
JIAOTONG UNIVERSIT 96 Supply Chain Management Lecture 5 Distribution Networks Instructor(s) Prof.Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering SCM by J.J.Gao SEIEE AU406
Supply Chain Management Instructor(s) SEIEE AU406 + - SCM by J. J. Gao Distribution Networks Prof. Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering Lecture 5

Outline The Role of Distribution in the Supply Chain Factors Influencing Distribution Network Design Design Options for a Distribution Network E-Business and the Distribution Network Distribution Networks in Practice Summary of Learning Objectives SEIEE AU406 4-2
+ - SEIEE AU406 4-2 Outline The Role of Distribution in the Supply Chain Factors Influencing Distribution Network Design Design Options for a Distribution Network E-Business and the Distribution Network Distribution Networks in Practice Summary of Learning Objectives

The Role of Distribution in the Supply Chain Distribution:the steps taken to move and store a product from the supplier stage to the customer stage in a supply chain 国 Distribution occurs between every pair of stages Distribution directly affects cost and the customer experience and therefore drives profitability Choice of distribution network can achieve supply chain objectives from low cost to high responsiveness Examples: Wal-Mart distribution helps company to provide high availability levels of common products in low price. Seven-Eleven Japan:distribution provides high level of customer responsiveness. SEIEE AU406 4-3
+ - SEIEE AU406 4-3 The Role of Distribution in the Supply Chain Distribution: the steps taken to move and store a product from the supplier stage to the customer stage in a supply chain Distribution occurs between every pair of stages Distribution directly affects cost and the customer experience and therefore drives profitability Choice of distribution network can achieve supply chain objectives from low cost to high responsiveness Examples: Wal-Mart : distribution helps company to provide high availability levels of common products in low price. Seven-Eleven Japan: distribution provides high level of customer responsiveness
Design distribution networks ■ Includes two phases: 国 Phase 1:design the broad structure of the distribution networks Whether the product should be sold directly or use intermediary. Where should the products be stored? How to deliver the products?Using carrier or not? Phase 2:Convert the broad structure to specific location,capability,capacity and demand allocation. The Phase 2 design will given in next lectures SEIEE AU406 4-4
+ - SEIEE AU406 Design distribution networks Includes two phases: Phase 1: design the broad structure of the distribution networks Whether the product should be sold directly or use intermediary. Where should the products be stored? How to deliver the products? Using carrier or not? Phase 2: Convert the broad structure to specific location, capability, capacity and demand allocation. The Phase 2 design will given in next lectures 4-4

Some example of distribution networks Before 2007,Dell distributes its PC directly to end customer.(wait for few days) ■ HP distribute through seller.(get PC immediately) ■ Starting from 2007,Dell also sells PC through retailer. Gateway:Open Gateway Country Stores,where customers could examine the products and have sales people help them configure a PC for their needs. However,Gateway chooses to sell no products at the stores, shop directly to customer. By April 2004,Gateway closed all its stores. Apple Computer,in contrast,has opened may retailer stores. These PC companies have chosen different distribution models.How to evaluate these choice?Which one is better? SEIEE AU406 4-5
+ - SEIEE AU406 Some example of distribution networks Before 2007, Dell distributes its PC directly to end customer.(wait for few days) HP distribute through seller. (get PC immediately) Starting from 2007, Dell also sells PC through retailer. Gateway: Open Gateway Country Stores, where customers could examine the products and have sales people help them configure a PC for their needs. However, Gateway chooses to sell no products at the stores, shop directly to customer. By April 2004, Gateway closed all its stores. Apple Computer, in contrast, has opened may retailer stores. 4-5 These PC companies have chosen different distribution models. How to evaluate these choice? Which one is better?

Some example of distribution networks P&G has chosen to distribute directly to large supermarket chains while obligation smaller players to buy P&G products from distributors. Texas Instruments,which once used only direct sales,now sells about 30%of its volume to 98%of its customers through distributor. The failure of Webvan Distributions play a much more significant role for consumer goods in India than US. W.W.Grainger use a hybrid way to store its products:store 200,000 unit for quick response;the other are delivered directly to customer. SEIEE AU406 4-6
+ - SEIEE AU406 P&G has chosen to distribute directly to large supermarket chains while obligation smaller players to buy P&G products from distributors. Texas Instruments, which once used only direct sales, now sells about 30% of its volume to 98% of its customers through distributor. The failure of Webvan Distributions play a much more significant role for consumer goods in India than US. W.W. Grainger use a hybrid way to store its products: store 200,000 unit for quick response; the other are delivered directly to customer. 4-6 Some example of distribution networks

