
1/12/2017 Introduction Guide to US Food Laws In the beginning,American laws were and Regulations mostly state laws SECOND EDITION As America grew,a need for more uniform Chapter 3 PatriciaA.Curtis law of the land also grew Federal,State, This chapter discusses the differences and Local Laws between State and Local laws and Federal Law Examples will be provided on how local regulations impact you and the foods you eat WILEY Blackwall Introduction National versus State Government Food Safety and Modernization Act(FSMA) First government was based on state laws initiated updates on food safety regulations Prior to the constitution,America was made States are changing their rules for local foods up of 13 colonies ruled by Great Britain rules vary from state to state loosen restrictions on farmers and cottage food producers with sales number below a limit rules are being established where none existed local food sales and the number of farmer's Original Thirteen Colonies markets have increased 。2010-6132 ·2009-5274 ·2000-2410
1/12/2017 1 Chapter 3 Federal, State, and Local Laws Introduction • In the beginning, American laws were mostly state laws • As America grew, a need for more uniform law of the land also grew • This chapter discusses the differences between State and Local laws and Federal Law • Examples will be provided on how local regulations impact you and the foods you eat Introduction • Food Safety and Modernization Act (FSMA) initiated updates on food safety regulations • States are changing their rules for local foods - rules vary from state to state - loosen restrictions on farmers and cottage food producers with sales number below a limit - rules are being established where none existed - local food sales and the number of farmer’s markets have increased 2010 – 6132 2009 – 5274 2000 - 2410 National versus State Government • First government was based on state laws • Prior to the constitution, America was made up of 13 colonies ruled by Great Britain

1/12/2017 National versus State Government The Articles of Confederation Congress given the No chiefExecutive After the Revolutionary War power to: No National Court System No Power to Draft Soldiers colonies formed a league of ·Declare War .No Power to Control Interstate friendship ·Make Peace Commerce ·Sign Treaties No Power to Enforce Treaties ·governed themselves ·Borrow Money articles of Confederation was drafted Establish an Army &Difficult to Pass Laws(2/3 vote) feared strong government Navy No National Currency ·Organize a Post ·Difficult to Amend This form of state government was too Office weak National versus State Government National versus State Government Government system was changed to Constitution was drafted to federalism,which is based on a sharing define the limits of the power of the of power between the national and state national government (local)governments define the relationship between the national government and the individual Opposite of this is a centralized state governments (unitary)government where national guarantee the rights of the citizens of government maintains all the power the United States
1/12/2017 2 After the Revolutionary War • colonies formed a league of friendship • governed themselves • articles of Confederation was drafted • feared strong government • This form of state government was too weak National versus State Government Constitution was drafted to • define the limits of the power of the national government • define the relationship between the national government and the individual state governments • guarantee the rights of the citizens of the United States National versus State Government • Government system was changed to federalism, which is based on a sharing of power between the national and state (local) governments • Opposite of this is a centralized (unitary) government where national government maintains all the power National versus State Government
