
计算机问题求解一论题3-7 树 2018年10月16日
计算机问题求解 – 论题3-7 - 树 2018年10月16日

Theorem 4.1 An edge e of a graph G is a bridge if and only if e lies on no cycle of G. 推论:Every edge in a tree is a bridge 问题1g 从应用的角度看。上述推论有何 指导意义?
Theorem 4.1 An edge e of a graph G is a bridge if and only if e lies on no cycle of G. 推论:Every edge in a tree is a bridge

For an n-vertex graph G(with n 1),the following are equiv- alent(and characterize the trees with n vertices). A)G is connected and has no cycles. B)G is connected and has n-1 edges. C)G has n-1 edges and no cycles. D)For u,vE V(G),G has exactly one 4,v-path 问题2: 如何证明一系列命题等价? 问题48 不能有回路对最小顶点度 数有什么影响? 问题3:有n-1条边的n点连通图,一定是树? 有n-1条边的无环连通图,一定连通n个点?
问题3:有n-1条边的n点连通图,一定是树? 有n-1条边的无环连通图,一定连通n个点?

树的性质的“极限性” a)Every edge of a tree is a cut-edge. b)Adding one edge to a tree forms exactly one cycle. c)Every connected graph contains a spanning tree. 间题5: 什么样的图生成树是唯一的,为什么? 如何构造一个连通图的生成树?
树的性质的“极限性
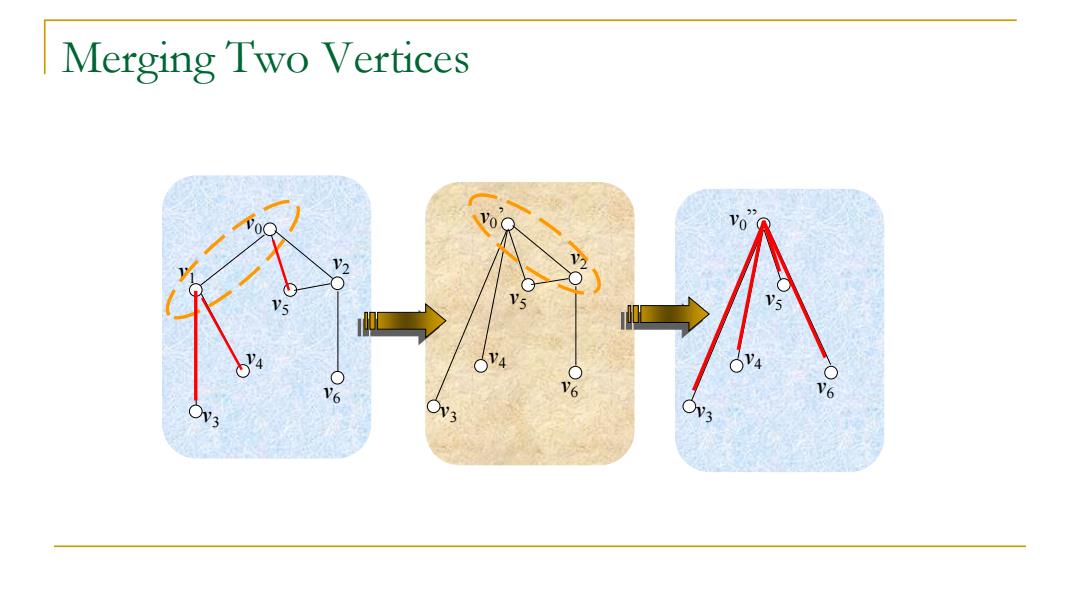