Design of distribution networks answers the following questions What value do these distributors provide? When should a distribution network include an additional stage such as a distributor? Distributors play a much more significant role for consumer goods distribution in a country such as India compared to the United States.Why might this be the case? Is the distributor networks suitable for W.W.Grainger? SEIEE AU406 4-7
+ - SEIEE AU406 What value do these distributors provide? When should a distribution network include an additional stage such as a distributor? Distributors play a much more significant role for consumer goods distribution in a country such as India compared to the United States. Why might this be the case? Is the distributor networks suitable for W. W. Grainger? 4-7 Design of distribution networks answers the following questions
Factors Influencing Distribution Network Design Distribution network performance evaluated along two dimensions at the highest level: Customer needs that are met(customer) Cost of meeting customer needs(supply chain) Distribution network design options must therefore be compared according to their impact on customer service and the cost to provide this level of service SEIEE AU406 4-8
+ - SEIEE AU406 4-8 Factors Influencing Distribution Network Design Distribution network performance evaluated along two dimensions at the highest level: Customer needs that are met(customer) Cost of meeting customer needs(supply chain) Distribution network design options must therefore be compared according to their impact on customer service and the cost to provide this level of service
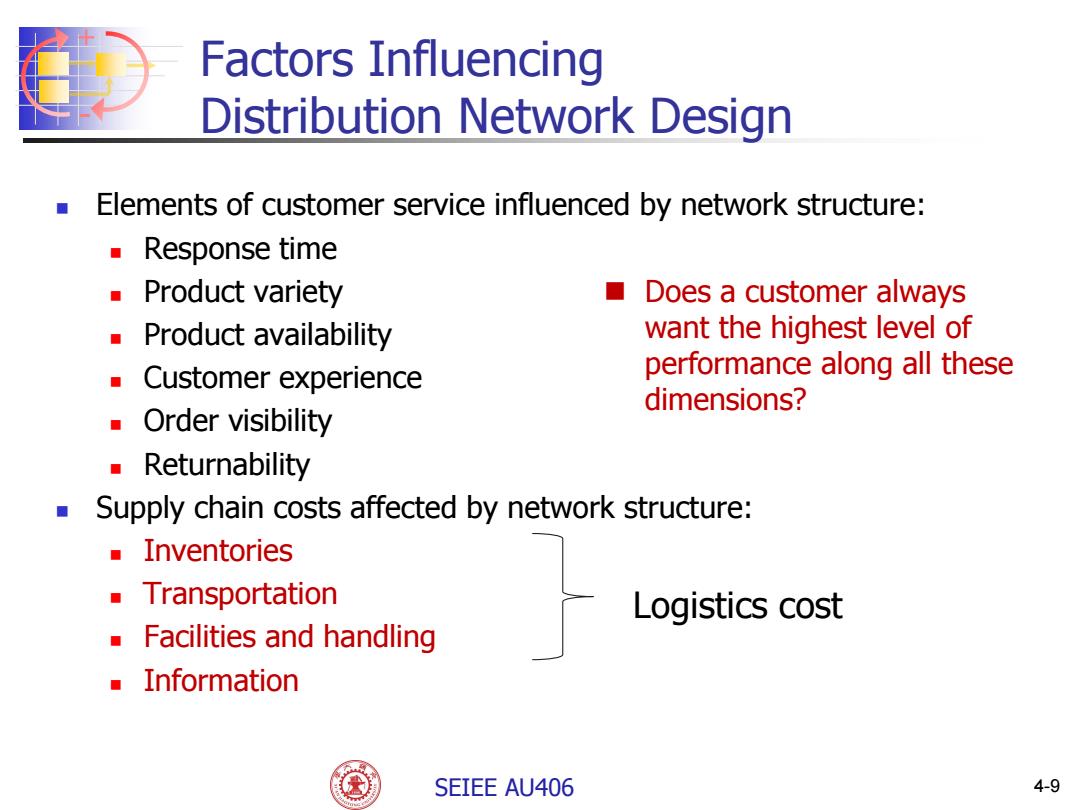
Factors Influencing Distribution Network Design Elements of customer service influenced by network structure: Response time Product variety Does a customer always Product availability want the highest level of Customer experience performance along all these dimensions? Order visibility Returnability Supply chain costs affected by network structure: ■Inventories Transportation Logistics cost Facilities and handling Information SEIEE AU406 4-9
+ - SEIEE AU406 4-9 Factors Influencing Distribution Network Design Elements of customer service influenced by network structure: Response time Product variety Product availability Customer experience Order visibility Returnability Supply chain costs affected by network structure: Inventories Transportation Facilities and handling Information Does a customer always want the highest level of performance along all these dimensions? Logistics cost

Example:Amazon and Barnes&Noble Address htp:im Google Books amazon.com BARNES&NOBLE BOOKSELLERS Save up to 4 shop All Departments Customers ordering a book at Amazon are willing to wait longer than those who drive to a nearby Barnes Noble store to get the same book. Customers can find a much larger variety of books at Amazon compared to the Barnes Noble store SEIEE AU406 SCM by J.J.Ga6
+ - SEIEE AU406 Example: Amazon and Barnes& Noble SCM by J. J. Gao10 Customers ordering a book at Amazon are willing to wait longer than those who drive to a nearby Barnes & Noble store to get the same book. Customers can find a much larger variety of books at Amazon compared to the Barnes & Noble store