
Cell Signaling EXTRACELLULAR SIGNAL MOLECULE RECEPTOR PROTEIN plasma membrane of target cell INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING PROTEINS ● EFFECTOR PROTEINS metabolic gene regulatory cytoskeletal enzyme protein protein altered altered gene altered cell metabolism expression shape or movement This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Section 1 Overview of cell signaling 1.Signal transduction lecricasig extracellular signal N molecule A N sound OUT intracellular signal molecule B out A B This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
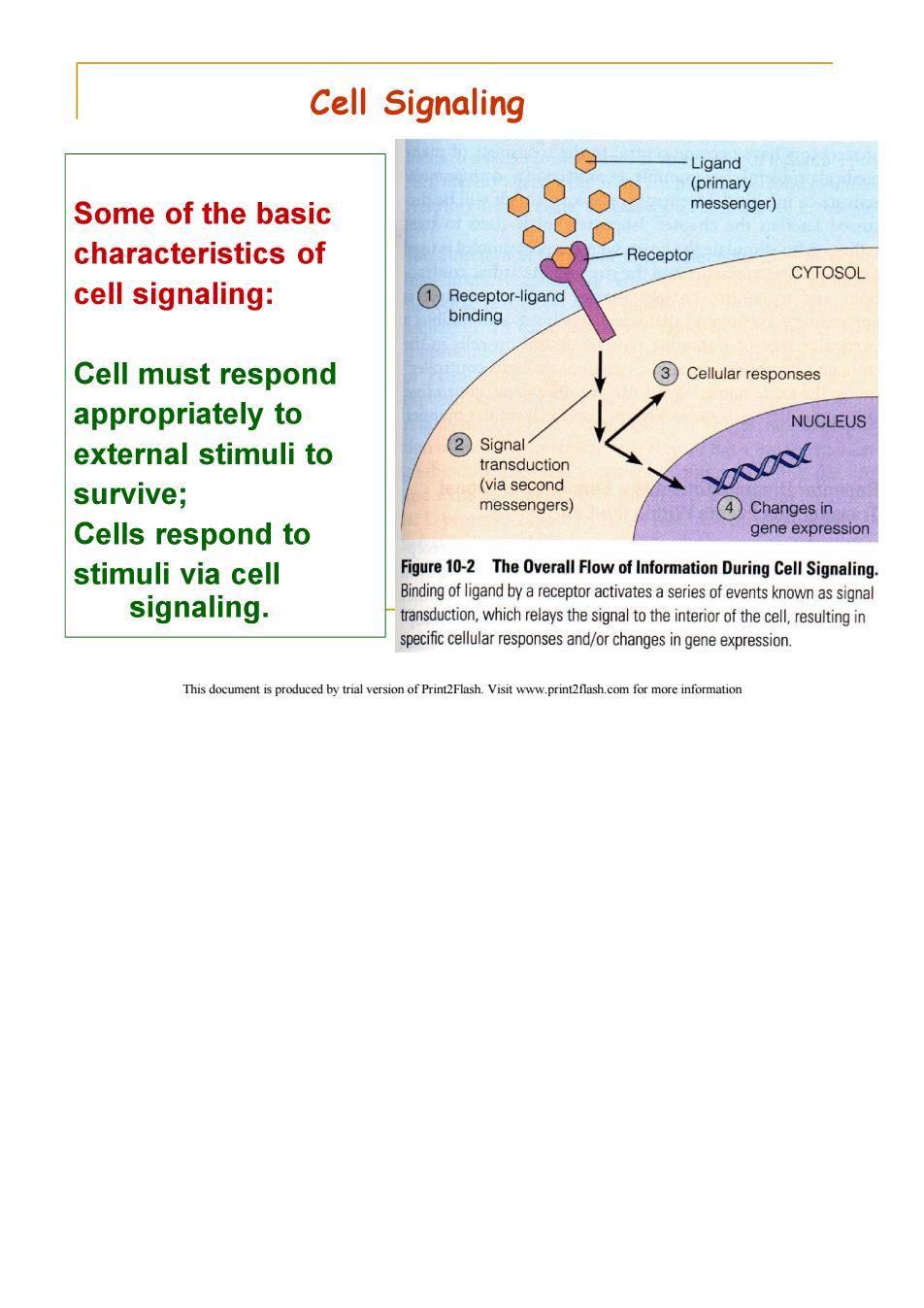
Cell Signaling Ligand (primary Some of the basic messenger) characteristics of Receptor CYTOSOL cell signaling: (①Receptor-.