Merging Two Vertices V6
Merging Two Vertices v0 v6 v2 v5 v4 v1 v3 v6 v2 v5 v4 v3 v0 ’ v6 v5 v4 v3 v0
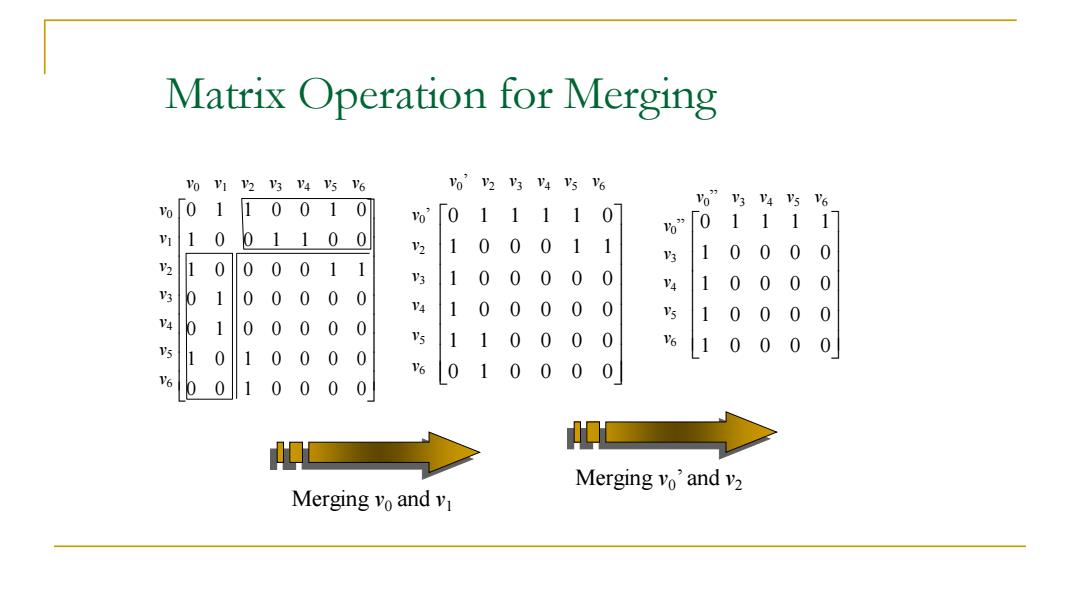
Matrix Operation for Merging Vo V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 Vo'23V45'6 %01 1 0010 %” V3 V4 V5 V6 %’ 0 1111 0 11117 1 01100 %” '2 1 0 0 011 3 1 0 0 0 0 z 10 0 0011 V3 10 000 0 4 1 0 00 0 3 01 0 0 000 V4 10 00 0 0 冬 1 0 00 0 40 1 0 0 00 0 的 11 0 0 0 6 s 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 00 0 1 0 V6 0 1 0 0 00 0 0 1 0 0 0 Merging vo'and v2 Merging vo and vi
Matrix Operation for Merging 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 v0 v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 v0 v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 Merging v0 and v1 v0” v3 v4 v5 v6 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 v0” v3 v4 v5 v6 v0 ’ v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 v0 ’ 0 1 1 1 1 0 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 Merging v0 ’ and v2
