
计算机问题求解一论题4-1 线性规划 2019年2月27日
计算机问题求解 – 论题4-1 - 线性规划 2019年2月27日
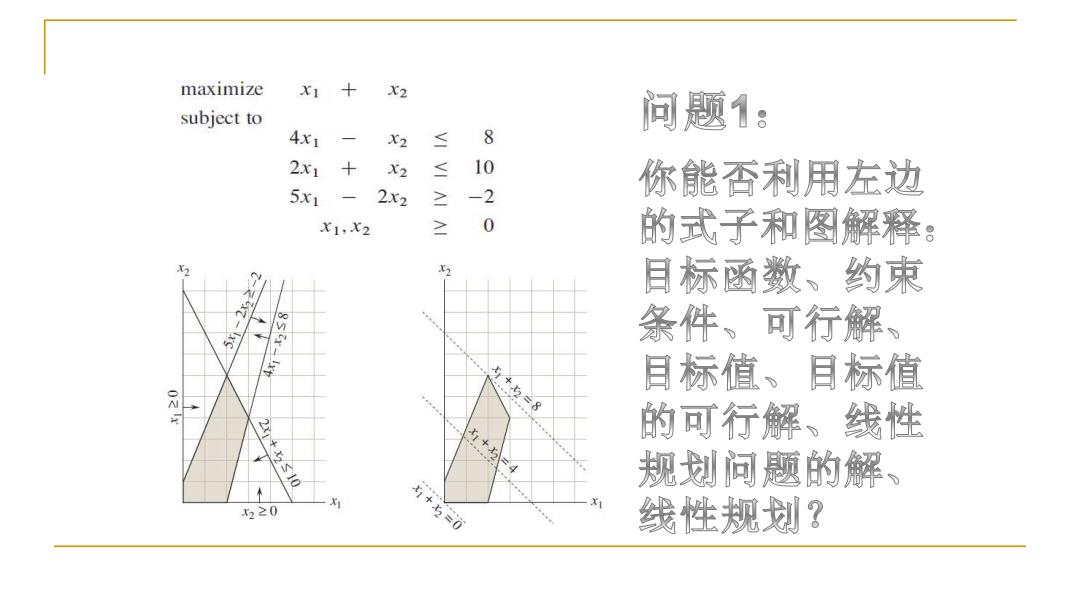
maximize X1 X2 subject to 问题1: 4x1 X2 ≤ 8 2x1 X2 ≤ 10 5x1 你能否利用左边 2x2 ≥ -2 X1,X2 ≥ 0 的式子和图解释: 222-2 目标函数、约束 条件、可行解、 =8 目标值、目标值 21+x10 x+x 的可行解、线性 规划问题的解、 5≥0 +=0 线性规划?
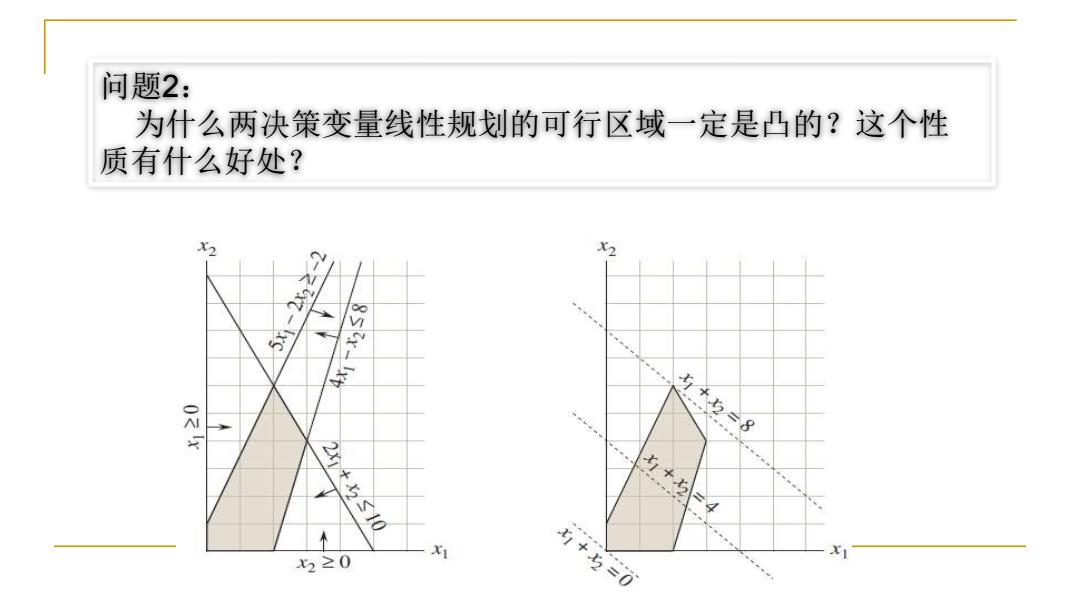
问题2: 为什么两决策变量线性规划的可行区域一定是凸的?这个性 质有什么好处? X2 X2 5x-2x22-2 2x4x2S10 x1+ 4 个 x2≥0 X1 +与=0
问题2: 为什么两决策变量线性规划的可行区域一定是凸的?这个性 质有什么好处?
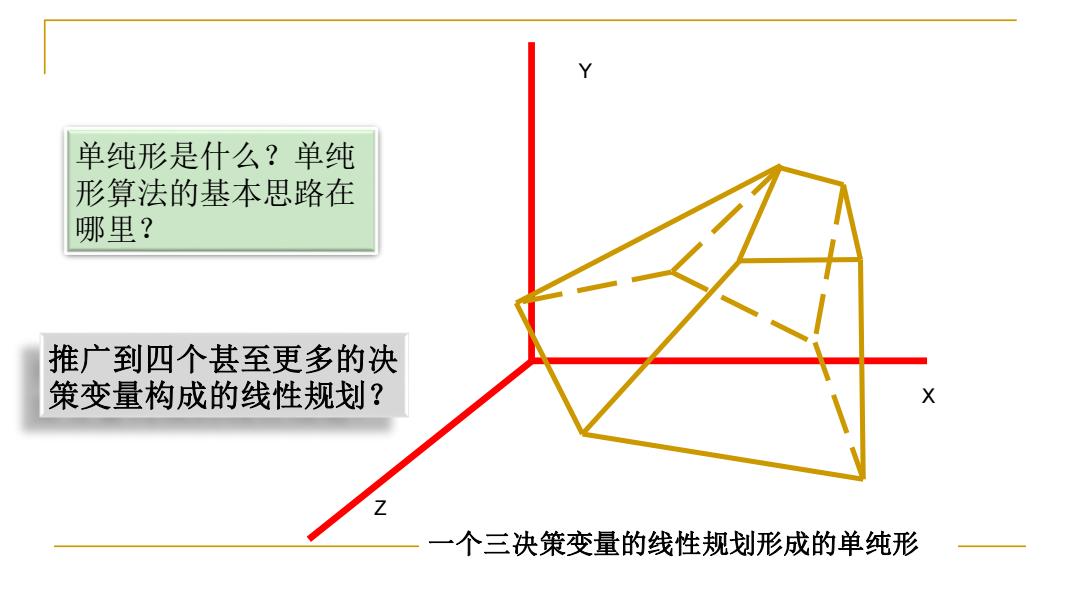
单纯形是什么?单纯 形算法的基本思路在 哪里? 推广到四个甚至更多的决 策变量构成的线性规划? Z 一个三决策变量的线性规划形成的单纯形
一个三决策变量的线性规划形成的单纯形 Y X Z 单纯形是什么?单纯 形算法的基本思路在 哪里? 推广到四个甚至更多的决 策变量构成的线性规划?

