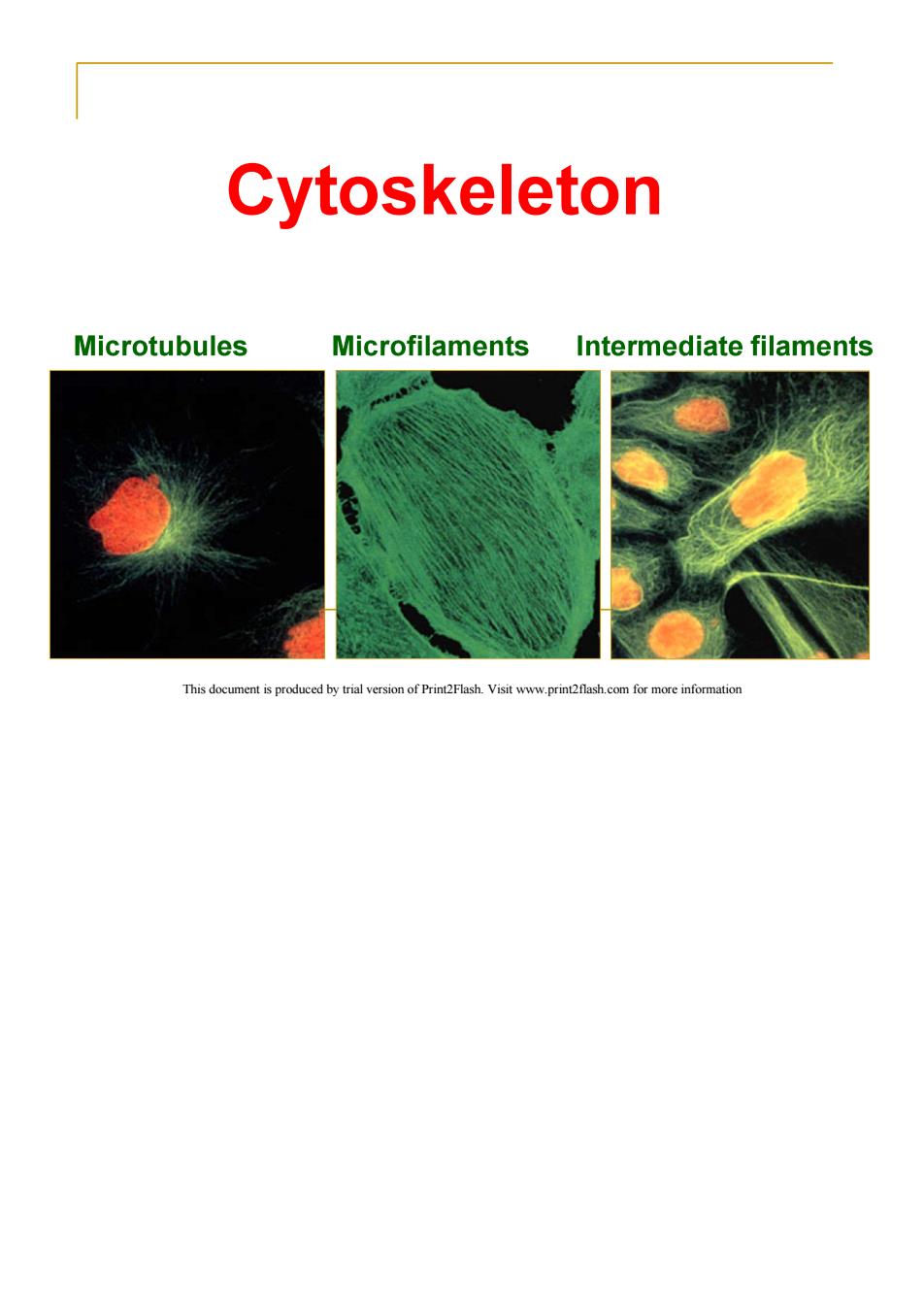
Cytoskeleton Microtubules Microfilaments Intermediate filaments This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Concept of Cytoskeleton (Narrow sense) The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments in eukaryotic cells.It provide structural integrity dynamics for cells; helps to move organelles and materials throughout cell;helps to move chromosomes during cell division. There are 3 basic components of the cytoskeleton: