
CHAPTER IV Hydrogeology
CHAPTER IV Hydrogeology

New words and phrases lithologic formations:岩层 pore:孔隙 Jupiter's moon Europa:木星的卫星 water table:地下水面 aquifer:含水层 phreatic surface:潜水面 aquitard:弱透水层 confined aquifer::承压含水层 artesian wells:自流井 vulnerability:弱点,攻击;易受伤;易受责 ecosystem:生态系统
New words and phrases lithologic formations:岩层 pore:孔隙 Jupiter's moon Europa:木星的卫星 water table:地下水面 aquifer:含水层 phreatic surface:潜水面 aquitard:弱透水层 confined aquifer:承压含水层 artesian wells:自流井 vulnerability: 弱点,攻击; 易受伤; 易受责 ecosystem: 生态系统

New words and phrases unconfined aquifer:潜水含水层 specific heat capacity:热容 precipitation:降水 hydrogeologists:水文地质学家 saltwater intrusion:海水入侵 sandstone:砂岩 limestone:石灰石 granite:花岗岩 crystalline rock:结晶岩 permafrost:永久冻土 arsenic:砷;三氧化二砷,砒霜 microbial::微生物的
New words and phrases unconfined aquifer:潜水含水层 specific heat capacity:热容 precipitation:降水 hydrogeologists:水文地质学家 saltwater intrusion:海水入侵 sandstone:砂岩 limestone:石灰石 granite:花岗岩 crystalline rock:结晶岩 permafrost:永久冻土 arsenic: 砷; 三氧化二砷, 砒霜 microbial:微生物的

Questions? Questions: 1:General introduction to confined aquifer? 2:What is groundwater? 3:What is seawater intrusion? 4:What is the specialty of GW in the capillary fringe?
Questions? Questions: 1:General introduction to confined aquifer? 2: What is groundwater? 3: What is seawater intrusion? 4: What is the specialty of GW in the capillary fringe?

Groundwater Groundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of lithologic formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water.The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table
Groundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of lithologic formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater
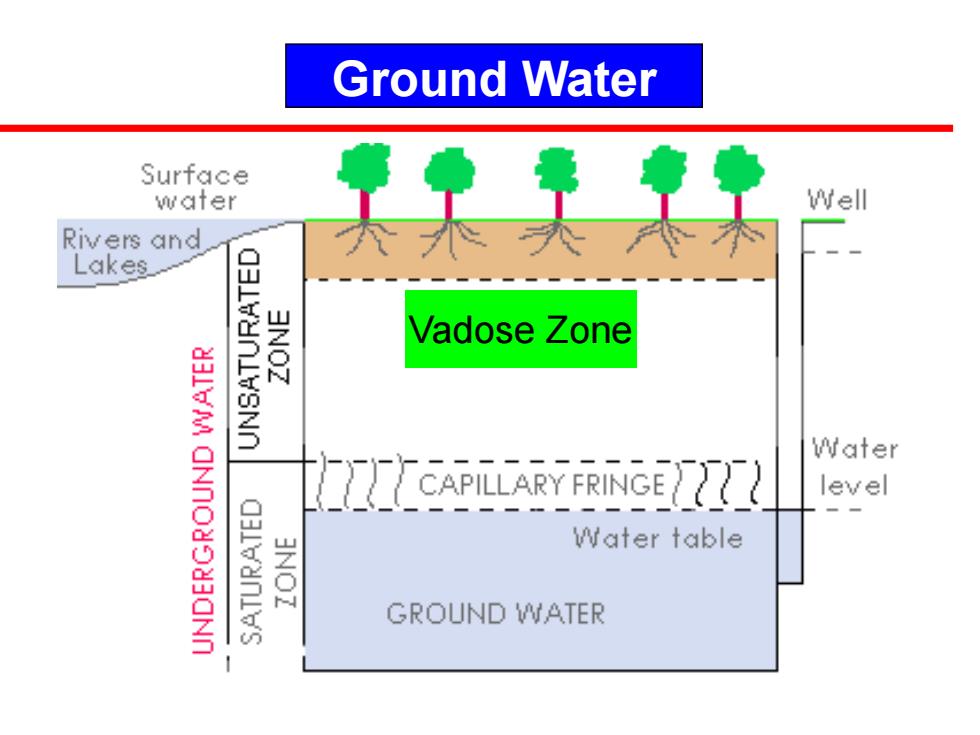
Ground Water Surface water Well Rivers and Lakes_ 3NOZ Vadose Zone Water level Water table 3NOZ GROUND WATER
Ground Water Vadose Zone
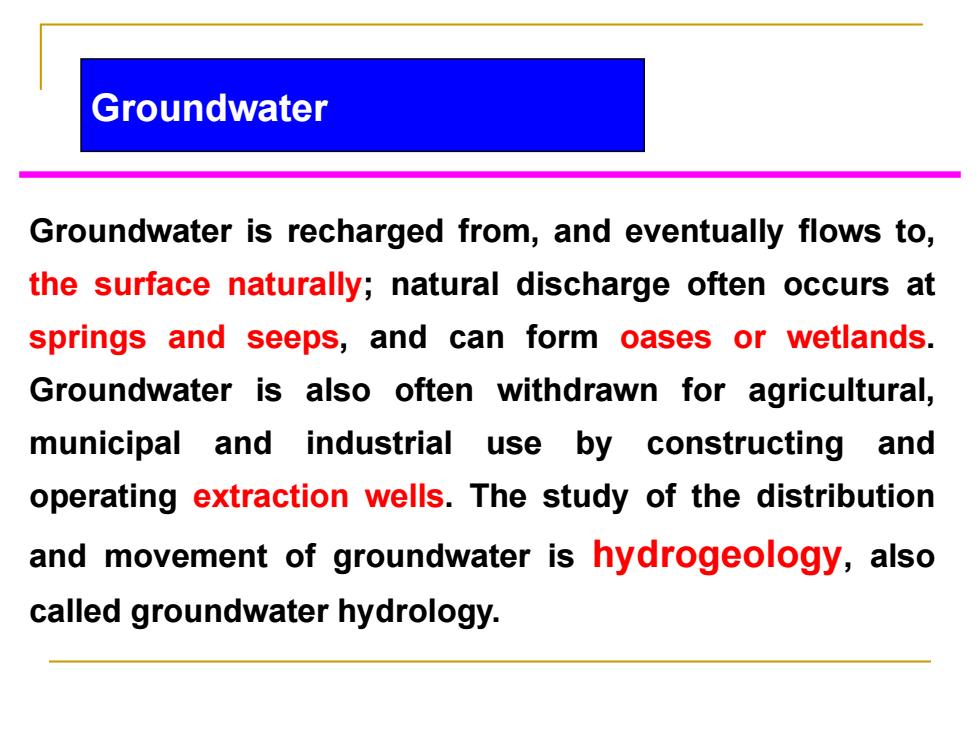
Groundwater Groundwater is recharged from,and eventually flows to, the surface naturally;natural discharge often occurs at springs and seeps,and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells.The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology,also called groundwater hydrology
Groundwater is recharged from, and eventually flows to, the surface naturally; natural discharge often occurs at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology. Groundwater