-ligand binding Cell must respond 3) Cellular responses appropriately to NUCLEUS external stimuli to ②Signal transduction survive; (via second YX messengers) (4Changes in Cells respond to gene expression stimuli via cell Figure 10-2 The Overall Flow of Information During Cell Signaling. Binding of ligand by a receptor activates a series of events known as signal signaling. transduction,which relays the signal to the interior of the cell,resulting in specific cellular responses and/or changes in gene expression. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
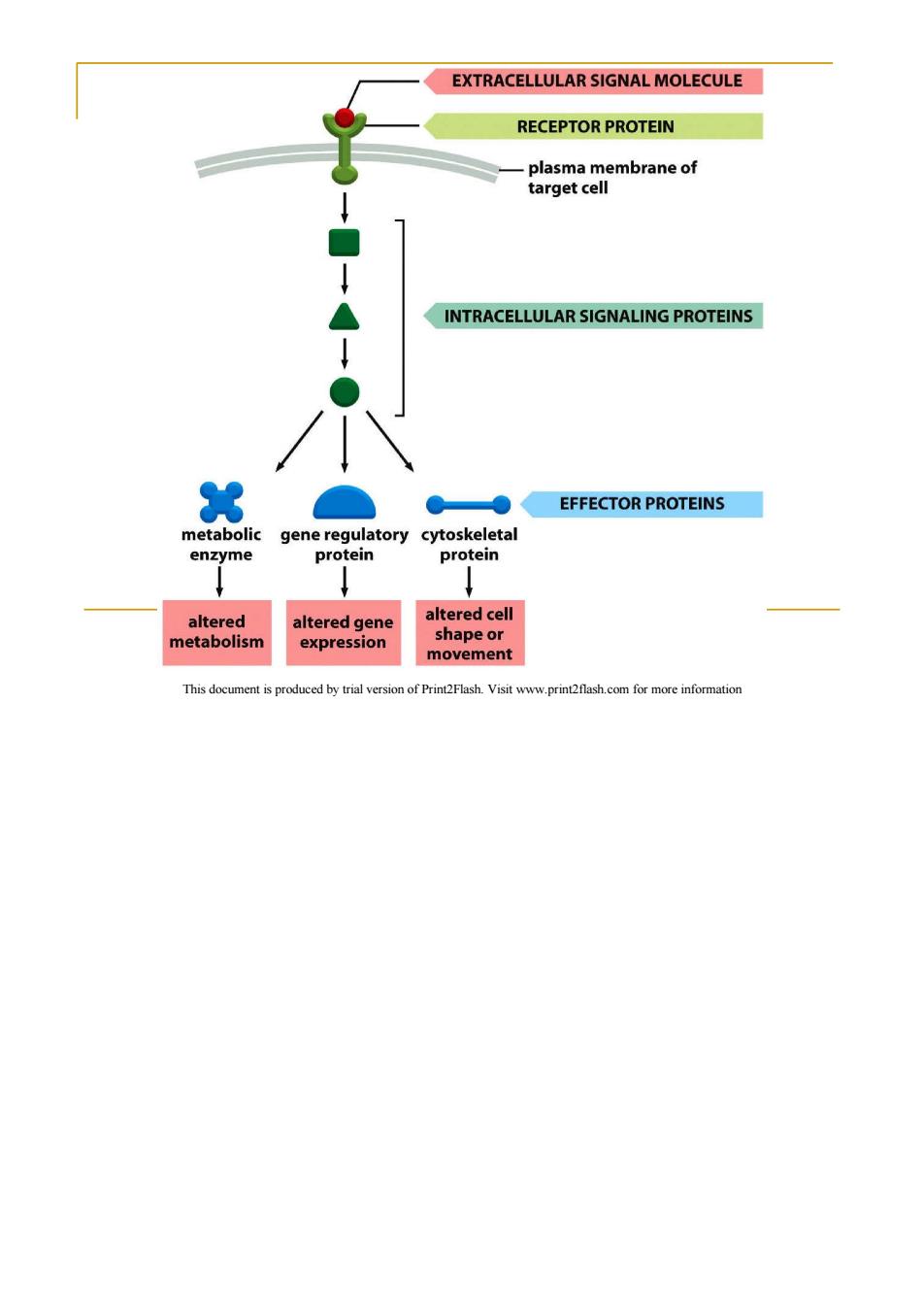
EXTRACELLULAR SIGNAL MOLECULE RECEPTOR PROTEIN plasma membrane of target cell INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING