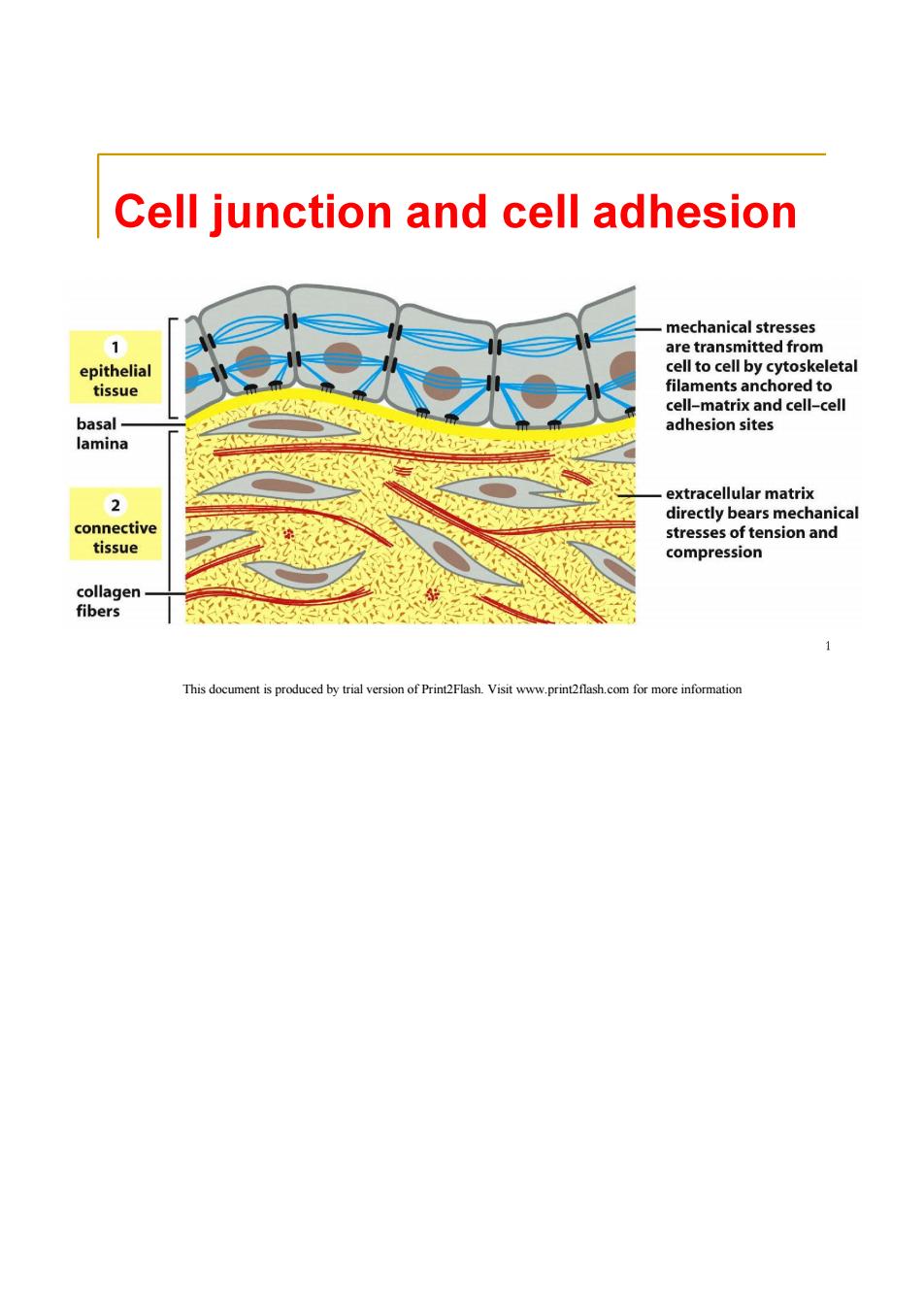
Cell junction and cell adhesion mechanical stresses 1 are transmitted from epithelial cell to cell by cytoskeletal tissue filaments anchored to cell-matrix and cell-cell basal- adhesion sites lamina extracellular matrix directly bears mechanical connective stresses of tension and tissue compression collagen fibers 1 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
Contents Cell junction and cell adhesion Cell junction 2 Cell adhesion molecules 2 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
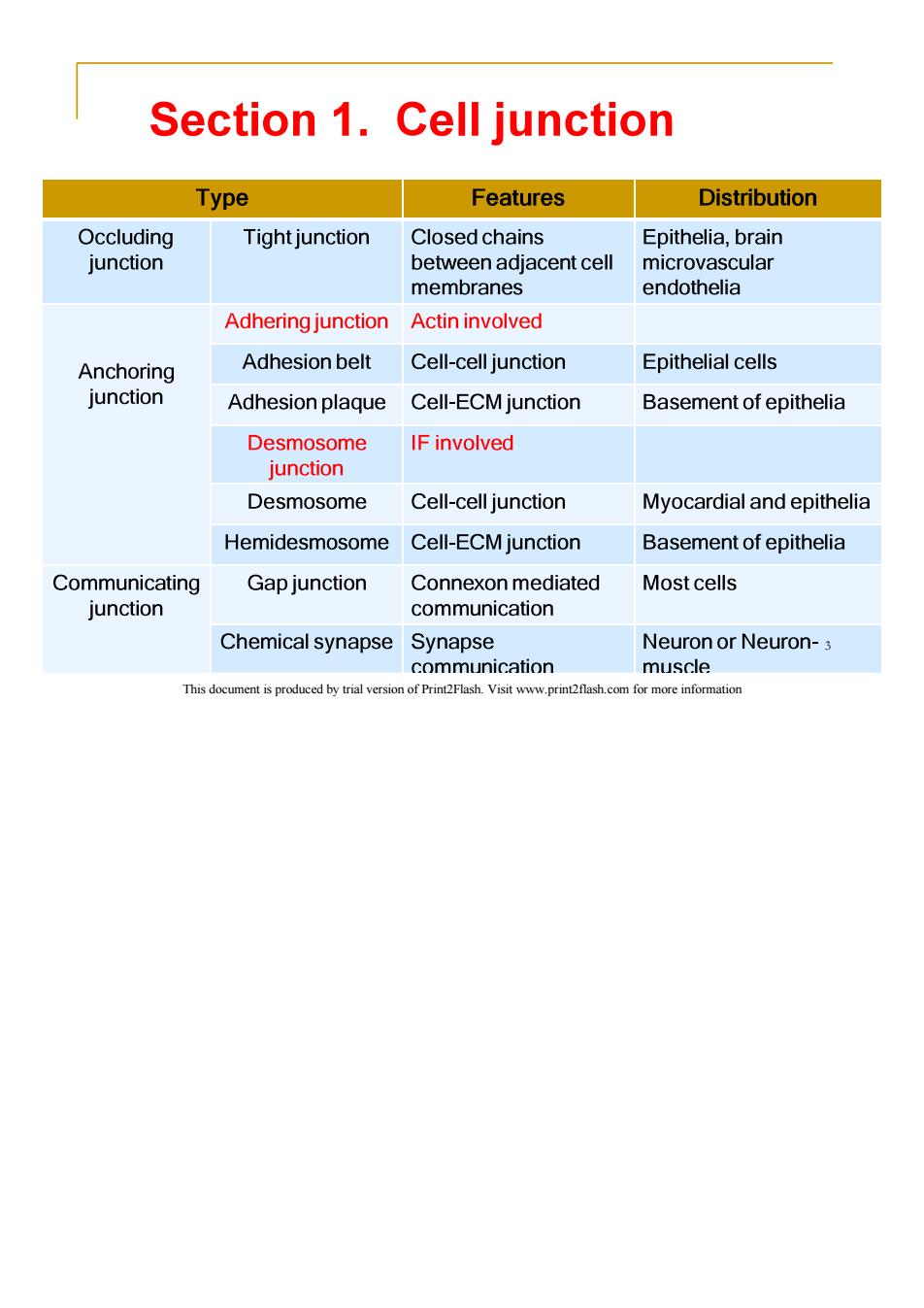
