
上充通大学 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Virus:Growth,quantification,replication and diversity Lecture 9-3 Essentials of Virology NGHAIJIAO TON NG Chen Feng School of Life Science and Biotechnology. Shanghai Jiao Tong University Email:cf2001@sjtu.edu.cn http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn
Lecture 9-3 Essentials of Virology Virus: Growth, quantification, replication and diversity Chen Feng School of Life Science and Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Email: cf2001@sjtu.edu.cn http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn

上泽充通大¥ SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 强 ■■品是是 9.11 Overview of Animal Viruses ANGHAIJIAO TONG 1日9G ■■盒
9.11 Overview of Animal Viruses
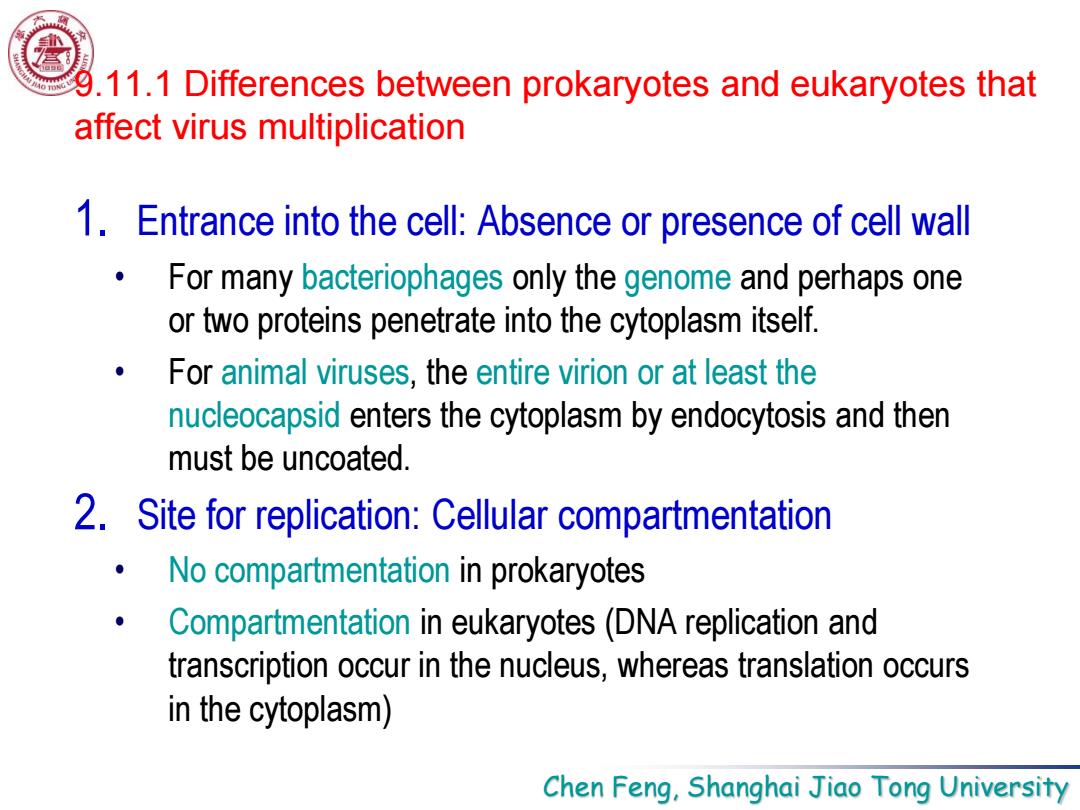
9.11.1 Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes that affect virus multiplication 1.Entrance into the cell:Absence or presence of cell wall For many bacteriophages only the genome and perhaps one or two proteins penetrate into the cytoplasm itself. For animal viruses,the entire virion or at least the nucleocapsid enters the cytoplasm by endocytosis and then must be uncoated. 