问题3: 如何理解下列语句 Although we cannot easily graph linear programs with more than two variables,the same intuition holds.If we have three variables,then each constraint corresponds to a half-space in three-dimensional space.The intersection of these half-spaces forms the feasible region
Although we cannot easily graph linear programs with more than two variables, the same intuition holds. If we have three variables, then each constraint corresponds to a half-space in three-dimensional space. The intersection of these half-spaces forms the feasible region

问题4: 线性规划问题中的不等 式能不能用严格的大于 或小于?
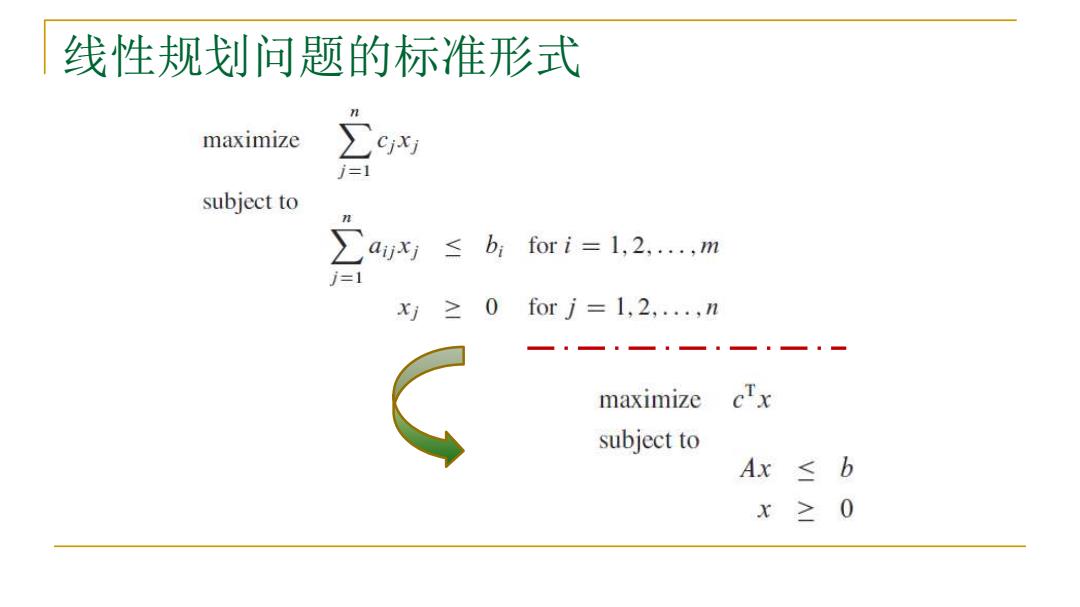
线性规划问题的标准形式 maximize j=1 subject to ax≤bi for i=1,2,,m j=1 x≥0forj=1,2,..,n maximize cTx subject to Ax ≤b x≥0
线性规划问题的标准形式

minimize -2x1+3x2 subject to x1+x2 =7 1- 2x2 4 X1 ≥0 问题5: 为什么说这不是“标准形式

mizing a linear function subject to linear constraints,into standard form.A linear program might not be in standard form for any of four possible reasons: 1.The objective function might be a minimization rather than a maximization. 2.There might be variables without nonnegativity constraints. 3.There might be equality constraints,which have an equal sign rather than a less-than-or-equal-to sign. 4.There might be inequality constraints,but instead of having a less-than-or- equal-to sign,they have a greater-than-or-equal-to sign

minimize -2x1+3x2 maximize 2x1 3x2 subject to subject to x1+ X2 =7 x1+ X2 =7 x1-2x2 4 → x1-2x2 ≤4 x1 0. X1 ≥0 问题6: 如何将它转化为标准形式?这 两个线性规划“一样”吗?