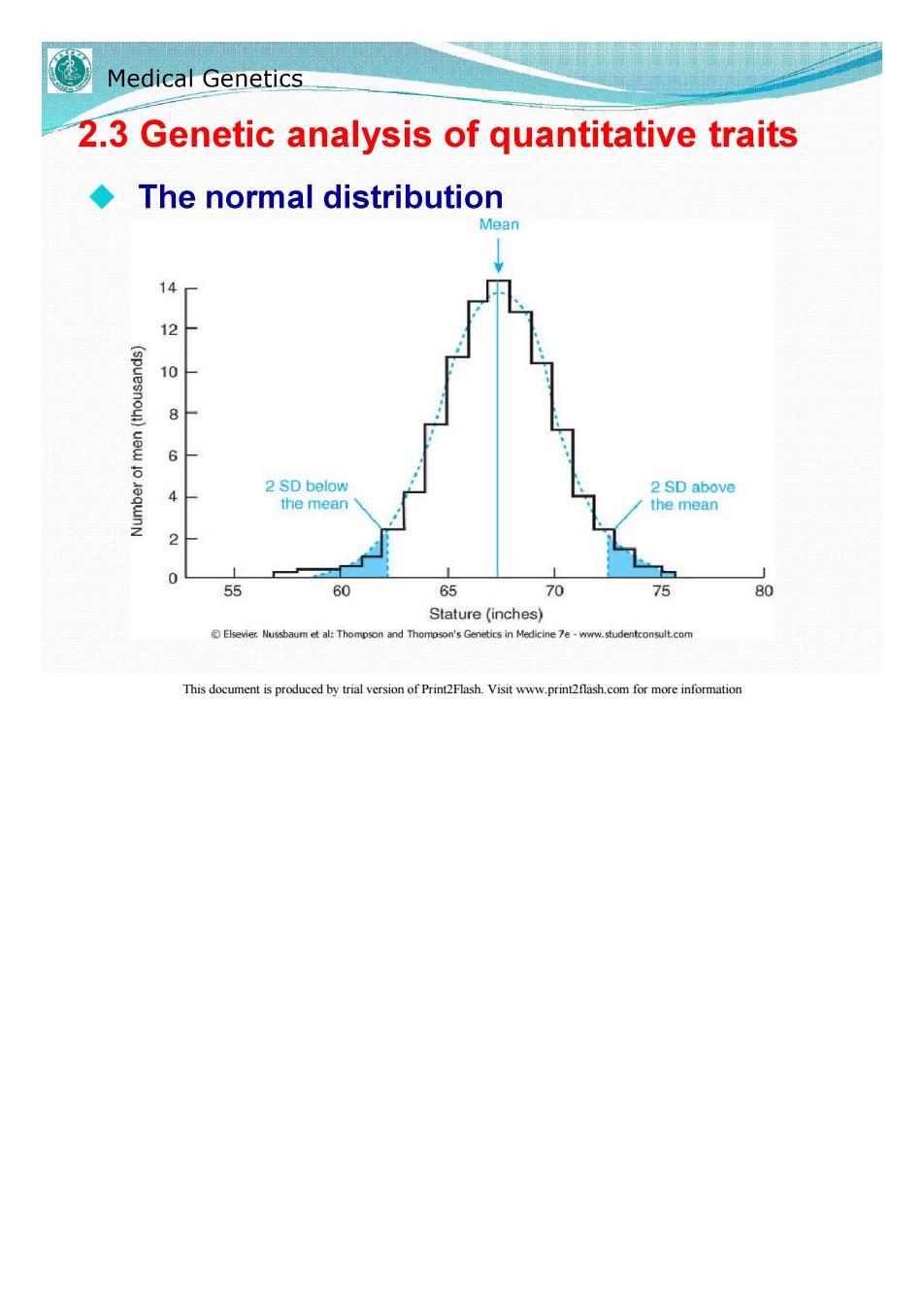
Medical Genetics 2.3 Genetic analysis of quantitative traits The normal distribution Mean 14 10 (spuesnou)uew jo eqwnN 6 2 SD below 2 SD above the mean the mean 2 1 55 60 65 70 75 80 Stature(inches) Elsevier.Nussbaum et al:Thompson and Thompson's Genetics in Medicine 7e-www.studentconsult.com This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Medical Genetics 2.4 Familial aggregation of quantitative traits ◆Heritability Variance in DZ pairs-Variance in MZ pairs Variance in DZ pairs The higher the heritability,the greater is the contribution of genetic differences among people in causing variability of the trait. ●h2 varies from0to1. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash. Visit www.print2flash.com for more information