
1/26/2016 Structure and Function of the Microbes Urinary System Learning Objective Invisible Invaders List the antimicrobial features of the Amazing Allies urinary system. Chapter 26 Microbial Diseases of the Urinary and Reproductive Systems Structure and Function of the Organs of the human urinary system,female Urinary System Urinary system Inferior vena ·Infection prevented -Two kidneys by: .removes waste from the blood these wastes are called urine urine to -Two ureters the kidneys Location:where ureters enter the urinary bladder -One urinary bladder -One urethra Acidity of urine female-conveys only urine -Mechanical flushing seminal 。malecar urine and Organs of the human of the urine urinary system,female
1/26/2016 1 Invisible Invaders Amazing Allies Chapter 26 Microbial Diseases of the Urinary and Reproductive Systems Structure and Function of the Urinary System Learning Objective List the antimicrobial features of the urinary system. Structure and Function of the Urinary System • Urinary system – Two kidneys Inferior vena cava Aorta • removes waste from the blood • these wastes are called urine – Two ureters • Urine pass through ureters into the bladder O i bl dd Kidneys Ureters Urinary – One urinary bladder – One urethra • female - conveys only urine • male – conveys urine and seminal fluid Urethra y bladder Organs of the human urinary system, female Organs of the human urinary system, female Inferior vena cava Aorta • Infection prevented by: Kidneys Ureters – Valves that prevent backflow of urine to the kidneys • Location: where ureters enter the urinary bladder Urethra Urinary – Acidity of urine bladder – Mechanical flushing of the urine

1/26/2016 Structure and Function of the Structure and Function of the Reproductive Systems Reproductive Systems Learning Objective Female reproductive system -Two ovaries Identify the portals of entry for Produce sex hormores and ovas (eggs) microbes into the female and male Two uterine (fallopian)tubes reproductive systems. ovum enters the uterine tubes where fertilization occurs fertilized ovum enters the uterus -The uterus,including the cervix fertilized egg implants in the wall embryo then fetus develop -The vagina -External genitals(vulva) Female Structure and Function of the reproductive organs Pubic bone Uter Reproductive Systems Urinary bladde Male reproductive system Urethr -Two testes Lab majus Side of female -System of ducts ·Epididymis Ductus(vas)deferens ·Ejaculatory duct .Urethra -Accessory glands -Penis 下ront vicw of fe ductive org .with the erine tube and es the into the move to creat ne tuhe
1/26/2016 2 Structure and Function of the Reproductive Systems Learning Objective Identify the portals of entry for microbes into the female and male reproductive systems. Structure and Function of the Reproductive Systems • Female reproductive system – Two ovaries • Produce sex hormones and ovas (eggs) – Two uterine (fallopian) tubes • ovum enters the uterine tubes where fertilization occurs • fertilized ovum enters the uterus – The uterus, including the cervix • fertilized egg implants in the wall • embryo then fetus develop – The vagina – External genitals (vulva) Female reproductive organs Uterine (fallopian) tube Rectum Fimbria Vagina Cervix Cli i A Urethra Urinary bladder Ovary Pubic bone Uterus Anus Side view section of female pelvis showing reproductive organs Labium majus Clitoris Uterine tube Labium minus Ovary Fimbria Cervix Vagina Uterus Ovary Front view of female reproductive organs, with the uterine tube and ovary to the left in the drawing sectioned. The fimbriae move to create fluid movement that moves the egg into the uterine tube. Endometrium Structure and Function of the Reproductive Systems • Male reproductive system – Two testes • produce sex hormones and sperm • sperm cells pass through a series of ducts – System of ducts • Epididymis • Ductus (vas) deferens • Ejaculatory duct • Urethra – Accessory glands – Penis