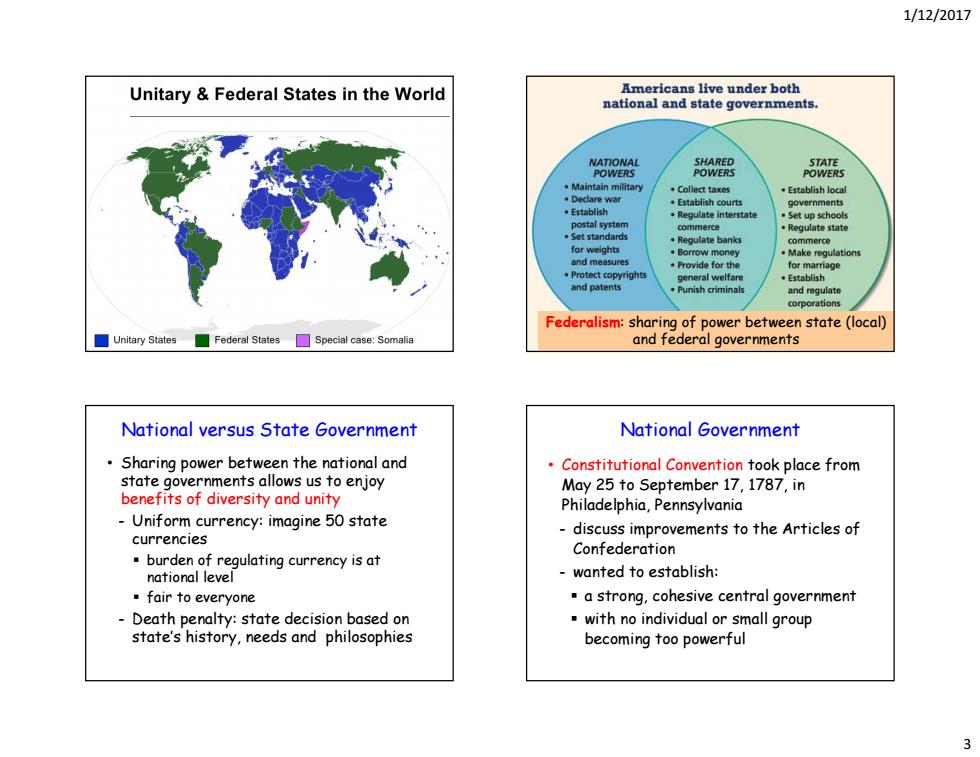
1/12/2017 Unitary Federal States in the World Americans live under both national and state governments. 器 POWERS ·Collect taxes ·Establishlocal 。Establish courts governments Regulate interstate Set up schools Set sta .Regulate state Regulate banks ommerce for weichts and measures orrow money Make regulations Protect copyrights Provide for the a90 and patents and reg corporations Federalism:sharing of power between state (local) ☐Unitary States☐Federal States☐Special case:Somalia and federal governments National versus State Government National Government Sharing power between the national and Constitutional Convention took place from state governments allows us to enjoy May 25 to September 17,1787,in benefits of diversity and unity Philadelphia,Pennsylvania Uniform currency:imagine 50 state discuss improvements to the Articles of currencies Confederation burden of regulating currency is at national level -wanted to establish: fair to everyone .a strong,cohesive central government Death penalty:state decision based on with no individual or small group state's history,needs and philosophies becoming too powerful
1/12/2017 3 Federalism: sharing of power between state (local) and federal governments • Sharing power between the national and state governments allows us to enjoy benefits of diversity and unity - Uniform currency: imagine 50 state currencies burden of regulating currency is at national level fair to everyone - Death penalty: state decision based on state’s history, needs and philosophies National versus State Government • Constitutional Convention took place from May 25 to September 17, 1787, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania - discuss improvements to the Articles of Confederation - wanted to establish: a strong, cohesive central government with no individual or small group becoming too powerful National Government
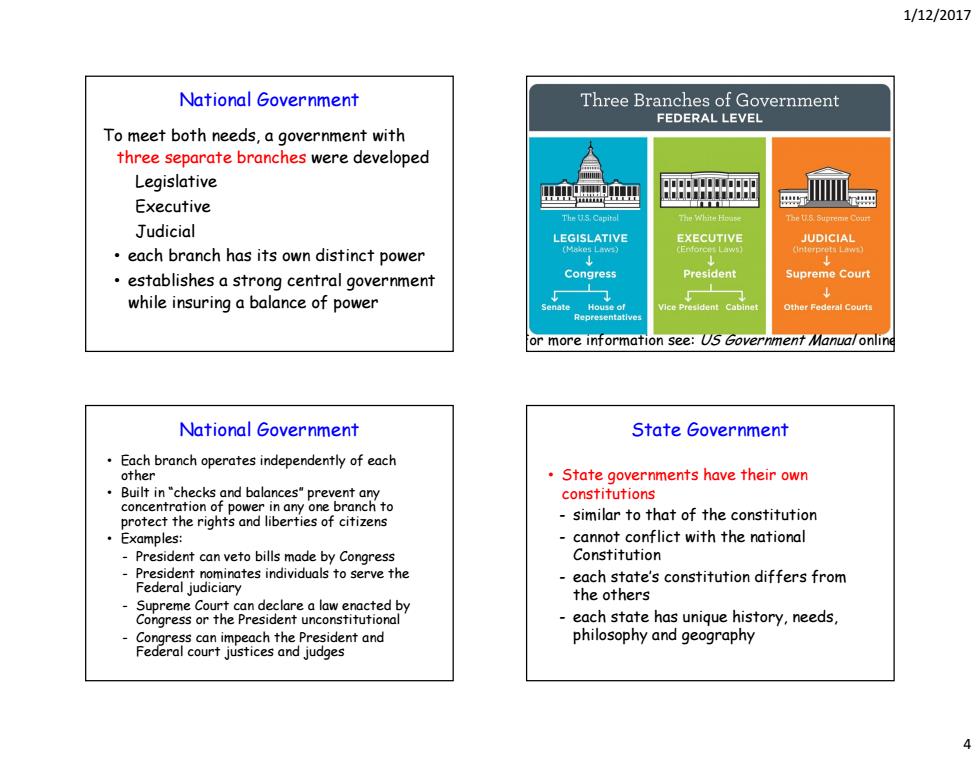
1/12/2017 National Government Three Branches of Government FEDERAL LEVEL To meet both needs,a government with three separate branches were developed Legislative 血画 Executive 瓜耍 The 5 Capitol Judicial LEGISLATIVE EXECUTIVE JUDICIAL each branch has its own distinct power Erdorce Law establishes a strong central government Congress President Supreme Court while insuring a balance of power enate ice President Cabine ather Federal Courts or more information see:Us Government Manua/online National Government State Government Each branch operates independently of each other State governments have their own in"checks and balancery prevenanh to constitutions concentration of power in protect the rights and liberties of citizens similar to that of the constitution ·Examples: cannot conflict with the national President can veto bills made by Congress Constitution President nominates individuals to serve the -each state's constitution differs from Federal judiciary the others Supreme Court can declare a law enacted by Congress or the President unconstitutional -each state has unique history,needs, Congress can impeach the President and philosophy and geography Federal court justices and judges
