
第1页共6页 北京化工大学2005一一2006学年第二学期 《材料导论II》期末考试试卷标准答案 材料科学与工程学院出卷人:赵静;审阅人:刘玲 I.What do the following abbreviations stand for?Translate the abbreviations into Chinese (10pts,1pt/Q) 1.BMC,bulk molding compound,块状模塑料 2.CMC,ceramic matrix composite,陶瓷基复合材料 3.DP,degree of polymerization,.聚合度 4.FRP,fiber-plastics,纤维增强塑料 5.LCPs,liquid crystal polymers,液晶聚合物 6.MMC,metal matrix composite,金属基复合材料 7.PMC,polymer matrix composite,聚合物基复合材 8.RTM,resin transfer molding,树脂转移模塑 9.SMC.sheet molding compo nd.片状模塑料 10.TP,thermoplastic. 热塑性塑料 II.Choose the BEST TERM to match the definition and translate the selected term into Chinese (10pts,1pt/Q) 1.Q)Sealants,密封胶 2.B)Adhesion粘合 3.)Whisker晶须 4.S)Specific strength比强度 7.T)Viscoelasticity粘弹性 &.J)Hysteresis滞后作用 9.)Flame retardants阻燃剂 10.L)Nanocomposites纳米复合材料 III.Choose the correct answer(s)to the following questions(30points,1pt/Q) 1
第 1 页 共 6 页 1 北京化工大学 2005 ——2006 学年第二学期 《 材料导论 II》期末考试试卷标准答案 材料科学与工程学院 出卷人:赵静;审阅人:刘玲 I. What do the following abbreviations stand for? Translate the abbreviations into Chinese (10pts, 1pt/Q) 1. BMC, bulk molding compound,块状模塑料 2. CMC, ceramic matrix composite,陶瓷基复合材料 3. DP, degree of polymerization,聚合度 4. FRP, fiber-reinforced plastics,纤维增强塑料 5. LCPs, liquid crystal polymers,液晶聚合物 6. MMC, metal matrix composite,金属基复合材料 7. PMC, polymer matrix composite,聚合物基复合材料 8. RTM, resin transfer molding,树脂转移模塑 9. SMC, sheet molding compound,片状模塑料 10. TP, thermoplastic,热塑性塑料 II. Choose the BEST TERM to match the definition and translate the selected term into Chinese (10pts, 1pt/Q) 1. Q) Sealants,密封胶 2. B) Adhesion 粘合 3. V) Whisker 晶须 4. S) Specific strength 比强度 5. G) Fiber loading 纤维载量 6. D) Degree of crystallinity 结晶度 7. T) Viscoelasticity 粘弹性 8. J) Hysteresis 滞后作用 9. H) Flame retardants 阻燃剂 10. L) Nanocomposites 纳米复合材料 III. Choose the correct answer(s) to the following questions (30points,1pt/Q)

第2页共6项 1.A) 16.A)&B) 2.B) 17.B) 18.C) 6.B)&C) 2L.B) 7.C) 22.D) 8. 23.D1 10.9 11.D) 26.C) 12.A) 27.A)&B) 13.B) 28. D) 14.B)&D) 29.A) 30.D IV.Fill in the blanks with correet words or phrases according to the basie concepts (10points,0.5pt/blank). 3. condensation,step reaction 4. Composite 5 oxidation addition,chain reaction Unsaturated,bifunctional 9. Alflow:Bwet 10.A)interply:B)intraply;C)interply /intraplay 11.A)h lymers,B)copolymers,C)terpolymers 12. Boron fiber V.True or false questions.If you think the statement is true,write the letter"T"; otherwise,write the letter"F"(15points.Ipt/Q) 3T 4F 2.T 5.T
第 2 页 共 6 页 2 1. A) 2. B) 3. B) & D) 4. C) 5. B) 6. B) & C) 7. C) 8. B) 9. C) 10. C) 11. D) 12. A) 13. B) 14. B) & D) 15. C) 16. A) & B) 17. B) 18. C) 19. B) & C) 20. B) 21. B) 22. D) 23. D) 24. C) 25. B) 26. C) 27. A) & B) 28. D) 29. A) 30. D) IV. Fill in the blanks with correct words or phrases according to the basic concepts (10points, 0.5pt/blank). 1. interface 2. Fiber 3. condensation, step reaction 4. Composite 5. oxidation 6. addition, chain reaction 7. Filler 8. Unsaturated, bifunctional 9. A)flow; B)wet 10. A) interply; B) intraply; C)interply /intraplay 11. A) homopolymers; B) copolymers; C) terpolymers 12. Boron fibers V. True or false questions. If you think the statement is true, write the letter “T”; otherwise, write the letter “F” (15points, 1pt/Q) 1. F 2. T 3. T 4. F 5. T