Microtubules(MT)(微管); Microfilaments(MF)(微丝); Intermediate filaments(lF)(中间纤维). This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
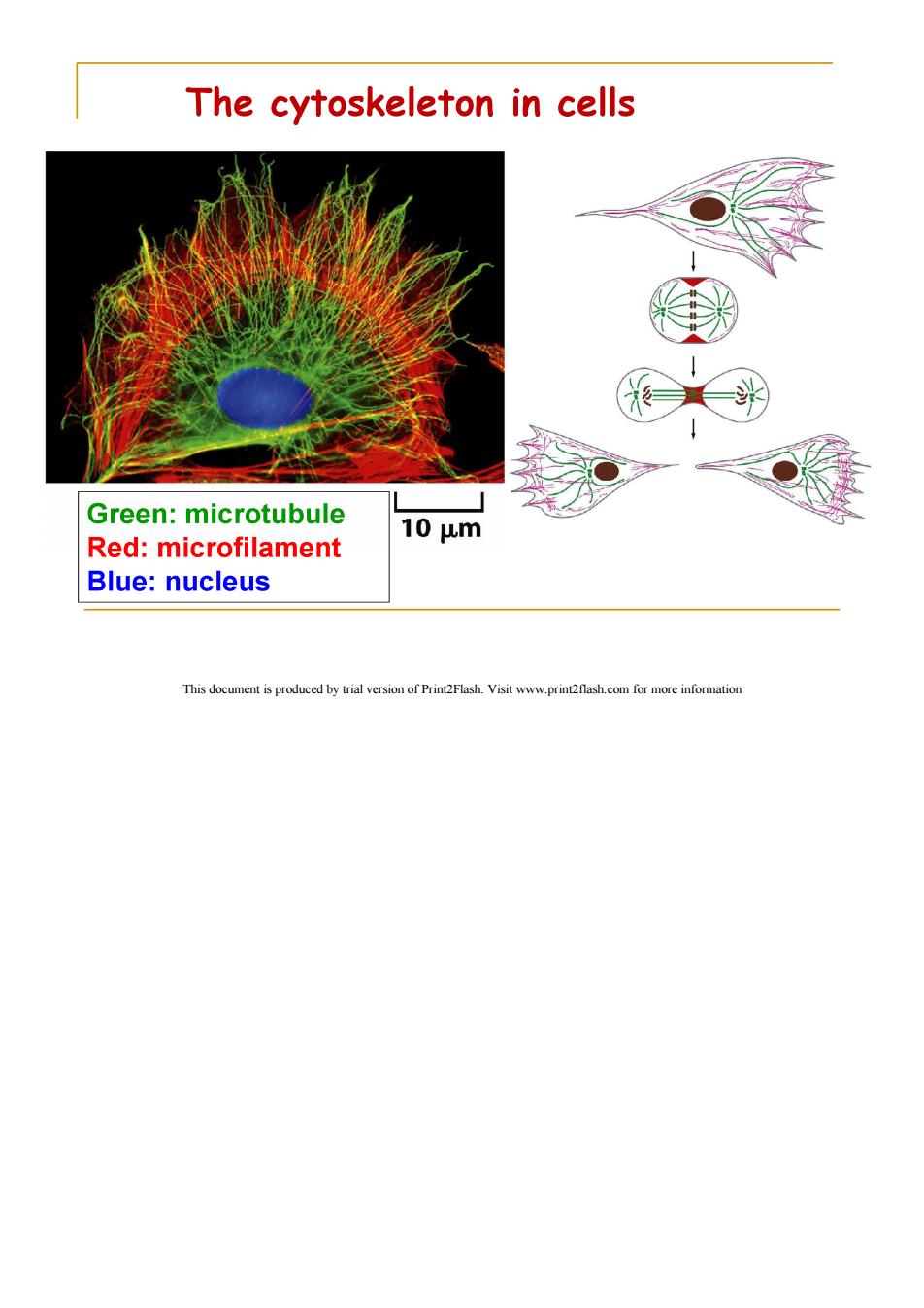
The cytoskeleton in cells Green:microtubule 10 um Red:microfilament Blue:nucleus This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
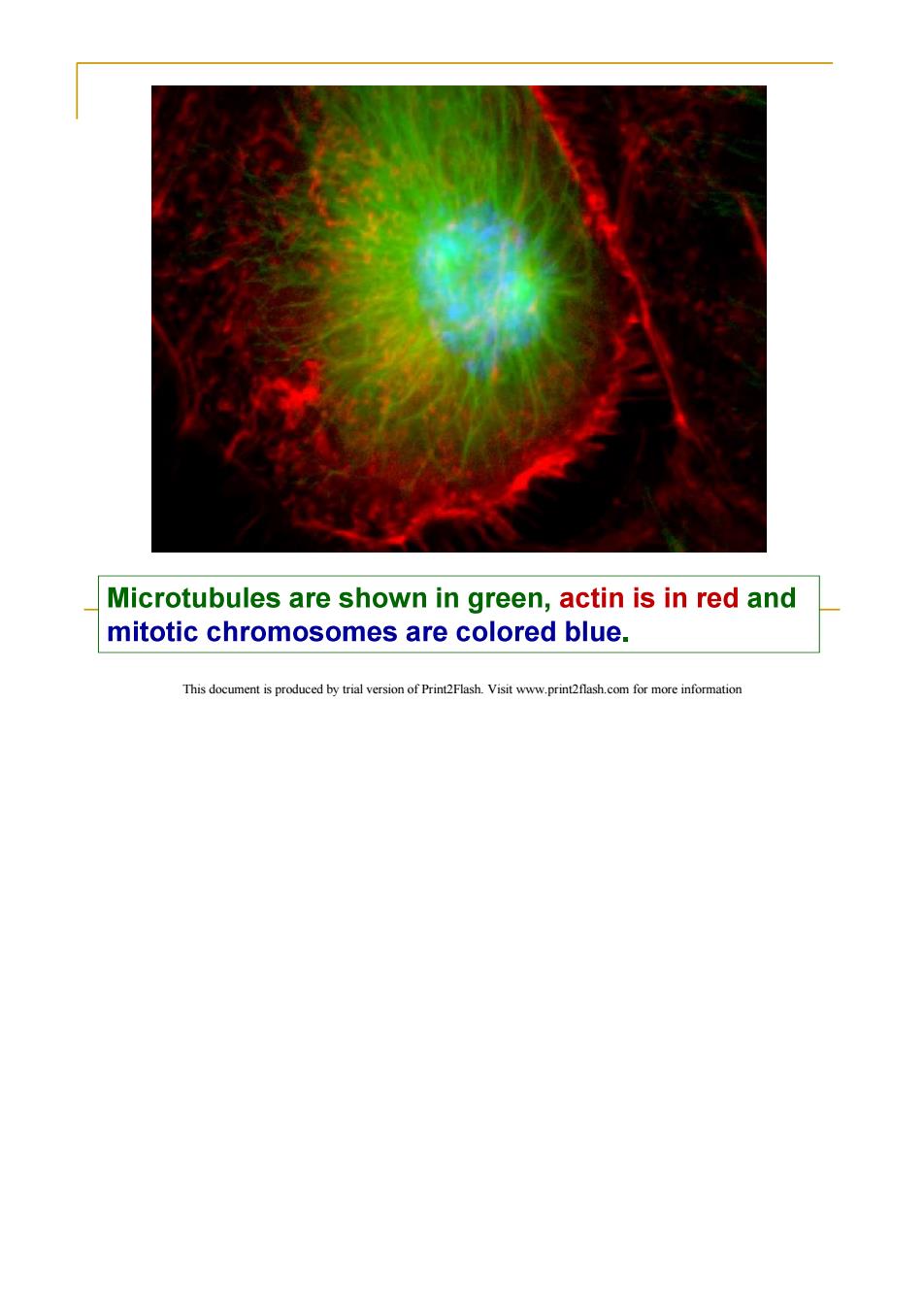
Microtubules are shown in green,actin is in red and mitotic chromosomes are colored blue. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more informatior