1/12/2017 4 To meet both needs, a government with three separate branches were developed Legislative Executive Judicial • each branch has its own distinct power • establishes a strong central government while insuring a balance of power National Government For more information see: US Government Manual online • Each branch operates independently of each other • Built in “checks and balances” prevent any concentration of power in any one branch to protect the rights and liberties of citizens • Examples: - President can veto bills made by Congress - President nominates individuals to serve the Federal judiciary - Supreme Court can declare a law enacted by Congress or the President unconstitutional - Congress can impeach the President and Federal court justices and judges National Government • State governments have their own constitutions - similar to that of the constitution - cannot conflict with the national Constitution - each state’s constitution differs from the others - each state has unique history, needs, philosophy and geography State Government

1/12/2017 State Government State Government First 100 years of US history states did most of the governing that Civil War-due to a rift formed between directly affected the people federal and state governments over the issue national government focused on foreign of sovereignty affairs 。 Several constitutional amendments were passed that spelled out the federal -Dual Federalism:(divided government's control over social and economic sovereignty)a political policy and protection of the civil rights of arrangement in which power is citizens divided between the federal and state governments in Dual Federalism continued as the federal clearly defined term government got stronger State Government State Government Civil War Amendments Civil War Amendments 14th Amendment-addresses citizenship rights and 13th Amendment-"Neither slavery nor equal protection of the laws involuntary servitude,except as a punishment for crime...shall exist within iterraled the United States" Equal Protection Clause:"No State shall deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the law" Privileges or Immunities Clause:"No State shall make 13TH AMENDMENT -Due Process Clause:"No State shall deprive any person of life,liberty.or property.without due process of the law
1/12/2017 5 • First 100 years of US history - states did most of the governing that directly affected the people - national government focused on foreign affairs State Government - Dual Federalism: (divided sovereignty) a political arrangement in which power is divided between the federal and state governments in clearly defined term • Civil War – due to a rift formed between federal and state governments over the issue of sovereignty • Several constitutional amendments were passed that spelled out the federal government’s control over social and economic policy and protection of the civil rights of citizens • Dual Federalism continued as the federal government got stronger State Government Civil War Amendments • 13th Amendment – “Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime … shall exist within the United States” State Government Civil War Amendments • 14th Amendment – addresses citizenship rights and equal protection of the laws - Citizenship Clause: “All persons born or naturalized in the US --- are citizens of the US” - Equal Protection Clause: “No State shall deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the law” - Privileges or Immunities Clause: “No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the US” - Due Process Clause: “No State shall deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of the law” State Government