Section 1.Cell junction Type Features Distribution Occluding Tight junction Closed chains Epithelia,brain junction between adjacent cell microvascular membranes endothelia Adhering junction Actin involved Anchoring Adhesion belt Cell-cell junction Epithelial cells junction Adhesion plaque Cell-ECM junction Basement of epithelia Desmosome IF involved junction Desmosome Cell-cell junction Myocardial and epithelia Hemidesmosome Cell-ECM junction Basement of epithelia Communicating Gap junction Connexon mediated Most cells junction communication Chemical synapse Synapse Neuron or Neuron-3 communication muscle This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
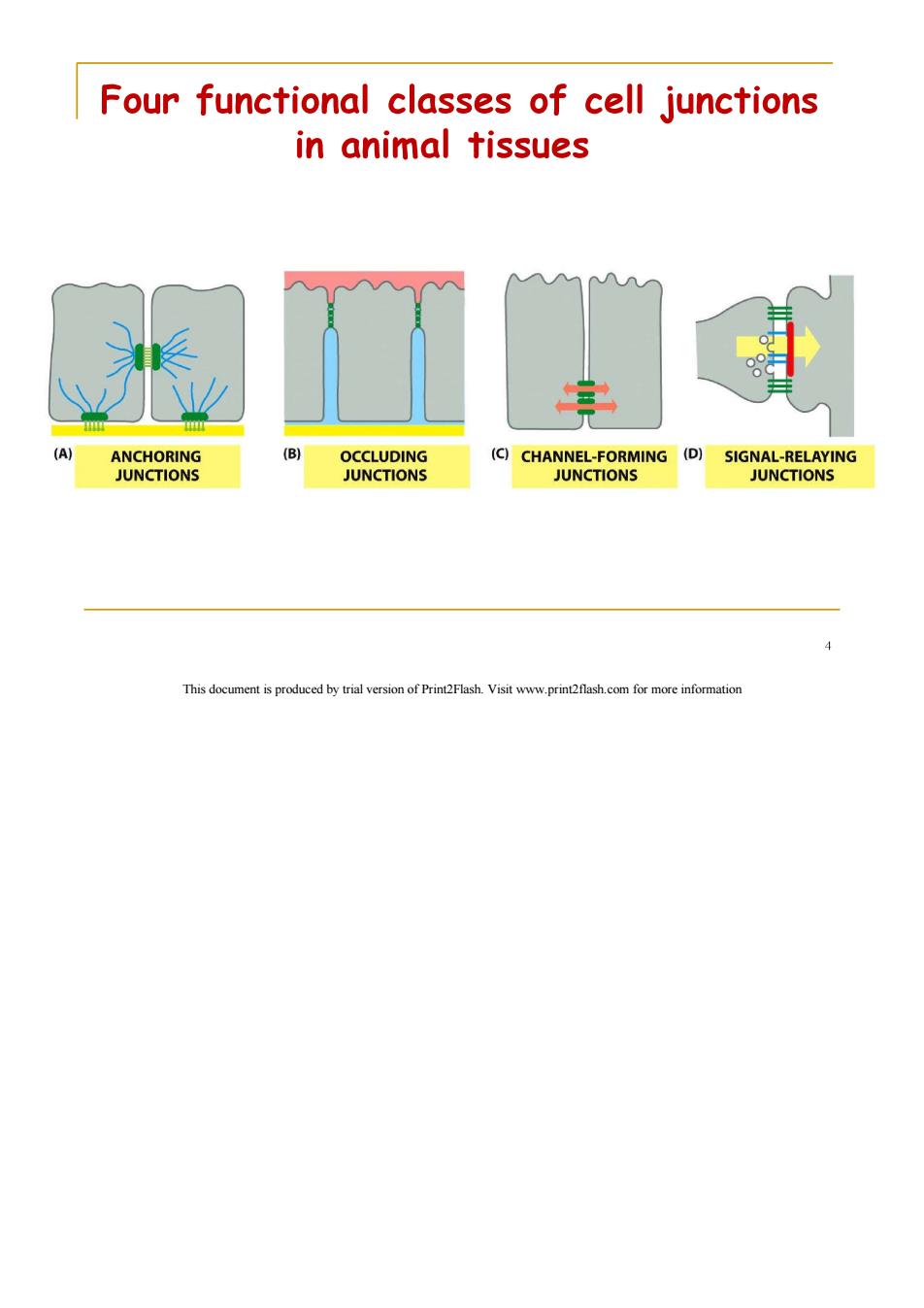
Four functional classes of cell junctions in animal tissues (A ANCHORING (B) OCCLUDING (C)CHANNEL-FORMING (D) SIGNAL-RELAYING JUNCTIONS JUNCTIONS JUNCTIONS JUNCTIONS This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
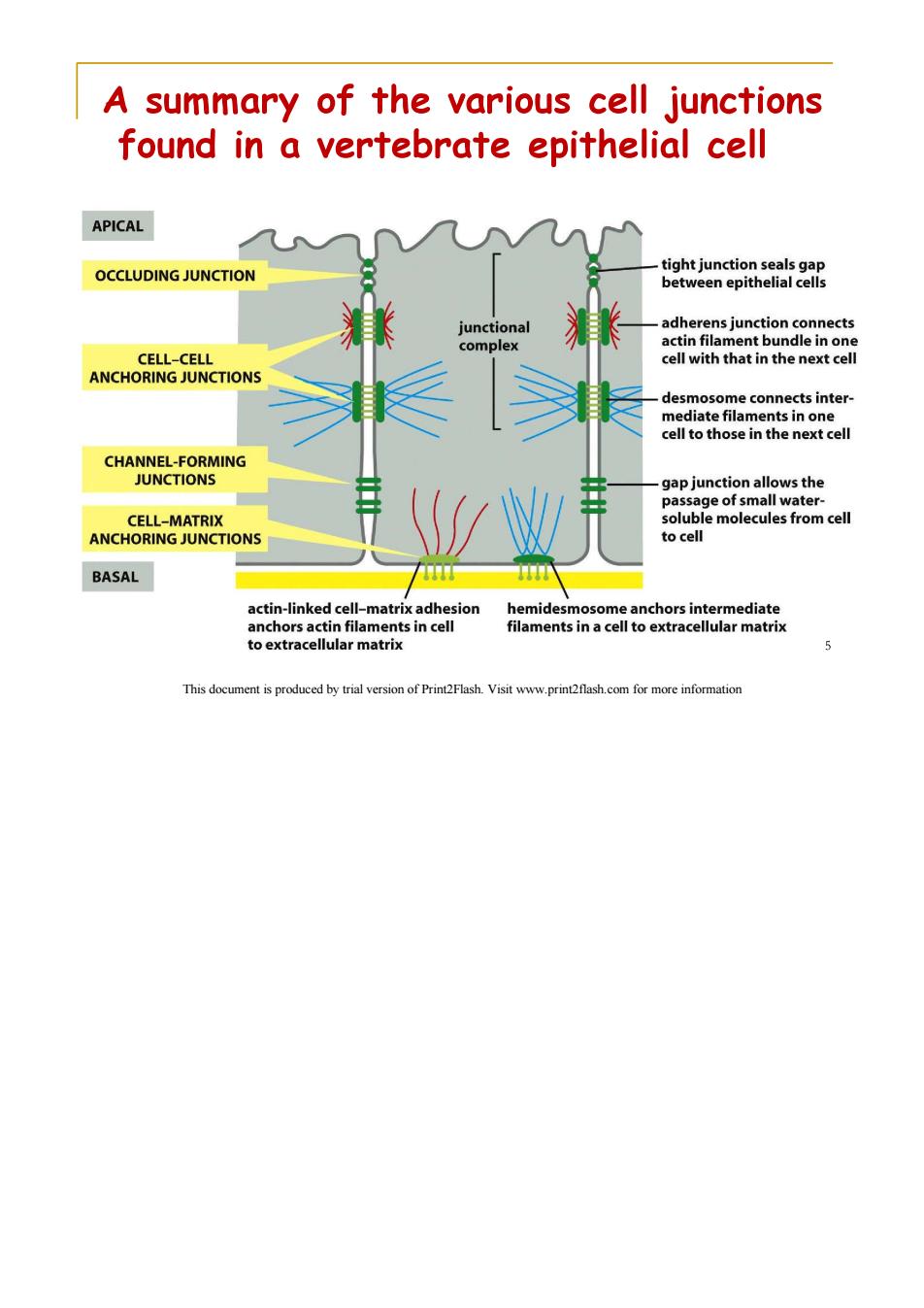
A summary of the various cell junctions found in a vertebrate epithelial cell APICAL OCCLUDING JUNCTION tight junction seals gap between epithelial cells junctional adherens junction connects complex actin