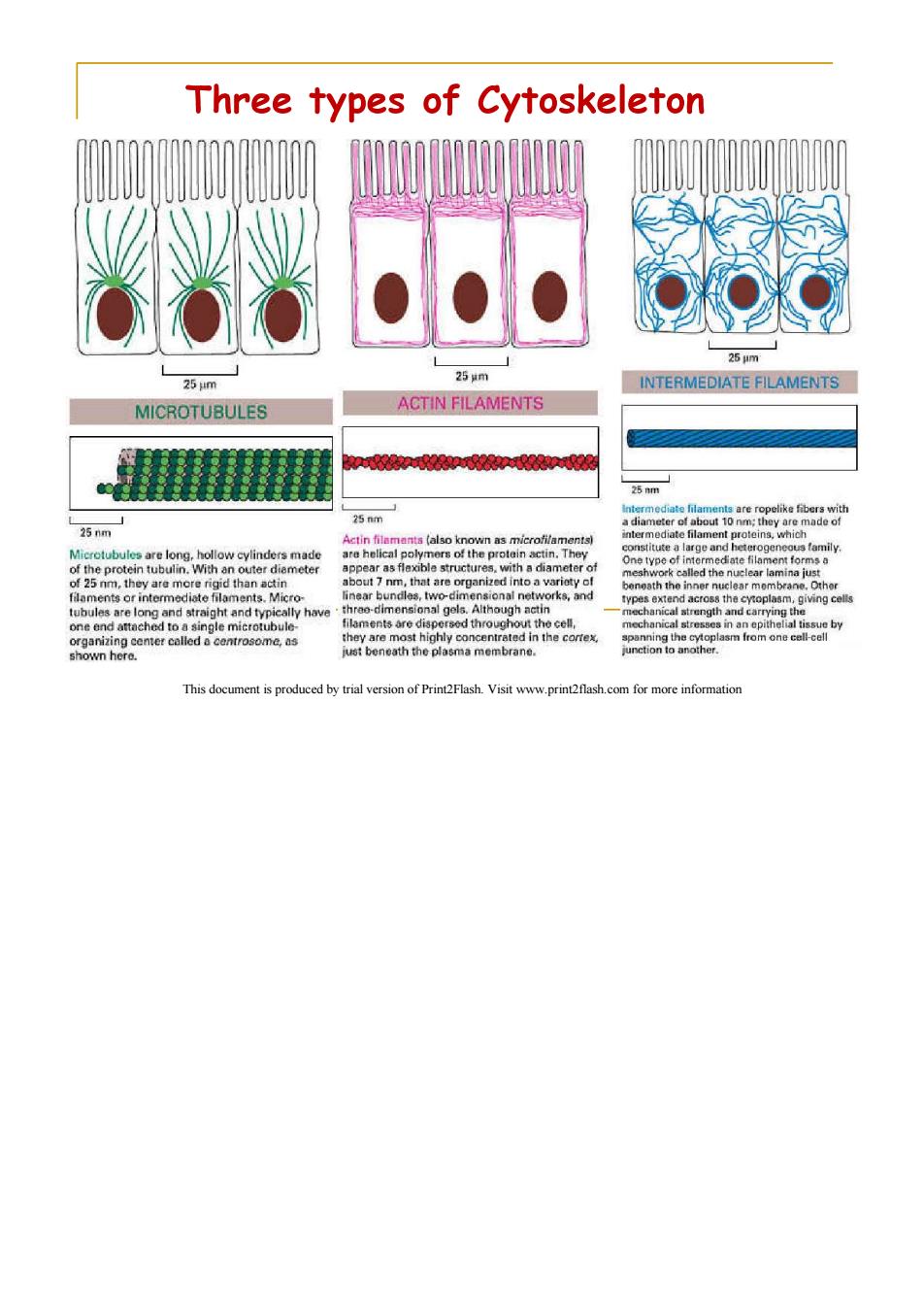
Three types of Cytoskeleton 254m 254m 25m INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS MICROTUBULES ACTIN FILAMENTS P您p0n般畅 25m Intermediate lilaments are ropelike fibers with 25 nm a diameter of about 10 nm;they are made of 25 nm Actin filamants (also known as microfilaments) intermediate filament proteins,which Microtubules are long,hollow cylinders made are helical polymers of the protein actin.They constitute a large and heterogeneous family of the