1/12/2017 State Government State Government Civil War Amendments In the 1930s,Great Depression brought the 15th Amendment-"The rights of citizens of end to dual federalism the US to vote shall not be denied or States could not cope with the economic abridged by the US or by any State on upheaval account of race,color,or previous condition President Roosevelt's New Deal brought in of servitude" cooperative federalism The New Deal National,state and local governments were The Three R's AMENDMENT FIFTEEN encouraged to work together on specific programs State Government Exclusive Powers of National and State Government Cooperative federalism Federal Government State Government gov't roles are not as clearly defined as Print Money Issue licenses with dual federalism Regulate interstate and Regulate intrastate business national and state gov'ts share policy international trade Make treaties and conduct Conduct elections responsibilities foreign policy both levels of gov't work together Declare war Establish local gov'ts simultaneously in the states.... Provide an army and navy Ratify amendments to the carrying out mandates passed Constitution by the federal gov't Establish post offices Take measures for public health and safety duplicating efforts of one Make laws needed to carry Exert powers not delegated another on a policy area out these powers to national gov't and is not prohibited by the States 6
1/12/2017 6 Civil War Amendments • 15th Amendment – “The rights of citizens of the US to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the US or by any State on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude” State Government • In the 1930s, Great Depression brought the end to dual federalism • States could not cope with the economic upheaval • President Roosevelt’s New Deal brought in cooperative federalism • National, state and local governments were encouraged to work together on specific programs State Government • Cooperative federalism - gov’t roles are not as clearly defined as with dual federalism - national and state gov’ts share policy responsibilities - both levels of gov’t work together simultaneously in the states …. carrying out mandates passed by the federal gov’t duplicating efforts of one another on a policy area State Government Exclusive Powers of National and State Government Federal Government State Government Print Money Issue licenses Regulate interstate and international trade Regulate intrastate business Make treaties and conduct foreign policy Conduct elections Declare war Establish local gov’ts Provide an army and navy Ratify amendments to the Constitution Establish post offices Take measures for public health and safety Make laws needed to carry out these powers Exert powers not delegated to national gov’t and is not prohibited by the States
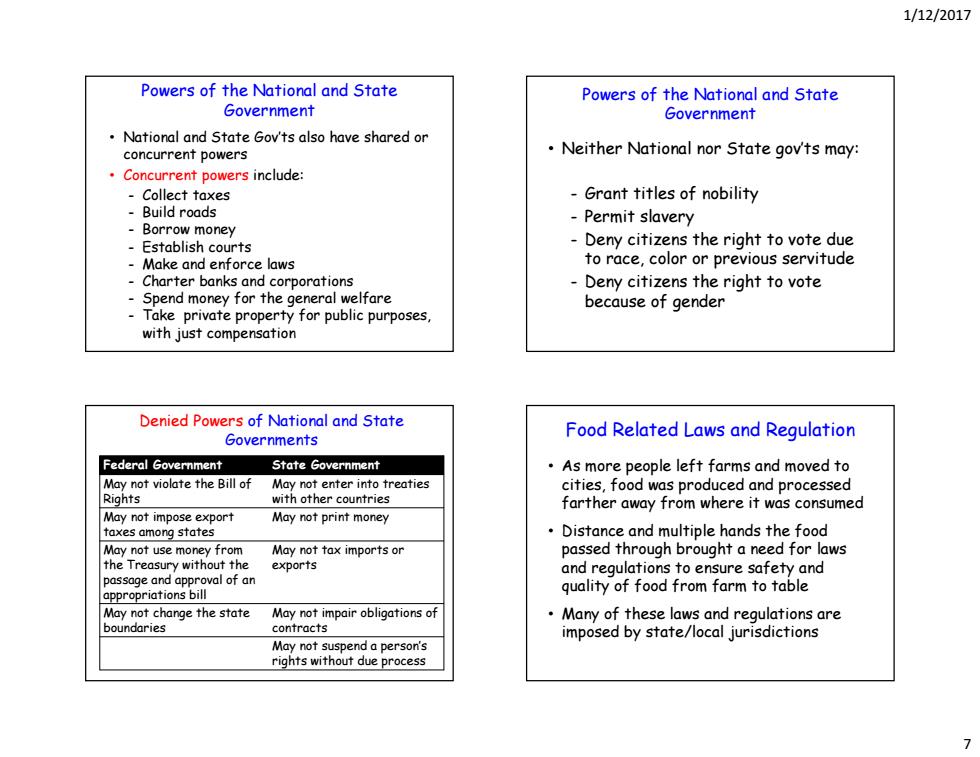
1/12/2017 Powers of the National and State Powers of the National and State Government Government National and State Gov'ts also have shared or concurrent powers Neither National nor State gov'ts may: Concurrent powers include: Collect taxes -Grant titles of nobility Build roads -Permit slavery Borrow money Establish courts Deny citizens the right to vote due Make and enforce laws to race,color or previous servitude Charter banks and corporations Deny citizens the right to vote Spend money for the general welfare -Take private property for public