filament bundle in one CELL-CELL cell with that in the next cell ANCHORING JUNCTIONS desmosome connects inter- mediate filaments in one cell to those in the next cell CHANNEL-FORMING JUNCTIONS gap junction allows the passage of small water- CELL-MATRIX soluble molecules from cell ANCHORING JUNCTIONS to cell BASAL actin-linked cell-matrix adhesion hemidesmosome anchors intermediate anchors actin filaments in cell filaments in a cell to extracellular matrix to extracellular matrix 5 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
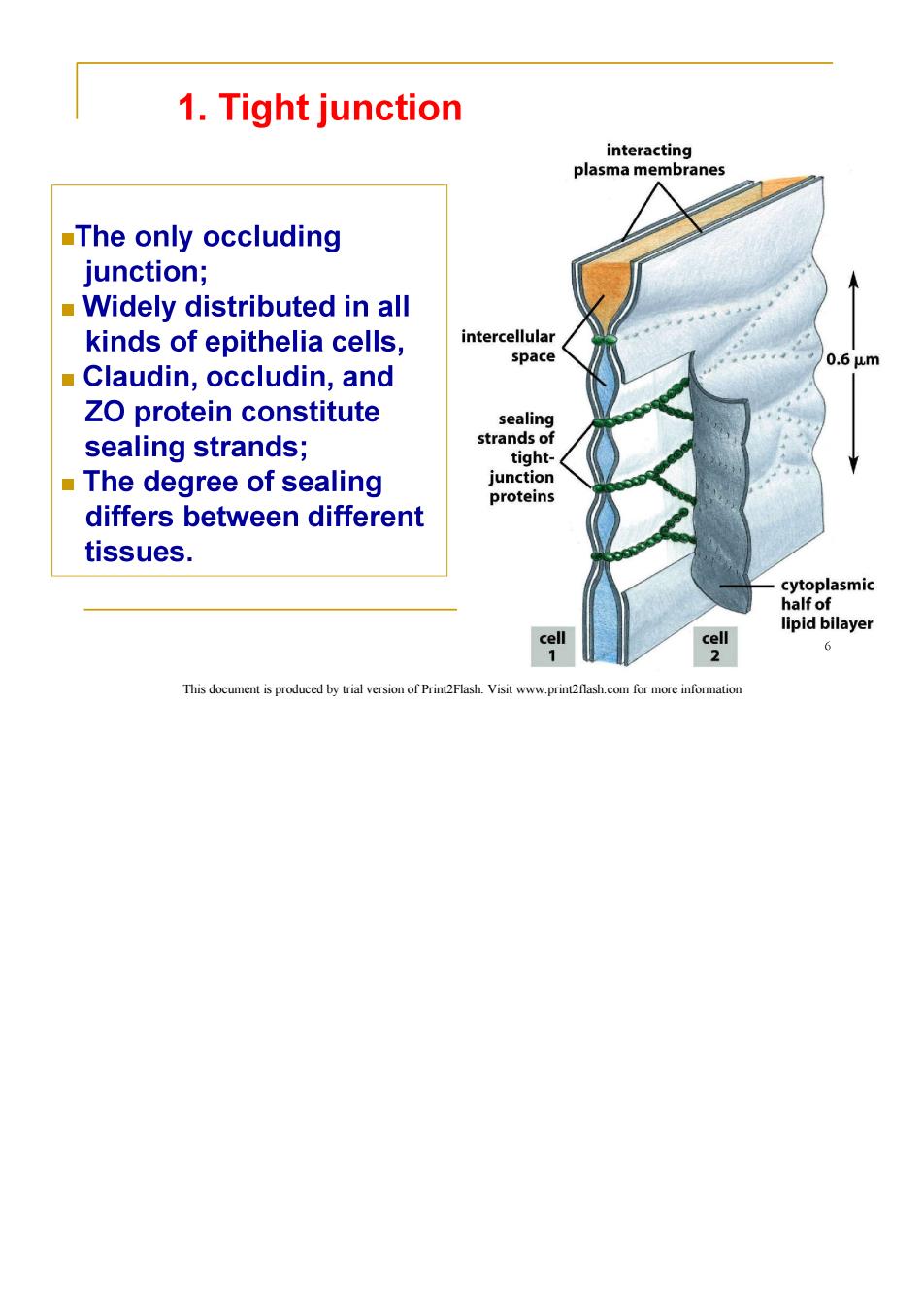