protein tubulin.With an outer diameter appear as flexible structures,with a diameter of One type of intermediate filament forms a meshwork called the nuclear lamina just of 25 nm,they are more rigid than actin about 7 nm,that are organized into a variety of beneath the inner nuclear mombrane.Other filaments or intermediate filaments.Micro- linear bundles,two-dimensional networks,and types extend across the cytoplasm,giving cells tubules are long and straight and typically have three-dimensional gels.Although actin mechanical strength and carrying the one end attached to a single microtubule- filaments are dispersed throughout the cell, mechanical stresses in an epithelial tissue by organizing center called a centrosome,as they are most highly concentrated in the cortex, spanning the cytoplasm from one cell-cell shown here. iust beneath the plasma membrane. junction to another. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
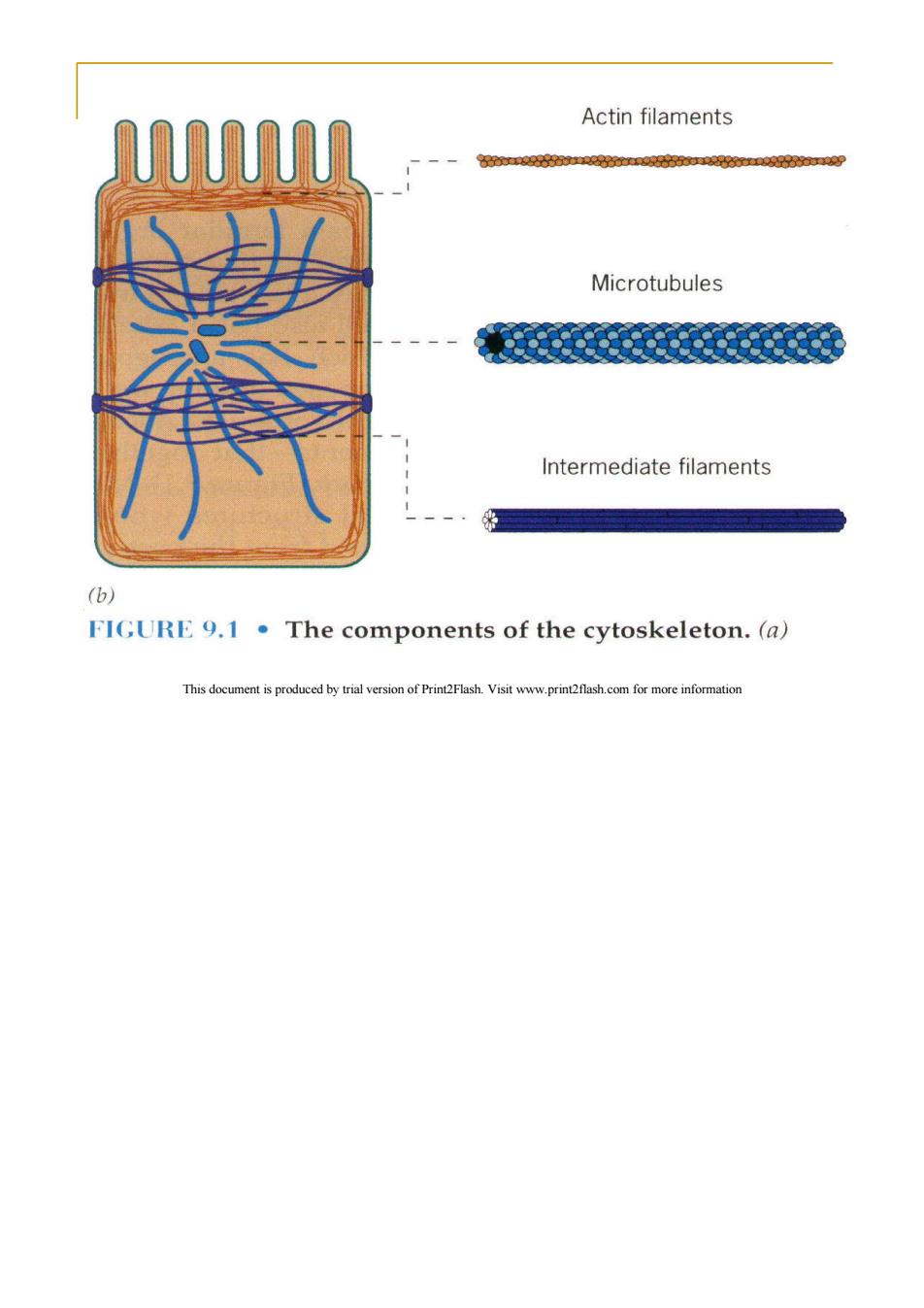