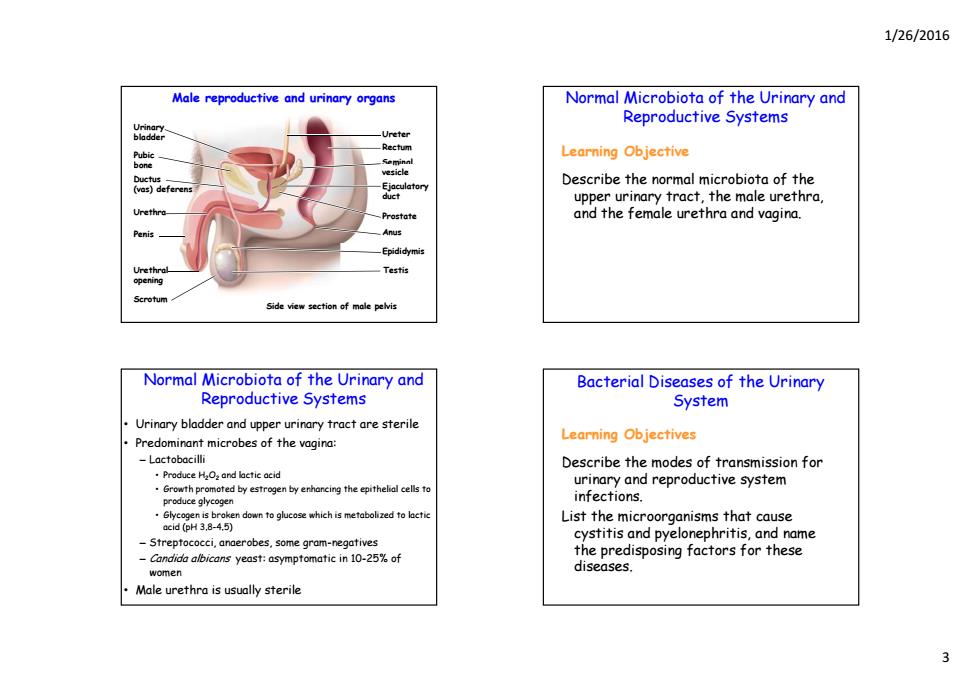
1/26/2016 Male reproductive and urinary organs Normal Microbiota of the Urinary and Reproductive Systems Learning Objective Describe the normal microbiota of the uct upper urinary tract,the male urethra, Prostate and the female urethra and vagina. Anus -Epididymis Testis opening Scrotum Side view section of male pelvis Normal Microbiota of the Urinary and Bacterial Diseases of the Urinary Reproductive Systems System Urinary bladder and upper urinary tract are sterile Predominant microbes of the vagina: Learning Objectives Lactobacilli Describe the modes of transmission for Produce Hand lactic acid Growth promoted by estrogen by enhancing the epithelial cells to urinary and reproductive system produce glycogen infections. Glycogen is broken down to glucose which is metabolized to lactic acid (PH 3.8-4.5) List the microorganisms that cause cystitis and pyelonephritis,and name -Streptococci,anaerobes,some gram-negatives Candida yeast:asymptomatic in 10-%of the predisposing factors for these women diseases. Male urethra is usually sterile
1/26/2016 3 Male reproductive and urinary organs Urinary bladder Pubic bone Seminal Rectum Ureter bone Ductus (vas) deferens Urethra Penis Anus Prostate Ejaculatory duct m vesicle Urethral opening Scrotum Side view section of male pelvis Testis Epididymis Normal Microbiota of the Urinary and Reproductive Systems Learning Objective Describe the normal microbiota of the upper urinary tract, the male urethra, and the female urethra and vagina. Normal Microbiota of the Urinary and Reproductive Systems • Urinary bladder and upper urinary tract are sterile • Predominant microbes of the vagina: – Lactobacilli • Produce H2O2 and lactic acid • Growth promoted by estrogen by enhancing the epithelial cells to produce glycogen • Glycogen is broken down to glucose which is metabolized to lactic acid (pH 3 8 acid (pH 3.8-4 5) . – Streptococci, anaerobes, some gram-negatives – Candida albicans yeast: asymptomatic in 10-25% of women • Male urethra is usually sterile Bacterial Diseases of the Urinary System Learning Objectives Describe the modes of transmission for urinary and reproductive system infections. List the microorganisms that cause cystitis and pyelonephritis, and name the predisposing factors for these diseases

1/26/2016 Bacterial Diseases of the Urinary System Cystitis inflammation of the urinary bladder Bacteria causing these diseases are found in the excreted urine Commonly caused by E.coli:also Staphylococcus ·Urethritis saprophyticus -An inflammation of the urethra Dysuria(difficult or painful urination):pyuria(pus) ·.Cystitis Eight times more common in women than men -Due to the short length of the urethra(less than 2 inches ·Ureteritis long)and close proximity to the anal opening -Infection of the ureters .Pyelonephritis -An inflammation of one or both kidneys 7 million urinary tract infections annually leukocyte esterase is a common enzyme Most due to Escherichia coll e health-care associated:90%of these Treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethexazole Pyelonephritis