1.Tight junction interacting plasma membranes The only occluding junction; Widely distributed in all kinds of epithelia cells, intercellular space 0.6um Claudin,occludin,and ZO protein constitute sealing sealing strands; strands of tight- The degree of sealing junction proteins differs between different tissues. cytoplasmic half of lipid bilayer cell cell 6 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
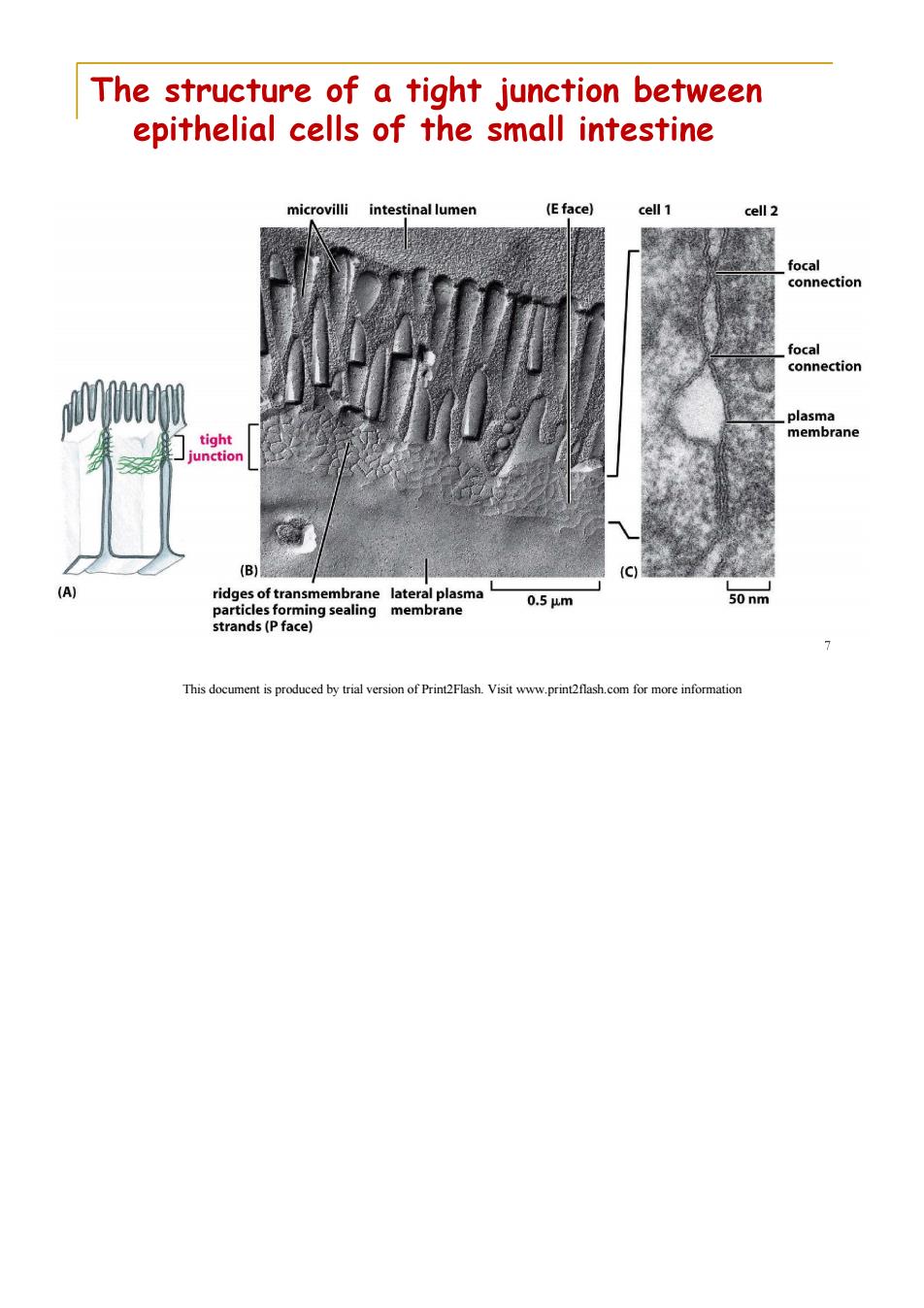
The structure of a tight junction between epithelial cells of the small intestine microvilli intestinal lumen (E face) cell 1 cell 2 focal connection