Actin filaments M 092o95029925P Microtubules Intermediate filaments (b) FIGURE 9.1 The components of the cytoskeleton.(a) This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
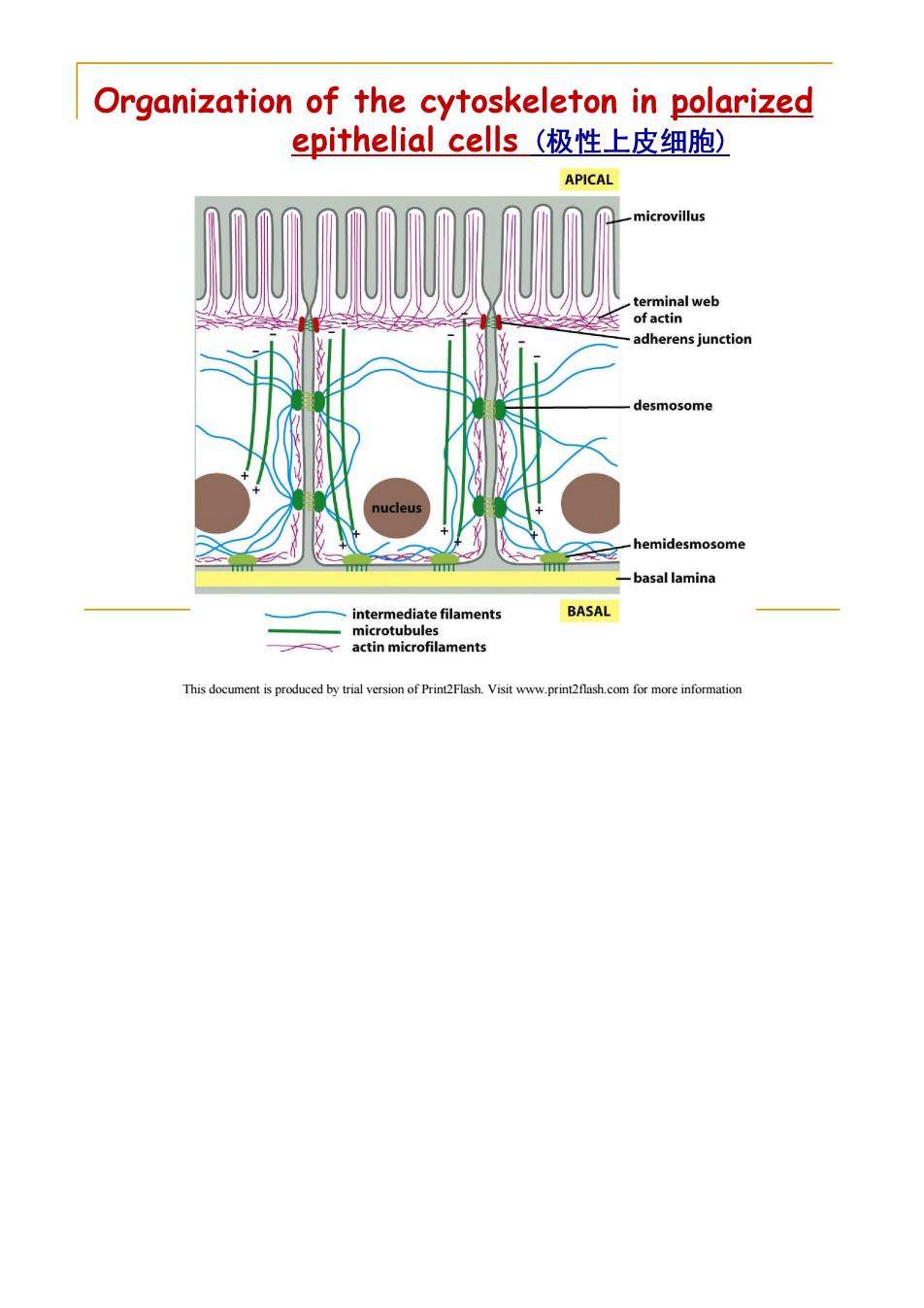
Organization of the cytoskeleton in polarized epithelial cells(极性上皮细胞) APICAL microvillus terminal web of actin adherens junction desmosome nucleus hemidesmosome basal lamina intermediate filaments BASAL microtubules actin microfilaments This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