Bacterial Diseases of the inflammation of one or both kidneys Reproductive Systems Untreated cases of cystitis Learning Objective 75%of cases caused by E.col Fever and back or flank pain List the causative agents,symptoms, Generally results in bacteremia methods of diagnosis,and treatments Can form scar tissue in kidneys and become for gonorrhea,nongonococcal urethritis life-threatening (NGU),pelvic inflammatory disease Diagnosis:>10,000 CFU/ml and a positive LE (PID),and syphilis. test Treatment with intravenous broad spectrum antibiotic such as cephalosporin
1/26/2016 4 Bacterial Diseases of the Urinary System • Bacteria causing these diseases are found in the excreted urine • Urethritis A i fl ti f th th Inferior vena cava Aorta – An inflammation of the urethra • Cystitis – An inflammation of the urinary bladder • Ureteritis – Infection of the ureters • Pyelonephritis Kidneys Ureters Urethra Urinary bladder – An inflammation of one or both kidneys • 7 million urinary tract infections annually – Most due to Escherichia coli – 900,000 cases are health-care associated; 90% of these are due to catheters Cystitis inflammation of the urinary bladder • Commonly caused by E. coli; also Staphylococcus saprophyticus • Dysuria (difficult or painful urination); pyuria (pus) • Eight times more common in women than men – Due to the short length of the urethra (less than 2 inches long) and close proximity to the anal opening • Diagnosis: >100 CFU/ml of potential pathogens and a p y ositive leukocyte esterase (LE) test - leukocyte esterase is a common enzyme found in white blood cells and is an indicator of an infection • Treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethexazole Pyelonephritis inflammation of one or both kidneys • Untreated cases of cystitis • 75% f d b 75% of cases caused by E li . co • Fever and back or flank pain • Generally results in bacteremia • Can form scar tissue in kidneys and become life-threatening • Diagnosis: >10,000 CFU/ml and a positive LE test • Treatment with intravenous broad spectrum antibiotic such as cephalosporin Bacterial Diseases of the Reproductive Systems Learning Objective List the causative agents, symptoms, methods of diagnosis, and treatments for gonorrhea, nongonococcal urethritis (NGU), pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) d s hilis (PID), and syphilis
1/26/2016 Bacterial Diseases of the Reproductive Systems STI Home Test Kits Collect samples at home and mail to a Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) lab -Also known as sexually transmitted infections -Screens for chlamydia,gonorrhea,and (STIs) trichomoniasis -Often no signs or symptoms ·Results in 1-2 weeks Over 30 types of infections Positive tests receive referrals to clinics -Bacteria are sensitive to environmental stress and require intimate contact for transmission ·Test for HIV -15 million new cases in the United States -OraQuick:oral test annually Test for urinary tract infections -Treatment with antibiotics and prevented with condoms -Uritest dipstick test STI Home Test Kits Gonorrhea Pros of at-home testing Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae -Gram-negative diplococcus More cases are diagnosed -Better access for patients -Quicker treatment Most age 15-24 Attaches to the epithelial mucosa by the fimbriae ·Cons of home-testing -Cost Found in eral-obe geal area,eyes.rectum -Privacy-hotlines must use pin numbers -Not all home test kits are equally accurate :6rSpsaga