PROTEINS 3 EFFECTOR PROTEINS metabolic gene regulatory cytoskeletal enzyme protein protein altered altered gene altered cell metabolism expression shape or movement This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
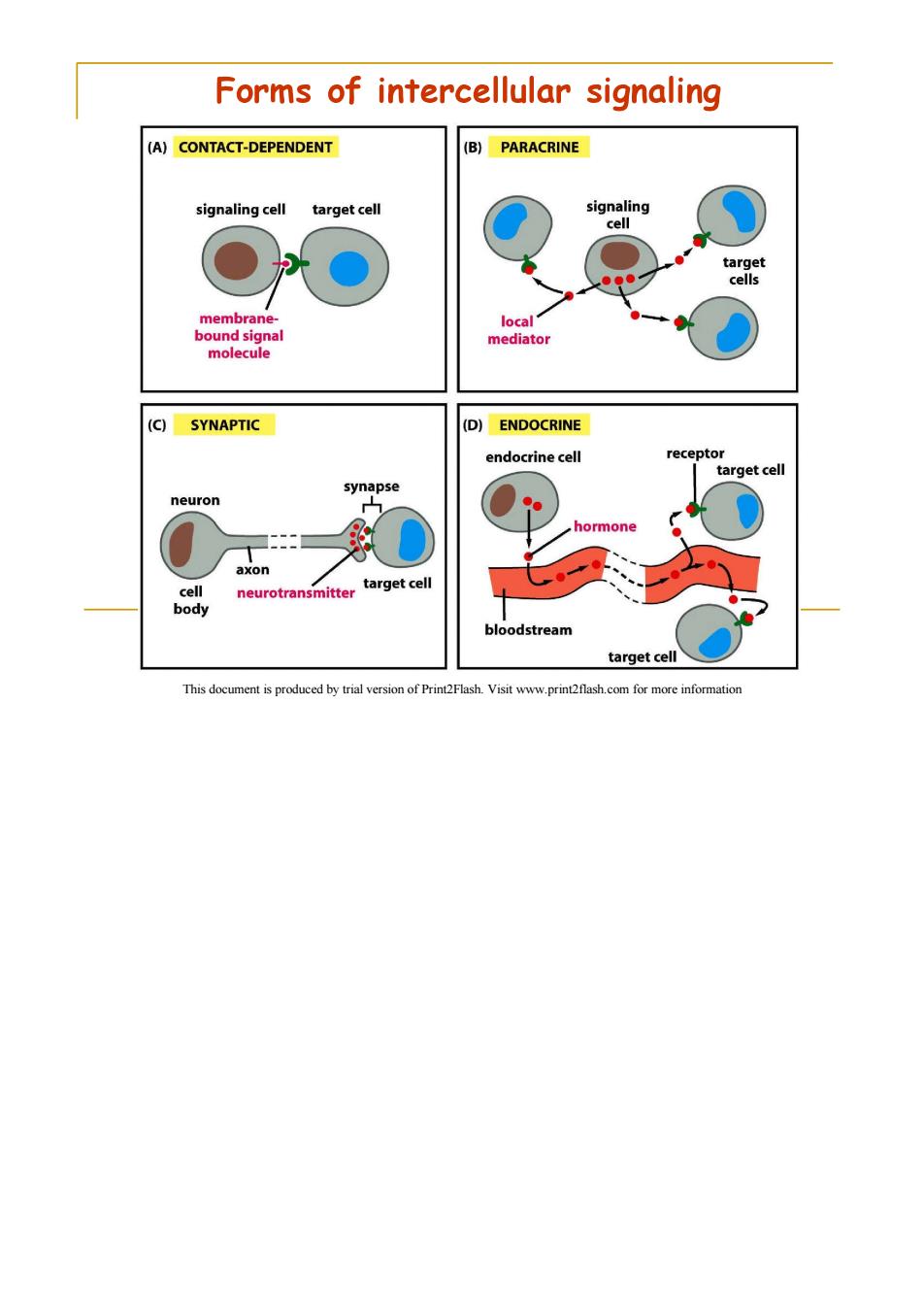
Forms of intercellular signaling (A)CONTACT-DEPENDENT (B)PARACRINE signaling cell target cell signaling cell target ●● cells membrane- local bound signal mediator molecule (C) SYNAPTIC (D)ENDOCRINE endocrine cell receptor target cell synapse neuron hormone axon cell neurotransmitter target cell body bloodstream target cell This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