2.Site for replication:Cellular compartmentation No compartmentation in prokaryotes Compartmentation in eukaryotes(DNA replication and transcription occur in the nucleus,whereas translation occurs in the cytoplasm) Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 9.11.1 Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes that affect virus multiplication 1. Entrance into the cell: Absence or presence of cell wall • For many bacteriophages only the genome and perhaps one or two proteins penetrate into the cytoplasm itself. • For animal viruses, the entire virion or at least the nucleocapsid enters the cytoplasm by endocytosis and then must be uncoated. 2. Site for replication: Cellular compartmentation • No compartmentation in prokaryotes • Compartmentation in eukaryotes (DNA replication and transcription occur in the nucleus, whereas translation occurs in the cytoplasm)

9.11.1 Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes that affect virus multiplication 3.mRNA synthesis and protein translation Polycistronic for bacteria Monocistronic for eukaryotes Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 3. mRNA synthesis and protein translation • Polycistronic for bacteria • Monocistronic for eukaryotes 9.11.1 Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes that affect virus multiplication
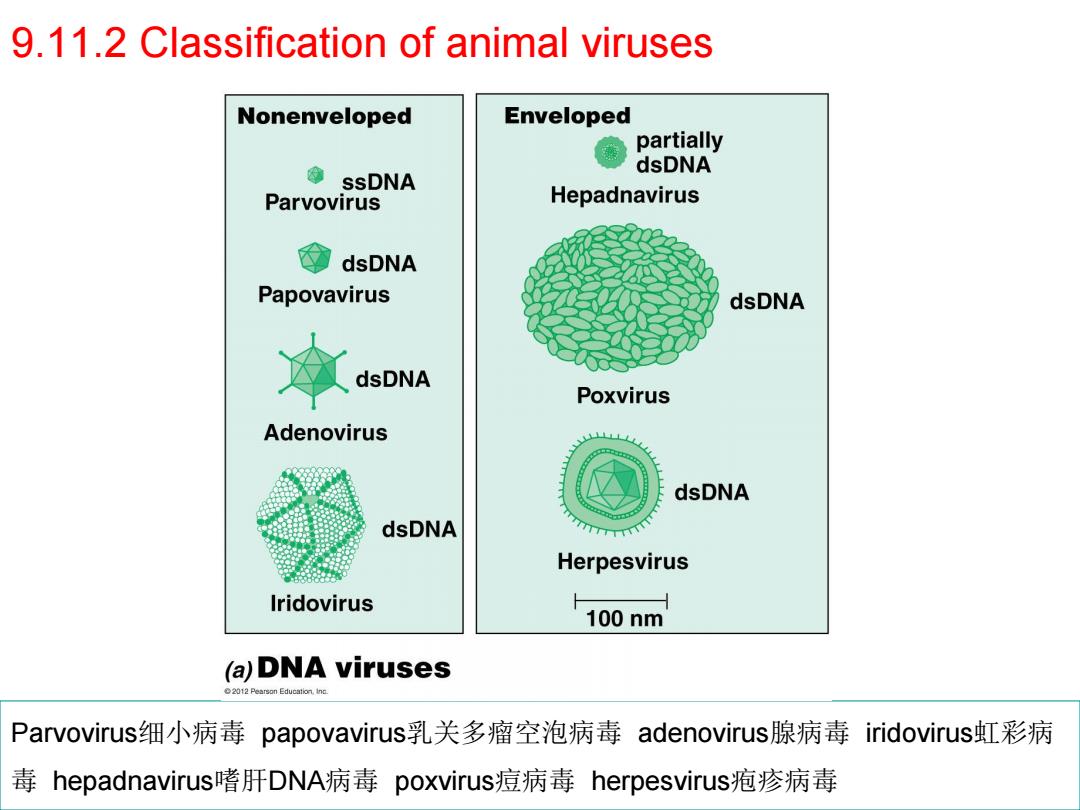
9.11.2 Classification of animal viruses Nonenveloped Enveloped partially 每 dsDNA ssDNA Parvovirus Hepadnavirus dsDNA Papovavirus dsDNA dsDNA Poxvirus Adenovirus dsDNA dsDNA Herpesvirus Iridovirus 100nm (a)DNA viruses 2012 Pearson Education,ing. Parvovirus细小病毒papovavirus乳关多瘤空泡病毒adenovirus.腺病毒iridovirus!虹彩病 毒hepadnavirust嗜肝DNA病毒 poxvirus痘病毒herpesvirus疱疹病毒
9.11.2 Classification of animal viruses Parvovirus细小病毒 papovavirus乳关多瘤空泡病毒 adenovirus腺病毒 iridovirus虹彩病 毒 hepadnavirus嗜肝DNA病毒 poxvirus痘病毒 herpesvirus疱疹病毒
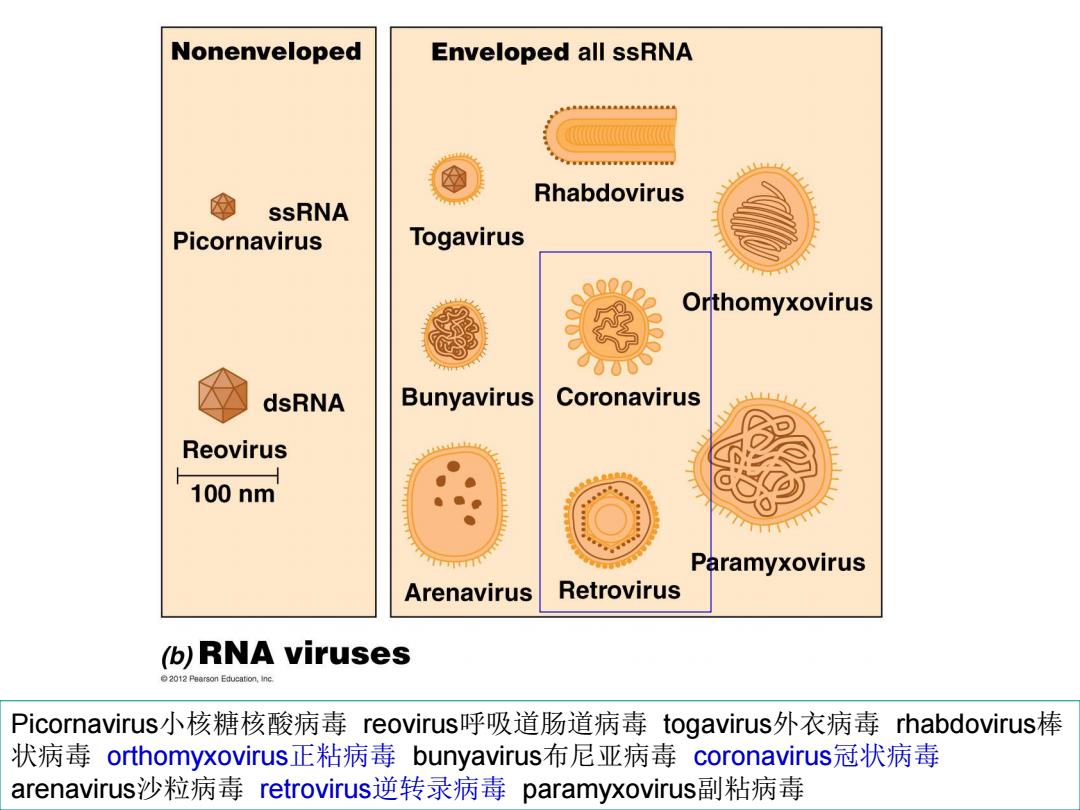
Nonenveloped Enveloped all ssRNA Rhabdovirus SsRNA Picornavirus Togavirus Orthomyxovirus dsRNA Bunyavirus Coronavirus Reovirus 100nm Paramyxovirus Arenavirus Retrovirus (b)RNA viruses 2012 Pearson Education,Inc. Picornavirus小核糖核酸病毒reovirus呼吸道肠道病毒togavirus外衣病毒rhabdovirus棒 状病毒orthomyxovirus正粘病毒bunyavirus布尼亚病毒coronavirus冠状病毒 arenavirus沙粒病毒retrovirus逆转录病毒paramyxovirus副粘病毒
Picornavirus小核糖核酸病毒 reovirus呼吸道肠道病毒 togavirus外衣病毒 rhabdovirus棒 状病毒 orthomyxovirus正粘病毒 bunyavirus布尼亚病毒 coronavirus冠状病毒 arenavirus沙粒病毒 retrovirus逆转录病毒 paramyxovirus副粘病毒
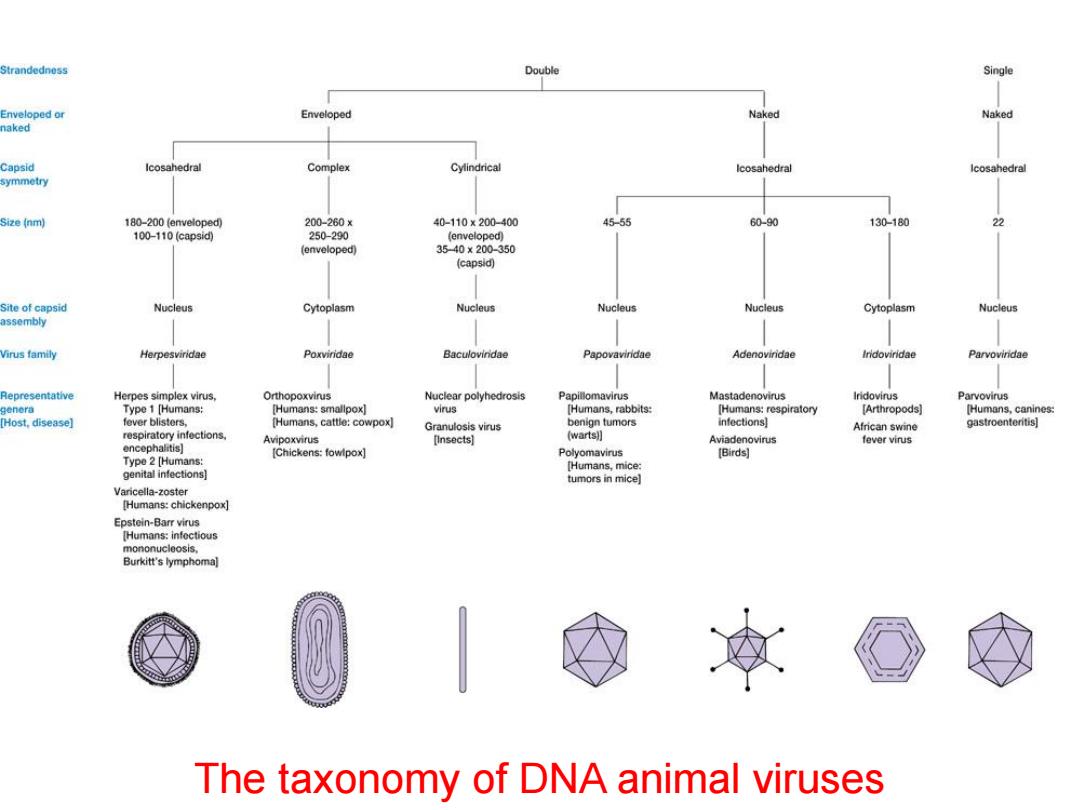