第3项共6 6.F 11.F 7.F 12.F 13.F 14F 10.F 15.T VI.Give a simple answer to the following questions(15points) 1.What are the two types aspects are they different from each other?(2pts The two types of glass fibers are E-glass and S-glass.They are different in composition. modulus of elasticity,and applications. 2.How does the crystallinity affect the optical properties of plastics?Give examples to explain the。 Tect.(3pts) The optical properties of plastics will be reduced by increasing the crystallinity of polymers.For examples.HDPE has a higher degree of crystallinity than LDPE therefore,HDPE is opaque while LDPE is transparent. 3.Name the polymerization ap an example to explain how the properties of polymers are improved by using this approach.(4pts) The polymerization approaches to improving the properties of polymers include copolymerization.terpolymerization.and multicomponent polymerization.For example. butyrene is tough but weak,and polystyrene is a britte polymer that has limited toughness and poor chemical t th with styrene,it is possible to obtain a chemically resistant,more rigid,and stronger plastic.Copolymerization of butadiene and styrene results in an elastomer;and the terpolymerization of acrylonitrile,butadiene,and styrene produces ABS plastics that are though and elastomeric,and have good chemical resistance. 4.Describe three methods in which adhesives develop their cured attraction between the substrate and the adherent.(3pts) The cured attraction between the substrate and the adherent can be developed by 1) removal of solvent;2)removal of external heat sources;3)blocking oxygen;4)Mix the separately stored resin and catalyst together tocause cross-inking of the resin. 5.What are the three major differences between carbon and graphite fibers?(3pts)
第 3 页 共 6 页 3 6. F 7. F 8. F 9. T 10. F 11. F 12. F 13. F 14. F 15. T VI. Give a simple answer to the following questions (15points) 1. What are the two types of glass fibers and what aspects are they different from each other? (2pts) The two types of glass fibers are E-glass and S-glass. They are different in composition, modulus of elasticity, and applications. 2. How does the crystallinity affect the optical properties of plastics? Give examples to explain the effect.(3pts) The optical properties of plastics will be reduced by increasing the crystallinity of polymers. For examples, HDPE has a higher degree of crystallinity than LDPE, therefore, HDPE is opaque while LDPE is transparent. 3. Name the polymerization approaches to improving the properties of polymers. Give an example to explain how the properties of polymers are improved by using this approach. (4pts) The polymerization approaches to improving the properties of polymers include copolymerization, terpolymerization, and multicomponent polymerization. For example, butyrene is tough but weak, and polystyrene is a brittle polymer that has limited toughness and poor chemical resistance. But through copolymerization of acrylonitrile with styrene, it is possible to obtain a chemically resistant, more rigid, and stronger plastic. Copolymerization of butadiene and styrene results in an elastomer; and the terpolymerization of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene produces ABS plastics that are though and elastomeric, and have good chemical resistance. 