2.Signal Molecules and Receptors 2.1 Signal molecules: Lipid-soluble hormones; Water-soluble hormones; nitric oxide (NO)and carbon monoxide(CO) as cellular messengers. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
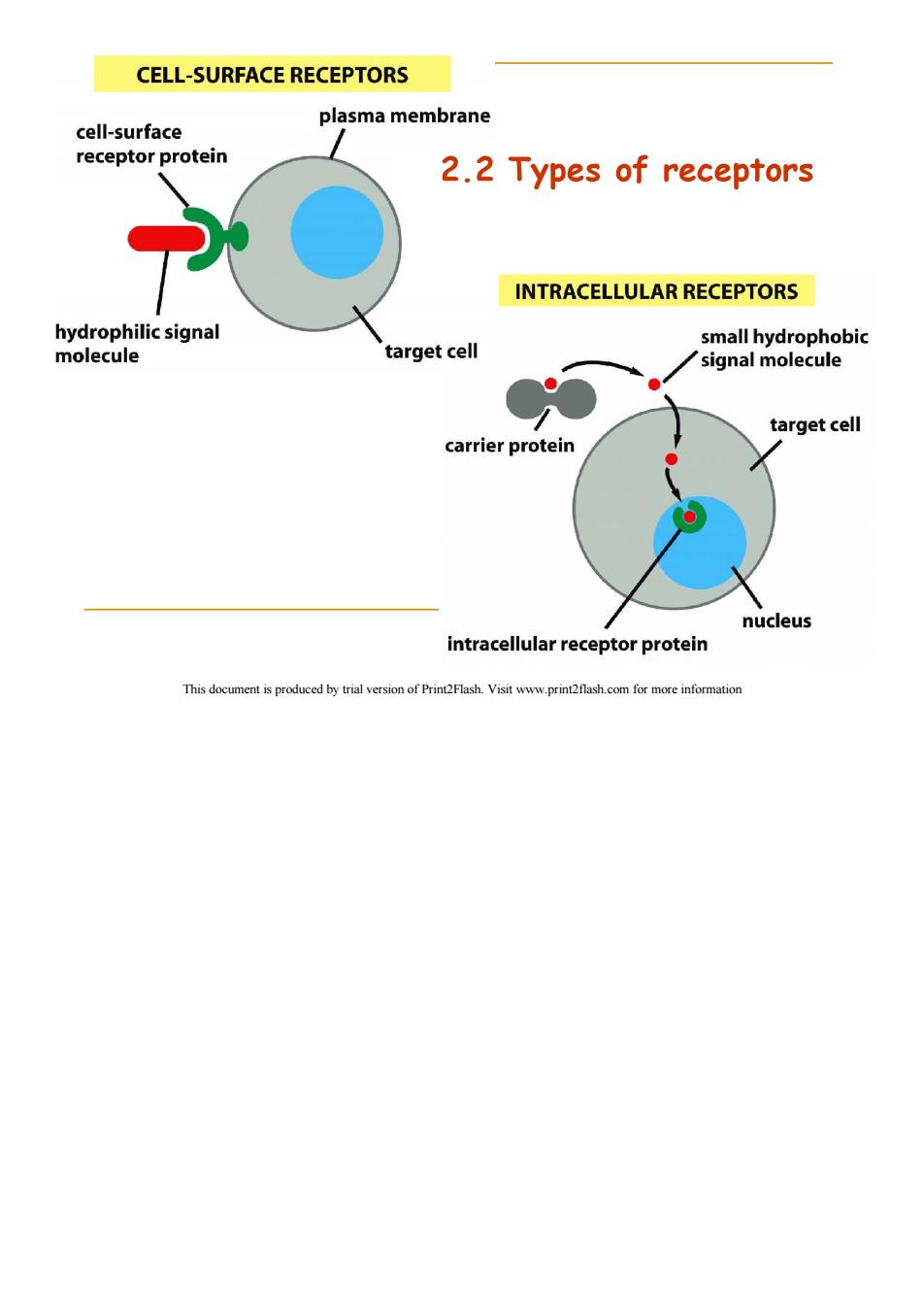
CELL-SURFACE RECEPTORS plasma membrane cell-surface receptor protein 2.2 Types of receptors INTRACELLULAR RECEPTORS hydrophilic signal small hydrophobic molecule target cell signal molecule target cell carrier protein nucleus intracellular receptor protein This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Cell surface receptors include three classes:glycoproteins (A)ION-CHANNEL-LINKED RECEPTOR IB)G-PROTEIN-LINKED RECEPTOR G prote activated enzyme or enzyme or ion channel IC)ENZYME-LINKED RECEPTOR inactive active catalytic catalytie dom湾in domin This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