purposes, because of gender with just compensation Denied Powers of National and State Governments Food Related Laws and Regulation Federal Government State Government As more people left farms and moved to May not violate the Bill of May not enter into treaties cities,food was produced and processed Rights with other countries farther away from where it was consumed May not impose export May not print money taxes among states Distance and multiple hands the food May not use money from May not tax imports or passed through brought a need for laws the Treasury without the exports and regulations to ensure safety and passage and approval of an appropriations bill quality of food from farm to table May not change the state May not impair obligations of Many of these laws and regulations are boundaries contracts imposed by state/local jurisdictions May not suspend a person's rights without due process
1/12/2017 7 • National and State Gov’ts also have shared or concurrent powers • Concurrent powers include: - Collect taxes - Build roads - Borrow money - Establish courts - Make and enforce laws - Charter banks and corporations - Spend money for the general welfare - Take private property for public purposes, with just compensation Powers of the National and State Government • Neither National nor State gov’ts may: - Grant titles of nobility - Permit slavery - Deny citizens the right to vote due to race, color or previous servitude - Deny citizens the right to vote because of gender Powers of the National and State Government Denied Powers of National and State Governments Federal Government State Government May not violate the Bill of Rights May not enter into treaties with other countries May not impose export taxes among states May not print money May not use money from the Treasury without the passage and approval of an appropriations bill May not tax imports or exports May not change the state boundaries May not impair obligations of contracts May not suspend a person’s rights without due process • As more people left farms and moved to cities, food was produced and processed farther away from where it was consumed • Distance and multiple hands the food passed through brought a need for laws and regulations to ensure safety and quality of food from farm to table • Many of these laws and regulations are imposed by state/local jurisdictions Food Related Laws and Regulation
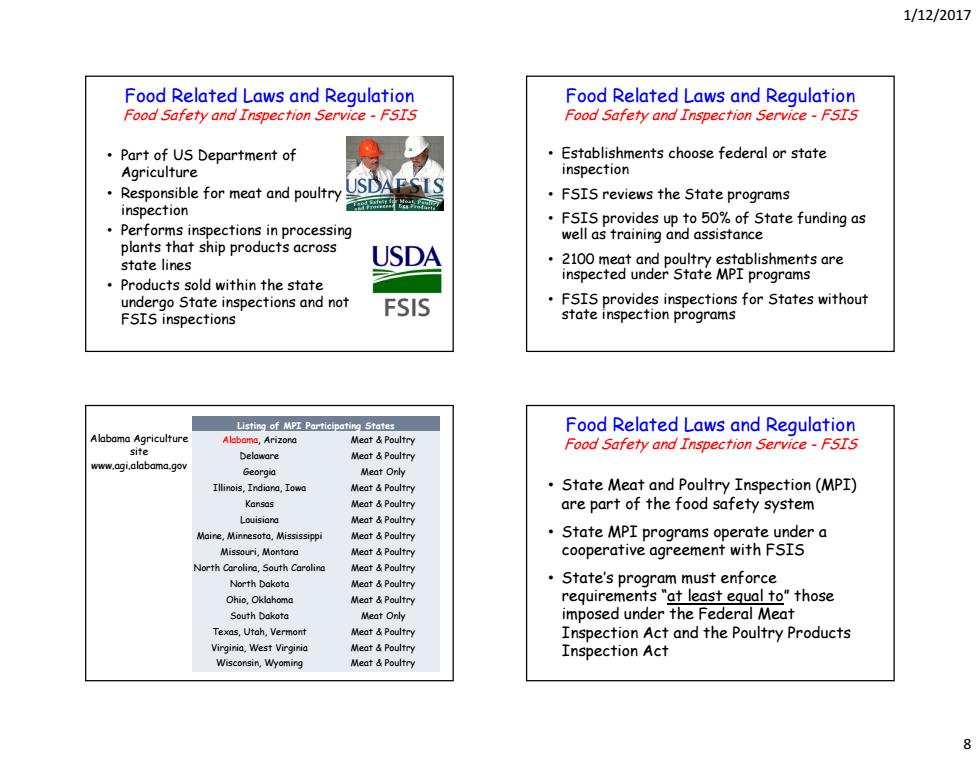
1/12/2017 Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service-FSIS Food Safety and Inspection Service-FSIS Part of US Department of Establishments choose federal or state Agriculture inspection Responsible for meat and poultry USDAESIS inspection 司 FSIS reviews the State programs FSIS provides up to 50%of State funding as Performs inspections in processing plants that ship products across well as training and assistance state lines USDA 2100 meat and poultry establishments are inspected under State MPI programs Products sold within the state undergo State inspections and not FSIS inspections FSIS FSIS provides inspections for States without state inspection programs Listing of MPI Participating States Food Related Laws and Regulation Alabama Agriculture Alabama,Arizora Meat Poultry Food Safety and Inspection Service-FSIS site Delaware Meat &Poultry www.agi.alabama.gov Georgia Meat Only Meat d Poultry State Meat and Poultry Inspection(MPI) Kansas Meat Poultry are part of the food safety system Meat Poultry Maire,Minnesota,Mississippi Meat &Poultry State MPI programs operate under a Missouri,Montara Meat &Poultry cooperative agreement with FSIS North Carolina.South Carolina Meat Poultry North Dakota Meat &Poultry State's program must enforce Ohio,Oklahoma Meat Poultry requirements "at least equal to"those South Dakota Meat Only imposed under the Federal Meat Texas,Utah.Vermont Meat &Poultry Inspection Act and the Poultry Products Virginia,West Virginia Meat Poultry Inspection Act Meat Poultry 8