4. Describe three methods in which adhesives develop their cured attraction between the substrate and the adherent. (3pts) The cured attraction between the substrate and the adherent can be developed by 1) removal of solvent; 2) removal of external heat sources; 3) blocking oxygen; 4) Mix the separately stored resin and catalyst together to cause cross-linking of the resin. 5. What are the three major differences between carbon and graphite fibers? (3pts)

第4页共6页 Caron and graphite fibers are different in carbon content,pyrolyzing temperature,and modulus of elasticity.Graphite fibers have higher carbon content,pyrolyzing temperature and modulus of elasticity than carbon fibers What is drawing to indicate the structure of a fiber-reinforced composite and their corresponding interfaces and interphase(3 pts). A fiber-reinforced composite is primarily composed of fiber,matrix,and coupling agent. fiber matrix Coupling agent interphase interfaces 2.Discuss the effect of crystallinity on the toughness,strength and density of polymers and exemplify an approach to improving the crystallinity of polymers?(3 pts) A:The strength and density of polymers increases with increasing the crystallinity of polymers.but the toughness of polymers decreases with an increase in the crystallinity of polymers.The crystallinity of polymers can be improved using proce ingmethods. such as extrusi drawing when these molecules are passing though a die,thus the crystallinty of polymers and in turn the strength of polymers is enhanced. 3.Figure 1 is the graphical plot of the tensile modulus of a unidirectional composite of reinforcing fiber Indicate which curve (Aor B)isfor isotrain condition?For a given volume fraction of fiber in a composite,which condition is more efficient in increasing the modulus?If the tensile modulus of the fiber and matrix is known,how can we
第 4 页 共 6 页 4 Caron and graphite fibers are different in carbon content, pyrolyzing temperature, and modulus of elasticity. Graphite fibers have higher carbon content, pyrolyzing temperature and modulus of elasticity than carbon fibers. VII. Complex questions. (10points) 1. What is a fiber-reinforced composite primarily composed of? Use a schematic drawing to indicate the structure of a fiber-reinforced composite and their corresponding interfaces and interphase (3 pts). A fiber-reinforced composite is primarily composed of fiber, matrix, and coupling agent. 2. Discuss the effect of crystallinity on the toughness, strength and density of polymers and exemplify an approach to improving the crystallinity of polymers? (3 pts) A: The strength and density of polymers increases with increasing the crystallinity of polymers, but the toughness of polymers decreases with an increase in the crystallinity of polymers. The crystallinity of polymers can be improved using processing methods, such as extrusion. In such doing, the amorphous polymers are oriented in the direction of drawing when these molecules are passing though a die, thus the crystallinty of polymers and in turn the strength of polymers is enhanced. 3. Figure 1 is the graphical plot of the tensile modulus of a unidirectional composite material loaded under isostrain and isostress conditions as a function of volume fraction of reinforcing fiber. Indicate which curve (A or B) is for isotrain condition? For a given volume fraction of fiber in a composite, which condition is more efficient in increasing the modulus? If the tensile modulus of the fiber and matrix is known, how can we fiber interfaces interphase Coupling agent matrix
