
JIAOTONG UNIVERSIT 96 Supply Chain Management Lecture 11 Optimal Level of Product Availability Instructor(s) Prof.Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering SEIEE AU406
Supply Chain Management Instructor(s) SEIEE AU406 + - Optimal Level of Product Availability Prof. Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering Lecture 11

Outline The importance of the level of product availability Factors affecting the optimal level of product availability Managerial levers to improve supply chain profitability Supply chain contracts and their impact on profitability Setting optimal levels of product availability in practice SEIEE AU406 12-2
+ - SEIEE AU406 12-2 Outline The importance of the level of product availability Factors affecting the optimal level of product availability Managerial levers to improve supply chain profitability Supply chain contracts and their impact on profitability Setting optimal levels of product availability in practice
The importance of the level of product availability The level of product availability is measured using the cycle service level or the fill rate The metrics for the amount of customer demand satisfied from available inventory The level of product availability=the customer service level>responsiveness of supply chain Need the balance between product availability and cost of inventory SEIEE AU406 12-3
+ - SEIEE AU406 The importance of the level of product availability The level of product availability is measured using the cycle service level or the fill rate The metrics for the amount of customer demand satisfied from available inventory The level of product availability=the customer service level responsiveness of supply chain Need the balance between product availability and cost of inventory 12-3

The importance of the level of product availability Nordstrom has focused on providing a high level of product availability and has used its reputation for responsiveness to become a successful department store chain. The prices at Nordstrom are higher than at a discount store,where the level of product availability is lower. Some power plants try to maintain several months of fuel supply to avoid any probability of running out. Most supermarkets carry only a few days'supply of product,and out-of-stock situations do occur with some frequency. SEIEE AU406 12-4
+ - SEIEE AU406 Nordstrom has focused on providing a high level of product availability and has used its reputation for responsiveness to become a successful department store chain. The prices at Nordstrom are higher than at a discount store, where the level of product availability is lower. Some power plants try to maintain several months of fuel supply to avoid any probability of running out. Most supermarkets carry only a few days’ supply of product, and out-of-stock situations do occur with some frequency. 12-4 The importance of the level of product availability

The importance of the level of product availability The Internet allows a customer to easily shop at an alternative store if the first choice is out of stock. This competitive environment puts pressure on online retailers to increase their level of availability. Different firms provide different levels of product availability. Every supply chain manager must use factors that influence the optimal level of product availability to target that optimal level and identify managerial levers that increase supply chain surplus SEIEE AU406 12-5
+ - SEIEE AU406 The Internet allows a customer to easily shop at an alternative store if the first choice is out of stock. This competitive environment puts pressure on online retailers to increase their level of availability. Different firms provide different levels of product availability. Every supply chain manager must use factors that influence the optimal level of product availability to target that optimal level and identify managerial levers that increase supply chain surplus 12-5 The importance of the level of product availability

Factors Affecting the Optimal Level of Product Availability ■Example of L.L.Bean The selling season for ski jackets is from November to February. L.L.Bean currently purchases the entire season's supply of ski jackets from the manufacturer before the start of the selling season High level of product availability>High inventory> High Cost SEIEE AU406 6
+ - SEIEE AU406 Example of L. L. Bean The selling season for ski jackets is from November to February. L.L.Bean currently purchases the entire season’s supply of ski jackets from the manufacturer before the start of the selling season High level of product availability High inventory High Cost 6 Factors Affecting the Optimal Level of Product Availability