1/12/2017 8 • Part of US Department of Agriculture • Responsible for meat and poultry inspection • Performs inspections in processing plants that ship products across state lines • Products sold within the state undergo State inspections and not FSIS inspections Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service - FSIS • Establishments choose federal or state inspection • FSIS reviews the State programs • FSIS provides up to 50% of State funding as well as training and assistance • 2100 meat and poultry establishments are inspected under State MPI programs • FSIS provides inspections for States without state inspection programs Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service - FSIS Listing of MPI Participating States Alabama, Arizona Meat & Poultry Delaware Meat & Poultry Georgia Meat Only Illinois, Indiana, Iowa Meat & Poultry Kansas Meat & Poultry Louisiana Meat & Poultry Maine, Minnesota, Mississippi Meat & Poultry Missouri, Montana Meat & Poultry North Carolina, South Carolina Meat & Poultry North Dakota Meat & Poultry Ohio, Oklahoma Meat & Poultry South Dakota Meat Only Texas, Utah, Vermont Meat & Poultry Virginia, West Virginia Meat & Poultry Wisconsin, Wyoming Meat & Poultry Alabama Agriculture site www.agi.alabama.gov • State Meat and Poultry Inspection (MPI) are part of the food safety system • State MPI programs operate under a cooperative agreement with FSIS • State’s program must enforce requirements “at least equal to” those imposed under the Federal Meat Inspection Act and the Poultry Products Inspection Act Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service - FSIS

1/12/2017 Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service-FSIS Food Safety and Inspection Service-FSIS Secretary of Agriculture imposes mandatory Cooperation with FSIS includes requirements for advisory assistance in planning and antemortem,postmortem,reinspection, developing the program sanitation technical and laboratory assistance and denaturing product sold not for food training funding to 50% maintaining records contingent upon administration of the providing access State program in a manner which the registering brokers,renderers wholesalers secretary together with the advisory control of dead,dying.disabled,dieseased committee deems adequate to effect the animals purpose Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service-FSIS Food and Drug Administration State program is subject to return to Public Health Service Act Federal inspection if: -1968,responsibility for provisions of State chooses to drop the program this act relative to food protection -Requirements defined in the Federal was transferred to the FDA- Meat Inspection Act are not met Commissioner of Food and Drugs FDA provides assistance to state and local gov'ts 39