focal connection plasma tight membrane junction (B) (A) ridges of transmembrane lateral plasma 0.5um 50nm particles forming sealing membrane strands(P face) 7 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more informatior

A model of a tight junction cell 1 UF UU cell 2 claudin occludin tight-junction proteins 8 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Function of tight junction Seal the gap between epithelia,isolate the tissue and outside,prevent material transition,ensure the environmental stability within the organization. The barrier to prevent lateral diffusion of membrane lipids and protein,keep the polarity of epithelial cells. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
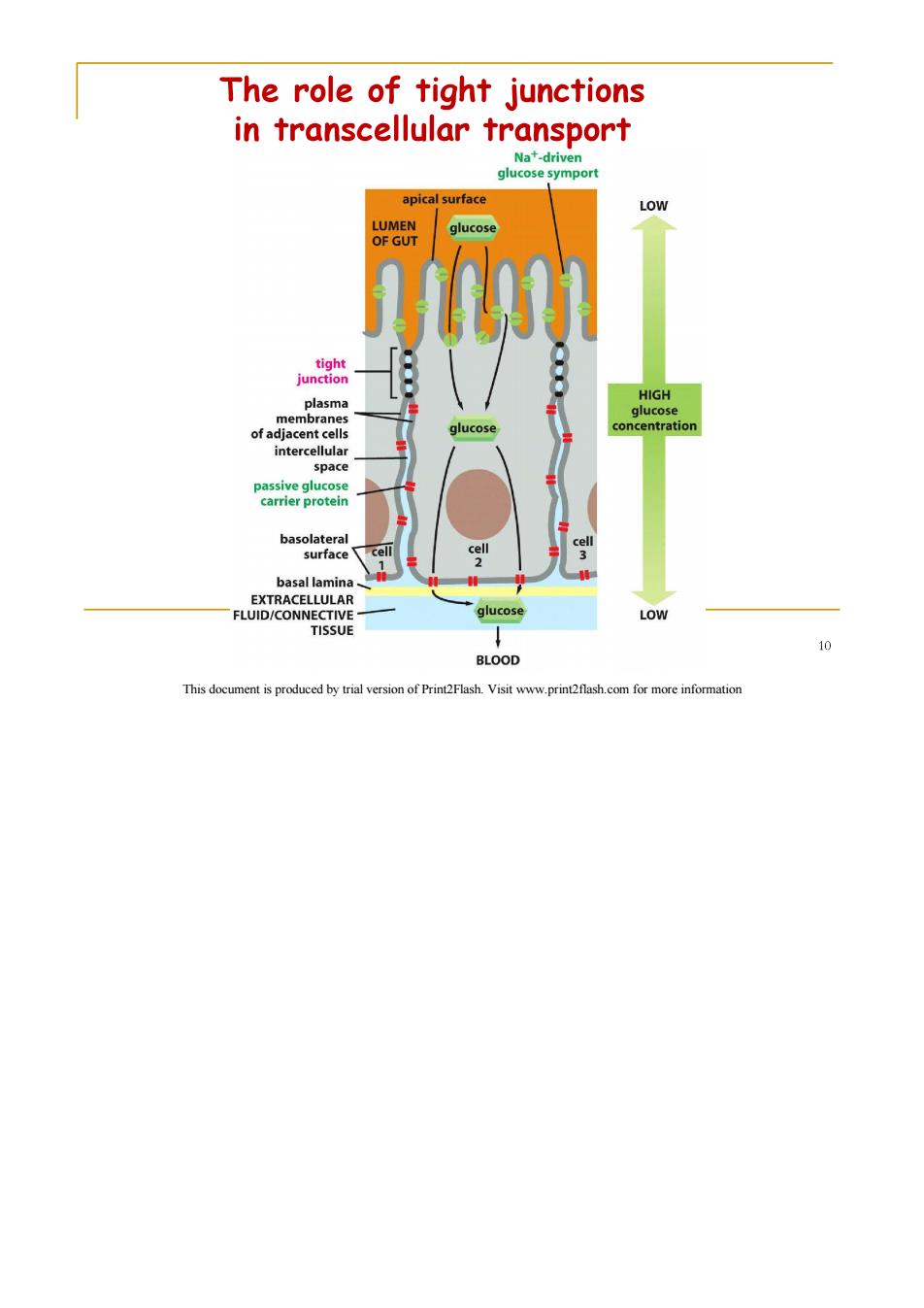
The role of tight junctions in transcellular transport Na+-driven glucose symport apical surface LOW LUMEN glucose OF GUT tight junction HIGH plasma glucose membranes of adjacent cells glucose concentration intercellular space passive glucose carrier protein basolateral cell surface cell cell basal lamina EXTRACELLULAR FLUID/CONNECTIVE glucose LOW TISSUE BLOOD This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information