Strandedness Double Single Enveloped or Enveloped Naked Naked naked Capsid Icosahedral Complex Cylindrical lcosahedral lcosahedral symmetry Size (nm) 180-200 (enveloped) 200-260× 40-110x200400 45-55 60-90 130-180 22 100-110 (capsid) 250-290 (enveloped) (enveloped) 3540×200-350 (capsid) Site of capsid Nucleus Cytoplasm Nucleus Nucleus Nucleus Cytoplasm Nucleus assembly Virus family Herpesviridae Poxviridae Baculovinidae Papovavindae Adenovindae Indoviridae Parvovindae Representative Herpes simplex virus, Orthopoxvins Nuclear polyhedrosis Papilomavirus Mastadenovirus Iridovirus Parvovirus genera Type 1 [Humans: [Humans:smallpox] virus [Humans,rabbits: [Humans:respiratory [Arthropods] [Humans,canines: Host.disease】 fever blisters. [Humans,cattle:cowpox] Granulosis virus benign tumors infections] African swine gastroenteritis】 respiratory infections. Avipoxvirus [Insects] warts】 Aviadenovirus fever virus encephalitis】 【Chickens:fowipox)] Polyomavirus [Birds] Type 2 [Humans: [Humans,mice: genital infections】 tumors in mice] Varicella-zoster [Humans:chickenpox] Epstein-Barr virus [Humans:infoctious mononucleosis. Burkitt's lymphoma] The taxonomy of DNA animal viruses
The taxonomy of DNA animal viruses
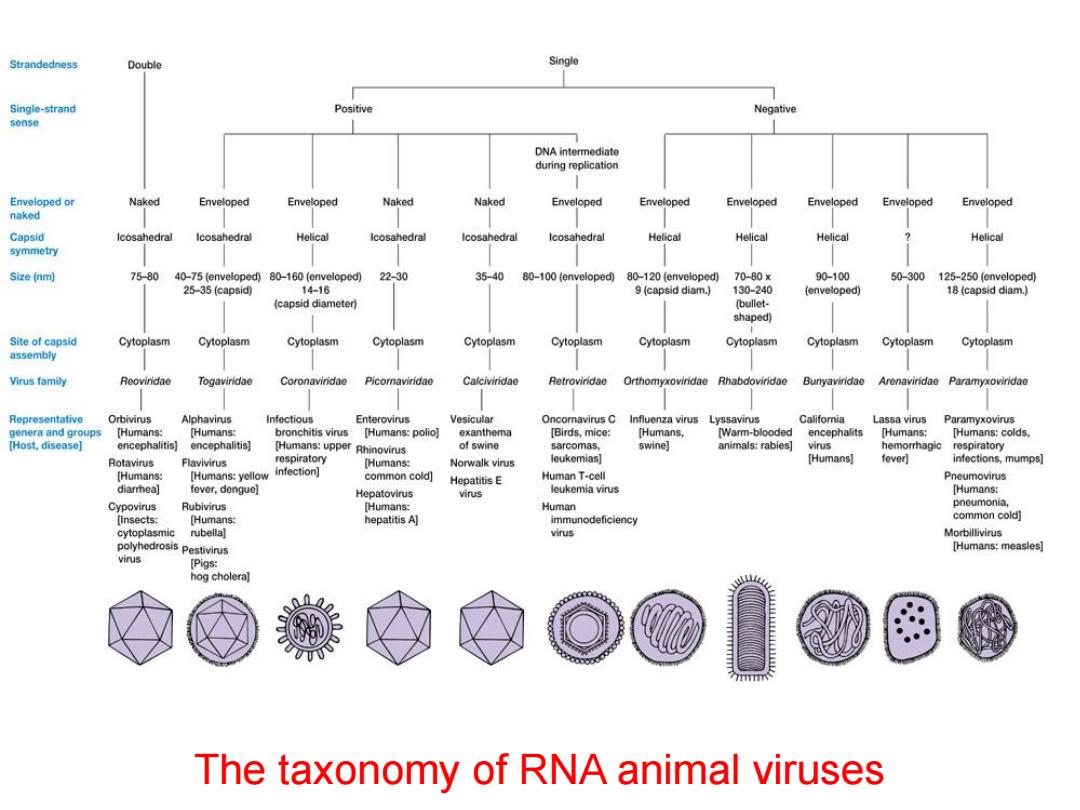