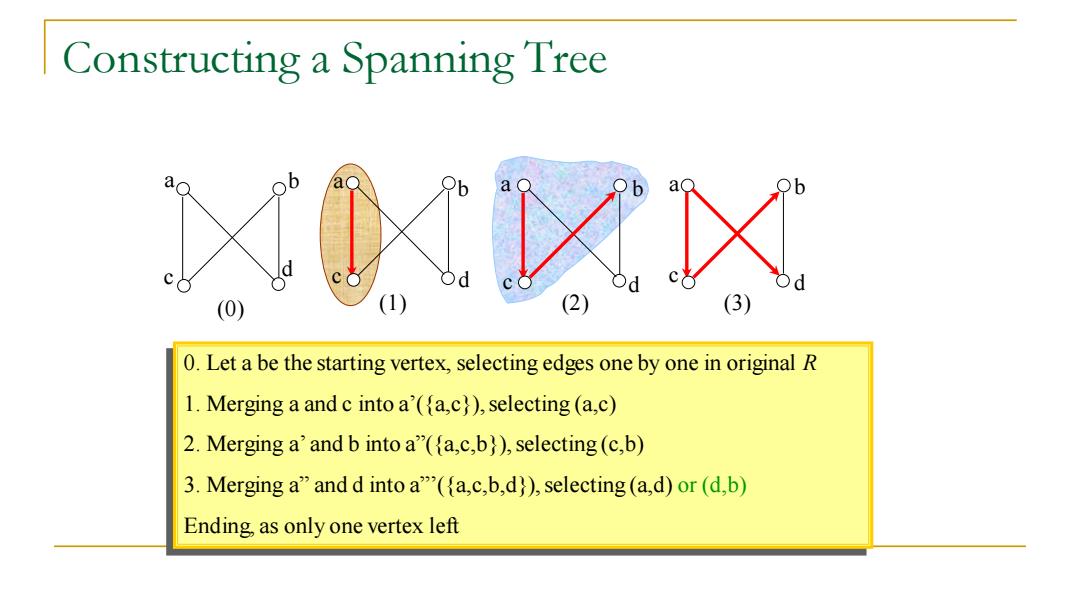
Constructing a Spanning Tree a a 1 2) 0.Let a be the starting vertex,selecting edges one by one in original R 1.Merging a and c into a'(fa,c)),selecting (a,c) 2.Merging a'and b into a"(fa,c,b)),selecting (c,b) 3.Merging a"and d into a"(a,c,b,d)),selecting (a,d)or(d,b) Ending,as only one vertex left
Constructing a Spanning Tree a b c d a b a b a b c c d c d d 0. Let a be the starting vertex, selecting edges one by one in original R 1. Merging a and c into a’({a,c}), selecting (a,c) 2. Merging a’ and b into a”({a,c,b}), selecting (c,b) 3. Merging a” and d into a”’({a,c,b,d}), selecting (a,d) or (d,b) Ending, as only one vertex left (0) (1) (2) (3)
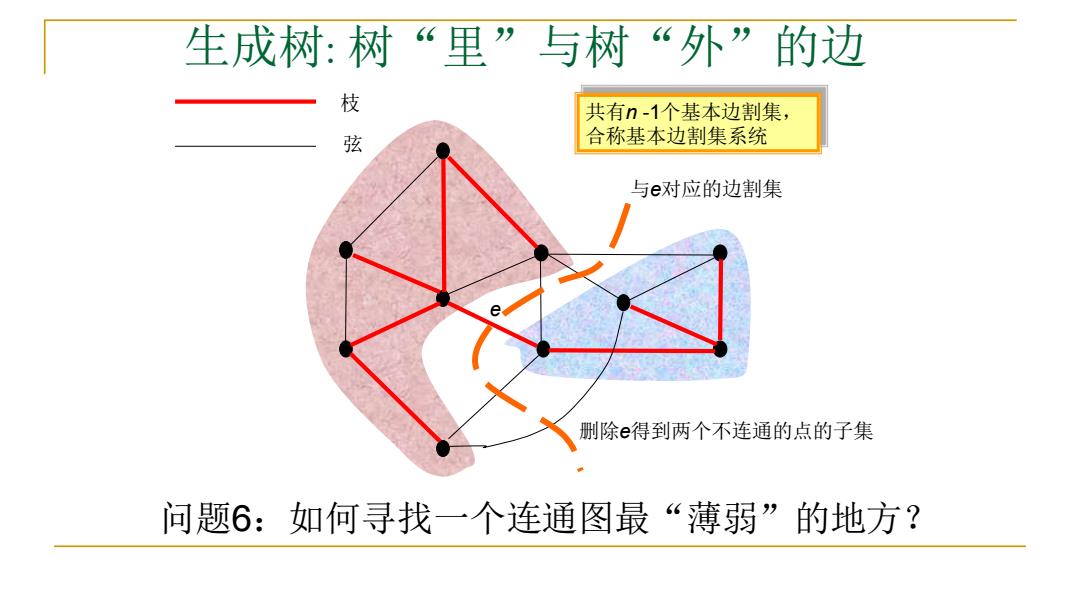
生成树:树“里”与树“外”的边 枝 共有n-1个基本边割集, 弦 合称基本边割集系统 与e对应的边割集 删除e得到两个不连通的点的子集 问题6:如何寻找一个连通图最“薄弱”的地方?
生成树: 树“里”与树“外”的边 枝 弦 e 删除e得到两个不连通的点的子集 与e对应的边割集 共有n -1个基本边割集, 合称基本边割集系统 问题6:如何寻找一个连通图最“薄弱”的地方?
