
计算机问题求解一论题3-2 。贪心算法 2018年09月18日
计算机问题求解 – 论题3-2 - 贪心算法 2018年09月18日

间题1: 你还记得什么是“Optimal Substructure”吗?该结构特 性对求解最优解间题有什么启 发?
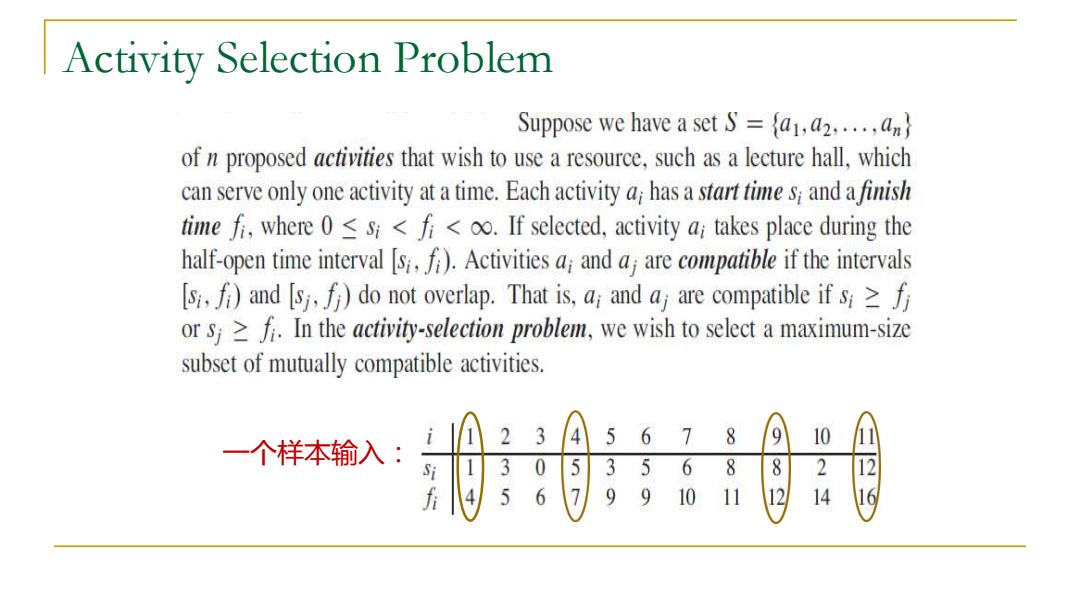
Activity Selection Problem Suppose we have a set S=fa,a2.... of n proposed activities that wish to use a resource,such as a lecture hall,which can serve only one activity at a time.Each activity a has a start time s and a finish timefi,wheres<f<o.If selected,activity ai takes place during the half-open time interval [)Activitiesa and a are compatible if the intervals [s)and [sj,)do not overlap.That is,a;and aj are compatible if si or sj In the activity-selection problem,we wish to select a maximum-size subset of mutually compatible activities. 一个样本输入: 5678 10 8 8 2 11 14 6
Activity Selection Problem 一个样本输入:

问题2: Activity Selection问题是否具 有“最优子结构”,为什么?

S表示开始时间不早于活动a的结束时间,而 结束时间早于α的结束时间的所有活动的集合。 If we denote the size of an optimal solution for the set S by ci,j],then we would have the recurrence ci,j川=ci,k]+c[k,j川+1 假设我们知道其中包含活动ak。 S,中最多相互兼容的活动数 0 c,小=} if Sij=0 max{c[i,k]+c[k,门+l}ifS≠0 kESij
Sij表示开始时间不早于活动ai的结束时间,而 结束时间早于aj的结束时间的所有活动的集合。 Sij中最多相互兼容的活动数 假设我们知道其中包含活动ak

动态规划解法 在上述递归关系中,4,可以是S中任一活动,每选定一个特 定的a,则确定特定的子问题。 动态规划方法按照合适的次序 解所有的子问题。 问题3: 是否有可能不必解所 有的子问题?
动态规划解法 在上述递归关系中,ak可以是Sij中任一活动,每选定一个特 定的ak , 则确定特定的子问题。动态规划方法按照合适的次序 解所有的子问题

问题4: 所谓“GREEDY”是指什 么?

Activity Selection:the Idea 要解的问题用Sk={a;∈S:≥}表示,S是原始问题所给的 所有活动的集合,则原始问题为S: ■ Greedy方法: 口选择完成时间最早的活动,假设是a; 口解子问题S1 Greedy可以指不同的“最”,但有的“最” 可以得到正确的解,有的“最”却未必!
Activity Selection: the Idea ◼ 要解的问题用 表示,S是原始问题所给的 所有活动的集合,则原始问题为S0 ; ◼ Greedy方法: ❑ 选择完成时间最早的活动,假设是a1 ; ❑ 解子问题S1。 Greedy可以指不同的“最”,但有的“最” 可以得到正确的解,有的“最”却未必!

如何去“编程表达”这样的递归式? RECURSIVE-ACTIVITY-SELECTOR (s.f.k,n) 1m=k+1 2 while m≤n and s[m<f[k] /find the first activity in Sk to finish 3 m=m+1 4 ifm≤n 5 return {am}URECURSIVE-ACTIVITY-SELECTOR(s,f.m.n) 6 else return 0 解子问题S1
如何去“编程表达”这样的递归式? 解子问题S1

GREEDY-ACTIVITY-SELECTOR(s,f) 1 n =s.length 2A={a1} 3k=1 4 for m 2 to n 问题5: 5 ifs[m≥f[k] 6 A=AUam 为什么不需 7 k m 要递归? 8 return A 问题68 为什么代价是幾性的?