1/12/2017 9 • Secretary of Agriculture imposes mandatory requirements for - antemortem, postmortem, reinspection, sanitation - denaturing product sold not for food - maintaining records - providing access - registering brokers, renderers wholesalers - control of dead, dying, disabled, dieseased animals Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service - FSIS • Cooperation with FSIS includes - advisory assistance in planning and developing the program - technical and laboratory assistance and training funding to 50% - contingent upon administration of the State program in a manner which the secretary together with the advisory committee deems adequate to effect the purpose Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service - FSIS • State program is subject to return to Federal inspection if: - State chooses to drop the program - Requirements defined in the Federal Meat Inspection Act are not met Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Safety and Inspection Service - FSIS • Public Health Service Act - 1968, responsibility for provisions of this act relative to food protection was transferred to the FDA – Commissioner of Food and Drugs - FDA provides assistance to state and local gov’ts Food Related Laws and Regulation Food and Drug Administration

1/12/2017 Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Related Laws and Regulation Food and Drug Administration Food and Drug Administration Food,Drug and Cosmetics Act National conferences govern FDA-state -Gives FDA authority to inspect and alliances take action with respect to retail food Federal and state officials meet establishments where food is held yearly to review and to revise after introduction into interstate procedures commerce States have voting authority States examine ordinances, operational manuals,and other issues to ensure all are working similarly Food Related Laws and Regulation Food Related Laws and Regulation Food and Drug Administration Food and Drug Administration National conferences govern FDA-state 3000 state and local gov't agencies alliances regulate the country's retail food industry -Federal and state officials meet Responsible for over 1 million food yearly to review and to revise establishments-restaurants and grocery procedures stores,vending machines,cafeterias, health-care facilities,schools,correctional States have voting authority facilities States examine ordinances, FDA regional food specialist provide operational manuals,and other issues training,program evaluation,technical to ensure all are working similarly assistance 10
1/12/2017 10 • Food, Drug and Cosmetics Act - Gives FDA authority to inspect and take action with respect to retail food establishments where food is held after introduction into interstate commerce Food Related Laws and Regulation Food and Drug Administration • National conferences govern FDA-state alliances - Federal and state officials meet yearly to review and to revise procedures - States have voting authority - States examine ordinances, operational manuals, and other issues to ensure all are working similarly Food Related Laws and Regulation Food and Drug Administration • National conferences govern FDA-state alliances - Federal and state officials meet yearly to review and to revise procedures - States have voting authority - States examine ordinances, operational manuals, and other issues to ensure all are working similarly Food Related Laws and Regulation Food and Drug Administration • 3000 state and local gov’t agencies regulate the country’s retail food industry • Responsible for over 1 million food establishments-restaurants and grocery stores, vending machines, cafeterias, health-care facilities, schools, correctional facilities • FDA regional food specialist provide training, program evaluation, technical assistance Food Related Laws and Regulation Food and Drug Administration