Strandedness Double Single Single-strand Positive Negative sense DNA intermediate during replication Enveloped or Naked Enveloped Enveloped Naked Naked Enveloped Enveloped Enveloped Enveloped Enveloped Enveloped naked Capsid lcosahedral Icosahedral Helical lcosahedral Icosahedral Icosahedral Helical Helical Helical Helical symmetry Size (nm) 75-80 40-75 (enveloped)80-160 (enveloped) 22-30 35-40 80-100 (enveloped) 80-120 (enveloped) 70-80× 90-100 50-300 125-250 (enveloped) 25-35(capsid) 14-16 9 (capsid diam.) 130-240 (enveloped) 18 (capsid diam.) (capsid diameter) (bullet- shaped) Site of capsid Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm assembly Virus family Togaviridae Coronavindae Picornaviridao Calciviridae Retroviridao Rhabdoviridae Bunyavindae Arenaviridae Paramyxoviridae Representative Orbivirus Alphavirus Infectious Enterovirus Vesicular Oncomavirus C Influenza virus Lyssavirus Califomia Lassa virus Paramyxovirus genera and groups [Humans: [Humans: bronchitis virus [Humans:polio] exanthema [Birds,mice: [Humans, [Warm-blooded encephalits [Humans: [Humans:colds [Host,disease] encephalitis] encephalitis] [Humans:upper Rhinovirus of swine sarcomas, swine] animals:rabies] virus hemorrhagic respiratory Rotavirus Flavivirus respiratory [Humans: Norwalk virs leukemias] [Humans fever] infections,mumps] [Humans: [Humans:yellow infection间 common cold] Hepatitis E Human T-cell Pneumovirus diarrhea] fever.dongue] Hepatovirus virus loukemia virus [Humans: Cypovirus Rubivirus [Humans: Human pneumonia, [Insects: [Humans: hepatitis A] immunodeficiency common cold] cytoplasmic rubella] virus Morbillivirus polyhedrosis Pestivirus [Humans:measles] virus [Pigs: hog cholera] The taxonomy of RNA animal viruses
The taxonomy of RNA animal viruses

9.11.3 Consequences of Virus Infection in Animal Cells 病毒感染动物细胞后的可能后果 Tumor cell Transformation division 转化为 Transformation 肿瘤细 into tumor cell 胞 Cell Lysis Virus 裂解感染 Death of Attachment cell and and penetration release of virus Persistent Virus infection multiplication Slow release 宿存感染 Cell of virus without fusion cell death Latent infection 潜伏感染 Virus present but not replicating 2012 Pearson Education.Inc
9.11.3 Consequences of Virus Infection in Animal Cells 病毒感染动物细胞后的可能后果 宿存感染 潜伏感染 裂解感染 转化为 肿瘤细 胞
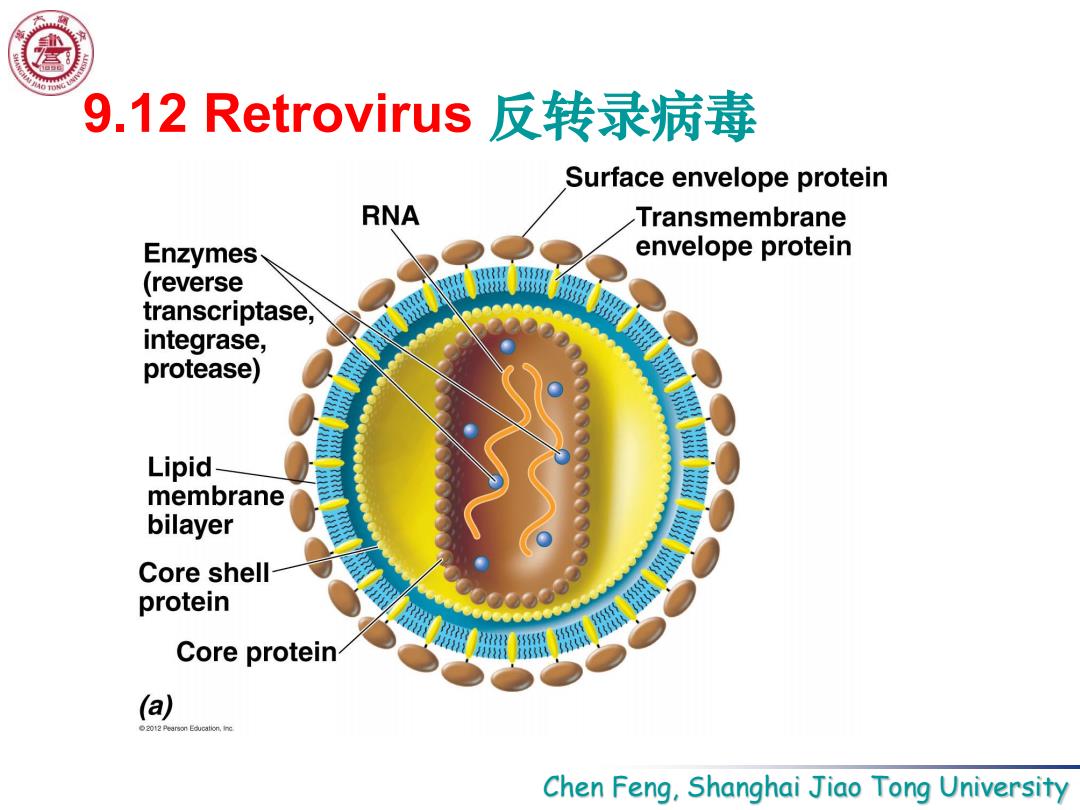
9.12 Retrovirus反转录病毒 Surface envelope protein RNA Transmembrane Enzymes envelope protein (reverse transcriptase, integrase, protease) Lipid membrane bilayer Core shell protein Core protein (a) 2012Pw Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 9.12 Retrovirus 反转录病毒