
JIAOTONG UNIVERSIT 96 Supply Chain Management Lecture 10 Safety Inventory Instructor(s) Prof.Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering SEIEE AU406
Supply Chain Management Instructor(s) SEIEE AU406 + - Safety Inventory Prof. Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering Lecture 10

Outline The role of safety inventory in a supply chain Determining the appropriate level of safety inventory Impact of supply uncertainty on safety inventory Impact of aggregation on safety inventory Impact of replenishment policies on safety inventory Managing safety inventory in a multi-echelon supply chain SEIEE AU406 2
+ - SEIEE AU406 2 Outline The role of safety inventory in a supply chain Determining the appropriate level of safety inventory Impact of supply uncertainty on safety inventory Impact of aggregation on safety inventory Impact of replenishment policies on safety inventory Managing safety inventory in a multi-echelon supply chain

The Role of Safety Inventory in a Supply Chain Forecasts are rarely completely accurate If average demand is 1000 units per week,then half the time actual demand will be greater than 1000,and half the time actual demand will be less than 1000;what happens when actual demand is greater than 1000? If you kept only enough inventory in stock to satisfy average demand,half the time you would run out o Safety inventory:Inventory carried for the purpose of satisfying demand that exceeds the amount forecasted in a given period SEIEE AU406 3
+ - SEIEE AU406 3 The Role of Safety Inventory in a Supply Chain Forecasts are rarely completely accurate If average demand is 1000 units per week, then half the time actual demand will be greater than 1000, and half the time actual demand will be less than 1000; what happens when actual demand is greater than 1000? If you kept only enough inventory in stock to satisfy average demand, half the time you would run out Safety inventory: Inventory carried for the purpose of satisfying demand that exceeds the amount forecasted in a given period

Example of Bloomingdale The store manager at Bloomingdale's orders in lots of 600 purses Demand for purses at Bloomingdale's averages 100 a week ■ Gucci takes three weeks to deliver the purses to Bloomingdale's ■ If there is no uncertainty,the store manager can place an order when the store has exactly 300 purses remaining. ■( Given demand fluctuations and forecast errors,actual demand over the three weeks may be higher or lower than the 300 purses forecasted. SEIEE AU406 4
+ - SEIEE AU406 Example of Bloomingdale The store manager at Bloomingdale’s orders in lots of 600 purses Demand for purses at Bloomingdale’s averages 100 a week Gucci takes three weeks to deliver the purses to Bloomingdale’s If there is no uncertainty, the store manager can place an order when the store has exactly 300 purses remaining. Given demand fluctuations and forecast errors, actual demand over the three weeks may be higher or lower than the 300 purses forecasted. 4
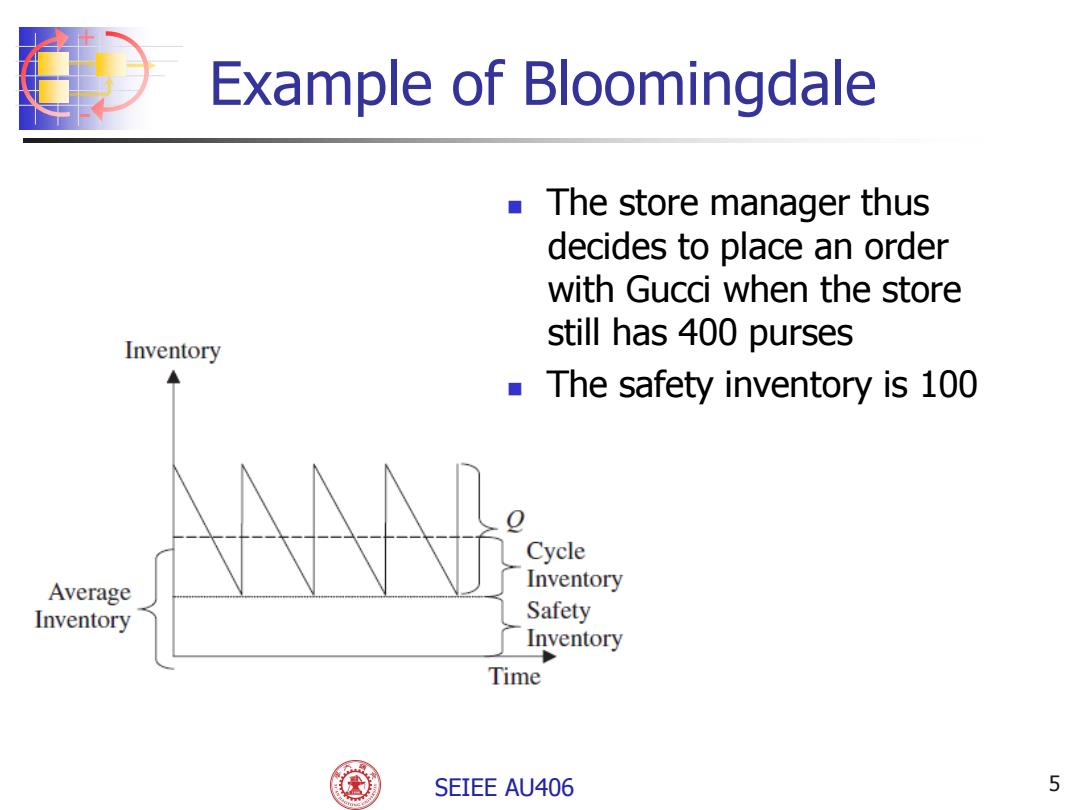
Example of Bloomingdale The store manager thus decides to place an order with Gucci when the store Inventory still has 400 purses The safety inventory is 100 Cycle Average Inventory Inventory Safety Inventory Time SEIEE AU406 5
+ - SEIEE AU406 5 The store manager thus decides to place an order with Gucci when the store still has 400 purses The safety inventory is 100 Example of Bloomingdale