1/26/2016 5 Bacterial Diseases of the Reproductive Systems • Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) – Al k Also known as sexuall t itt d i f ti lly transmitt ed i n fections (STIs) – Often no signs or symptoms – Over 30 types of infections – Bacteria are sensitive to environmental stress and require intimate contact for transmission – 15 million new cases in the United States annually – Treatment with antibiotics and prevented with condoms STI Home Test Kits • Collect samples at home and mail to a lab – Screens for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis • Results in 1–2 weeks • Positive tests receive referrals to clinics • Test for HIV – OraQuick: oral test • Test for urinary tract infections – Uritest dipstick test STI Home Test Kits • Pros of at-home testing – More cases are dia gnosed – Better access for patients – Quicker treatment • C f h Cons of home-t ti es ng – Cost – Privacy – hotlines must use pin numbers – Not all home test kits are equally accurate Gonorrhea • Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae – Gram-negative diplococcus • 300 000 i th 300,000 cases in th e United States annually • Most age 15-24 • Attaches to the epithelial mucosa by the fimbriae – Invades the spaces between the col ith li l ll lumnar epithelial cells • Found in oral-pharyngeal area, eyes, rectum, urethra, cervix opening • Causes inflammation • Forms pus due to high leukocytes • Oral-pharyngeal gonorrhea and anal gonorrhea
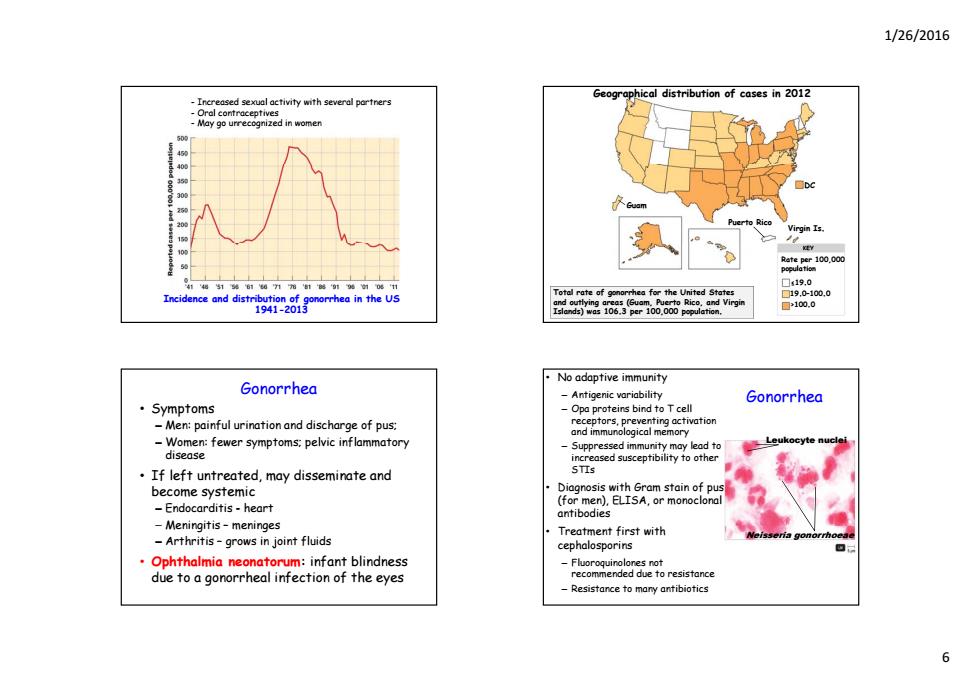
1/26/2016 -Increased sexual activity with several portners Geographical distribution of cases in 2012 ral contraceptives May go urrecognized in women Virgin Is. 100.000 有福第07带制前0的06中 □s19.0 Incidence and doorhea in the 5 Total rate of gonorrhea for the United States ☐19.0-100.0 ☐100.0 No adaptive immunity Gonorrhea -Antigenic variability Gonorrhea Symptoms -Opa proteins bindtoTcell -Men:painful urination and discharge of pus: -Women:fewer symptoms:pelvic inflammatory mm Le cyte disease If left untreated,may disseminate and become systemic Diagnosis with Gram stain of pu -Endocarditis-heart (for men),ELISA,or monoclonal antibodies -Meningitis-meninges Treatment first with -Arthritis-grows in joint fluids cephalosporins Ophthalmia neonatorum:infant blindness Fluoroquinolones not due to a gonorrheal infection of the eyes recommended due to resistance Resistance to many antibiotics 6
1/26/2016 6 - Increased sexual activity with several partners - Oral contraceptives - May go unrecognized in women Incidence and distribution of gonorrhea in the US 1941-2013 Geographical distribution of cases in 2012 Guam Puerto Rico Virgin Is. DC Rate per 100,000 population ≤19.0 19.0–100.0 >100.0 Total rate of gonorrhea for the United States and outlying areas (Guam, Puerto Rico, and Virgin Islands) was 106.3 per 100,000 population. KEY Gonorrhea • Symptoms – Men: painful urination and discharge of pus; – Women: fewer syp p y m toms; pelvic inflammatory disease • If left untreated, may disseminate and become systemic – Endocarditis - heart – Meningitis – meninges – Arthritis – grows in joint fluids • Ophthalmia neonatorum: infant blindness due to a gonorrheal infection of the eyes Gonorrhea • No adaptive immunity – Antigenic variability – Opa proteins bind to T cell receptors, preventing activation and immunological memory – Suppressed immunity may lead to Leukocyte nuclei increased susceptibility to other STIs • Diagnosis with Gram stain of pus (for men), ELISA, or monoclonal antibodies • Treatment first with cephalosporins – Fluoroquinolones not recommended due to resistance – Resistance to many antibiotics Neisseria gonorrhoeae