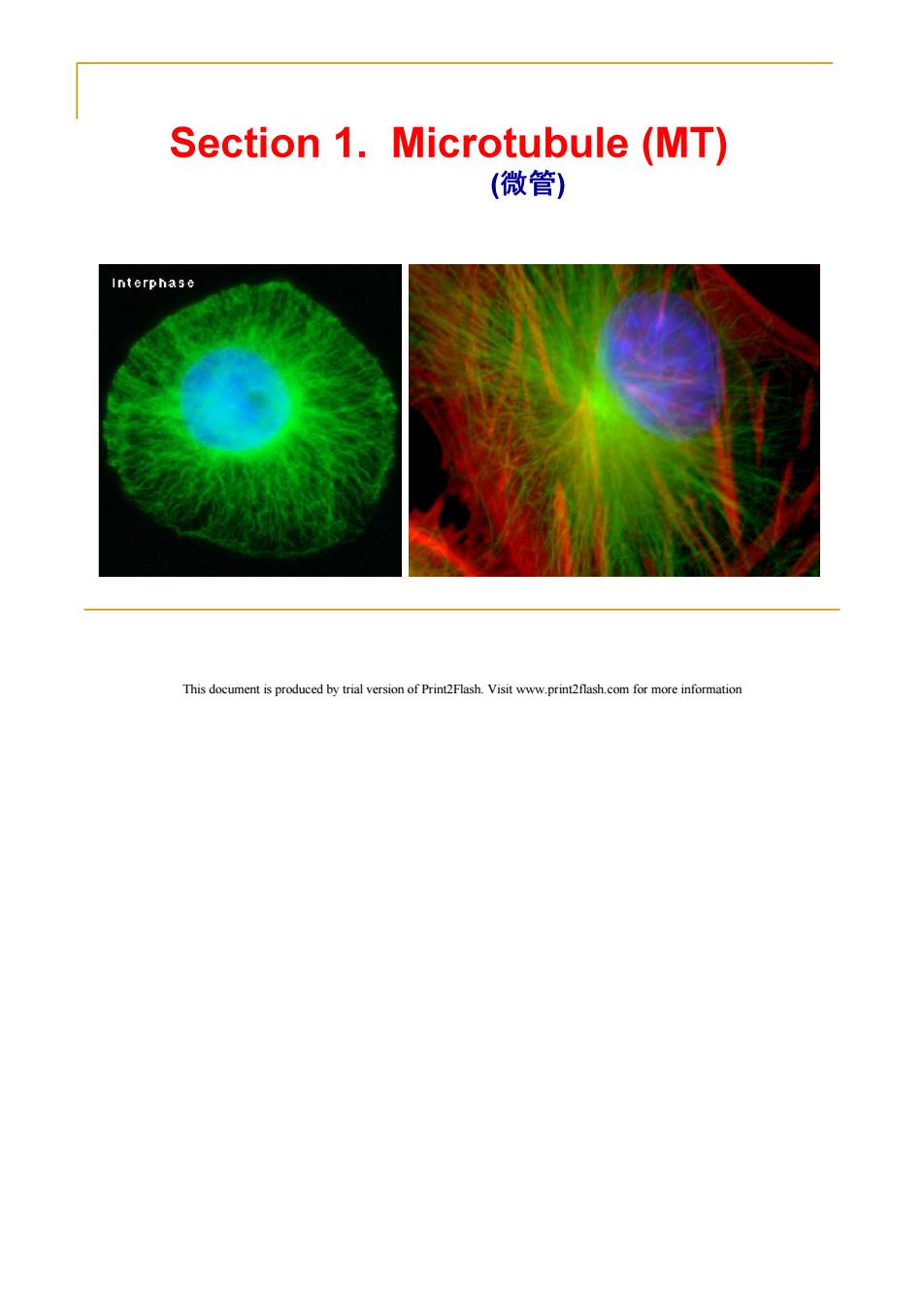
Section 1.Microtubule(MT) (微管) Interphase This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Microtubules Hollow cylindrical structure composed of microtubule proteins and microtubule associated proteins. Presented in cytosol. a Control of the membranous organelle positioning and intracellular material transport; take part in the assembly of flagella(鞭毛), cilia(纤毛),centrosomes(中心体),spindle(纺锤体); regulate cell motility,cell division and cell morphology. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.printflash.com for more information
