
JPKIc 结构盘注原黑 Chapter 4 Shear strenth of rc beams T写
Chapter 4 Shear strength of RC beams

JPKIC 结构设计原理 Teprimeipledtstmtcturgdesign The main content of this chapter: Oblique cross-section flexural members of the mechanical characteristics and failure modes. OOblique section of bending members the main factor for shear strength. Flexural oblique shear strength formula for conditions. Such a high degree of web reinforcement beams of the preliminary design steps. O Resisting moment mapping. Check all of bearing capacity and structural requirements OConstruction oblique shear strength calculations
⚫ Oblique cross-section flexural members of the mechanical characteristics and failure modes. ⚫ Oblique section of bending members the main factor for shear strength. Flexural oblique shear strength formula for conditions. ⚫ Such a high degree of web reinforcement beams of the preliminary design steps. ⚫ Resisting moment mapping. Check all of bearing capacity and structural requirements. ⚫ Construction oblique shear strength calculations. The main content of this chapter:

JPKIC 箱构其原黑 Bending moment M and shear force under the action of Q: Calculation of flexural strength-the main bar Bending moment M and shear force under the action of Q: blique sctionstrengtcation-web reinforcement Web reinforcement:stirrups and bent(oblique)reinforced Beams without web reinforcement:only the reinforced longitudinal beams without web reinforcement design
Calculation of flexural strength - the main bar Oblique section strength calculation - web reinforcement Asb Asv , Bending moment M and shear force under the action of Q: As As , Web reinforcement: stirrups and bent (oblique) reinforced Bending moment M and shear force under the action of Q: Beams without web reinforcement: only the reinforced longitudinal beams without web reinforcement design

JPKIC 结构设计原理 Teprimeipledtstmtcturgdesign 4.1 oblique section by bending the force characteristics and failure modes In order to facilitate the characteristics of shear failure,often based on beams without web reinforcement,and then extended by the beams without web reinforcement to the beams with web reinforcement
In order to facilitate the characteristics of shear failure, often based on beams without web reinforcement, and then extended by the beams without web reinforcement to the beams with web reinforcement § 4.1 oblique section by bending the force characteristics and failure modes
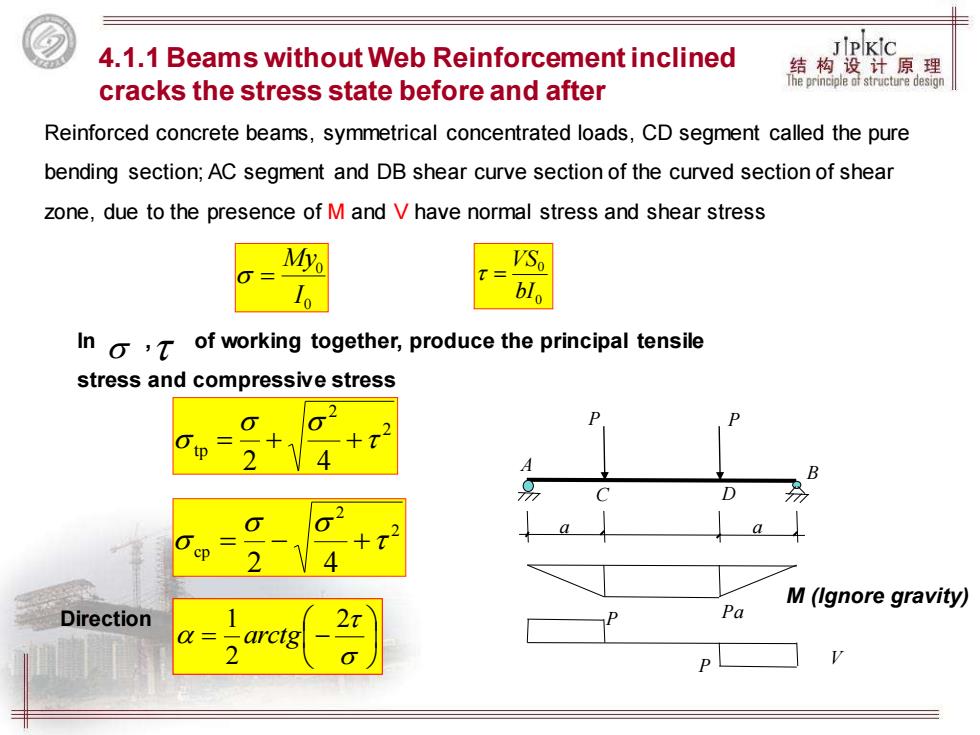
4.1.1 Beams without Web Reinforcement inclined JPKIc 结构设计原理 cracks the stress state before and after The principle of structure design Reinforced concrete beams,symmetrical concentrated loads,CD segment called the pure bending section;AC segment and DB shear curve section of the curved section of shear zone,due to the presence of M and V have normal stress and shear stress Myo blo In o ,T of working together,produce the principal tensile stress and compressive stress tp cp M(Ignore gravity) Direction Pa arctg
P P A C D B a Pa a P P V M (Ignore gravity) Reinforced concrete beams, symmetrical concentrated loads, CD segment called the pure bending section; AC segment and DB shear curve section of the curved section of shear zone, due to the presence of M and V have normal stress and shear stress 0 0 I My = 0 0 bI VS = In , of working together, produce the principal tensile stress and compressive stress 2 2 tp 2 4 = + + 2 2 cp 2 4 = − + = − 2 2 1 arctg Direction 4.1.1 Beams without Web Reinforcement inclined cracks the stress state before and after