1/26/2016 Nongonococcal Urethritis(NGU) Pelvic Inflammatory Disease(PID) Nonspecific urethritis (NSU) Extensive bacterial infection of the female pelvic -Any inflammation of the urethra not caused by organs N.gonorrhoeae Polymicrobial infection,usually: ·Caused by -Chlamydia trachomatis -Mycoplasma hominis Chronic abdominal pain -Ureaplasma urealyticum Salpingitis:infection of the uterine tubes Painful urination and watery discharge:often Most serious form of PID asymptomatic:pelvic inflammatory disease(PID) in women .Diagnosis:culture or PCR Scarring can cause infertility or ectopic pregrancy (ovum implanted in the tube instead of uterus) Treatment with doxycycline and azithromycin Treatment with doxycycline and cefoxitin The U.S.incidence and distribution of primary and Syphilis secondary syphilis Coused by Treponema pallidum -Gram-neaative spirochete -Grows slowly in cell culture -Relies on the host for many rutrients mough skin breaks and /o.0 Induces an inflammatory response which leads to 5g in the United in2012 tissue damage Enters the bloodstream invading other tissues Stable incidence in the United States Islands)was 5.1 cases per 100.000 populetion. >
1/26/2016 7 Nongonococcal Urethritis (NGU) • Nonspecific urethritis (NSU) – Any inflammation of the urethra not caused by N. gonorrhoeae • Caused by: – Chlamydia trachomatis – Mycoplasma hominis – Ureaplasma urealyticum • Painf y g; f ul urination and watery discharge; often asymptomatic; pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women • Diagnosis: culture or PCR • Treatment with doxycycline and azithromycin Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) • Extensive bacterial infection of the female pelvic organs • Polym f , y icrobial infection, usually: – N. gonorrhoeae – C. trachomatis • Chronic abdominal pain • Salpingitis: infection of the uterine tubes – Most serious form of PID – Bacteria attach to the sperm and travel to the uterine tubes – Scarring can cause infertility or ectopic pregnancy (ovum implanted in the tube instead of uterus) • Treatment with doxycycline and cefoxitin Syphilis • Caused by Treponema pallidum – Gram-negat e sp rochete ive spirochete – Grows slowly in cell culture – Relies on the host for many nutrients • Invades the mucosa or through skin breaks and enters the bloodstream • No obvious virulence factors but produces lip po roteins that cause inflammation • Induces an inflammatory response which leads to tissue damage • Enters the bloodstream invading other tissues • Stable incidence in the United States The U.S. incidence and distribution of primary and secondary syphilis Guam Puerto Rico Virgin Is. DC KEY Rate/100,000 population ≤0.2 0 21 2 2 Geographical 0.21–2.2 >2.2 g p distribution of cases in 2012 Primary and secondary syphilis rates in the United States and territories (Guam, Puerto Rico, and Virgin Islands) was 5.1 cases per 100,000 population. Incidence of syphilis in the United States, 1941–2013