Role of Safety Inventory Average inventory =cycle inventory +safety inventory There is a fundamental tradeoff: Raising the level of safety inventory provides higher levels of product availability and customer service Raising the level of safety inventory also raises the level of average inventory and therefore increases holding costs Compaq and Dell in PCs 1990 Nordstrom,Macy's,and Saks during the 2008-2009 recession SEIEE AU406 6
+ - SEIEE AU406 6 Role of Safety Inventory Average inventory =cycle inventory +safety inventory There is a fundamental tradeoff: Raising the level of safety inventory provides higher levels of product availability and customer service Raising the level of safety inventory also raises the level of average inventory and therefore increases holding costs Compaq and Dell in PCs 1990 Nordstrom, Macy’s, and Saks during the 2008–2009 recession

Key Questions to Answer in Planning Safety Inventory What is the appropriate level of product availability? How much safety inventory is needed for the desired level of product availability? What actions can be taken to improve product availability while reducing safety inventory? SEIEE AU406 7
+ - SEIEE AU406 7 Key Questions to Answer in Planning Safety Inventory What is the appropriate level of product availability? How much safety inventory is needed for the desired level of product availability? What actions can be taken to improve product availability while reducing safety inventory?

Determining the Appropriate Level of Safety Inventory Measuring demand uncertainty Measuring product availability Replenishment policies Evaluating cycle service level and fill rate Evaluating safety level given desired cycle service level or fill rate Impact of required product availability and uncertainty on safety inventory SEIEE AU406 8
+ - SEIEE AU406 8 Determining the Appropriate Level of Safety Inventory Measuring demand uncertainty Measuring product availability Replenishment policies Evaluating cycle service level and fill rate Evaluating safety level given desired cycle service level or fill rate Impact of required product availability and uncertainty on safety inventory

Determining the Appropriate Level of Demand Uncertainty a Appropriate level of safety inventory determined by: supply or demand uncertainty desired level of product availability Higher levels of uncertainty require higher levels of safety inventory given a particular desired level of product availability Higher levels of desired product availability require higher levels of safety inventory given a particular level of uncertainty SEIEE AU406 9
+ - SEIEE AU406 9 Determining the Appropriate Level of Demand Uncertainty Appropriate level of safety inventory determined by: supply or demand uncertainty desired level of product availability Higher levels of uncertainty require higher levels of safety inventory given a particular desired level of product availability Higher levels of desired product availability require higher levels of safety inventory given a particular level of uncertainty

Measuring Demand Uncertainty Notations: D:Average demand per period p:Standard deviation of demand(forecast error)per period Usually assume the demand follows normal distribution Lead time is the gap between when an order is placed and when it is received.In our discussion,we denote the lead time by L. SEIEE AU406 10
+ - SEIEE AU406 10 Measuring Demand Uncertainty Notations: Usually assume the demand follows normal distribution Lead time is the gap between when an order is placed and when it is received. In our discussion, we denote the lead time by L