Groundwater Groundwater is hypothesized to provide lubrication that can possibly influence the movement of faults.It is likely that much of the Earth's subsurface contains some water,which may be mixed with other fluids in some instances.Groundwater may not be confined only to the Earth
Groundwater is hypothesized to provide lubrication that can possibly influence the movement of faults. It is likely that much of the Earth's subsurface contains some water, which may be mixed with other fluids in some instances. Groundwater may not be confined only to the Earth. Groundwater

Some basic concepts of Aquifers An aquifer is a layer of relatively porous substrate that contains and transmits groundwater.When water can flow directly between the surface and the saturated zone of an aquifer,the aquifer is unconfined.The deeper parts of unconfined aquifers are usually more saturated with groundwater since gravity causes water to flow downward
Some basic concepts of Aquifers An aquifer is a layer of relatively porous substrate that contains and transmits groundwater. When water can flow directly between the surface and the saturated zone of an aquifer, the aquifer is unconfined. The deeper parts of unconfined aquifers are usually more saturated with groundwater since gravity causes water to flow downward
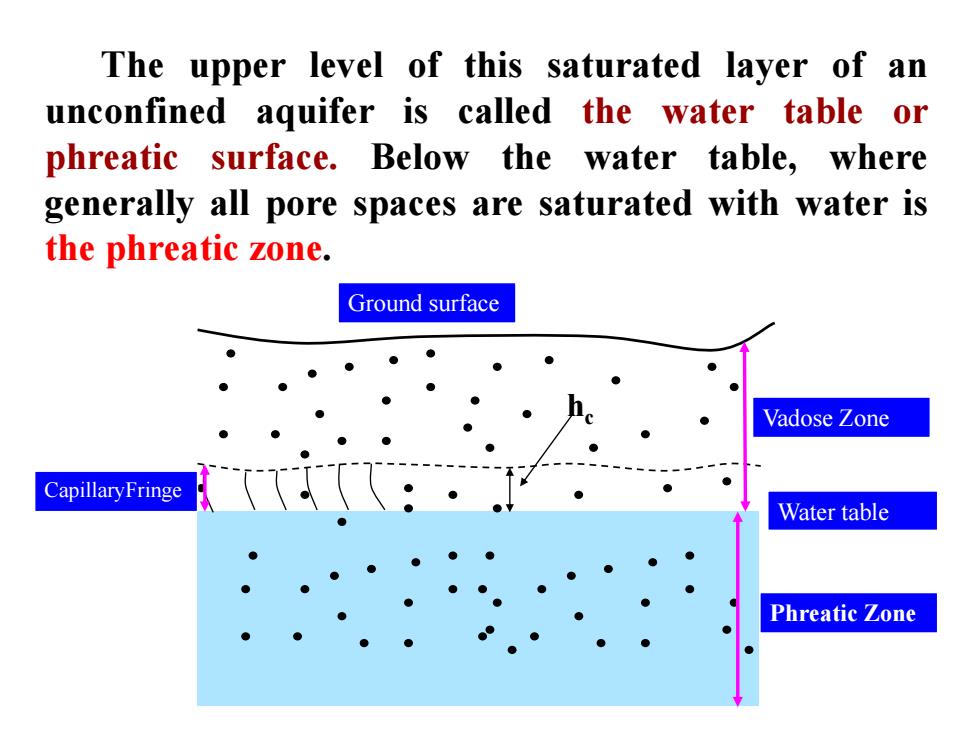
The upper level of this saturated layer of an unconfined aquifer is called the water table or phreatic surface.Below the water table,where generally all pore spaces are saturated with water is the phreatic zone. Ground surface Vadose Zone Capillary Fringe Water table Phreatic Zone
The upper level of this saturated layer of an unconfined aquifer is called the water table or phreatic surface. Below the water table, where generally all pore spaces are saturated with water is the phreatic zone. Ground surface hc Vadose Zone CapillaryFringe Phreatic Zone Water table