1/26/2016 Syphilis Primary stage Syphilis ·Tertiary stage Disappears affer 2 weeks -Appear years after latency if left untreated ·Secondary stage Due to cell-mediated immune reactions -Gummatous syphilis:gummas on many organs Due to an inflammatory response -Cardiovascular syphilis:weakens the aorta Latent period (after 2-4 yrs) -No symptoms -Neurosyphilis:affects the CNS:dementia -Not usually infectious except for the fetus compared to causing Congenital:neurological damage to the stillbirth in the first two stages) fetus Syphilis Viral Diseases of the Reproductive Microscopic tests Systems :nibdeare ot formed yet fo cal Learning Objective -Direct fluorescent-antibody test (DFA-TP)with monocloral antibodies Discuss the epidemiology of genital Nontreponemal serological tests(response to lipids) herpes and genital warts. 一a2eeavB8eeewseesech bode t relee Treponemal-type serological tests -Enzyme immunoassay (ETA) 一B时repeml antbody b Treatment with benzathine penicillin
1/26/2016 8 Syphilis • Primary stage – Chancre at the site of infection about 3 weeks after exposure • Painless and highly infectious • Disappears after 2 weeks • Secondary stage – Skin and mucosal rashes, especially on palms and soles • Due to an inflammatory response • L t t i d ( ft 2 Latent period (after 2-4 yrs) – No symptoms – Not usually infectious except for the fetus compared to causing stillbirth in the first two stages) Syphilis • Tertiary stage – Appear years after latency if left untreated • Due to cell-mediated immune reactions – Gummatous syphilis: gummas on many organs – Cardiovascular syphilis: weakens the aorta – Neurosyphilis: affects the CNS; dementia • Congenital: neurological damage to the fetus Syphilis • Microscopic tests – First stage; antibodies are not formed yet for serological tests – Di t fl nt Direct fluorescent-antib d t t ntibody test (DFA-TP) with m n l n l ith monoclonal antibodies • Nontreponemal serological tests (response to lipids) – Slide agglutination VDRL test (venereal disease research laboratory test/ antibodies) – Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test (antibodies to released ag ) ents and not to the bacterium) • Treponemal-type serological tests – Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) – Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test (FTA-ABS) • Treatment with benzathine penicillin Viral Diseases of the Reproductive Systems Learning Objective Discuss the epidemiology of genital herpes and genital warts
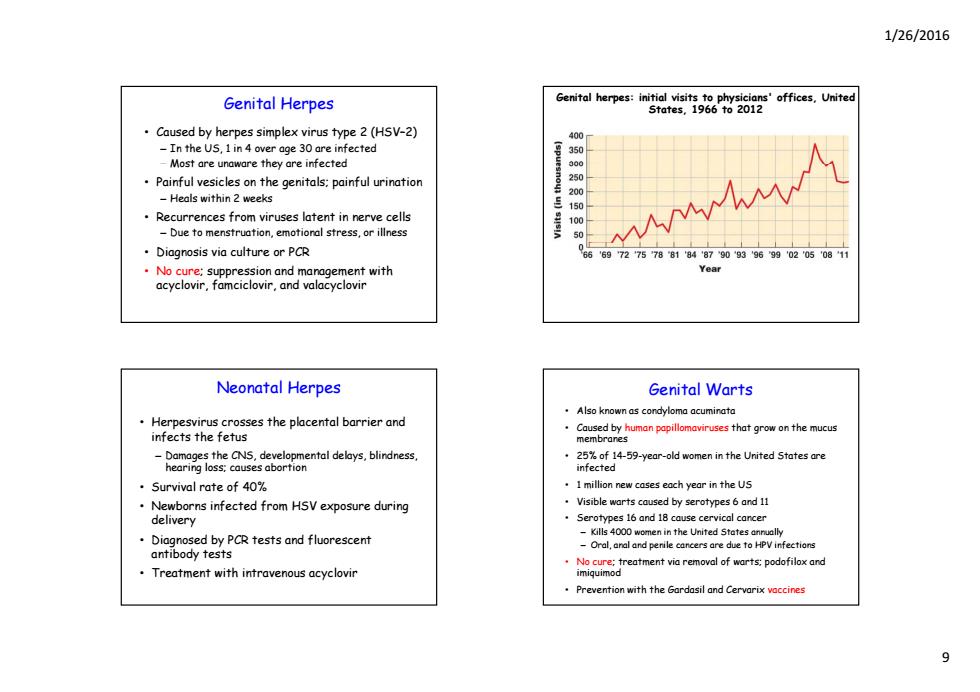
1/26/2016 Genital Herpes Genital herpes:initial visits to physicians'offices.United States,1966 to 2012 Caused by herpes simplex virus type 2(HSV-2) 400 In the US,1 in 4 over age 30 are infected 350 -Most are unaware they are infected Painful vesicles on the genitals;painful urination -Heals within 2 weeks 200 Recurrences from viruses latent in nerve cells 100 Due to menstruation,emotional stress,or illness 50 Diagnosis via culture or PCR 0c6 7578818487909396990205081 No cure:suppression and management with Year acyclovir,famciclovir,and valacyclovir Neonatal Herpes Genital Warts Also known as condyloma acuminata Herpesvirus crosses the placental barrier and infects the fetus -Damages the CNS,developmental delays,blindness, 25%of 14-59-year-old women in the United States are hearing loss:causes abortion infected ·Survival rate of4o% 1 million new cases each year in the US Newborns infected from HSV exposure during Visible warts caused by serotypes 6 and 11 delivery Serotypes 16 and 18 cause cervical cancer -Kills 4000 women in the United States annually Diagnosed by PCR tests and fluorescent -Oral,anal and penile cancers are due to HPVinfections antibody tests No cure;treatment via removal of warts:podofilox and Treatment with intravenous acyclovir imiquimod Prevention with the Gardasil and Cervarix vaccines 9