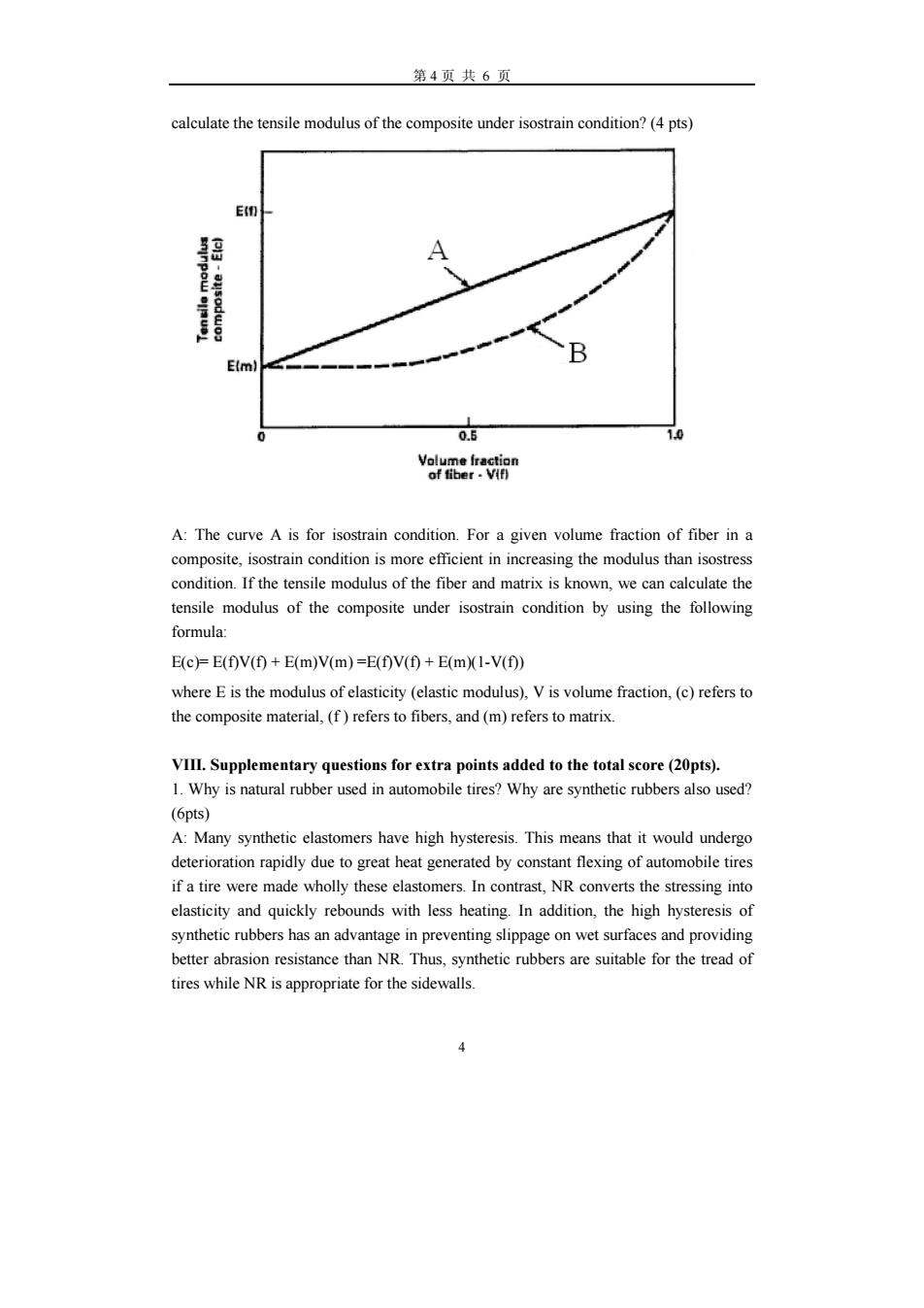
第4页共6页 calculate the tensile modulus of the composite under isostrain condition?(4 pts) 0话 10 vea6瑞 A:The curve A is for isostrain condition.For a given volume fraction of fiber in a tensile modulus of the composite under isostrain condition by using the following formula: E(c)=E(f)V(f)+E(m)V(m)=E(f)V(f)+E(mX(1-V(f)) where E is the modulus of elasticity (elastic modulus)Vis volume fraction,(c)refers to the composite material,(f)refers tofibers,and (m)refers to matrix. VIII.Supplementary questions for extra points added to the total score(20pts). 1.Why is natural rubber used in automobile tires?Why are synthetic rubbers also used? (6pts Many have high hysteresis.This means hat deterioration rapidly due to great heat generated by constant flexing of automobile tires if a tire were made wholly these elastomers.In contrast.NR converts the stressing into elasticity and quickly rebounds with less heating In addition,the high hysteresis of age on wet surfaces and providing better abrasion resistance than NR.Thus rs are suitable for the tread of tires while NR is appropriate for the sidewalls
第 4 页 共 6 页 4 calculate the tensile modulus of the composite under isostrain condition? (4 pts) A: The curve A is for isostrain condition. For a given volume fraction of fiber in a composite, isostrain condition is more efficient in increasing the modulus than isostress condition. If the tensile modulus of the fiber and matrix is known, we can calculate the tensile modulus of the composite under isostrain condition by using the following formula: E(c)= E(f)V(f) + E(m)V(m) =E(f)V(f) + E(m)(1-V(f)) where E is the modulus of elasticity (elastic modulus), V is volume fraction, (c) refers to the composite material, (f ) refers to fibers, and (m) refers to matrix. VIII. Supplementary questions for extra points added to the total score (20pts). 1. Why is natural rubber used in automobile tires? Why are synthetic rubbers also used? (6pts) A: Many synthetic elastomers have high hysteresis. This means that it would undergo deterioration rapidly due to great heat generated by constant flexing of automobile tires if a tire were made wholly these elastomers. In contrast, NR converts the stressing into elasticity and quickly rebounds with less heating. In addition, the high hysteresis of synthetic rubbers has an advantage in preventing slippage on wet surfaces and providing better abrasion resistance than NR. Thus, synthetic rubbers are suitable for the tread of tires while NR is appropriate for the sidewalls