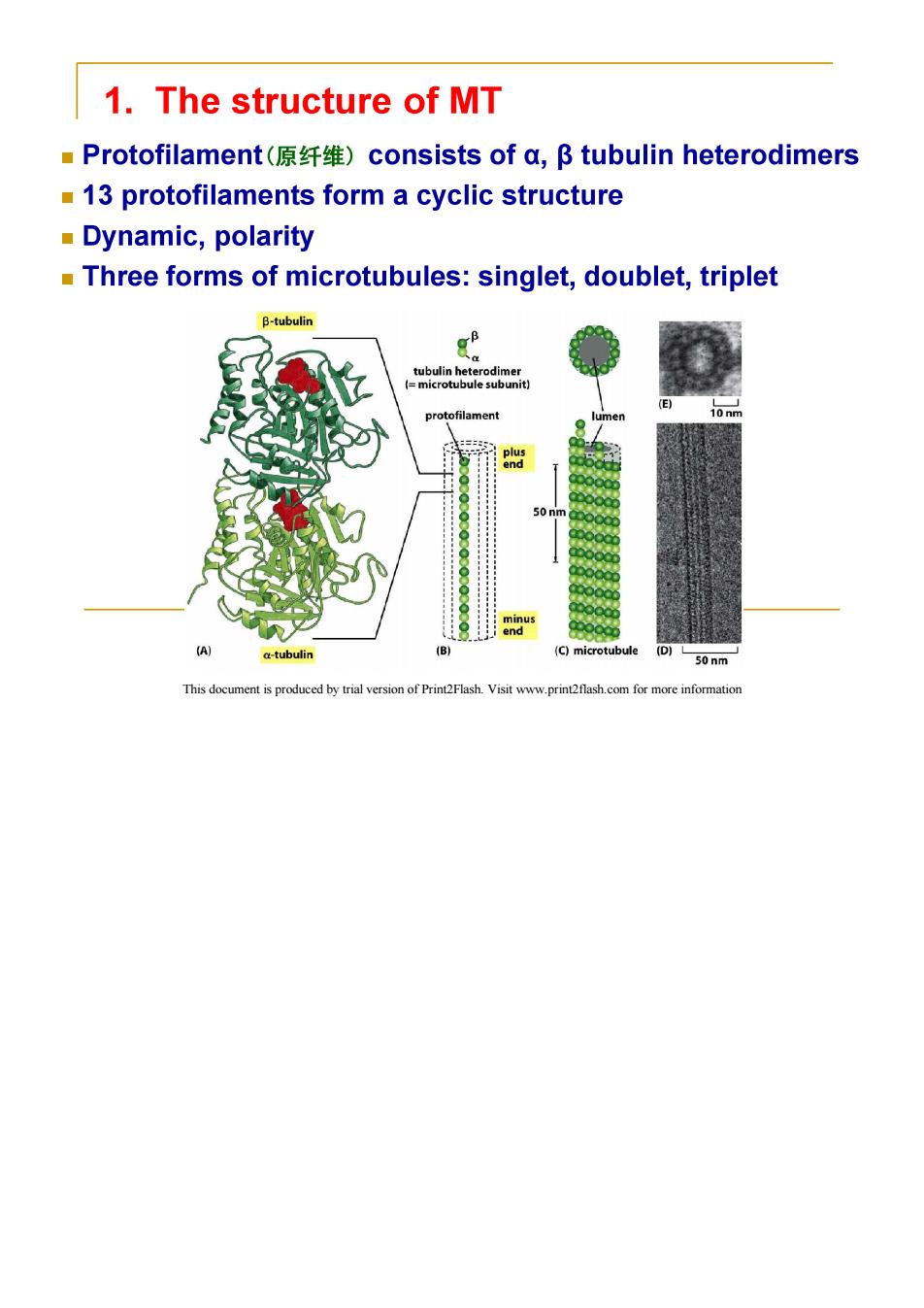
1.The structure of MT Protofilament(原纤维)consists of a,阝tubulin heterodimers 13 protofilaments form a cyclic structure Dynamic,polarity Three forms of microtubules:singlet,doublet,triplet B-tubulin g。 tubulin heterodimer (=microtubule subunit) protofilament 10 nm plus end 50nm minus end (A) a-tubulin (B) (C)microtubule 50nm This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information