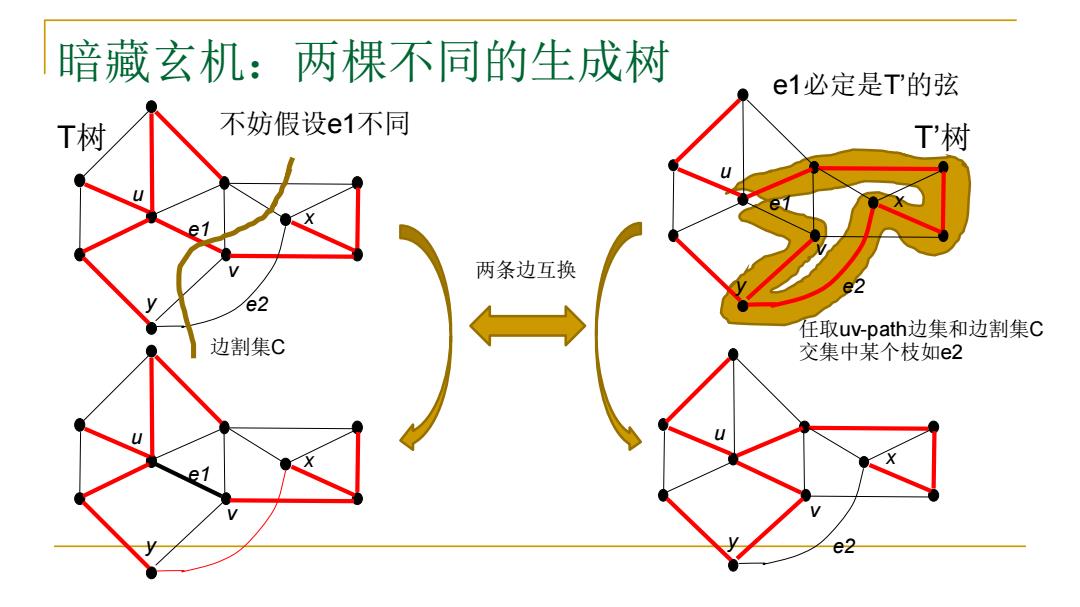
暗藏玄机:两棵不同的生成树 e1必定是T'的弦 T树 不妨假设e1不同 T'树 两条边互换 e2 e2 任取uv-path边集和边割集C 边割集C 交集中某个枝如e2 e2
暗藏玄机:两棵不同的生成树 两条边互换 e2 u v x y e1 u v x y e1 e2 u v x y T树 e1 e2 u v x y 不妨假设e1不同 T’树 e1必定是T’的弦 任取uv-path边集和边割集C 边割集C 交集中某个枝如e2

生成树的“变换” 定理:T与T均是图G的生成树,存在eeET,但eE,证明:必有e'∈E,但e'E,满足:T {e}U{e}和T-{eU{e}均是G的生成树。 证明概要: 设e=uv,T-{e}必含两个连通分支,设为T,T2。 .T是连通图,T'中有uv-通路,其中必有一边满足其两个端点x,y分别在T,T,中,设其为e ,显然T-{eU{e}是生成树。 而TU{e}必含唯一回路,且该回路中必定包含e’。将e'从该回路中删去,得到T*=T {eU{e}。显然,T-{eU{e}是生成树。 问题7:这个定理会被 用于证明最小生成树 算法的正确性,你能 大致推测出怎么用吗? -T中的通路
生成树的“变换” ◼ 定理:T与T'均是图G的生成树,存在eET , 但eET',证明:必有e'ET' , 但e'ET , 满足:T- {e}⋃{e'}和T'-{e'}⋃{e}均是G的生成树。 ❑ 证明概要: 设e=uv, T-{e}必含两个连通分支,设为T1 , T2。 T‘是连通图,T’中有uv-通路,其中必有一边满足其两个端点x,y分别在T1 , T2中,设其为e ‘ ,显然T-{e}⋃{e’}是生成树。 而T‘⋃{e}必含唯一回路,且该回路中必定包含e’。将e’从该回路中删去,得到T*=T‘- {e’}⋃{e} 。显然, T'-{e'}⋃{e}是生成树。 u e v x e' y T1 T2 T'中的通路 问题7:这个定理会被 用于证明最小生成树 算法的正确性,你能 大致推测出怎么用吗?