第4项共6页 2.Give examples to explain how the properties of polymers are influenced by the structure or processing methods of polymers.(4pts) Polypropylene (PP)is a good example to explain the relationship between the structur and properties of polymers.For instance.if PP is isotactic.then it has a high degree of crystallinity,PP in turn becomes useful materials for refrigerators,washing machines. bumpers.However,if PP is atactic.it then has amorphous structure.and the corresponding materials are sticky liquid,and they are useless. 3.Discuss the factors influencing the properties of fiber-reinforced composites.(6pts) The properties of fiber-reinforced composites depend on the fiber,the matrix and processing methods.The fiber influence the properties of fiber-reinforced composites through its loading aspect ratio,(inluding straightness.degree of knitting interlacing).and defects in atomic structure or macrodefects on the surfaces of the fibers The matrix's ability to adhere to the fibers,as well as its inherent toughness,also makes a contribution.The processing method that affects performance of composite is the degree to which the fibers are saturated with wet matrix,leaving few or no voids. 4.Define the term of"wind angle"for filament winding.How do the hoop tensile strength and axial tensile strength change with wind angle?(4pts) The properties of composites are influenced by A:The"wind angle"is measured between the axis of the mandrel and the lay of the filaments.The tangent of this angle is the ratio of the circumference of the mandrel and the pitch of the filaments.The hoop tensile strength increases with wind angle,while the axial tensile strength decreases with wind angle
第 4 页 共 6 页 4 2. Give examples to explain how the properties of polymers are influenced by the structure or processing methods of polymers. (4pts) Polypropylene (PP) is a good example to explain the relationship between the structure and properties of polymers. For instance, if PP is isotactic, then it has a high degree of crystallinity, PP in turn becomes useful materials for refrigerators, washing machines, bumpers. However, if PP is atactic, it then has amorphous structure, and the corresponding materials are sticky liquid, and they are useless. 3. Discuss the factors influencing the properties of fiber-reinforced composites. (6pts) The properties of fiber-reinforced composites depend on the fiber, the matrix and processing methods. The fiber influence the properties of fiber-reinforced composites through its loading, aspect ratio, orientation (including straightness, degree of knitting, interlacing), and defects in atomic structure or macrodefects on the surfaces of the fibers. The matrix’s ability to adhere to the fibers, as well as its inherent toughness, also makes a contribution. The processing method that affects performance of composite is the degree to which the fibers are saturated with wet matrix, leaving few or no voids. 4. Define the term of “wind angle” for filament winding. How do the hoop tensile strength and axial tensile strength change with wind angle? (4pts) The properties of composites are influenced by A: The “wind angle” is measured between the axis of the mandrel and the lay of the filaments. The tangent of this angle is the ratio of the circumference of the mandrel and the pitch of the filaments. The hoop tensile strength increases with wind angle, while the axial tensile strength decreases with wind angle