PKIC 结构设计原理 Teprimepledstmicturgdesign B 9 c- 分分 C D The picture shows a simply supported beam without web reinforcement,the role of two symmetrical concentrated loads(CD segment called the pure bending section;AC cut curved section and DB section above)
The picture shows a simply supported beam without web reinforcement, the role of two symmetrical concentrated loads (CD segment called the pure bending section; AC cut curved section and DB section above) B A' D' 1 C' C B σ τ 2 3 A a a F F B' 2 1 3 σcp σtp σcp σtp σcp σtp τ2 σ σ τ1 τ3 2 1 3 >45o 45o <45o 主拉应力 主压应力
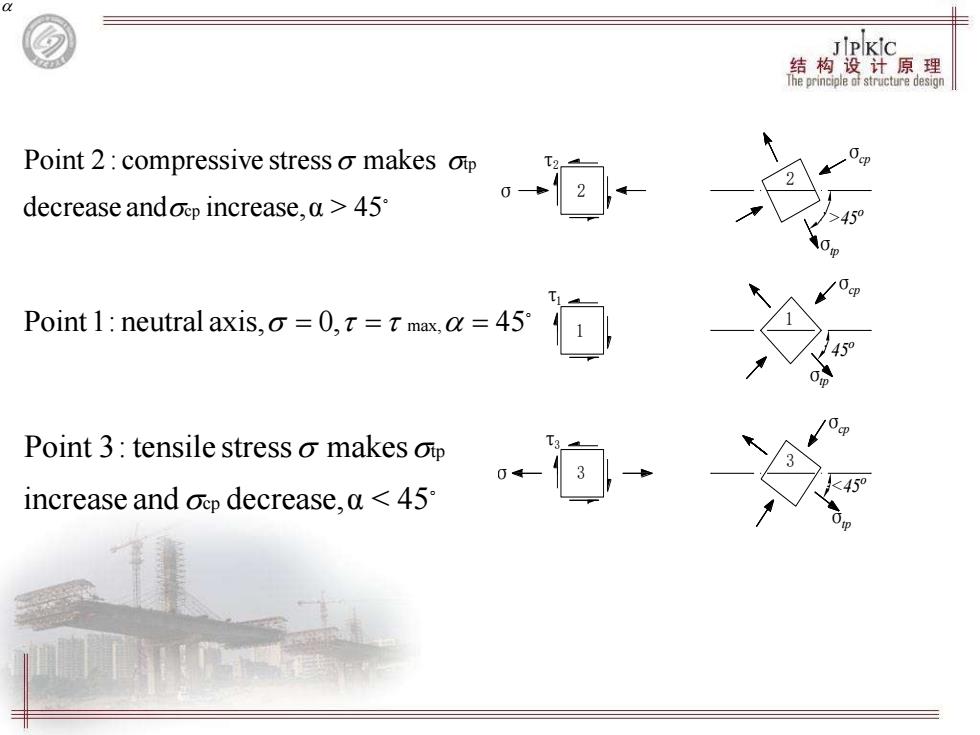
JPKIc 结构盘注原裸 Point 2:compressive stress o makes oip decrease andoep increase,a>45 2← Point 1:neutral axis,=0,=T max.a=45 Point 3:tensile stress o makes oip increase and oep decrease,a <45
B A' D' 1 C' C B σ τ 2 3 A a a F F B' 2 1 3 σcp σtp σcp σtp σcp σtp τ2 σ σ τ1 τ3 2 1 3 >45o 45o 45 Point 2 : compressive stress makes cp tp 。 increase and decrease,α < 45 Point 3: tensile stress makes cp tp