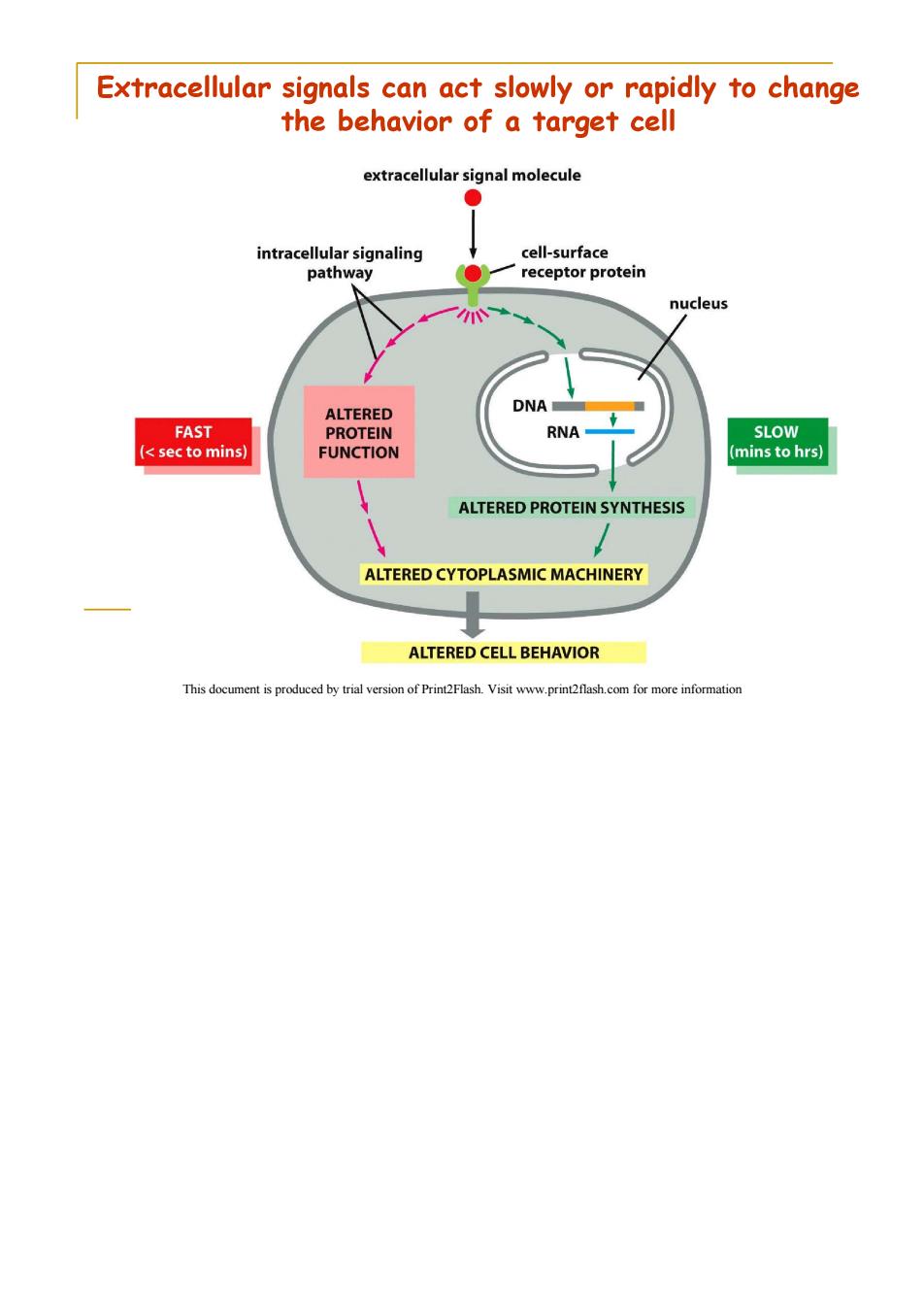
Extracellular signals can act slowly or rapidly to change the behavior of a target cell extracellular signal molecule intracellular signaling cell-surface pathway receptor protein nucleus ALTERED DNA FAST PROTEIN RNA SLOW (sec to mins) FUNCTION (mins to hrs) ALTERED PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ALTERED CYTOPLASMIC MACHINERY ALTERED CELL BEHAVIOR This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

2.3 Second messengers and molecular switch Second messengers: The first second messenger molecular-cAMP. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1971. cAMP,cGMP,Ca2+,DAG,IP3 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information