1/26/2016 9 Genital Herpes • Caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV–2) – In the US, 1 in 4 over age 30 are infected – Most are unaware they are infected • Painful vesicles on the genitals; painful urination – Heals within 2 weeks • Recurrences from viruses latent in nerve cells – Due to menstruation, emotional stress, or illness • Diagnosis via culture or PCR • No cure; suppression and management with acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir Genital herpes: initial visits to physicians' offices, United States, 1966 to 2012 Neonatal Herpes • Herpesvirus crosses the placental barrier and infects the fetus – Damages the CNS, developmental delays, blindness, hearing loss; causes abortion • Survival rate of 40% • Newborns infected from HSV exposure during delivery • Diagnosed by PCR tests and fluorescent antibody tests • Treatment with intravenous acyclovir Genital Warts • Also known as condyloma acuminata • Caused by human papillomaviruses that grow on the mucus membranes • 25% of 14-59-year-old women in the United States are infected • 1 million new cases each year in the US • Visible warts caused by serotypes 6 and 11 • Serotypes 16 and 18 cause cervical cancer – Kills 4000 women in the United States annually – Oral, anal and penile cancers are due to HPV infections • No cure; treatment via removal of warts; podofilox and imiquimod • Prevention with the Gardasil and Cervarix vaccines

1/26/2016 Fungal Disease of the Reproductive Candidiasis Systems Caused by Candida albicans Learning Objective Discuss the epidemiology of candidiasis. -Part of the normal flora of the vagina -Due to opportunistic overgrowth caused by: ·Antibiotic use ·Diabetes ·Hormones Oral candidiasis:thrush Vulvovaginal candidiasis:vaginitis Yeasty.thick,yellow discharge Treatment with clotrimazole or fluconazole Protozoan Disease of the Reproductive Systems .Caused by Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomoniasis Learning Objectives 8 million cases per year Only STI caused by a protozozan Discuss the epidemiology of Grows when normal acidity of the trichomoniasis. vagina is disturbed List reproductive system diseases that Half of the cases are asymptomatic can cause congenital and neonatal Considered relatively benign infections,and explain how these infections can be prevented. Diagnosis with microscopic Treatment with metronidazole 0
1/26/2016 10 Fungal Disease of the Reproductive Systems Learning Objective Discuss the epidemiology of candidiasis. Candidiasis • Caused by Candida albicans – Grows on the mucosa of the mouth, the intestinal tract, and the genitourinary tract – Part of the normal flora of the vagina – Due to opportunistic overgrowth caused by: • Antibiotic use • Diabetes • Hormones • Oral d d can i iasis: th h rus • Vulvovaginal candidiasis: vaginitis • Yeasty, thick, yellow discharge • Treatment with clotrimazole or fluconazole Protozoan Disease of the Reproductive Systems Learning Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of trichomoniasis. List reproductive system diseases that can cause congenital and neonatal infections, and explain how these infections can be prevented. • Caused by Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomoniasis – Normal inhabitant of the vagina and urethra in men • 8 million cases per year • Only STI caused by a protozozan • Grows when normal acidity of the vagina is disturbed • Half of the cases are asymptomatic • Considered relatively benign • I it ti n nd p fus f ul nish Irritation and a profuse foul, greenish yellow frothy discharge • Diagnosis with microscopic identification or a DNA probe • Treatment with metronidazole