JPKIc 结构设计原理 Teprimepledstmicturgdesign Oblique section failure reasons: Since under the action of bending moment and shear together,M and V, respectively,in the produce section of the normal stress and shear stress,causing the principal tensile stress and compressive stress,when the principal tensile stress tp>ft,that is generated oblique crack,the failure surface And the beam axis bias. said inclined section failure
⚫ Since under the action of bending moment and shear together, M and V, respectively, in the produce section of the normal stress and shear stress, causing the principal tensile stress and compressive stress, when the principal tensile stress tp> ft, that is generated oblique crack, the failure surface And the beam axis bias. ––– said inclined section failure. Oblique section failure reasons:
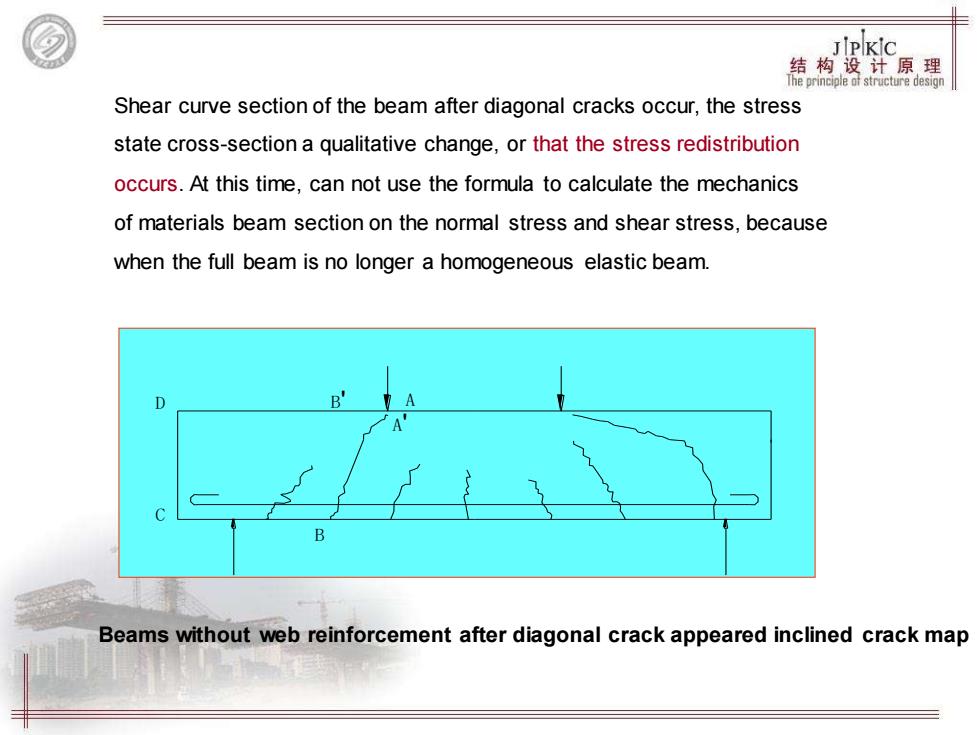
JPKIc 箱构试原果 Shear curve section of the beam after diagonal cracks occur,the stress state cross-section a qualitative change,or that the stress redistribution occurs.At this time,can not use the formula to calculate the mechanics of materials beam section on the normal stress and shear stress,because when the full beam is no longer a homogeneous elastic beam. D Beams without web reinforcement after diagonal crack appeared inclined crack map
图4-2 斜裂缝出现后的应力状态 b) C QA D a) C D B Ts a MB B Qd c B' Sa MA z Qc A' A Dc B' A' A Beams without web reinforcement after diagonal crack appeared inclined crack map Shear curve section of the beam after diagonal cracks occur, the stress state cross-section a qualitative change, or that the stress redistribution occurs. At this time, can not use the formula to calculate the mechanics of materials beam section on the normal stress and shear stress, because when the full beam is no longer a homogeneous elastic beam

JPKIC 结构设计原理 Teprnimeipletstrmicturgdesign Stress redistribution phenomenon: B AVc D De Inclined cracks appear before the V by the total cross section of shear resistance.Diagonal crack appears,by B some section of the shear V AA/ resistance,shear pressure area is reduced .'AA/shear stress and compressive stress increases Inclined cracks appear before the bar of any cross-section of longitudinal section of tensile stress at the moment by the Me decision.Diagonal crack appears,the tensile stress in longitudinal reinforcement cross-section inclined cracks the top section from the bending moment at the Ma decision. .longitudinal reinforcement tensile stress increased significantly
Stress redistribution phenomenon: ⚫Inclined cracks appear before the VA by the total cross section of shear resistance. Diagonal crack appears, by some section of the shear VA AA / resistance, shear pressure area is reduced ∴ AA / shear stress and compressive stress increases ⚫Inclined cracks appear before the bar of any cross-section of longitudinal section of tensile stress at the moment by the MB decision. Diagonal crack appears, the tensile stress in longitudinal reinforcement cross-section inclined cracks the top section from the bending moment at the MA decision. ∴ longitudinal reinforcement tensile stress increased significantly 图4-2 斜裂缝出现后的应力状态 b) C VA D C B Ts a MB B vd c B' Sa MA z Vc A' A Dc A