Factors Affecting the Optimal Level of Product Availability Cost of overstocking the products Co Cost of understocking the products →Cu Possible scenarios Seasonal items with a single order in a season Demand during stockout is backlogged Demand during stockout is lost The company has to decide the size of the order SEIEE AU406 12-7
+ - SEIEE AU406 12-7 Factors Affecting the Optimal Level of Product Availability Cost of overstocking the products Cost of understocking the products Possible scenarios Seasonal items with a single order in a season Demand during stockout is backlogged Demand during stockout is lost The company has to decide the size of the order
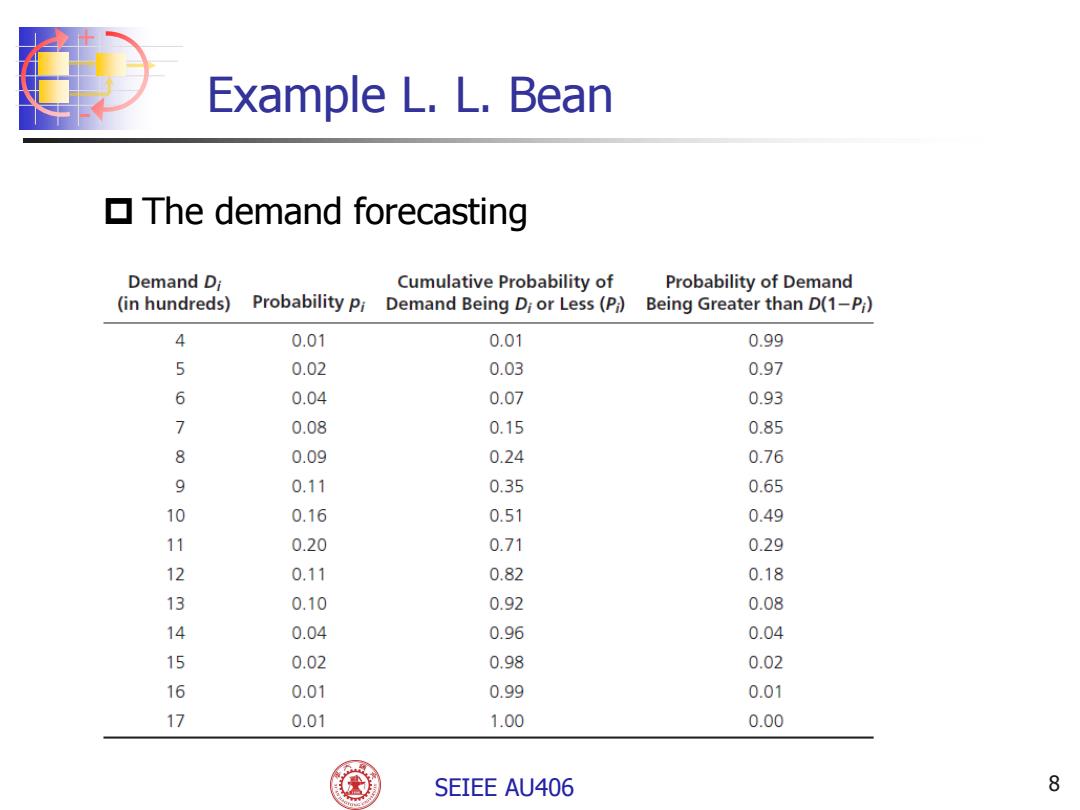
Example L.L.Bean The demand forecasting Demand Di Cumulative Probability of Probability of Demand (in hundreds) Probability pi Demand Being Di or Less(Pi) Being Greater than D(1-Pj) 4 0.01 0.01 0.99 5 0.02 0.03 0.97 6 0.04 0.07 0.93 7 0.08 0.15 0.85 8 0.09 0.24 0.76 9 0.11 0.35 0.65 10 0.16 0.51 0.49 11 0.20 0.71 0.29 12 0.11 0.82 0.18 13 0.10 0.92 0.08 14 0.04 0.96 0.04 15 0.02 0.98 0.02 16 0.01 0.99 0.01 17 0.01 1.00 0.00 SEIEE AU406 8
+ - SEIEE AU406 8 Example L. L. Bean The demand forecasting

Example L.L.Bean Cost of the products c=45 ▣Retail price pa=$1O0 Discounted price =$50 Holding and transportation cost for season =$10 Salvage value s=50-10=$40 The profit of each sold parkas =p-c=$100-45=55 The loss of each discounted parkas c-s=5 Cost of Overstocking: Co=c-s=$5 Cost of Understocking:C=p-c=$55 SEIEE AU406 9
+ - SEIEE AU406 9 Cost of the products c=$45 Retail price p= $100 Discounted price = $50 Holding and transportation cost for season = $10 Salvage value s= 50-10 =$40 The profit of each sold parkas =p-c= $100- $45=$55 The loss of each discounted parkas = c-s =$5 Example L. L. Bean Cost of Overstocking: Cost of Understocking:

Example L.L.Bean The expected profit from ordering 1,000 parkas is given as 10 7 Expeted profit =(p-)-(1.000-D)(cs)1.00(p) =$49.900 To decide whether to order 1,100 parkas,evaluate the extra 100. Expected profit from the extra 100 parkas 5,500 X Prob(demand 1,100) -500×Prob(demand<1,100)=$5,500×0.49-$500×0.51=$2,440 SEIEE AU406 10
+ - SEIEE AU406 The expected profit from ordering 1,000 parkas is given as 10 Example L. L. Bean To decide whether to order 1,100 parkas, evaluate the extra 100